Expression of miR-9-5p and RHOA in aluminum-induced rat cognitive dysfunction
JIA Yun-jing, ZHONG Bin, LI Chen-yu, GAN Jue-fang, LIAN Chun-rong, LI Sha-sha, LING Yan-wu
Youjiang Medical College for Nationalities, Baise 533000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the possible mechanism of microRNA-9-5p(miR-9-5p) and Ras homologous gene family A (RHOA) in aluminum-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats.Methods: According to the principle of randomization, 48 Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups (n=12) of blank control, low dose, medium dose and high dose.The blank control group was gavaged daily saline, and the other three dose groups were given daily gavage AlCl3 aqueous solution at three doses of 25 mg/kg, 50 mg/kg, and 100 mg/kg to create a rat model of cognitive impairment for three months.The water maze (MWM) positioning navigation experiment was used to record the time t(s), namely, the incubation period, on the platform of rats, and the incubation period of each group was used to determine whether the rats in the infected group had learning and memory impairment.Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and Nissl stains observed the pathological changes of nerve cells in the hippocampus of the four groups.Western blot detected the protein expression levels of RHOA and cranial neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in fresh rat hippocampal tissues.RT-qPCR detected the mRNA expression of miR-9-5p, RHOA, and BDNF in rat hippocampal tissues.Results: The results of Morris water maze positioning navigation test showed that the incubation period of each group was calculated on the 1st, 3rd and 5th days of the experiment, and the motor incubation period of the infected group was higher than that of the control group.The results of HE staining showed that the rat nerve cells in the control group were morphologically intact, the staining was clear,the nucleus was clearly visible, and the edge of the cell membrane was sharp.The rat neurons in the infected group were damaged to varying degrees, the nucleus gradually dissolved,the cytoplasmic staining became deeper, the edges of the cell membrane were blurred and disordered, and the cells were deformed and arranged disordered.The results of Nissl staining showed that the well-stained Nissl body particles were visible in the nerve cells of rats in the control group, and the dissipation of Nissl bodies in the nerve cells of the infected group was reduced, and the staining was shallow.The results of RT-qPCR showed that compared with the control group, the mRNA expression of miR-9-5p and BDNF was decreased in the infected group, and the mRNA expression of RHOA was increased (P<0.05 or P<0.001).The Western blot results showed that compared with the control group, the relative expression of BDNF in the three infected groups was decreased, and the relative expression of RHOA increased (P<0.05).Conclusion: In aluminum-induced cognitive impairment, miR-9-5p is downregulated and RHOA is upregulatd.
1.Introduction
Aluminium is a non-essential element in the human body, but its abundance, combined with widespread human use, makes aluminium-related toxicity particularly relevant to human health.As China’s economy develops and the development of aluminium mines in Guangxi continues to expand, the pressure for high aluminium exposure in populations in aluminium mining areas continues to increase.According to epidemiological data, longterm aluminium exposure can lead to cognitive dysfunction [Mild Cognitive Dysfunction (MCD)].Mild cognitive dysfunction is an intermediate stage between normal age-related changes in the brain and dementia, and is widely considered to be a precursor to Alzheimer’s disease (AD).Understanding the pathogenesis of mild cognitive dysfunction is important for early detection and intervention in AD[1].
microRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of non-coding RNAs that are widely distributed in eukaryotes.It has been shown to have regulatory roles in development, growth, differentiation and neurodegenerative processes[2].A single miRNA molecule can regulate a variety of genes, making miRNAs a potential therapeutic target for multifactorial diseases, such as brain disorders.
In this study, we investigated the expression of miR-9-5p and RHOA in aluminum-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental animals
Forty-eight SPF grade Wistar rats, male and female, weighing 160-220 g, aged 6-8 weeks (purchased from Changsha Tianqin Biotechnology Co., Ltd, Hunan Province, License No.SCXK(Xiang) 2022-0011).
