基于文獻計量學的富硒小麥研究現狀可視化分析

摘 要:硒(Se)元素是人體必需的微量元素之一,富硒小麥是缺硒群體最有效、最重要的一種補硒食物,因而備受全球關注。為了全面了解富硒小麥的研究現狀,并預測未來發展趨勢,采用文獻計量學法對Web of Science(WOS)數據庫中涉及硒和小麥的901篇研究文獻進行歸納分析。研究結果表明,全球該領域的文獻呈逐年增長的趨勢,且資源環境科學和植物營養學是該領域發文量最多的學科方向。基于WOS檢索到的相關文獻和關鍵詞的共現分析,總結出該領域的2個熱點研究內容,即硒元素在小麥中的生物強化作用、硒元素對脅迫條件下小麥的緩解作用,以期為未來富硒小麥的科研探索和推廣應用提供參考。
關鍵詞:硒;小麥;文獻計量學;Web of Science數據庫;VOSviewer軟件;Bibliometric軟件
中圖分類號:S154.4;S512.1+1 文獻標志碼:A 文章編號:1674-7909(2024)12-60-7
DOI:10.19345/j.cnki.1674-7909.2024.12.013
0 引言
作為抗氧化性元素,硒元素具有保護心血管、抗肝細胞壞死、延緩衰老和提高人體免疫力等功效[1-2]。據報道,全世界有42個國家和地區缺硒,而我國是缺硒和貧硒的重災區之一[3]。世界衛生組織(WHO)和聯合國糧農組織(FAO)規定,健康人群的膳食硒供給量為50~250 μg/d,而我國居民平均硒攝入量(26~32 μg/d)遠低于該標準[4]。據了解,食用富含硒元素的食品是一種最有效的補硒方式。為此,中共中央、國務院印發的《“健康中國2030”規劃綱要》明確指出,國家有關部門正在積極組織與富硒農產品相關的標準制度的制定和修訂,為多地富硒農業的發展奠定基礎。同時,農業農村部印發的《全國鄉村產業發展規劃(2020—2025年)》明確指出,鼓勵開發包括富硒產品在內的營養健康系列化產品。