不同栽培措施對(duì)水稻基肥氮素利用率及產(chǎn)量的影響
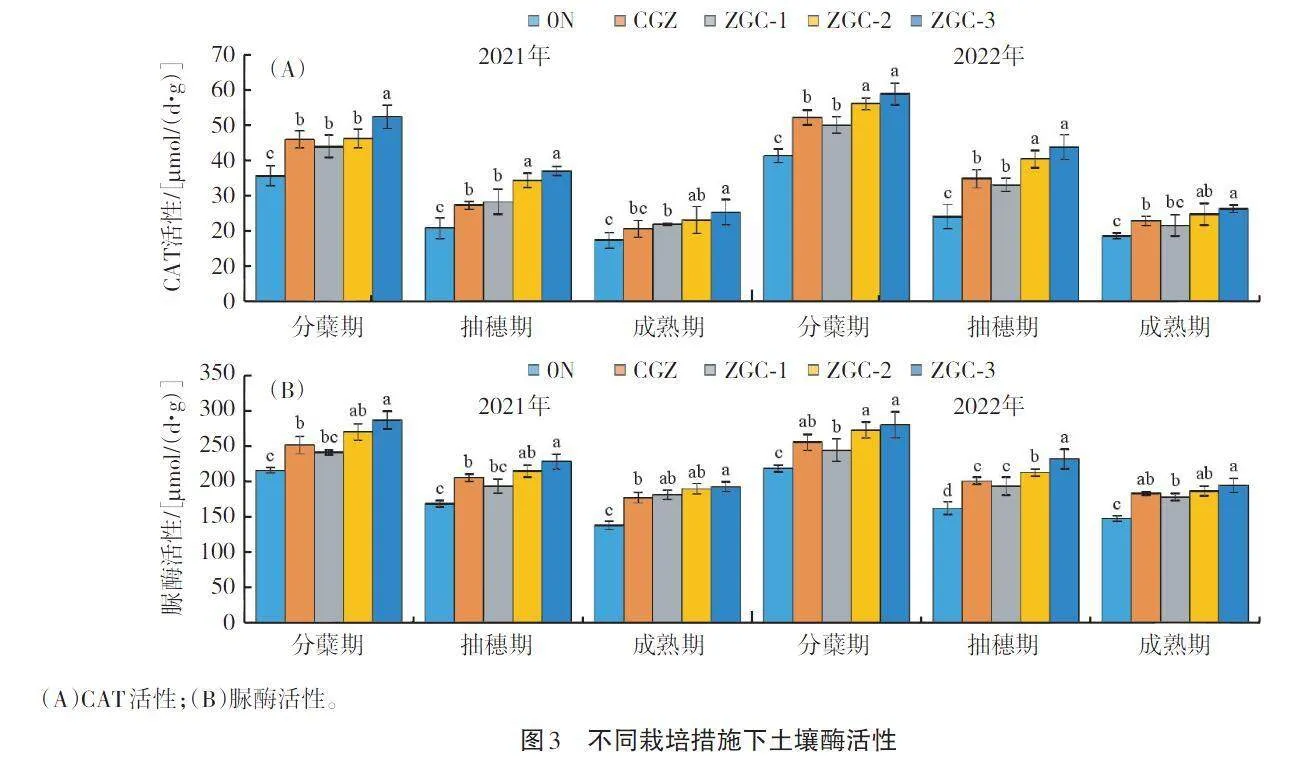
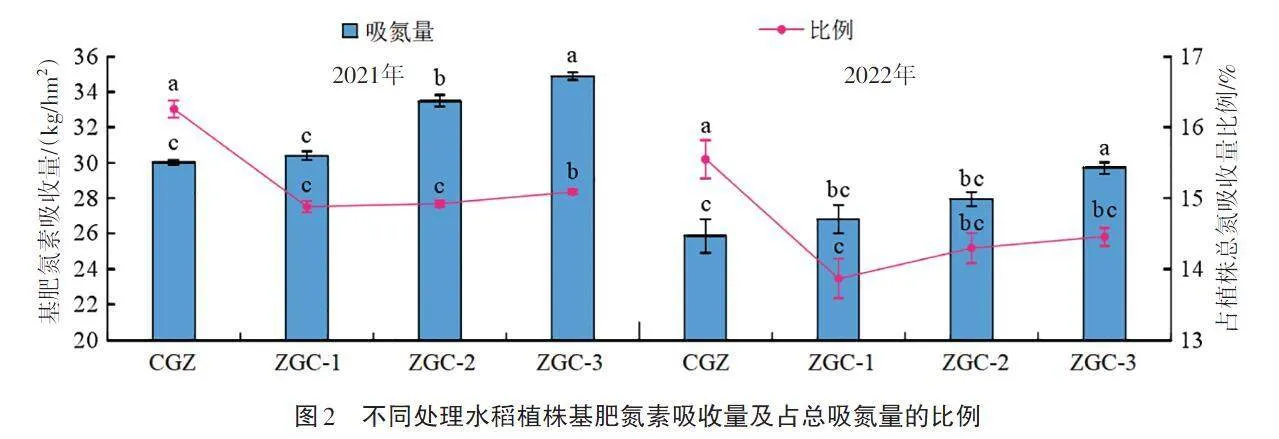
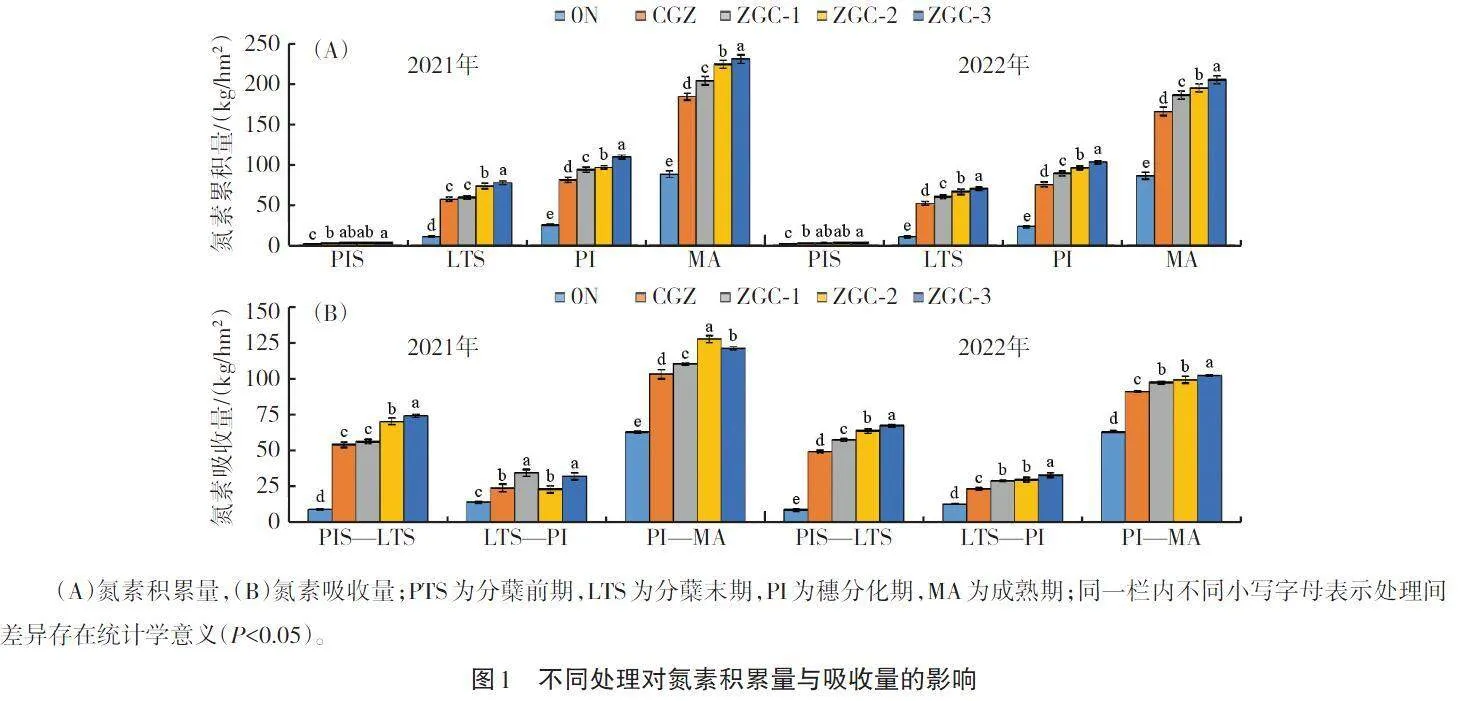
摘要 為評(píng)估不同栽培措施對(duì)水稻基肥氮素利用率和產(chǎn)量的影響,本研究以水稻品種瑋兩優(yōu)8612為試驗(yàn)材料,利用15N標(biāo)記示蹤技術(shù)分析不同栽培措施下水稻產(chǎn)量、植株氮素的吸收和轉(zhuǎn)化率以及土壤酶活性。結(jié)果表明,改良灌溉管理和優(yōu)化施肥策略有利于增加水稻植株氮素的積累與吸收,增加產(chǎn)量,其中輕干濕交替灌溉配合有機(jī)肥的綜合管理措施(ZGC-3)效果較佳;此外,綜合管理措施有利于提高土壤酶活性,增強(qiáng)土壤生物化學(xué)活性。研究證實(shí)了綜合栽培管理措施可有效提升水稻產(chǎn)量和氮肥利用效率,以及減少對(duì)環(huán)境影響。
關(guān)鍵詞 栽培;水稻;氮素利用;15N示蹤;土壤酶活性
中圖分類號(hào) S511" " 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼 A" " 文章編號(hào) 1007-7731(2024)15-0009-05
DOI號(hào) 10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2024.15.003
Effects of different cultivation measures on nitrogen utilization efficiency of"basal fertilizer and rice yield
YANG Zhouhua
