Effective sideband cooling in an ytterbium optical lattice clock
Jin-Qi Wang(王進起) Ang Zhang(張昂) Cong-Cong Tian(田聰聰) Ni Yin(殷妮) Qiang Zhu(朱強)Bing Wang(王兵) Zhuan-Xian Xiong(熊轉賢) Ling-Xiang He(賀凌翔) and Bao-Long Lv(呂寶龍)
1State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics,Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Wuhan 430071,China
2Key Laboratory of Atomic Frequency Standards,Innovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Wuhan 430071,China
3University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
Keywords: sideband cooling,ytterbium,optical atomic clock,optical lattice
State-of-the-art optical atomic clocks based on ytterbium(171Yb) and strontium (87Sr) lattice clock have reached a frequency instability on the order of the magnitude around 10-19and total uncertainty of approximately 10-18.[1-6]Such accurate optical atomic clocks surpass the performance of the best133Cs primary standards by at least two orders of magnitude,[7,8]and promote the redefinition of the SI second in approximately 2028.[9,10]The higher stability of optical atomic clocks show many important applications,such as searching for variations in fundamental constants,[11]hunting for topological defect dark matter,[12]detecting gravitational waves[13]and relativistic geodesy.[1,14,15]
For an optical lattice clock,cold atoms as a role of quantum reference are tightly confined in the Lamb-Dicke region of the lattice where the 1st Doppler shift is eliminated. The frequency of the lattice laser is tuned to the magic wavelength,so the differential AC Stark shift between the upper state and lower state of a clock transition is also canceled.[16,17]In the lattice,atoms occupy different motional states and obey a thermal Boltzmann distribution. When atoms are interrogated by a clock laser, an inhomogeneous excitation emerges due to the motional state dependent Rabi frequency. This inhomogeneous excitation degrades the identity of the Fermi atoms and induces an additional collision shift.[18,19]Furthermore,the inhomogeneous excitation degrades the coherence of the ensemble and limits the potential interrogation time andQfactor of the clock spectrum. Therefore,cooling atoms in the lattice to the ground motional state is an important technique for improving the performance of an optical lattice clock.
For a tightly confined system with quantized motional states, resolved sideband cooling is a very effective method to realize a motional ground state occupation. It is widely used in ultracold atom preparation,[20]the quantum information process,[21]quantum metrology based on trapped ions,[22]and cooling of micro-mechanical oscillators.[23]A variety of strategies such as stimulated Raman sideband cooling[24]and degenerate Raman sideband cooling[20]have been realized. In a resolved sideband cooling, a closed cycling transition with a radiative linewidth far less than the vibration frequency is usually required. To increase the Rabi rate for this kind of narrow transition,two schemes are generally considered. One is continuous sideband cooling where the metastable upper state is coupled with a short-lived state to broaden the linewidth,and the other is pulsed sideband cooling where a pulsed red sideband pumping with a strong laser intensity followed by a pulsed repumping is repeated.[22]Ytterbium, as an excellent candidate for accurate optical clock,usually gets further cooling by pulsed sideband cooling mode.
In this paper, we demonstrate experimental research on pulsed Raman sideband cooling in the171Yb optical lattice clock. A sequence comprised of interleaved 578 nm cooling pulses resonant on 1st-order red sideband and 1388 nm repumping pulses is carried out to transfer atoms into the motional ground state. We succeed decreasing the axial temperature of atoms in the lattice from 6.5 μK to less than 0.8 μK with the trap depth around 24μK,corresponding to an average axial motional quantum number〈nz〉<0.03. Rabi oscillation spectrum is measured to evaluate sideband cooling effect on inhomogeneous excitation. The maximum excitation fraction is increased from 0.8 to 0.86, indicating an enhanced atomic coherence of the ensemble.
The experimental setup for our171Yb optical lattice clock has been described in detail in Refs. [25,26], and the related laser arrangement for this experiment is shown in Fig.1. The 1D optical lattice is formed by counter-propagating two laser beams at 759 nm,and the frequency of the lattice laser is controlled at the magic wavelength. So that the AC Stark shift produced by the lattice laser is canceled out. The clock laser is separated into two beams in the setup. One beam is overlapped with the lattice laser and is focused on atoms for sideband cooling. The other is used to interrogate the cold atoms and enters the vacuum chamber from the highly reflected end mirror for the optical lattice. Reflected 578 nm light from this end mirror is used for fiber noise cancellation of the optical path. The waists of the lattice laser and clock laser are approximately 45 μm and 100 μm, respectively, so that the clock laser covers the lattice beam for uniform cooling. And the 578 nm clock laser is locked to a 10 cm reference cavity with a frequency instability around 2×10-15@1 s, whose spacer and mirror substrates are made of ultra-low expansion(ULE)glass and fused silicon respectively. The frequency drift of 578 nm laser is typically below 0.08 Hz/s.

