Research on Pneumatically Actuated 6-DOF Parallel Robot Based on SimMechanics
LIU Yingchao, LI Jun, WANG Wei
1. Pneumatic Technology Center, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China;2.Zoomlion Co., LTD, Changsha 410000, China
ResearchonPneumaticallyActuated6-DOFParallelRobotBasedonSimMechanics
LIU Yingchao1*, LI Jun1, WANG Wei2
1.PneumaticTechnologyCenter,HarbinInstituteofTechnology,Harbin150001,China;2.ZoomlionCo.,LTD,Changsha410000,China
This paper is concerned with the practical application study of a pneumatically actuated Stewart-Gough platform with 6-degrees of freedom (6-DOF). Considering the characteristics of the pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot, the mathematical model of pneumatic servo system is established, and SimMechanics module is also introduced to build the mechanical model of the pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot. The modeling of pneumatic-mechanical systemof the parallel robot avoids the complex modeling process of Stewart platform. Simulation and test processes are carried. The processes show that the test results correlate well with the simulation result, and the simulation model can be used to describe the real motion of the 6-DOF parallel robot. The effect of pneumatic servo control system is achieved.
6-DOF parallel robot, pneumatically actuated, servo, SimMechanics
1.Introduction
The first prototype of the 6-DOF parallel mechanism was first introduced by Gough and White hallasatyre-testing machine. Since then, a wide variety of mechanisms have been benefited from this design. Owning to the advantages of rapid response speed, big stiffness, strong bearing capacity and having no accumulative error, the parallel robots are widely applied in all kinds of training simulators, ship and submarine docking platforms, parallel machine tools, dexterous robots and dynamic movie or entertainment equipment[1-3]. However, what are widely used today are hydraulic and electric 6-DOF parallel robots. Reports concerning pneumatically driving parallel robots are limited.
There are advantages of pneumatic system: flexibility, security, low cost, no pollution, but on the other hand, the compressibility of gas makes the pneumatic system uncontrollable and nonlinear[4]. Considering the characteristic of pneumatic system, the mathematical model of pneumatic servo system is established. The simulation model of the whole pneumatic-mechanical system is build up and verified by some experiments. Pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot is sure to have a wide development space in the future[5].
2.Pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot
The pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot mainly includes the upper platform, the lower platform, the upper hinges, the lower hinges and six cylinders, as shown in Fig.1. The ideal trajectory of moving platform is set and the displacement signals are sent to the six pneumatic cylinders through the inverse solution module, which are controlled by servo controller. The robot can move in various degrees of freedom under the actions of cylinders.
3.System model
One single branch of the pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot just needs to be considered for the reason that there are certain symmetries in the robot.

Fig.1 Pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot
3.1.Pneumaticservosystemmodel
The trajectory tracking characteristics of the entire robot are determined by the characteristics of thepneumatic servo system, which serve as the driver of the 6-DOF parallel robot[5-7]. However, it is difficult to build an accurate pneumatic model for its strong nonlinearity. Some reasonable assumptions need to be made to simplify the mathematical model. Assuming that the working medium in the pneumatic system is ideal gas, the process is adiabatic process and the influence of gas leak is ignored. The pneumatic servo system model is established according to the gas dynamics theories.
The mass flow of the servo valve can be expressed as:
(1)
WhereQis the mass flow rate of the valve,Ris the ideal gas constant,pHis the high pressure,pLis the low pressure, andkis the adiabatic exponent.
The compressible fluidmasscontinuity equation is:
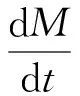
(2)
WhereMis the gas flow quality,V1,V2is the left and right cylinder cavity volume respectively,Q1、Q2is the left and right cavity flow of the cylinder respectively. According to the law of mass conservation and gas state equation:
(3)
In order to simplify the calculation, two cavity temperatures is replaced by ambient temperatureTwhen temperature fluctuation is not too bigduring the working process, and the calculation error caused by the temperature change can be neglected. The pressure differential equation can be described as follows:

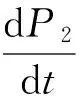
(4)
According to the Newton’s second law, the cylinder piston force balance equation is:
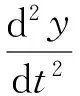
(5)
WhereFLis the external load on the cylinder,Ffis the friction force on the cylinder.