在谷類作物中,小麥對硒元素的富集能力最強[5],可吸收環境中的硒元素,并將其轉化成富硒籽粒,是人體攝入硒元素的重要來源之一[6]。同時,小麥是世界上重要的糧食作物,在保障國家糧食安全戰略方面發揮著重要作用,但有關富硒小麥的研究進展尚不清晰。所以,筆者采用文獻計量學法來對富硒小麥的研究現狀和未來發展趨勢進行歸納分析,以期為未來富硒小麥的科研探索和推廣應用提供參考。
1 數據來源與研究工具
1.1 數據來源
文中所有與富硒小麥有關的文獻數據全部來自科學網(Web of Science,WOS),利用高級檢索,輸入檢索式(TS=“selenium” AND TS=“wheat”),并將數據庫限制在WOS核心合集,共檢索出2009—2024年發表的、涉及硒元素和小麥內容的研究文獻901篇,并用Excel、Bibliometric、VOSviewer等文本挖掘軟件工具對這些文獻的研究方向、出版年份、國家、作者、機構、關鍵詞等進行綜合性可視化分析。
1.2 研究工具
用Excel軟件對“富硒小麥”的相關文獻數據進行合并、統計、分析等處理,并繪制出相關圖表。用VOS viewer軟件、R語言(Bibliometric包)等文獻可視化工具對收集到的相關文獻進行文本挖掘和精練處理,對文獻的研究方向、出版年份、國家、作者、機構、關鍵詞等數據進行整理分析,并繪制出圖表,旨在系統地梳理該領域的研究現狀、揭示該領域研究熱點,并對未來發展趨勢進行預測。
2 結果與分析
2.1 年度文獻產出分析
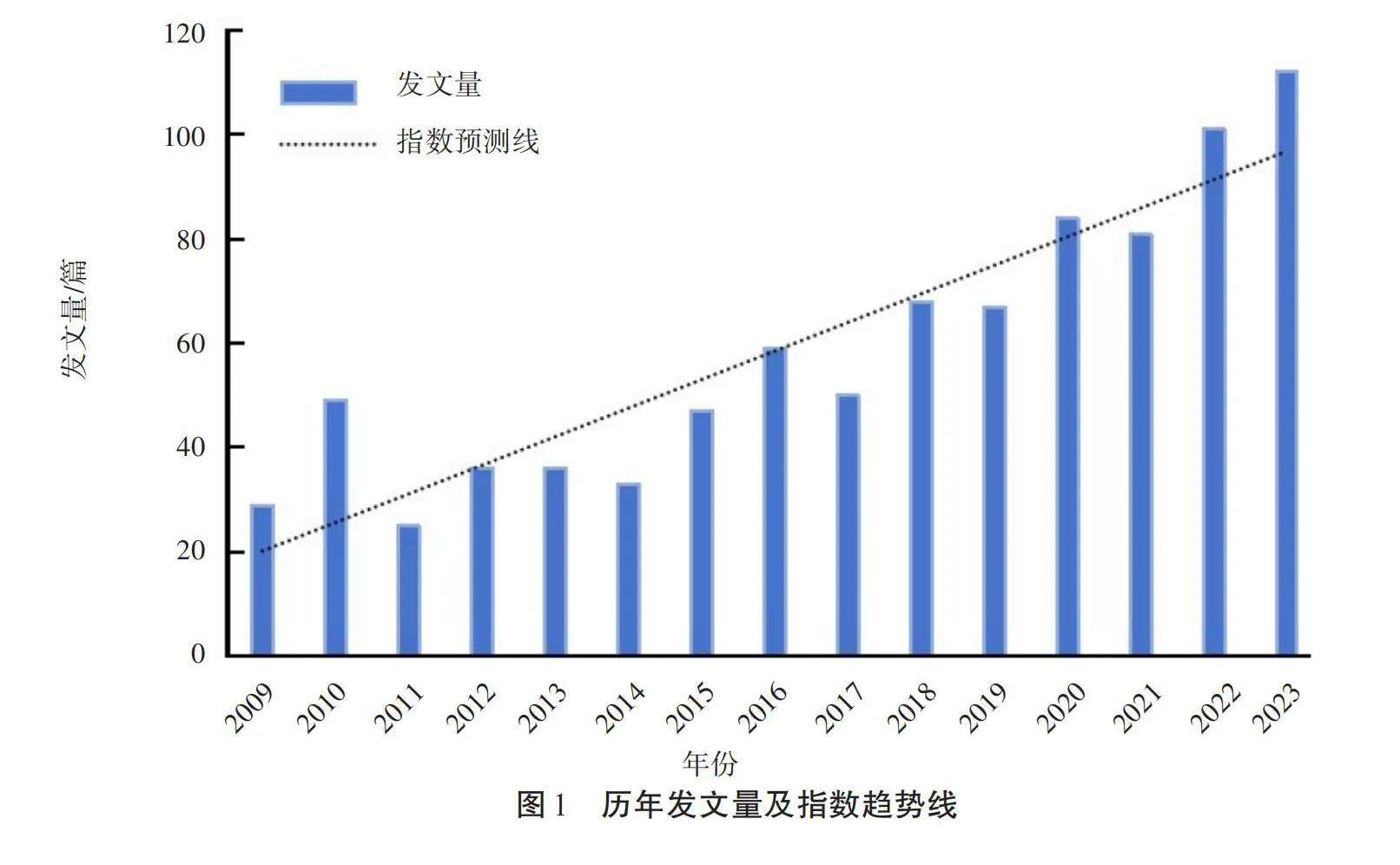
從WOS數據庫中共檢索到901篇與富硒小麥相關的文獻,如圖1所示。對這些文章按照年份進行分類后可知,首次檢索到與富硒小麥相關的文章是在2009年。從整體來看,2009—2023年,相關文獻的發表量呈逐年上升趨勢;從2016年開始,每年發文量均在50篇以上,從2022年開始,每年發文量均在100篇以上。從歷年發文量及變化趨勢可知,富硒小麥是該領域的熱門研究內容,也能從側面反映出相關科學家對富硒小麥內容的重視逐年增加。