Fig.1. Schematic of the optical setup for sideband cooling. The clock laser for sideband cooling is combined the lattice laser with a dichroic mirror.
It shows the related energy levels for171Yb sideband cooling in Fig. 2(a). The cold atoms in the optical lattice are first stimulated by the 578 nm clock laser in resonance with the peak of the red detuned sideband spectrum of the clock transition, which pumps atoms from the ground state|1S0,n〉to the meta-stable excited state|3P0,n-1〉. Then,repumping laser at 1388 nm in resonance with the3P0→3D1transition is illuminated,so that the atoms in3P0are transferred to3D1.Subsequently,the atoms in3D1states spontaneously decay to the ground state|1S0,n-1〉via3P1states. In this cycle,atoms are transferred from motional state|n〉to|n-1〉. Figure 2(b)shows the time sequence for sideband cooling. In the experiment,the sideband cooling laser at 578 nm and the repumping laser at 1388 nm alternately irradiate atoms. The intensity of 578 nm cooling laser is approximately 5 mW and the detuning is-55 kHz. A 0.3 ms cooling pulse followed by 0.3 ms repumping pulse is iterated 100 times during a total time of 60 ms.After applying the sideband cooling sequence,the populations in the3P0and1S0states are measured using shelving detection technique with a 399 nm strong excitation resonant on1S0-1P1.

Fig.2. (a)Related energy levels for sideband cooling in Yb lattice clock. (b)The time sequence diagram for sideband cooling.
When cold Yb atoms are trapped in the Lamb-Dicke regime, 1st Doppler shift and recoil shift are highly suppressed. A typical sideband spectrum with a narrow carrier transition and broad red and blue sideband transitions can be resolved when 578 nm laser frequency is scanned across the clock transition in stepping mode.[27]Spectrum profile carries information about the lattice and temperature of the atoms.Axial trap frequency and trap depth can be inferred from the sharp edge of red and blue sidebands away from the carrier.Axial temperature of the cold atoms can be estimated according to the ratio of integrated cross sections of red sideband and blue sideband using following formulae:while the transverse temperature can be extracted from the shape of the shallow edges of red and blue sidebands facing the carrier.

When the cold atoms are interrogated using a 100 ms Rabi pulse,typical motional sideband spectrum is obtained,shown in Fig.3 with jointed red solid dots.From the spectrum,the axial trap frequencyvzis determined to be 63 kHz,the transverse trap frequencyvris determined to be 240 Hz, and the lattice trap depth is estimated to be about 24 μK. The ratio of cross sections of the red sideband and blue sideband is measured to be 0.64, corresponding to axial temperature of about 6.5 μK and an average axial motional quantum number〈nz〉≈1.6.The transverse temperature is fitted about 8 μK according to the shallow edges of the red and blue sidebands facing the carrier. It is slightly higher than the axial temperature due to probe light heating during interrogation,which can be further decreased by shortening the Rabi pulse.Sideband spectrum after sideband cooling is also shown in Fig.3 with jointed blue solid dots. After sideband cooling, the red sideband almost vanishes,and the blue sideband becomes much narrower. The ratio of cross sections between the red sideband and blue sideband is measured to be less than 0.03, corresponding to axial temperature of cold atoms less than 0.8 μK and an average axial motional quantum number〈nz〉<0.03. Transverse temperature of the cold atoms keeps almost no change during the sideband cooling process.