The whole simulation model of the pneumatic servo system is shown in Fig.2.
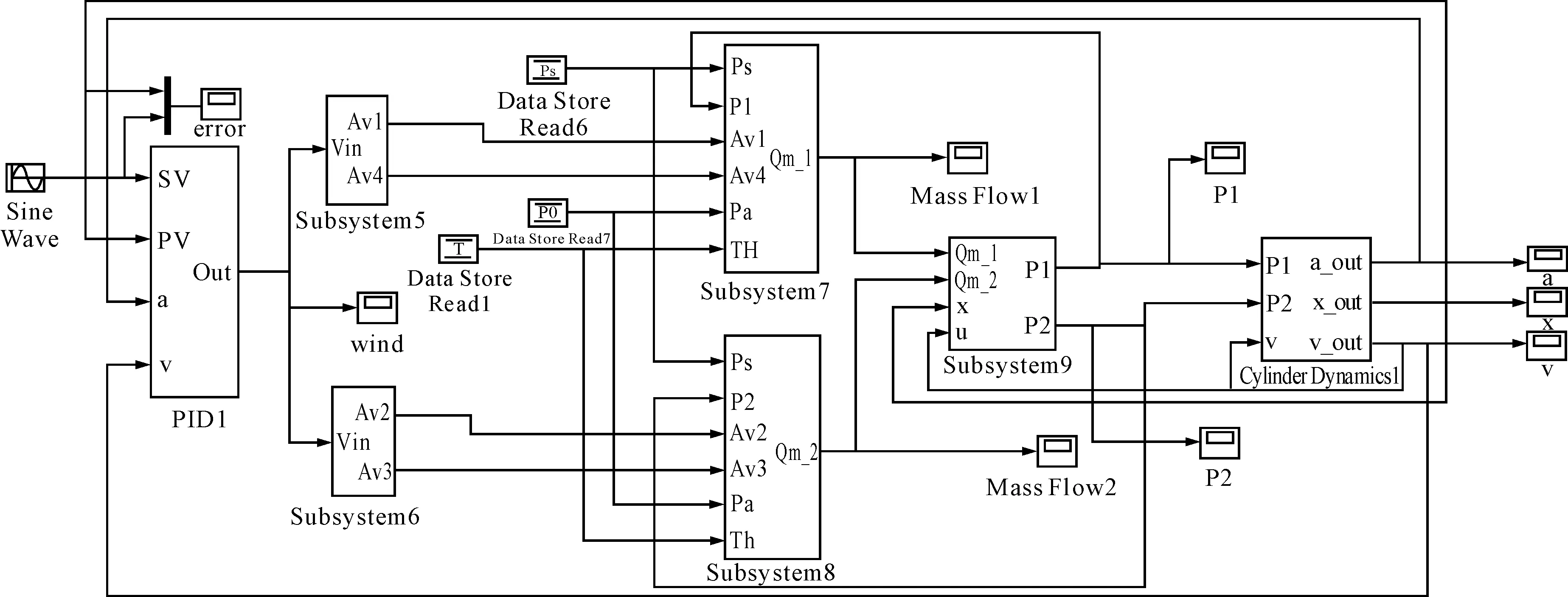
Fig.2 Pneumatic servo system model
3.2.Mechanicalmodel
SimMechanics module library mainly includes the rigid body sub-module, the motion hinge sub-module, sensor and actuator sub-module, etc. Each component is connected through the nodes. Each module contains a large number of components corresponding to the actual system such as rigid body, frame, hinge, actuators and sensors, etc. Different models can be set up with the combination of each module. In addition, SimMechanics can also be connected to the control system models of Simulink.