2.2 Main reagents
Alcl3 (Guangdong Guanghua Chemical Factory Co., Ltd.); BCA kit(Biyuntian Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); RhoA and BDNF antibodies(Hangzhou Hua’an Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); ECL development kit (Mona Biotechnology Co., Ltd.); PCR primers (Shanghai Bioengineering Co., Ltd., Guangzhou Founengene Co., Ltd.); total RNA extraction kit (Beijing Solabao Technology Co., Ltd.); realtime fluorescence quantitative PCR (Mona Biotechnology Co., Ltd.);cDNA synthesis kit (Mona Biotechnology Co., Ltd.).
2.3 Methods
2.3.1 Grouping and animal model construction
The rats were first acclimatized for one week after arrival.Each rat was numbered and 48 rats were divided into four groups according to the method of random number table, i.e.control group (n=12),low dose group (n=12), medium dose group (n=12) and high dose group (n=12).The model of cognitive impairment was established by preparing 10 g/L of AlCl3solution with saline according to the modelling method in reference[3,4] and gavaged for three months at 25, 50 and 100 mg/kg for the low dose group, medium dose group and high dose group respectively.
2.3.2 Morris water maze positioning navigation test
After the rats had been poisoned, the water maze was filled with water to cover the platform and ink was added to the water for the navigation test.The day before the start of the experiment, each rat was placed in the water maze and swam in order to get used to the water environment.When the experiment started, each rat was placed in the water from each of the four quadrants along the edge and the time was timed to end when the rat swam onto the platform.For rats that did not swim onto the platform 1 min later, they were placed on the platform for 20 s to form a memory for a total of 5 days.Based on the latency period, the learning memory capacity of the rats can be tested.
2.3.3 HE stain and Nissler stain
Rats were anesthetized with 3% sodium pentobarbital by intraperitoneal injection, saline was instilled from the apical point,then 4% paraformaldehyde was drip-fixed into the rat tissues, and immediately after the end of the procedure, the head was severed and the brain tissues were removed, put into 4% paraformaldehyde for 48 h and then gradient dehydration, embedding to make wax blocks, sectioning (4 μm), spreading, baking, dewaxing and then hematoxylin-eosin and Nirvana staining were performed, followed by observation under 200x light microscopy.
2.3.4 RT-qPCR
The rats were immediately decapitated after anesthesia and execution, fresh hippocampal tissues were extracted, ground using a low-temperature high-speed grinder, total RNA was extracted using a total RNA kit, and its concentration and purity were detected using a spectrophotometer.cDNA was synthesized using a cDNA synthesis kit with total RNA as the template and then amplified.miR-9-5p was analyzed using U6 as the internal reference (U6 validation primers were purchased from Fuso Genetics, item no.The expression levels of miR-9-5p, RhoA and BDNF were analyzed by using 2-△△Ctwith GAPDH as internal reference.The primer names and sequences are shown in Table 1.
2.3.5 Western Blot
After the rats were executed, the right heart ear was cut open and the apical end was perfused with saline until saline flowed from the right heart ear, the head was severed and fresh brain tissue was removed, followed by an operation on ice to peel out fresh hippocampal tissue, which could be stored in a -80 ℃ refrigerator.Before the experiment started, the tissue homogenate was lysed to extract total protein, and according to the operation instructions of the BCA kit, after determining the concentration of each group of protein samples, the upper sample buffer and the samples were then denatured by adding boiling water for 10 min.After electrophoresis,the samples were transferred to PVDF membrane for sealing (5%skimmed milk powder) for 2 h.The membrane was washed 3 times with TBST, the primary antibody was incubated overnight at 4 ℃,the primary antibody was washed 5 times with TBST, the secondary antibody was incubated for 1 h, the membrane was washed 5 times with TBST and the ECL solution was added dropwise for imaging.The bands were analysed for grey scale values.
2.4 Statistical processing
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 26.0 software,and all experimental results were expressed as (±s ).Data were compared between groups using the one-way, one-factor ANOVA test at α=0.05.
3.Results
3.1 Comparison of the incubation period of the Morris Water Maze positioning navigation experiment in various groups of rats
The low, medium and high dose groups were given Alcl3 aqueous solution by gavage (25, 50 and 100 mg/kg) and the blank control group was given saline by gavage.
