鎳–磷–碳化硼化學復合鍍層的研制
KARTHIKEYAN S, VENKATACHALAM G, SRINIVASAN K N, VASUDEVAN T, NARAYANAN S
鎳–磷–碳化硼化學復合鍍層的研制
KARTHIKEYAN S*, VENKATACHALAM G, SRINIVASAN K N, VASUDEVAN T, NARAYANAN S
在由碳酸鎳15 g/L、次磷酸32 mL/L、次磷酸鈉15 g/L、乳酸32 mL/L、乙酸18 g/L、丙酸3 mL/L、二甲胺1.7 g/L及碳化硼(即B4C)0 ~ 25 g/L組成的穩定鍍液中,采用化學鍍的方法在低碳鋼上制備了Ni–P–B4C復合鍍層。其顯微硬度采用韋氏硬度法測量,耐磨性用Taber磨耗試驗機測量,微觀形貌和組織采用掃描電鏡和X射線衍射進行分析,耐蝕性以動電位極化及電化學阻抗譜測定。碳化硼的摻入提高了鎳–磷合金基體的顯微硬度、耐磨性和耐蝕性。Ni–P–B4C復合鍍層顆粒粗大,具有爆米花式組織結構。
化學鍍;鎳磷合金;碳化硼;復合鍍層;耐蝕性;顯微硬度;耐磨性
1 Introduction
Electroless plating baths typically include a metal salt, a chelator for metal species, a reducing agent for metal and stabilizers to retard the trend of reducing agent to promote the reduction and deposition of metal, e.g. surfaces without discrimination or in the bulk solution. Chemical nickel plating baths of the prior art contained sulfate as divalent anion. It was found that sulfate ions create environmental problems while treating the spent electroless nickel plating baths and also it is very difficult to separate sulfate ions from the plating effluents. Due to difficulties in processing spent plating baths containing sulfate ions, land filling is often a preferred method. Typically sulfate is withdrawn from plating solutions by treatment with lime.
There is no doubt that the unique properties of nickel coatings such as hardness, resistance to corrosion and wear, etc., have created their trend of modern surface engineering[1-5]. The ability to codeposit fine composite particles with electrolytic nickel plating is a major step in the extension of various processes for surface engineering[6]. The main objective of the incorporation of composite particles is to improve the mechanical properties. Various composite coatings such as Ni–P–Al2O3[2], Ni–P–SiC[6-7], Ni–P–MoS2[8]and Ni–P–diamond[9], etc., have been reported in literatures. However, very little information is available for the electroless deposition of Ni–P–B4C.
This paper addresses the incorporation B4C into Ni–P matrix. The mechanical properties of composite coatings were characterized by Vickers hardness measurements and Taber abrasion resistance. AC impedance and potentiodynamic polarization measurements were performed for evaluation of the corrosion resistance of composite coatings. SEM and XRD studies were used for determining the surface morphology of coatings.
2 Experimental
The bath used in this study had the following composition.

B4C particles were mixed with a small amount of wetting agent as propitiatory sludge prior to addition. A mild steel with dimensions 3 cm × 5 cm × 0.6 cm was used as substrate for the codeposition. Before plating, the substrate was subjected to pretreatment such as alkaline degreasing and acid pickling in 10% HCl at room temperature. The bath was mechanically agitated with 200 r/min. The deposit thickness was measured using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy (AMI, USA). The determination of phosphorus in the deposits involves the complete precipitation of phosphorus as ammonium phosphomolybdate, dissolution of the precipitate in HNO3and back titration of excess HNO3. Nickel was analyzed by complexometric titration using EDTA with murexide as indicator.
Ni–P–B4C composite deposits were dissolved in HNO3solution completely. B4C particles did not react with HNO3, and were precipitated in the solution. The entire solution was placed for one week in order to completely precipitate B4C particles. Then the B4C particles were separated out and dried at 95 °C for 16 h. Finally, the dried B4C particles were weighed in an electronic balance with an accuracy of 0.01 mg. The content of B4C particles in composite coatings was calculated by the equation:
w = (weight of B4C / weight of coating) × 100%.