2.2 發文期刊分析
從WOS中共檢索到308種刊登過富硒小麥相關文獻的期刊,對其中刊登該領域文獻數量大于10篇的期刊(見表1)進行比較分析。其中,Plant and Soil為發文量最大的期刊,共發表39篇文章,占全部文獻數量的比例為4.33%;其次為Agronomy-Basel、Frontiers in Plant Science、Food Chemistry、Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry和Plants-Basel,這5個期刊刊登該領域文獻數量均大于或等于20篇,占全部文獻數量的比例均大于2%,主要集中在農業科學、食品化學等領域;其余期刊的發文數量為10~20,占全部文獻數量的比例均小于2%,主要集中在資源環境、植物營養等領域。
2.3 作者及研究機構分析
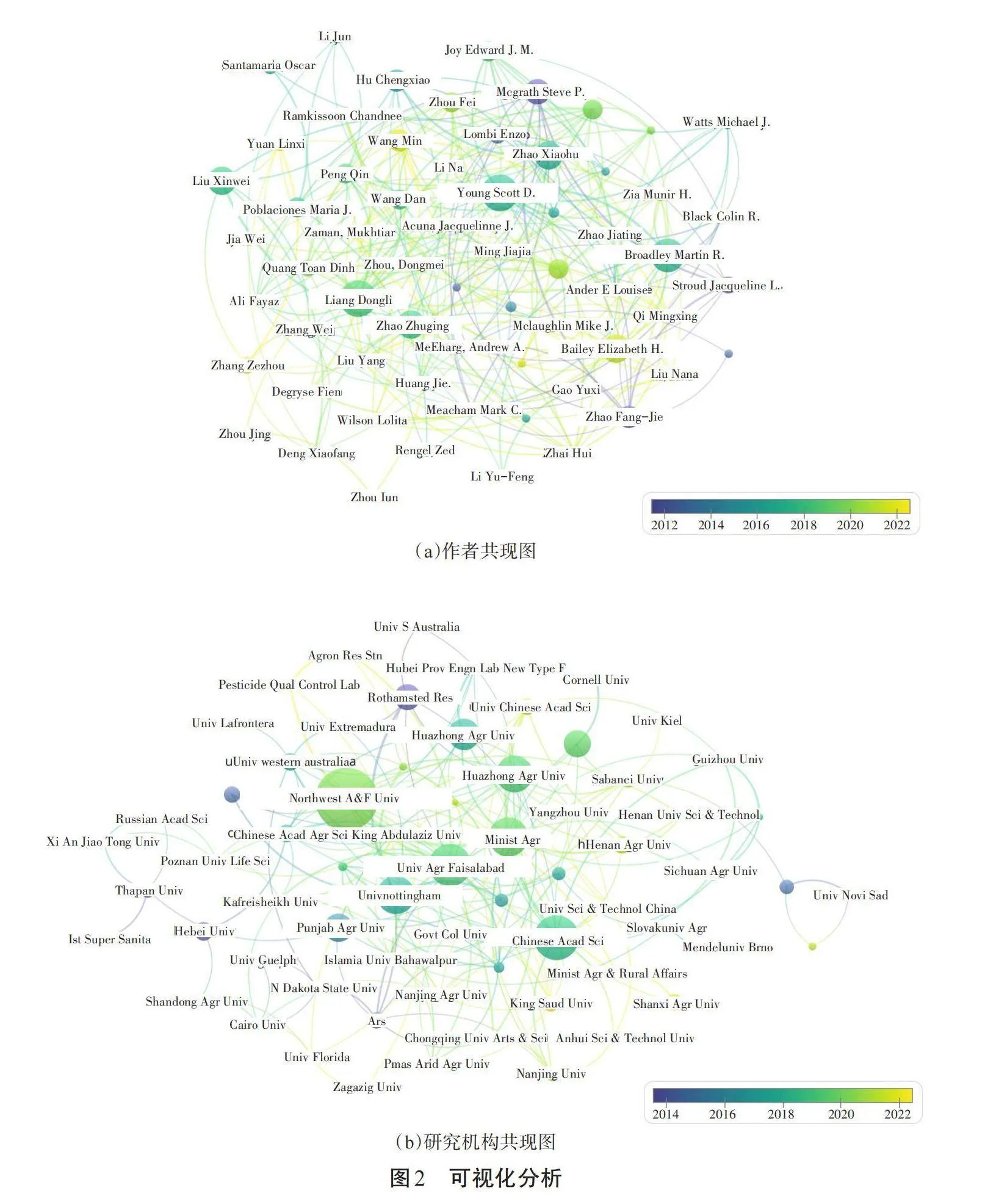
對WOS檢索到的相關文獻的作者及研究機構進行可視化分析,結果如圖2所示,主要機構發文情況見表2。圖2(a)為作者共現圖,顯現出的作者發文量均大于6篇,且以Liang Dongli、Scott D. Young的發文量最多,其次是Broadley Martin R.、Bailey Elizabeth H.、Zhao Xiaohu、Liu Xinwei和Zhao Zhuqing(發文量為10~13篇),發文時間為2016—2020年。
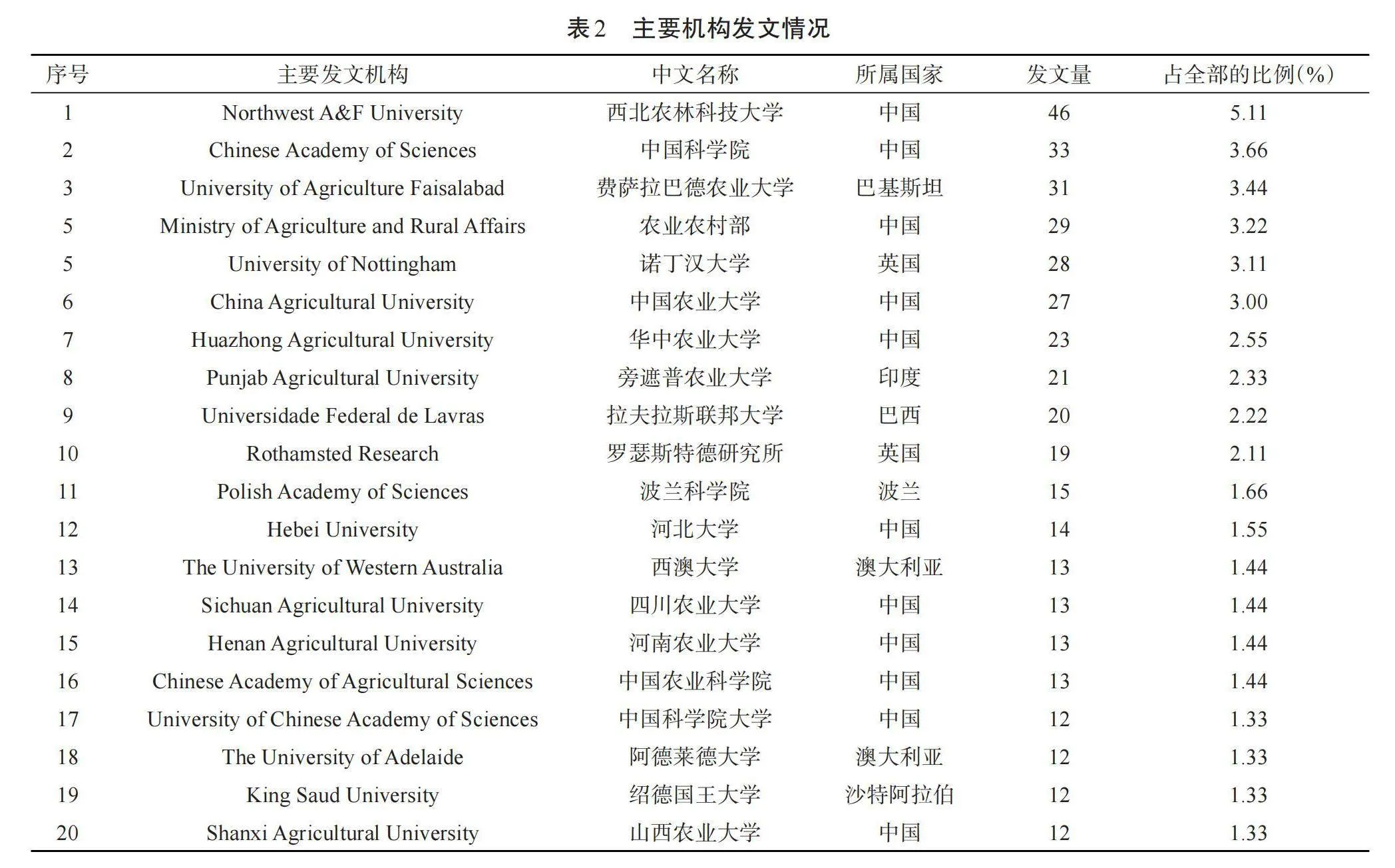