Fig.3. Sideband spectrum before(red solid dots)and after(blue solid dots)sideband cooling process with a 100 ms Rabi pulse.
We have also recorded axial temperatures of the cold atoms at different trap depths before and after sideband cooling, as shown in Fig. 4. Before sideband cooling, the axial temperature linearly increases with the trap depth,and the ratio of the axial temperature and the trap depth is fitted to be 0.24(7). After sideband cooling,the axial temperature slightly increases with the trap depth,and the ratio of the axial temperature and the trap depth is fitted to be 0.02(2). These linear relationships between atomic temperature and trap depth in our horizontal optical lattice indicate the operational magic wavelength formulae developed by NIST group,[28]which can also be used for the AC Stark shift evaluation in our lattice clock.
In optical lattice, the thermal distribution of cold atoms on vibrational states will induce an inhomogeneous excitation and degrade the coherence of trapped atoms. To investigate the effect of inhomogeneous excitation, Rabi oscillation as a function of Rabi pulse duration is measured,shown in Fig.5.We tune the frequency of the probe laser resonant on the clock carrier transition,and then record the excitation fraction at different Rabi pulse duration. In Fig. 5, curves in red dots and blue dots are the data before and after sideband cooling respectively. After sideband cooling, the maximum excitation fraction is obviously increased from 0.8 to 0.86,and the Rabi frequency is also decreased from 330 Hz to 310 Hz.

Fig. 4. The axial temperatures before (red circles) and after (blue squares)sideband cooling process along with the lattice depth.
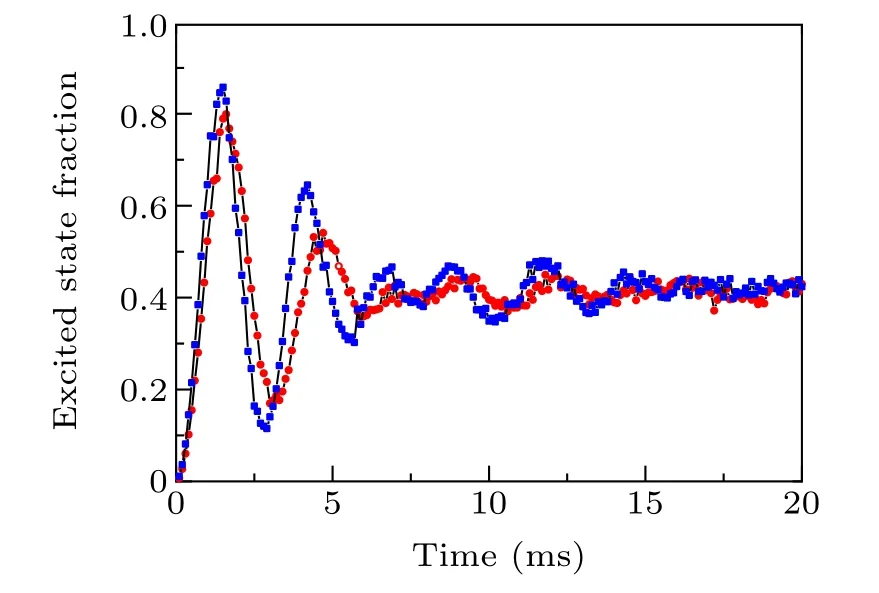
Fig. 5. Rabi oscillations on Rabi pulse duration before (red dots) and after(blue dots)sideband cooling process. Trap depth is fixed at 24μK.
In summary,we have demonstrated experimental research on pulsed Raman sideband cooling in171Yb optical lattice clock. We successfully decrease the axial temperature of atoms in the lattice from 6.5 μK to less than 0.8 μK, corresponding to an average axial motional quantum number〈nz〉<0.03. Rabi oscillation spectrum is also used to evaluate the effect of sideband cooling on inhomogeneous excitation. The maximum excitation fraction is increased from 0.8 to 0.86, indicating the quantum coherence enhancement of the ensemble. Our work will be beneficial to improve performance of Yb lattice clock.
Acknowledgment
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.U20A2075).
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Erratum to“Accurate determination of film thickness by low-angle x-ray reflection”
- Anionic redox reaction mechanism in Na-ion batteries
- X-ray phase-sensitive microscope imaging with a grating interferometer: Theory and simulation
- Regulation of the intermittent release of giant unilamellar vesicles under osmotic pressure
- Bioinspired tactile perception platform with information encryption function
- Quantum oscillations in a hexagonal boron nitride-supported single crystalline InSb nanosheet