The Vickers hardness measurement of electroless deposits both in the as-plated and heat-treated conditions were evaluated at a load of 100 g with a diamond pyramid indenter technique where time of indentation was 15 s. The results were an average of 10 times measurements. Taber abrasion resistance test with CS-10 abrasive wheel having a load of 1 kg for 1 000 cycles was performed on both Ni–P and Ni–P–B4C deposits. For the studies of corrosion, EG&G Princeton Applied Research’s Model 6310 was used for potentiodynamic polarization and impedance measurements. To that extent, one cm2electrolessly deposited Ni–P and Ni–P–B4C were used as working electrodes. Platinum of 4 cm2and saturated calomel electrode (SCE) were used as auxiliary and reference electrodes, respectively. The electrolyte was 3.5wt% NaCl solution. SEM micrographs were described for determining the surface morphology of coatings at a magnification of ×5 000. X-ray diffraction (XRD, model ES1640A) measurements were conducted to find the phase transition.
3 Results and discussion
3. 1 SEM measurements
The surface morphology and microstructure of Ni–P coating and Ni–P–B4C composite are shown in Figure 1a to 1d, which indicates that Ni–P and Ni–P–B4C have spherical regular shape. It is obvious that the distribution of B4C particles in the layer increases with increasing B4C concentration in the bath. Uniform distribution of B4C in the composite was obtained for the coating prepared with 15 g/L of B4C. During heat treatment, the voids of coatings are reduced due to precipitation hardening of B4C along with the formation of Ni3P in the matrix. In the case of Ni–P–B4C system, the figures show the presence of coarse-grained composite particles with popcorn-like structure[6-7].
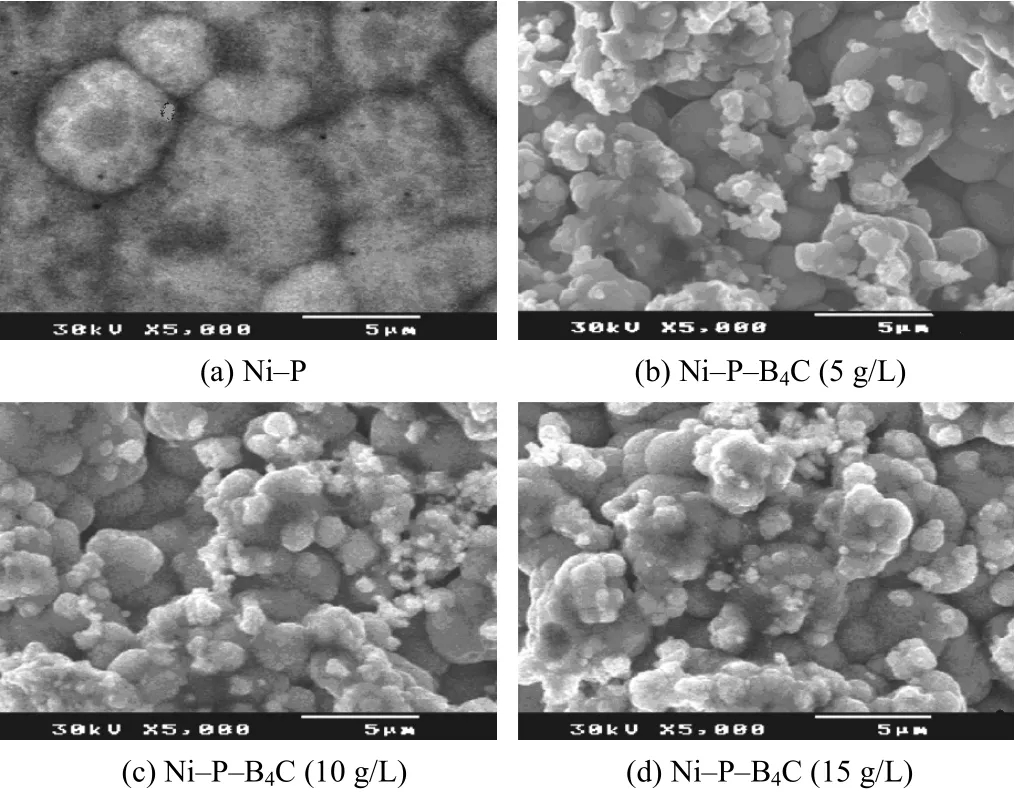
Figure 1 SEM images of electrolessly deposited coatings圖1 化學鍍層的掃描電鏡照片
3. 2 XRD Studies
According to the data from X-ray diffraction (see Figure 2), it is revealed that Ni2P3, Ni5P2and Ni3P phases are formed by heat treatment of Ni–P–B4C composite which eventually lead to an increase in hardness by precipitation hardening. The presence of B4C particles was also confirmed. Similar results were reported earlier for Ni–P–SiC and Ni/diamond coatings[7,9].