Latency times were recorded on days 1, 3 and 5 of training for the locomotor navigation experiment, and the time to find the plateau was significantly greater in the drug-infected group than in the control group.On the first day of training, compared to the blank control group, the low and medium dose groups were not statistically significant and the high dose group was statistically significant(P<0.05); on the third day of training, compared to the blank control group, the results of the low dose group were not statistically significant and the medium and high dose groups were statistically significant (P<0.05); on the fifth day of training, compared to the blank control group, the low dose group was not statistically significant and the medium and high dose groups were statistically significant (P<0.05, P<0.001) compared to the blank control group on the fifth day of training.The results are shown in Table 2.
Tab 2 Comparison of latency after training in the Morris Water Maze positioning navigation experiment in four groups (s, ±s)
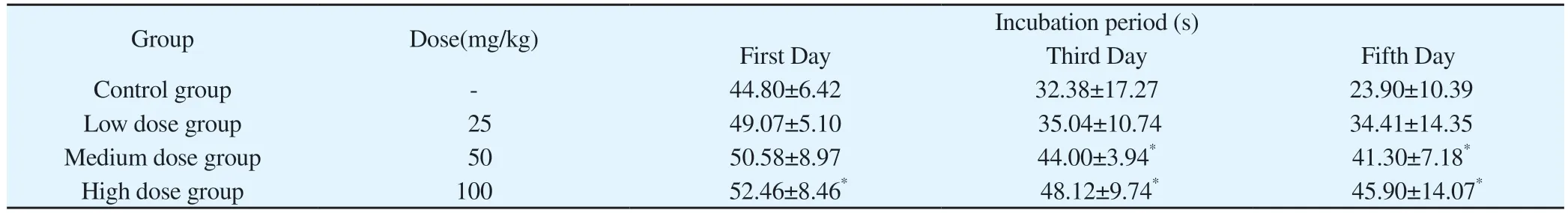
Tab 2 Comparison of latency after training in the Morris Water Maze positioning navigation experiment in four groups (s, ±s)
Note: Compared with control group, *P<0.05.
Group Dose(mg/kg) Incubation period (s)First Day Third Day Fifth Day Control group - 44.80±6.42 32.38±17.27 23.90±10.39 Low dose group 25 49.07±5.10 35.04±10.74 34.41±14.35 Medium dose group 50 50.58±8.97 44.00±3.94* 41.30±7.18*High dose group 100 52.46±8.46* 48.12±9.74* 45.90±14.07*
3.2 Comparison of the results of HE staining experiments on hippocampal sections in the control and dose groups
The HE staining results showed that the nerve cells in the control rats had no edema, were well arranged, with normal structure,clearly visible nuclei, abundant cytoplasm and clear staining, sharp and clear edges of the cytosol, and no obvious pathological changes.The nerve cells in the low, medium and high dose groups began to show different degrees of disorganization, nucleus consolidation,rupture, lysis, deep staining of the nucleus, blurring of the cell membrane, and several pathological changes, which increased the damage to the nerve cells.Compared with the control group, the changes in the high-dose group were most obvious.See Figure 1.
3.3 Comparison of the results of Nissler staining experiments on hippocampal sections in the control and dose groups
The results of Nissl staining showed that the hippocampal neurons in the control group were closely arranged and clearly stained, with clear staining of Nissl body particles in the cytoplasm and normal cell morphology.As the dose of staining increased, disorganized cell arrangement, reduced dissipation of intracellular Nissl body particles and variable cell morphology were seen in the stained group.See Figure 2.