由研究機構共現圖和發文量前20名的研究機構的發文情況可知,發文量前20名的研究機構主要來自中國、巴基斯坦、英國、印度、巴西、波蘭、澳大利亞和沙特阿拉伯。其中,來自中國的研究機構有11個。發文量最多的機構是西北農林科技大學,共發表46篇文章,占全部發文量的5.11%,發文時間主要集中在2020年左右;其次是中國科學院、費薩拉巴德農業大學、農業農村部、諾丁漢大學、中國農業大學,發文量分別為33篇、31篇、29篇、28篇、27篇,分別占全部發文量的3.66%、3.44%、3.22%、3.11%、3.00%,發文時間主要集中在2020年以前。此外,河南農業大學、中國農業科學院、中國科學院大學、阿德萊德大學、紹德國王大學、山西農業大學的發文量為12~13篇,占全部比例的1.33%~1.44%,雖然這些機構的發文量排名偏后,但發文時間主要集中在2022年左右,距今較近,有潛力成為今后幾年該領域的主要發文機構。
2.4 關鍵詞分析
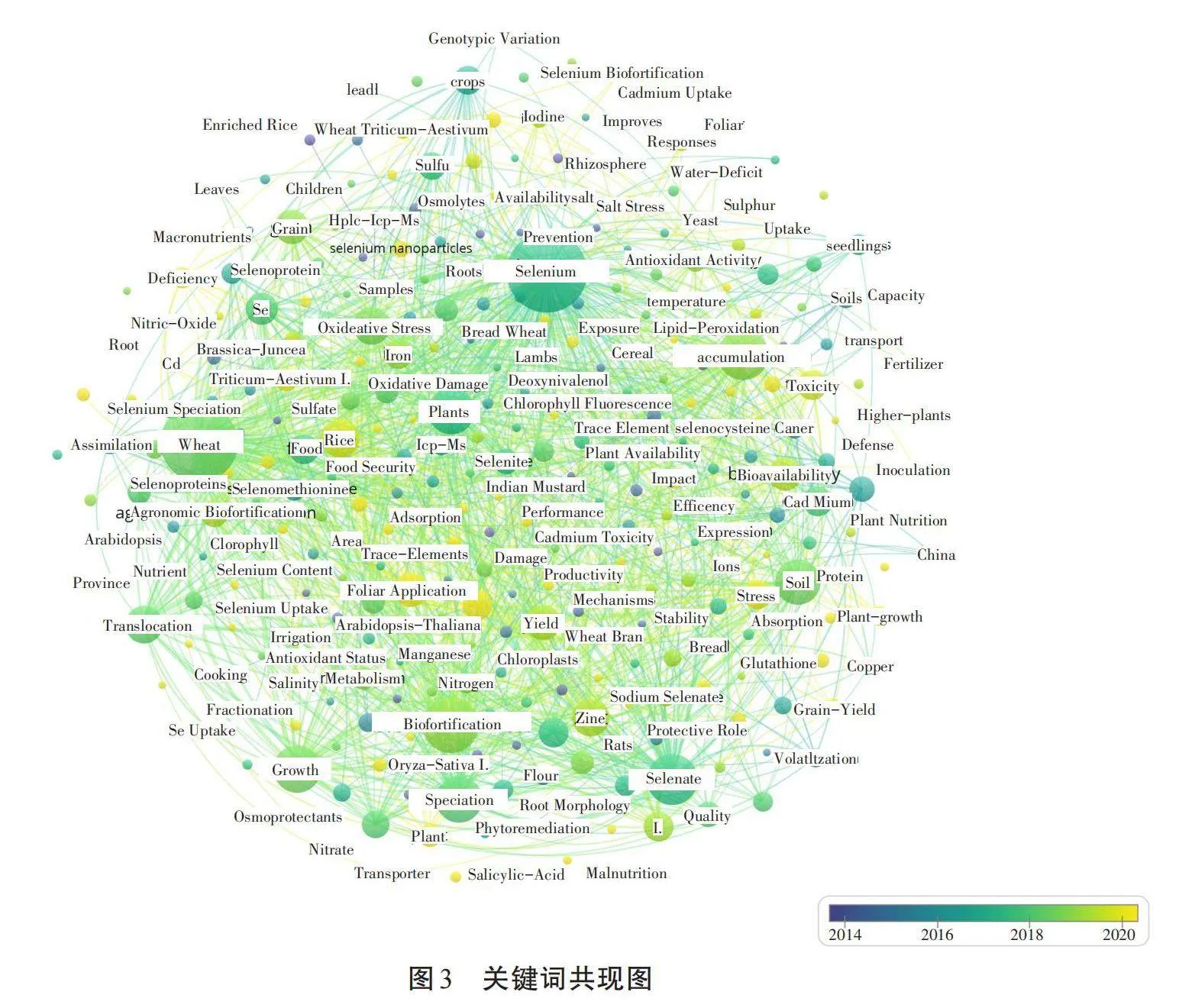
使用VOSviewer軟件對WOS檢索到的關鍵詞進行可視化分析,結果如圖3所示。由圖3可知,除了selenium、wheat這2個搜索用的關鍵詞外,在2020年之前,wheat、biofortification、selenate、growth、accumulation、speciation、translocation等關鍵詞的出現頻數較高,表明2020年之前的富硒小麥研究主要集中在使用硒酸鹽來促進小麥對硒元素吸收、轉運及積累方面,即小麥硒元素生物強化。2020年以后,foliar application、deficiency、stress、Cd等關鍵詞的出現頻數較高,表明2020年以后主要關注硒元素對逆境下的小麥的緩解作用。
3 熱點研究內容
基于WOS檢索到的該領域相關文獻,并結合關鍵詞進行共現分析,整理歸納出目前與富硒小麥相關的2個熱點研究內容,即硒元素對小麥具有生物強化作用、緩解重金屬脅迫的影響。
3.1 硒元素對小麥的生物強化作用