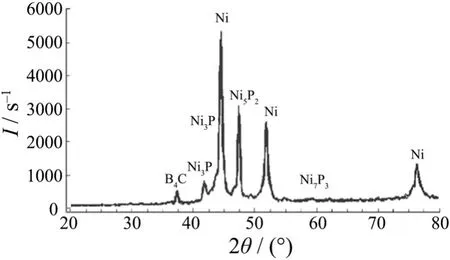
Figure 2 XRD pattern of electroless Ni–P–B4C composite coating after heat treatment圖2 Ni–P–B4C化學復合鍍層熱處理后的X射線衍射譜
3. 3 Chemical composition of deposits
The effect of B4C concentrations in the bath on the percentage of nickel and phosphorous in the deposit is shown in Table 1. In all the systems studied, the increasing concentration of particulate causes a decrease in the percentage of nickel and phosphorus contents in deposit. An optimal concentration of 15 g/L is recommended for B4C dosage in the bath. Beyond this concentration, collision among the moving particles inhibit the plating process.
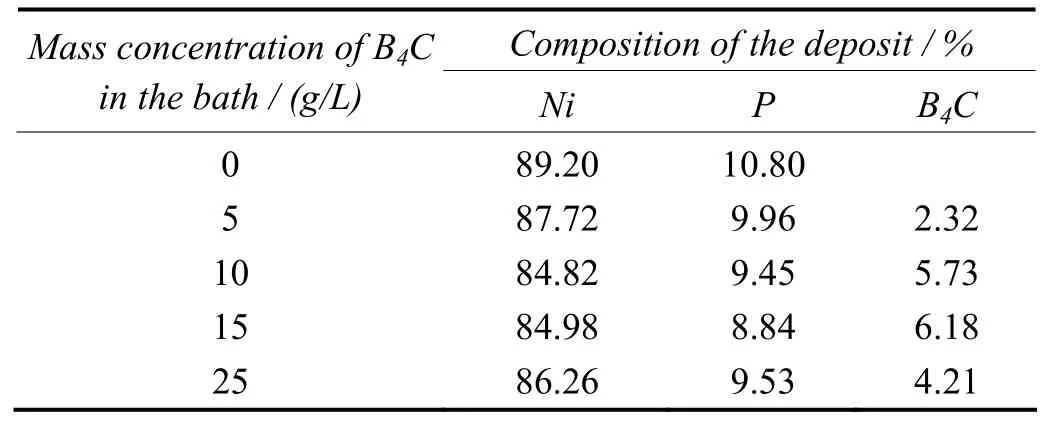
Table 1 Effect of mass concentration of B4C particles in bath on chemical composition of deposit表1 鍍液中B4C顆粒的質量濃度對鍍層化學成分的影響
3. 4 Hardness measurements
The results of the hardness test obtained for Ni–P–B4C composite coatings are presented in Table 2. It is observed from the table that the hardness values are more dependent on the B4C content in deposit. The Ni–8.84%P–6.18%B4C coating prepared from the bath containing 15 g/L B4C exhibits higher hardness than the Ni–10.80%P coating prepared without B4C in bath in both as-plated and heat-treated conditions. The increased hardness in the case of the composite after heat treatment is attributed to the precipitation of intermetallic phases induced by B4C particles. The composite is supposed to have large amounts of Ni3P phase which is responsible for the cured film. Thus, the higher hardness value of the Ni–8.84%P–6.18%B4C can be attributed to both the hard particles and Ni3P rich matrix[10,12].