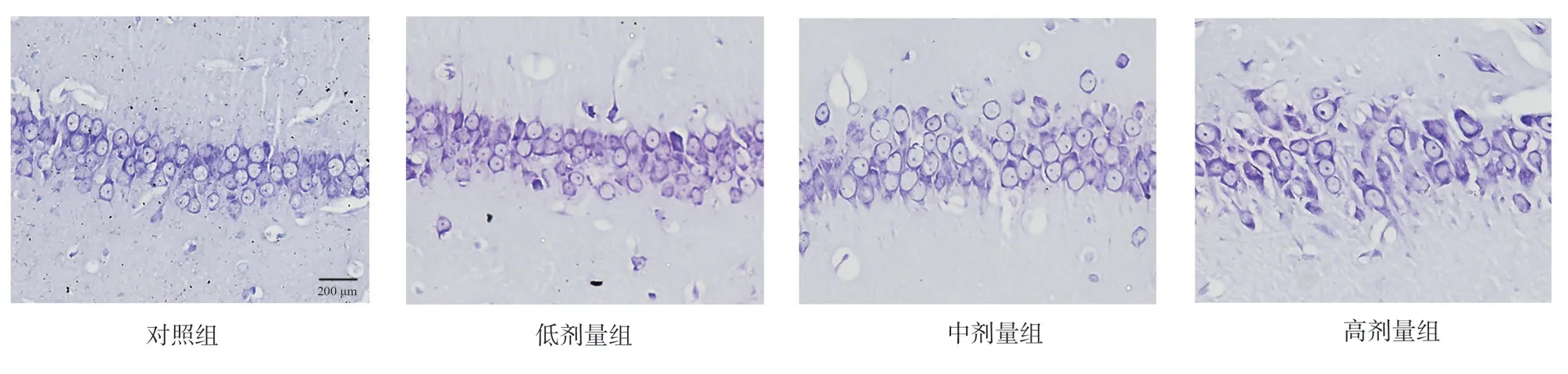
Fig 2 Comparison of Nymphali staining of hippocampal tissue in rat groups (×200)
3.4 Comparison of miR-9-5p, RHOA and BDNF mRNA expression in hippocampal tissues of rats in control and dose groups
Compared with the control group, the expression of miR-9-5p was significantly decreased in the low, medium and high dose groups,with no statistically significant difference in the low dose group and statistically significant difference in the medium and high dose groups (P<0.05 orP<0.001); compared with the control group, the expression of RHOA was significantly increased, with statistically significant difference in all cases (P<0.05 or P<0.001); compared with the control group, the The expression of BDNF was all significantly decreased compared with the control group, where the difference was not statistically significant in the low dose group and statistically significant in the middle and high dose groups (P<0.05).See Figure 3, Table 3.
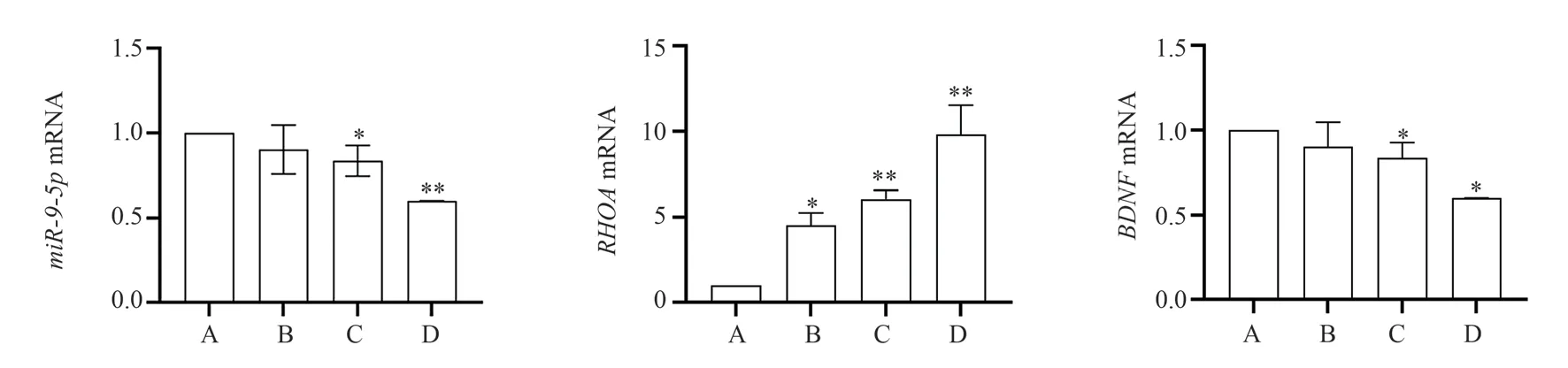
Fig 3 Comparison of miR-9-5p, RHOA and BDNF mRNA expression in rat groups
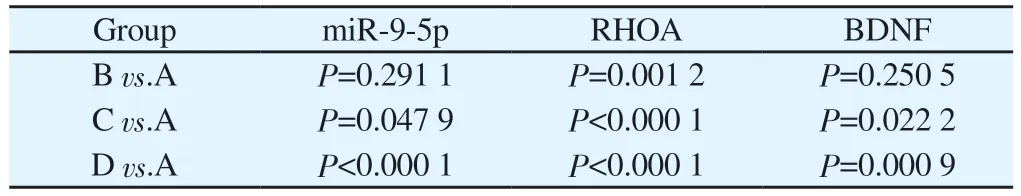
Tab 3 P values of RT-qPCR results in each group
3.5 Comparison of RHOA and BDNF protein expression in hippocampal tissues of rats in control and dose groups
Compared with the control group, the expression of RHOA protein was increased in both the dyed groups, with the relative expression in the medium and high dose groups being statistically different from the control group atP<0.05; the expression of BDNF protein was decreased in both the dyed groups, with the medium and high dose groups being statistically different from the control group atP<0.05.See Table 4, Figure 3.