In this parallel robot, each branch of the parallel robot is made up of two universal hinges, two rigid bodies and a cylindrical pair. SimMechanics is introduced to build one single branch of the mechanical model in Fig.3, and the integrated mechanical model of 6-DOF parallel robot is shown in Fig.4.
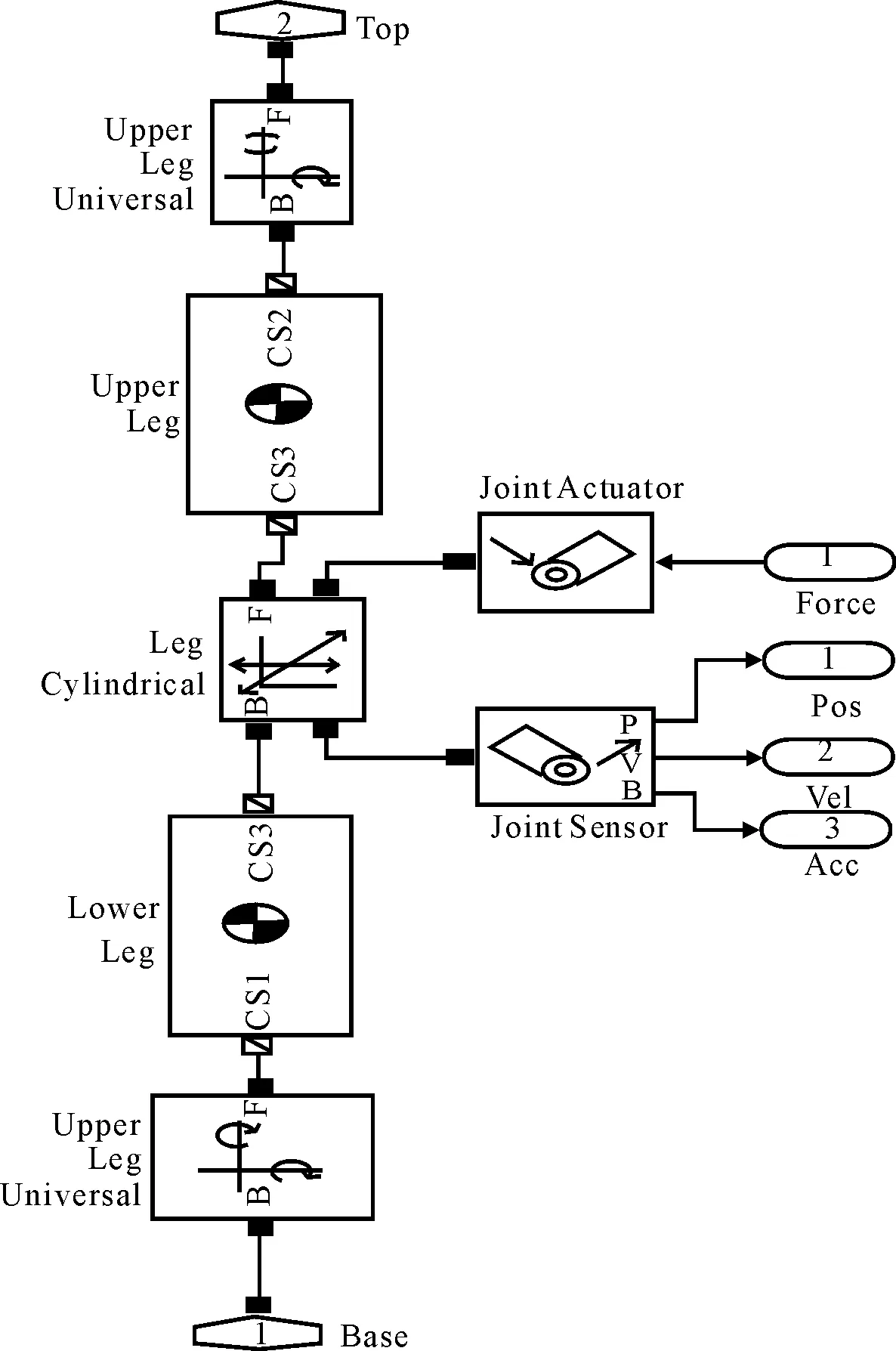
Fig.3 One branch mechanical model
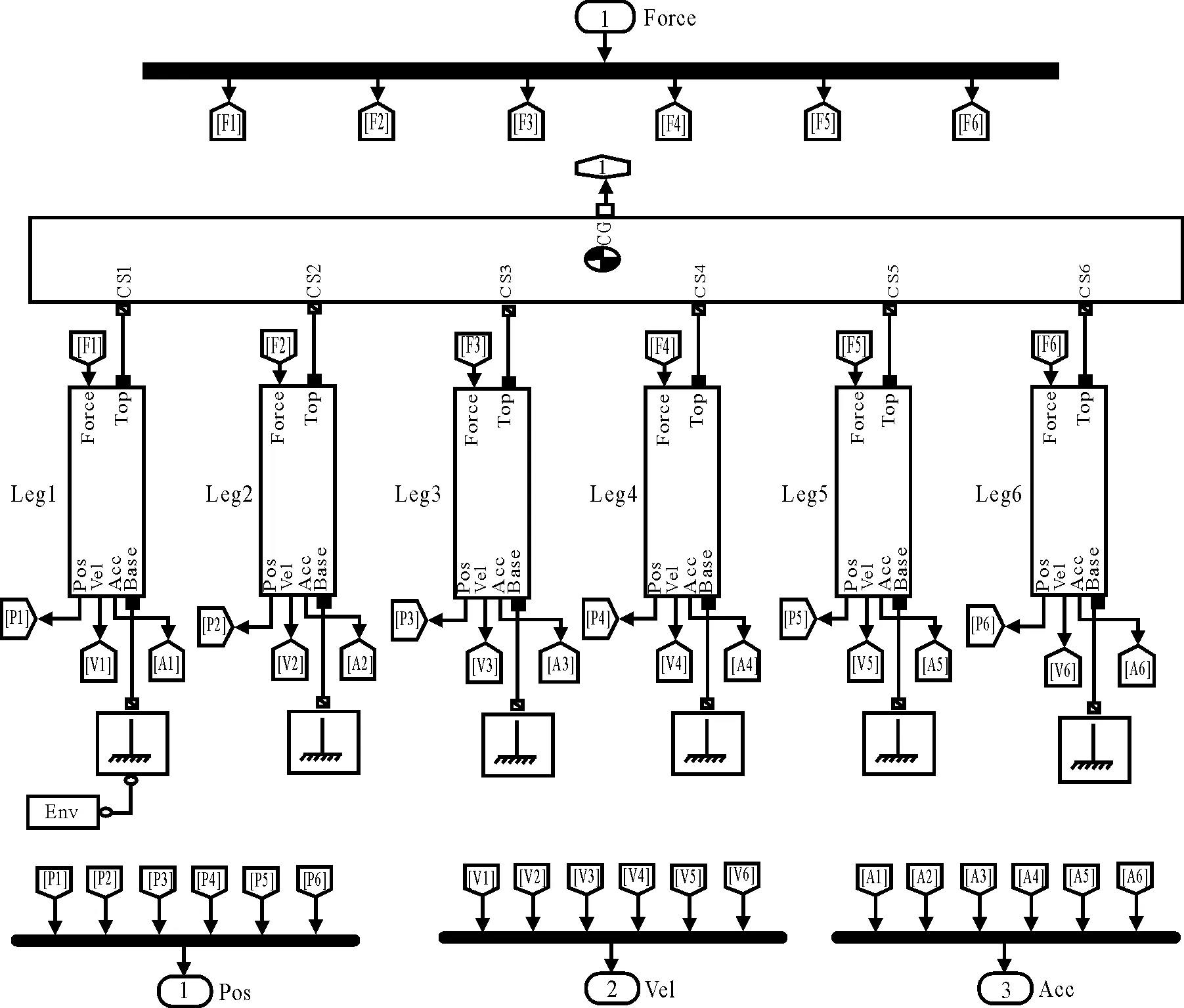
Fig.4 The integrated mechanical model
3.3.Theintegratedpneumatic-mechanicalmodel
The integrated pneumatic-mechanical simulation model of the 6-DOF parallel robot is shown in Fig.5, which is composed of the ideal trajectory signal module, the inverse solution module, the pneumatic servo control module and the mechanical module. The ideal trajectory of six degrees of freedom of the platform is set by ideal trajectory signal module, and the ideal elongation or shortening signals of six cylinders are worked out by the inverse solution module. Corresponding controlled quantities are set by servo controller, which are based on the deviation signals, to control the movement of the parallel robot.