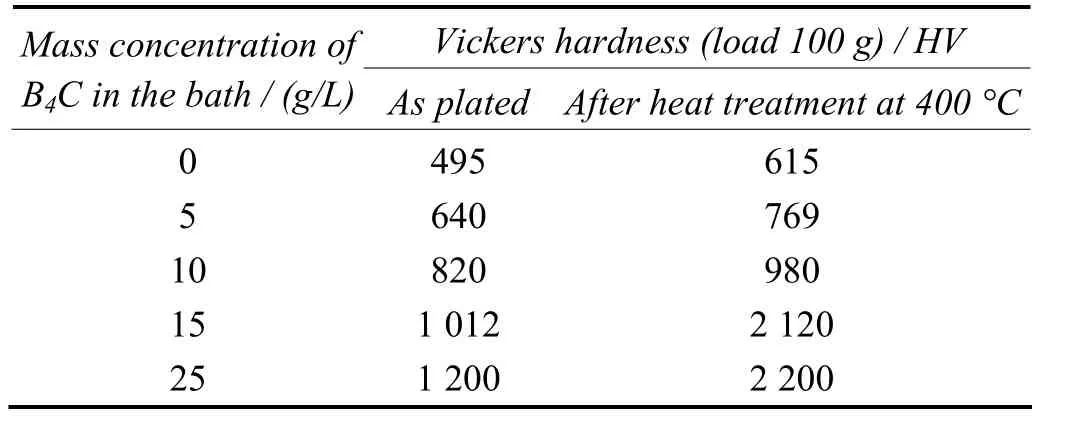
Table 2 Effect of mass concentration of B4C particles in bath on coating microhardness表2 鍍液中B4C顆粒的質量濃度對鍍層顯微硬度的影響
3. 5 Wear resistance studies
The results of the measurement of wear resistance for the composite coatings are presented in Table 3. The wear resistance of Ni–8.84%P–6.18%B4C is found to be higher than the Ni–10.80%P coating, suggesting that the improved result is evidently due to the B4C content. Even though the coatings prepared with 25 g/L exhibited higher abrasion resistance, the rate of its deposition was slow due to the collision among the entrapped particles. The wear resistance of all deposits is greatly enhanced after heat treatment at 400 °C[9,11]. Hence the coating prepared with 15 g/L B4C in bath is found as a recommended dosage for getting better performance.
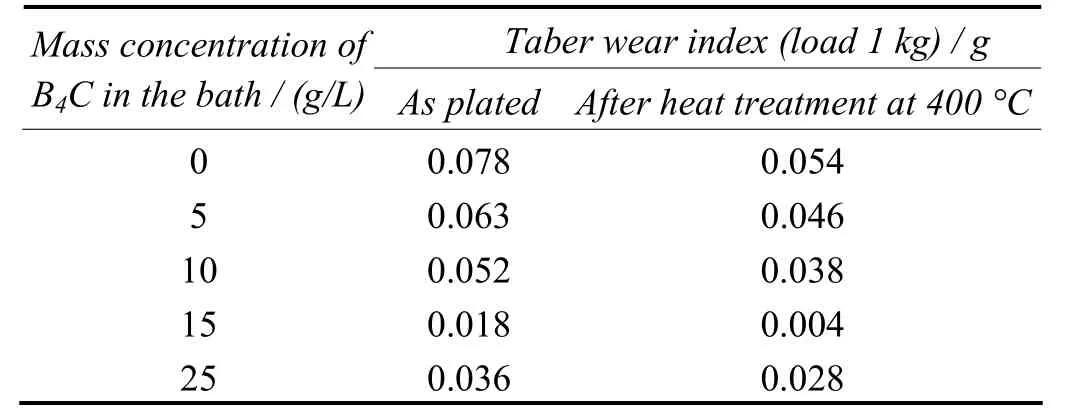
Table 3 Effect of mass concentration of B4C particles in bath on abrasion resistance of electrolessly deposited coatings表3 鍍液中B4C顆粒的質量濃度對化學鍍層耐磨性的影響
3. 6 Corrosion resistance measurements
Table 4 gives the corrosion resistance of Ni–P–B4C and Ni–P deposits evaluated by potentiodynamic polarization. It is clearly shown that the Ni–8.84%P–6.18%B4C coating has improved resistance to corrosion as compared with the Ni–10.08%P coating. The results of AC impedance measurement (see Table 5) clearly indicate that the Rtvalue is 2 873 ?·cm2for the Ni–8.84%P–6.18%B4C composite coating and 942 ?·cm2for the Ni–10.80%P coating. The above results indicate that the composite coating has higher resistance to corrosion than Ni–P coating in marine environment. The greater corrosion resistance of the composite coating is attributed to the uniform dispersion of B4C particles and also less porosity[7,11-12].