硒元素是一種有益元素,對保障人類、動物和某些植物的健康起到至關重要的作用,但其在大陸地殼中的分布并不均勻,導致人體對硒元素的攝入量嚴重受限[4,7]。硒元素主要以硒酸鹽和亞硒酸鹽的形式被作物吸收[8-9],而谷物(如小麥等)是人類攝入硒元素的主要來源之一,并最終進入食物鏈[4]。
硒生物強化是一種采用農藝和遺傳策略的農業過程[10-12],是提高硒元素在食物鏈中必需營養素含量的有效方法之一,通過增強作物吸收和積累外源硒的能力來提高外源硒在作物中的有效性,從而生產出富硒作物,提高硒元素在動物或人體中的含量,保障動物和人類的健康[13]。相關研究主要集中在近10 a,主要由中國、波蘭、巴基斯坦等國家開展優化硒生物強化方法[14-15]、提高硒肥料效率[16-17]及作物硒元素含量[2,17]等方面的研究。大量研究已證實,適量施用硒肥能有效提高大部分作物的硒元素含量[18-19]。目前,根據成分的差異可將硒肥分為無機硒肥、有機硒肥和新型富硒肥[13,20-21]。其中,無機硒肥包括硒酸鈉、亞硒酸鈉[22-23],有機硒肥包括氨基酸硒肥、腐殖酸硒肥、富硒酵母硒肥等,新型富硒肥包括納米硒肥等[20,24]。此外,常用的亞硒酸鹽和硒酸鹽葉面噴施處理均能促進小麥各部位對硒元素的吸收[8],但硒酸鹽處理以增加籽粒和根系中的硒元素積累為主,硒酸鹽處理以提高葉片和秸稈中硒元素的積累為主[25]。對施肥方式而言,土壤施硒肥的效果易受土壤吸附、作物各部位轉運速度的影響,而葉面施硒肥的效果受作物葉面蒸騰作用的影響較大,且這2種施肥方式的應用效果受作物種類、土壤類型、硒肥施用量、施用時期、氣候條件等因素的影響[22,26]。綜上所述,葉面噴施的富硒效果一般優于土壤施硒,這可能是因為作物葉片利用角質層和氣孔來吸收硒元素,減少土壤吸附等因素的影響,從而提高對硒元素的吸收利用率[22]。
3.2 硒元素對小麥緩解重金屬脅迫的影響