4.Simulation and analysis
4.1.Simulationofpneumaticservosystem
In this study, the initial signal of the pneumatic servo system is set as:x=0.05sin(2τ), and the simulation result is shown in Fig.6.
4.2.Simulationoftheparallelrobotsystem
The main structural parameters of the robot are shown in Tab.1. Owning to the differences in the characteristics of various degrees of freedom and the strong nonlinearity of pneumatic system, the controller parameters need to be adjusted appropriately, and the velocity and acceleration feedback are introduced to form a closed loop control at the same time, to achieve the good control effect. The simulation results are shown in Fig.7.
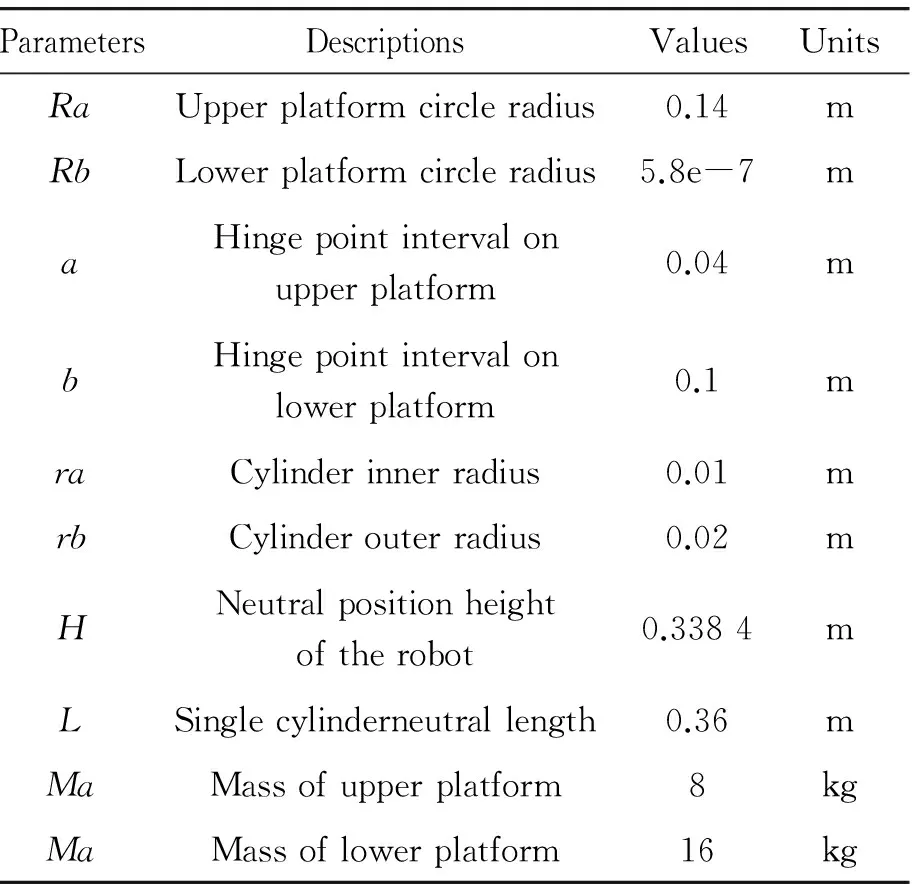
Tab.1 Main parameters of the 6-DOF parallel robot