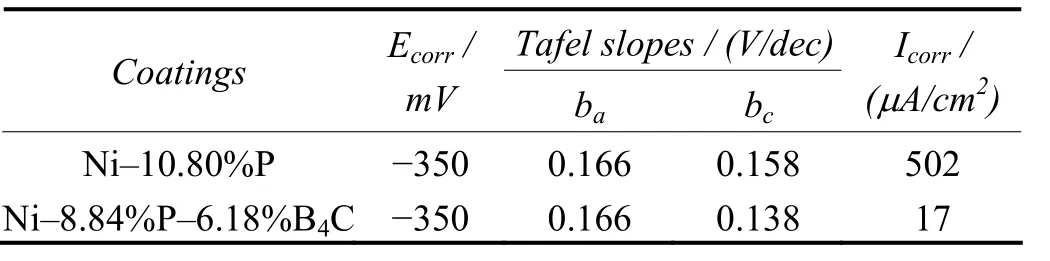
Table 4 Evaluation of corrosion resistance of coatings in 3.5wt% NaCl solution by potentiodynamic polarization studies表4 采用動電位極化方法評價鍍層在質量分數為3.5%的NaCl溶液中的耐蝕性
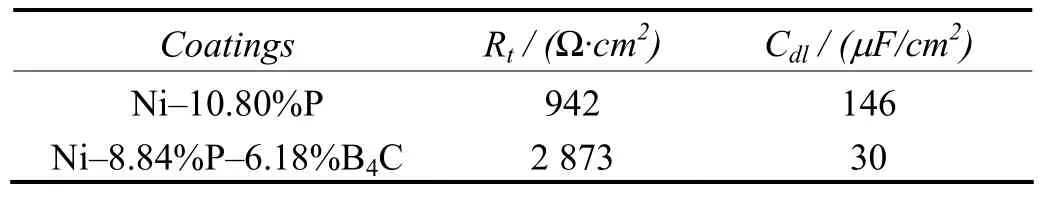
Table 5 Evaluation of corrosion resistance of coatings in 3.5wt% NaCl solution by AC impedance measurement表5 采用交流阻抗測量評價鍍層在質量分數為3.5%的NaCl溶液中的耐蝕性
4 Conclusions
(1) A suitable bath was optimized based on nickel carbonate, hypophosphorous acid, sodium hypophosphite and lactic acid to form electroless Ni–P and Ni–P–B4C composite coatings.
(2) The composite coatings exhibited enhanced hardness and wear resistance as compared with Ni–P coating both in as-plated and heat-treated conditions.
(3) The increase in charge transfer resistance (Rt) and the decrease in double-layer capacitance (Cdl) confirm the superior corrosion resistance of composite deposits.
(4) XRD results confirm the existence of Ni–P, Ni3P and Ni5P2phases in the matrix. SEM studies show the incorporation of B4C in Ni–P deposits.
[1] DUTKEWYCH O B, HOFFMANN L A. Replenishment of electroless nickel solutions: US, 3876434 [P]. 1975–04–08.
[2] AGARWALA R C, AGARWALA V, Electroless alloy/composite coatings: A review [J]. Sādhanā, 2003, 28 (3/4): 475-493.
[3] DATTA P K, BEDINGFIELD P B, LEWIS D B, et al. Structure and phase changes accompanying treatment of electroless Ni–B alloy coating [C] // Proceedings of 2nd International Electroless Nickel Conference, 1991: 139-153.
[4] KUO K H, WU Y K, LIANG J Z, et al. The metastable phases formed in amorphous Ni–P alloys during crystallization [J]. Philosophical Magazine A, 1985, 51 (2): 205-222.