(Agricultural and Rural Comprehensive Service Center of Dashi Township, Taihu Lake County, Anqing 246400, China)
Abstract To evaluate the effects of different cultivation measures on the nitrogen utilization efficiency of basal fertilizer and rice yield base fertilizer, the rice variety Weiliangyou 8612 was used as the experimental material, and the rice yield, plant nitrogen absorption and conversion rate, and soil enzyme activity under different cultivation measures were analyzed using 15N labeling and tracing technology. The results showed that improving irrigation management and optimizing fertilization strategies were beneficial for increasing nitrogen accumulation and absorption in rice plants, and increasing yield. Among them, the comprehensive management measure of light dry wet alternation irrigation combined with organic fertilizer(ZGC-3)had the better effect. In addition, comprehensive management measures are beneficial for improving soil enzyme activity and enhancing soil biochemical activity. The study confirmed the effectiveness of comprehensive cultivation management strategies in improving rice yield and nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency, as well as reducing environmental impact.
Keywords cultivation; rice; nitrogen utilization; 15N tracer; soil enzyme activities
氮肥的有效利用對(duì)于促進(jìn)農(nóng)業(yè)生產(chǎn)可持續(xù)發(fā)展具有重要作用。氮素利用率直接關(guān)系到水稻作物的產(chǎn)量與品質(zhì),且對(duì)環(huán)境存在潛在影響。實(shí)際農(nóng)業(yè)生產(chǎn)中,氮肥利用率偏低不僅造成資源浪費(fèi),還在一定程度上引發(fā)了環(huán)境問題,如溫室氣體排放和水體富營(yíng)養(yǎng)化等[1-2]。當(dāng)前,相關(guān)學(xué)者聚焦于通過各種栽培措施提高氮素利用率的研究,謝昊等[3]研究表明,通過增密減氮、前氮后移和增施餅肥等栽培措施處理,可以提高植株的氮肥吸收利用效率,且具有改善土壤質(zhì)量的作用;丁周宇等[4]研究了栽培措施對(duì)水稻氮素吸收利用的影響,采用秸稈還田+深耕+緩釋肥方式提高了氮肥利用率;李敏等[5]研究表明,控水增密簡(jiǎn)單栽培能明顯提高水稻中后期氮素積累量,促進(jìn)氮素由營(yíng)養(yǎng)器官向穗部轉(zhuǎn)運(yùn)。……