Since there are certain symmetries of the parallel robot, this paper only considered four directions of movement: the translation alongY, andZaxis, and the rotation aroundY, andZaxis. According to the overall simulation model in Fig.5, the step-response signals are in putted respectively under the influence of PID control. The simulation results are listed in Fig.7:
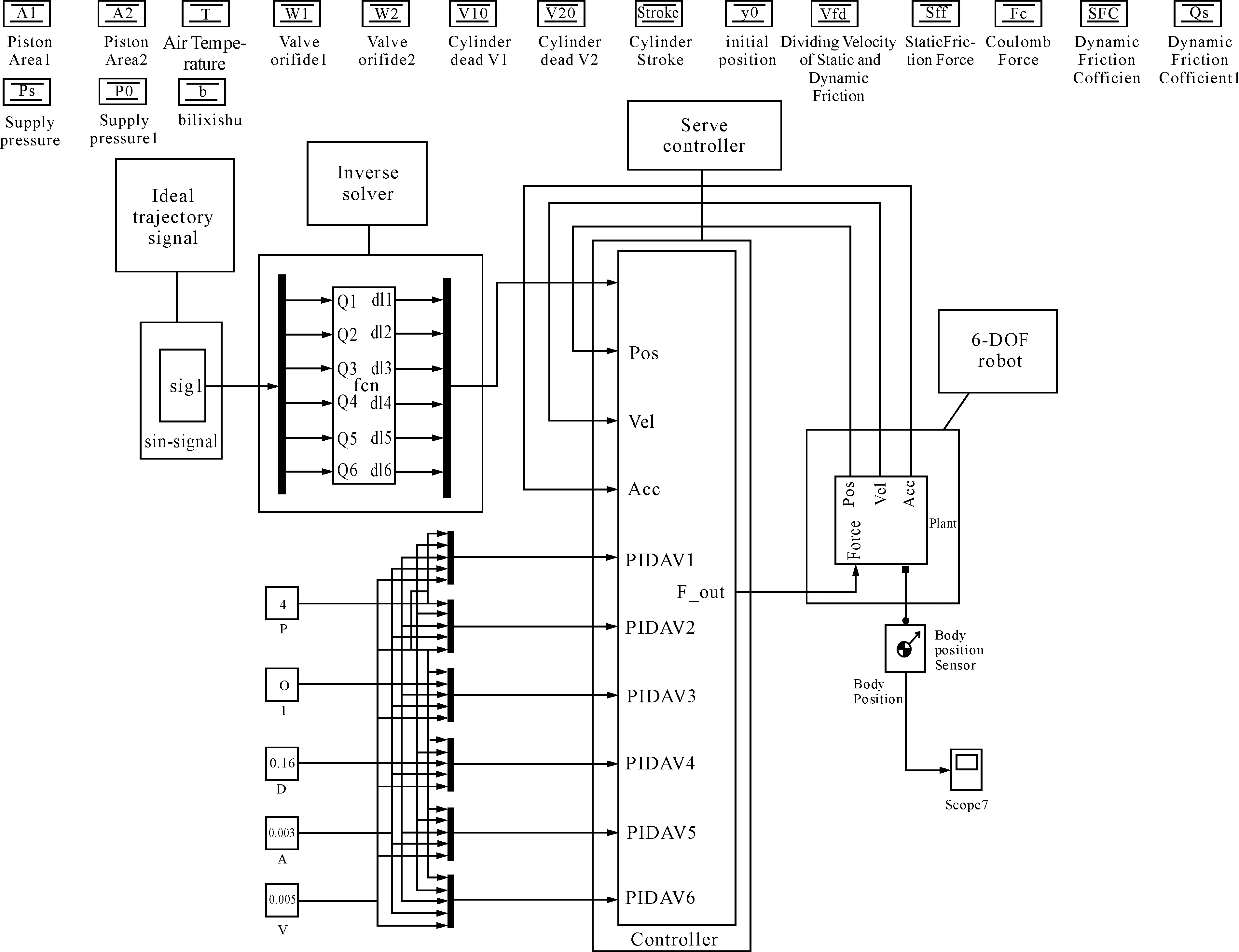
Fig.5 The integrated pneumatic-mechanical simulation model

Fig.6 Cylinder displacement
4.3.Experimentresults
To verify the simulation results, the practicality model of the mechanism was established (Fig.1). The step-response signals are input respectively, which are the same as the step signals of simulation. The results are shown as follows in Fig.8.