對植物而言,施用適量硒肥不僅能促進植株生長發育,還能緩解重金屬對小麥的脅迫作用。例如,硒元素能顯著減少小麥中鎘、砷、鉛等重金屬元素的積累[17,27-28],能提高小麥對鎘、汞等重金屬元素脅迫的耐受性[28-31]。有研究表明,硒元素緩解重金屬對小麥的脅迫作用是一個包含多種生理機制的綜合效應,主要包含以下3個方面:硒元素能促進植物細胞在重金屬元素脅迫下去除過多的活性氧,從而減輕細胞的氧化損傷[1,32-33];硒元素參與調控重金屬離子在植物體內的運輸和分布,減輕重金屬脅迫造成的損害[17,34-36];硒元素與重金屬元素結合會形成硒-重金屬復合物,促進植物螯合素的生成,從而減少重金屬離子在植物體內的積累[37-41]。
綜上所述,硒元素在植物對重金屬脅迫的響應中發揮著重要作用,但目前的研究主要集中在生理機制方面,未來應深入研究硒元素參與植物對環境脅迫響應的分子機制,可為硒元素在環境修復和農業開發中的實際應用提供重要的理論支持。所以,施硒肥既能降低作物中的重金屬含量,也能提高作物食用部位的硒含量,建議在中、低污染土壤中施用硒肥。
4 結束語
富硒小麥是缺硒群體最有效和最重要的一種補硒食物。近年來,富硒小麥產業受到國家的重視和扶持,同時隨著人們生活水平的提高,對功能活性食物的需求也在增加,富硒小麥產業發展迅速,展現出較好的應用前景,是農業領域的研究熱點。因此,筆者采用文獻統計學方法來采集數據,并用Bibliometric、VOSviewer等文本挖掘軟件工具對富硒小麥相關文獻的數據進行綜合性可視化分析。通過直觀知識圖譜的呈現,明確該領域的發展現狀和未來趨勢,以期推動富硒小麥產業實現高質量發展。
參考文獻:
[1]KURIA A,TIAN H D,LI M,et al. Selenium status in the body and cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2021,61(21):3616-3625.