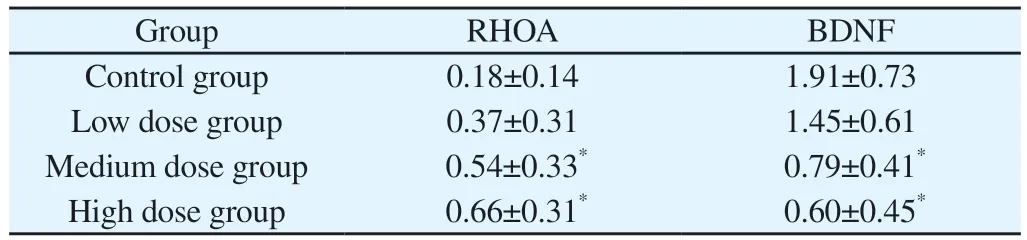
Tab 4 Comparison of relative expression of RHOA and BDNF proteins in rat hippocampal tissues
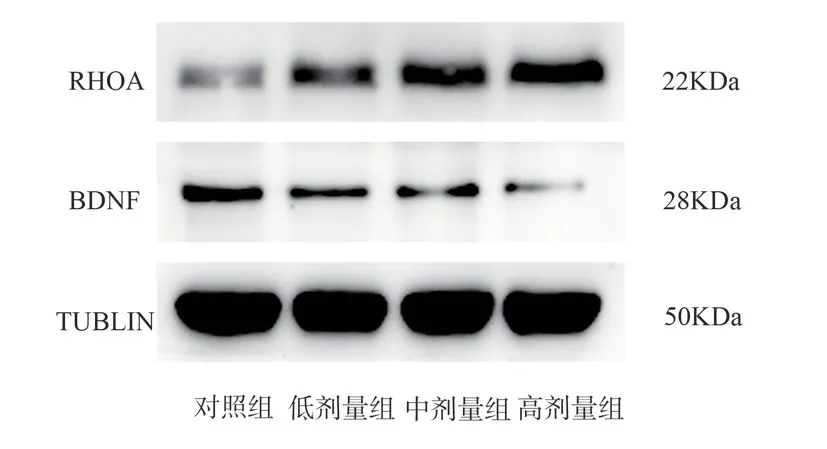
Fig 4 Relative expression of RHOA and BDNF proteins in rat hippocampal tissues of each group
4.Discussion
Aluminium (Al) is one of the most widely-extended metals in the earth’s crust.Its abundance, coupled with widespread human use,makes the toxicity associated with Al particularly relevant to human health.Al has been repeatedly shown to be neurotoxic, accelerating brain ageing, which in turn leads to brain disorders, most initially manifesting as cognitive dysfunction, which may then progress to Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, etc.Although initial successes have been achieved through the efforts of many scholars,the mechanisms of Al-induced cognitive impairment are not yet fully understood.