The results show that these characteristics of step response in each freedom are different from each other. For the reason that the frequency characteristics of pneumatically actuated 6-DOF parallel robot are different in each freedom, translation alongYaxis has over shoot and rotation aroundZaxis has concussion.
It can be seen from Fig.7 and Fig.8 that actual system has slower response, but in general, the experimental data correlate well with the simulation results.
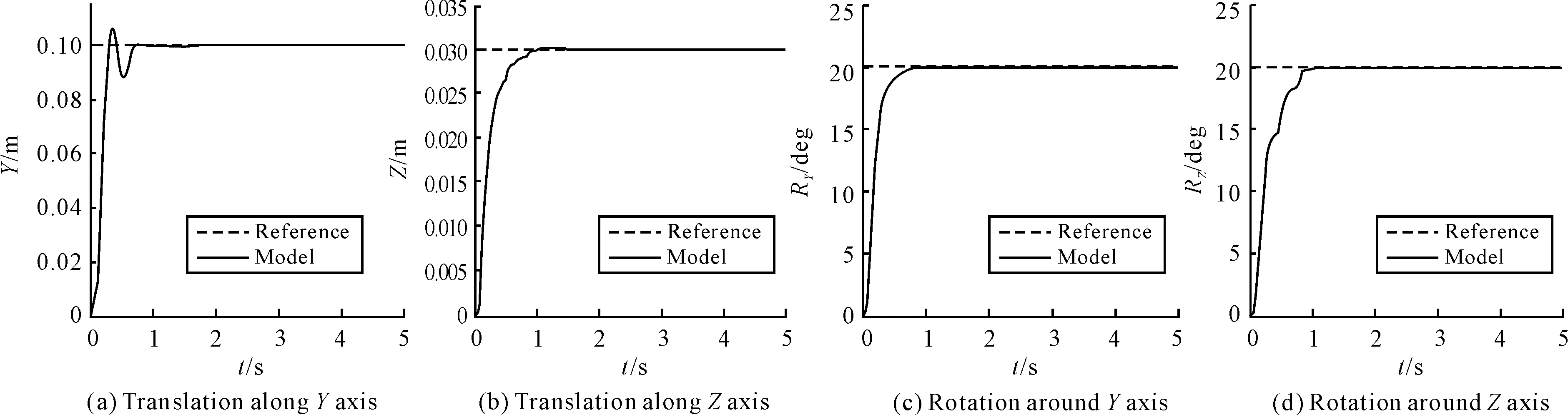
Fig.7 Step response (simulation)
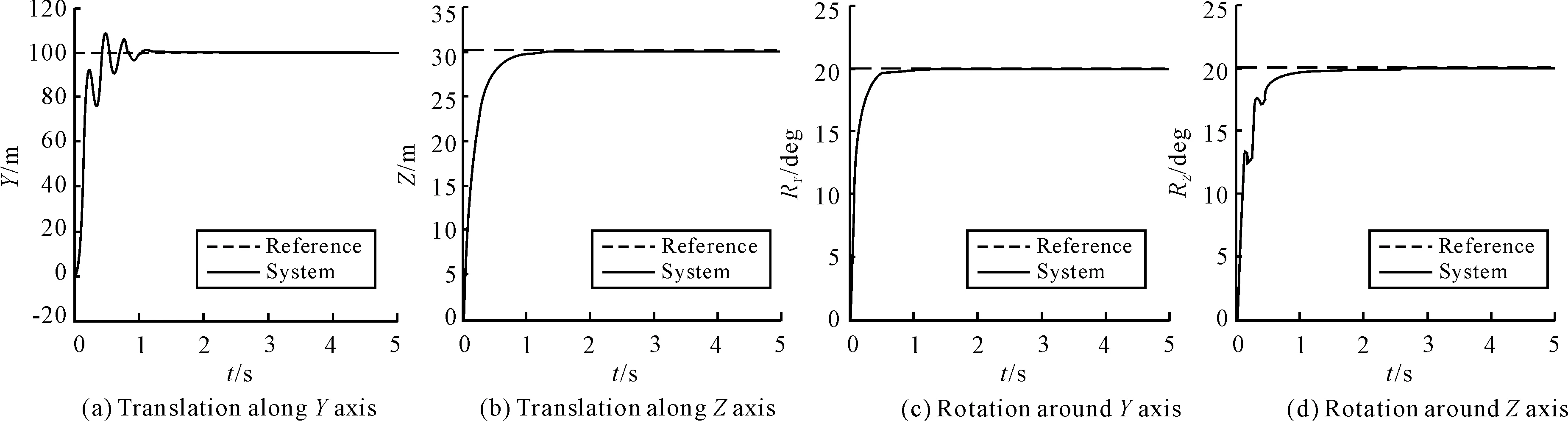
Fig.8 Step response (experiment)
5.Conclusions
1) In this paper, a modeling method based on SimMechanics has been proposed to establish the mechanical model of the robot, which avoids the complex modeling process of Stewart platform. The models of pneumatic servo system and robot system have been established and verified by simulation and experiment.
2) The practicality model has been build up and controlled by host computer. The experiment results show that the simulation data agree well with experimental results, and the simulation model can be used to describe the real motion of the 6-DOF parallel robot. In addition, the advantages of pneumatically actuated parallel mechanism such as low cost, non-pollution, simple structure, safe and reliability will sure to make it have a wide development space in the future.
[1] Stewart D. A platform with six degree-of-freedom[J]. Proc. of the Institute for Mechanical Engineering,1965,(1):371-386.