[2]YAN G X,WU L,HOU M Y,et al.Effects of selenium application on wheat yield and grain selenium content:a global meta-analysis[J].Field Crops Research,2024,307:109266.
[3]LI X Y,WANG F,FENG X L,et al.A nationwide investigation of trace elements in rice and wheat flour in China:levels,spatial distributions and implications for human exposure[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2023,30(30):75235-75246.
[4]RAYMAN M P.Selenium intake,status,and health:a complex relationship[J].Hormones (Athens,Greece),2020,19(1):9-14.
[5]DUBORSKá E,?EBESTA M,MATULOVá M,et al.Current strategies for selenium and Iodine biofortification in crop plants[J].Nutrients,2022,14(22):4717.
[6]SCHIAVON M,NARDI S,DALLA VECCHI
A F,et al.Selenium biofortification in the 21st century:status and challenges for healthy human nutrition[J].Plant Soil,2020,453(1/2):245-270.
[7]ROMAN M,JITARU P,BARBANTE C.Selenium biochemistry and its role for human health[J].Metallomics,2014,6(1):25-54.
[8]WANG M,ALI F,WANG M K,et al.Understanding boosting selenium accumulation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) following foliar selenium application at different stages,forms,and doses[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research International,2020,27(9):717-728.
[9]KIELISZEK M.Selenium-fascinating microelement,properties and sources in food[J].Molecules,2019,24(7):1298.
[10]GALINHA C,SáNCHEZ-MARTíNEZ M,PACHECO A M G,et al.Characterization of selenium-enriched wheat by agronomic biofortification[J].Journal of Food Science and Technology,2015,52(7):4236-4245.
[11]ISLAM M Z,PARK B J,KANG H M,et al.Influence of selenium biofortification on the bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of wheat microgreen extract[J].Food Chemistry,2020,309:125763.
[12]SORS T G,ELLIS D R,SALT D E.Selenium uptake,translocation,assimilation and metabolic fate in plants[J].Photosynthesis Research,2005,86(3):373-389.
[13]CHEN P,SHAGHALEH H,HAMOUD Y A,et al.Selenium-containing organic fertilizer application affects yield,quality,and distribution of Selenium in wheat[J].Life,2023,13(9):1849.
[14]DI X R,QIN X,ZHAO L J,et al.Selenium distribution,translocation and speciation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) after foliar spraying selenite and selenate[J].Food Chemistry,2023,400:134077.
[15]LACHMAN J,MIHOLOVá D,PIVEC V,et al.Content of phenolic antioxidants and selenium in grainof einkorn(Triticum monococcum),emmer (Triticum dicoccum)and spring wheat (Triticum aestivum) varieties[J].Plant Soil amp; Environment,2011,57(5):235-243.
[16]WANG Q,YU Y,LI J X,et al.Effects of different forms of selenium fertilizers on Se accumulation, distribution and residual effect in winter wheat-summer maize rotation system[J].Journal of Agricultural amp; Food Chemistry,2017,65(6):1116-1123.
[17]LIU Y X,HUANG S H,JIANG Z B,et al.Selenium biofortification modulates plant growth,microelement and heavy metal concentrations,selenium uptake,and accumulation in black-grained wheat[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2021,12:748523.
[18]ZHANG L H,YANG J Y,FU Z,et al.Pathway and driving forces of selenite absorption in wheat leaf blades[J].Plant,Soil and Environment,2019,65(12):609-614.
[19]LIU H D,XIAO C M,QIU T,et al.Selenium regulates antioxidant, photosynthesis,and cell permeability in plants under various abiotic stresses: a review[J].Plants,2022,12(1):44.