[5] NARAYAN R, PANDEY A. Electroless Ni–PTFE composite coatings [C] // Proceedings of 12th National Convention of Metallurgists and Material Scientists. 1997: 98-106.
[6] KARTHIKEYAN S, SRINIVASAN K N, VASUDEVAN T, et al. Characterization of electroless Ni–P–SiC composite coatings [J]. Bulletin of Electrochemistry, 2001, 17 (3): 127.
[7] XINMIN H, ZONGANG D. The wear characteristics of Ni–P–SiC composite coatings [J]. Transactions of the Institute of Metal Finishing, 1992, 70 (2): 84-86.
[8] SRINIVASAN K N, JOHN S, KARTHIKEYAN S, et al. Studies on electroless nickel–phosphorous molybdenum sulphide composite coatings [J]. Transactions of the Metal Finishers’ Association of India [J]. 2003, 12 (3/4): 143-147.
[9] REDDY V V N, RAMAMOORTHY B, NAIR P K. Studies on electroless Ni–P/diamond composite coatings [C] // Proceedings of 18th AIMTDR Conference. Kharagpur: Indian Institute of Technology, 1998: 440-444.
[10] SHARMA S B, R. C AGARWALA R C, AGARWALA V, et al. Wear and friction behaviour of Ni–P–ZrO2–Al2O3composite electroless coatings [R]. International Conference on Mechanical Engineering 2001. Dhaka: Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology, 2001.
[11] KARTHIKEYAN S, NEELAKANDAN M A. Characteristics of electroless Ni–P–graphite composite coatings [J]. Journal of Electroplating & Finishing, 2006, 25 (4): 1-4.
[12] IZZARD M, DENNIS J K. Deposition and properties of electroless nickel/graphite coatings [J]. Transactions of the Institute of Metal Finishing, 1987, 65 (3): 85-89.
Development of electroless Ni–P–B4C composite coatings
S. Karthikeyan1,*, G. Venkatachalam2, K. N. Srinivasan3, T. Vasudevan4, S. Narayanan5
(1. Materials Division, School of Advanced Sciences, VIT University, Vellore-632014, Tamilnadu, India; 2. Design Division, School of Mechanical and Building Sciences, VIT University, Vellore-632014, Tamilnadu, India; 3. IMF Division, Central Electrochemical Research Institute (CECRI), Karaikudi-630006, Tamilnadu, India; 4. Centre for Multifunctional Materials, Kalasalingam University, Tamilnadu, India; 5. Manufacturing Division, School of Mechanical and Building Sciences, VIT University, Vellore, Tamilnadu, India)
Ni–P–B4C composite coatings were prepared on mild steel by electroless plating from a stable bath containing nickel carbonate 15 g/L, hypophosphorous acid 32 mL/L, sodium hypophosphite 15 g/L, lactic acid 32 mL/L, acetic acid 18 g/L, propionic acid 3 mL/L, dimethylamine 1.7 g/L, and boron carbide (B4C) particles 0-25 g/L. The microhardness of the composite coatings was examined by Vickers tester, the wear resistance by Taber abrasion tester, the microscopic morphology and structure by SEM and X-ray diffraction, and the corrosion resistance by potentiodynamic polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The incorporation of B4C increases the microhardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of the Ni–P alloy matrix. The Ni–P–B4C composite coating features a popcorn-like structure with coarse-grained composite particles.
electroless plating; nickel–phosphorus alloy; boron carbide; composite coating; corrosion resistance; microhardness; wear resistance
TQ153.12
A
1004 – 227X (2011) 06 – 0018 – 04
date: 2010–11–15 Revised date: 2011–01–05
S. Karthikeyan, (E-mail) skarthikeyanphd@yahoo.co.in, drskarthikeyanphd@gmail.com.
Biography: S. Karthikeyan (1975–), male, graduated with gold medal in M. Sc (Chemistry) from Alagappa University, Karaikudi, India and obtained his PhD degree in industrial chemistry (electroless plating) from the same university in 2002. He has published 35 research papers in leading national and international journals . He is having 11 years teaching and research experience. He has been awarded young scientist fellowship for the year 2005-06 by TNSCST, India. His research interest includes electroless plating of metals and composites, electroplating and corrosion inhibition.
[ 編輯:溫靖邦 ]