[2] Girone M, Burdea G, Bouzit M, et al. A Stewart platform-based system for ankle telerehabilitation[J]. Autonomous Robots, 2001, 10(2): 203-212.
[3] ZHANG H P, Ikeo S, Takahashi K, et al. Study on the Condensation of Water in a Pneumatic System[J]. Proceeding of the Second JHPS International Symposium on Fluid Power, 2006:589-594.
[4] SUN Jian, DING Yongsheng, HAO Kuangrong. A new simulation platform of parallel mechanism based on SimMechanics[J]. Computer Simulation, 2010(1):56.
[5] MENG Qiang, HE Jingfeng, HAN Junwei. The overall dynamic model of electric 6-SPU-type parallel robot[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010(1): 83-86.
[6] ZHANG Yushu, LI Jun. A simulation study on pneumatic 6-DOF parallel platform based on ADAMS and SIMULINK[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2013, 41(9): 134-137.
[7] HUANG Zhen, LING Fukong, YUE Fafang. Parallel robot mechanism theory and control[D]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 1997.
2013-06-20
*LIU Yingchao.E-mail: lyingchao_hit@163.com
10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2013.24.013
- 機(jī)床與液壓的其它文章
- Current Cloud Computing Security Concerns from Consumer Perspective
- Simulation of Hydraulic Servo System for High-Speed Injection Molding Machine by AMESim
- Mechanical Amplifier for Giant Magnetostrictive Materials and Piezoelectric Materials
- 基于FANUC-0iTD的刀尖圓弧半徑補(bǔ)償應(yīng)用研究
- 基于無(wú)線的數(shù)控機(jī)床聯(lián)網(wǎng)
- 渦流技術(shù)在應(yīng)力檢測(cè)中的應(yīng)用