[20]LEI H D,ZHOU M G,LI B,et al Humic acid chelated selenium is suitable for wheat biofortification[J] Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2023,103(10):4887-4898.
[21]KIKKERT J,BERKELAAR E.Plant uptake and translocation of inorganic and organic forms of selenium[J].Archives of Environmental Contamination amp; Toxicology,2013,65(3):458-465.
[22]YUAN Z Q,LONG W X,LIANG T,et al.Effect of foliar spraying of organic and inorganic selenium fertilizers during different growth stages on selenium accumulation and speciation in rice[J].Plant and Soil,2022,486(1/2):87-101.
[23]ALORI E T,GLICK B R,BABALOLA O O.Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture[J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2017,8:971.
[24]KHAN M K,PANDEY A,HAMURCU M,et al.Insight into the prospects for nanotechnology in wheat biofortification[J].Biology,2021,10(11):1123.
[25]WANG Q,YU Y,LI J X,et al.Effects of different forms of selenium fertilizers on Se accumulation, distribution and residual effect in winter wheat-summer maize rotation system[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(6):1116-1123.
[26]HUANG R,BA?UELOS G S,ZHAO J R,et al.Comprehensive evaluation of factors influencing selenium fertilization biofortification[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2024,104(10):6100-6107.
[27]FENG R W,WANG L Z,YANG J G,et al.Underlying mechanisms responsible for restriction of uptake and translocation of heavy metals (metalloids) by selenium via root application in plants[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,402:123570.
[28]GU X Z,WEN X,YI N,et al.Effect of foliar application of silicon,selenium and zinc on heavy metal accumulation in wheat grains in field studies[J].Environmental Pollutants and Bioavailability,2022,34(1):246-252.
[29]MANZOOR M,ABDALLA M A,HUSSAIN M A,et al.Silicon-selenium interplay imparts cadmium resistance in wheat through an up-regulating antioxidant system[J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2023,25(1):387.
[30]LAI X,YANG X,RAO S,et al.Advances in physiological mechanisms of selenium to improve heavy metal stress tolerance in plants[J].Plant Biology(Stuttgart, Germany),2022,24(6):913-919.
[31]JIANG H Y,LIN W Q,JIAO H P,et al.Uptake,transport,and metabolism of selenium and its protective effects against toxic metals in plants: a review[J].Metallomics,2021,13(7):mfab040.
[32]ZENG R,FAROOQ M U,WANG L,et al.Study on differential protein expression in natural selenium-enriched and non-selenium-enriched rice based on iTRAQ quantitative proteomics[J].Biomolecules,2019,9(4):130.
[33]ZHANG H,FENG X B,ZHU J M,et al.Selenium in soil inhibits mercury uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J].Environmental Science and Technology,2012,46(18):10040-10046.
[34]SCHIAVON M,PILON-SMITS E A H.The fascinating facets of plant selenium accumulation-biochemistry,physiology,evolution and ecology[J].New Phytologist,2017,213(4):1582-1596.
[35]LIN L,ZHOU W H,DAI H X,et al.Selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice[J].Journal of hazardous materials,2012,235:343-351.
[36]SIEPRAWSKA A,KORNAS A,FILEK M.Involvement of selenium in protective mechanisms of plants under environmental stress conditions-review[J].Acta Biologica Cracoviensia. Series Botanicas,2015,57(1):9-20.
[37]AN Z,SUO L,ZHAO L,et al.Effects of selenium on uptake and distribution of trace elements and heavy metals in millet[J].Fresenius Environmental Bulletin,2017,26(8):5037-5040.
[38]PRIYA A K,GNANASEKARAN L,DUTTA K,et al.Biosorption of heavy metals by microorganisms: evaluation of different underlying mechanisms[J].Chemosphere,2022,307(Part 4):135957.
[39]HAWRYLAK-NOWAK B,HASANUZZAM
AN M,MATRASZEK-GAWRON R.Mechanisms of selenium-induced enhancement of abiotic stress tolerance in plants[J].Plant Nutrients and Abiotic Stress Tolerance,2018:269-295.
[40]GHORAI M,KUMAR V,KUMAR V,et al.Beneficial role of selenium (Se) biofortification in developing resilience against potentially toxic metal and metalloid Stress in crops: recent trends in genetic engineering and omics approaches[J].Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition,2022,22(2):2347-2377.
[41]GUPTA M,GUPTA S.An overview of selenium uptake, metabolism, and toxicity in plants[J].Frontiers in plant science,2017,7(1):234638.