Alzheimer’s disease is currently the most common form of dementia, characterised by memory and intellectual decline, bizarre behaviour and moodiness, ultimately leading to loss of self-care,and is estimated to account for 60%~70% of dementia patients worldwide, a situation that is not promising[5].According to current research, the main pathogenesis of AD is accelerated by mutations in two types of genes, amyloid and progerin, leading to the conversion of β-amyloid polypeptides into neuritic plaques, the main pathological features of which are the formation of neuritic plaques of amyloid β-peptides and neurogenic fibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau[6,7].Mild cognitive impairment occurs during the progression from normal cognition to dementia, and the cognitive abilities of older people can be divided into four stages as they age: from having normal cognitive abilities, to subjective cognitive dysfunction, to mild cognitive impairment, and finally to the development of dementia[8].This suggests that AD is a form of dementia that manifests as progressive cognitive impairment.In this study, the water maze behavioural experiment, HE staining and Nissler staining demonstrated that all three aluminium-stained groups had different degrees of learning memory impairment, as well as neuronal damage in the hippocampal region.The success of the present experimental cognitive impairment model was confirmed.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), as non-coding RNAs, can regulate a variety of target genes, making miRNAs a potential therapeutic target for a variety of brain diseases.Studies have shown that miRNAs are involved in a variety of signalling pathways associated with the pathogenesis of AD, including those for Aβ production and clearance, neuroinflammation and neurogenesis.In turn, cognitive dysfunction can further develop into AD, so it is particularly important to investigate the mechanisms of miRNAs and cognitive dysfunction.It has been found that miR-9-5p is associated with a variety of neurodegenerative diseases associated with cognitive impairment, such as Alzheimer’s disease[9] Parkinson’s disease[10].It has been shown that miR-9-5p is downregulated early in AD mice[9].And in our group’s previous study, we analyzed the expression profiles of serum exosomal miRNAs in people with high-aluminum cognitive impairment by second-generation high-throughput sequencing technology, constructed a network regulatory map between miRNAs and MAPK signaling pathway letter-related target genes in aluminum-induced cognitive impairment using Cytoscape software, and screened that has-miR-9-5p controlled RHOA through down-regulation expression in serum exosomes of patients with hyperaluminium cognitive impairment[11].In this experiment, to verify the results, rats with Al-induced cognitive impairment were created for comparison with normal rats to validate this conclusion.
RhoA and its many downstream proteins are involved in a variety of signaling pathways in the nervous system.There is evidence for a role of aberrant RhoA signalling in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease and Parkinson’s disease[12].Activation of RHOA may lead to neuronal growth and development, inhibition of axonal regenerative function and other activities[13-15].It was found that RhoA expression was increased in reactive microglia in APP/PS1 transgenic and protofibrillar Aβinjected mouse models[16].It has also been found that non-steroids[17,18] and statins[19] can reduce Aβ production by inhibiting RHOArelated signalling pathways, suggesting that inhibition of RHOA expression could inform AD treatment.This is consistent with the RT-qPCR and Western Blot results of RHOA in this experiment.
BDNF is one of the most widely distributed and extensively studied neurotrophic factors in the mammalian brain and is critical in translating synaptic activity into long-term synaptic memory.Defects in BDNF signalling have been reported to contribute to the pathogenesis of several major diseases, such as Huntington’s disease,Alzheimer’s disease, depression, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and anxiety disorders[20].Thus, the expression of BDNF directly affects the level of cognition in the brain.In this experiment, BDNF was downregulated at different levels in the aluminium-tainted group compared to the control group.
In this experiment, the experimental model was established by gavaging Alcl3 to the rats in the experimental group, and then the rats in the low-dose, medium-dose and high-dose groups were detected to have different degrees of reduced learning and memory abilities through the water maze behavioural experiment.This indicated that the aluminium-induced cognitive impairment model was successfully established.Subsequently, we visualized the neuronal damage in the hippocampal region of the three poisoned groups by pathological techniques.Next, we validated the conclusions drawn by our group in the population data screening to the animal model through molecular biology experiments, and the results showed that miR-9-5p was down-regulated and RHOA expression levels were up-regulated in the low-dose, medium-dose and high-dose groups.Therefore, we speculate that the mechanism of cognitive impairment in rats caused by aluminum may be related to the down-regulation of miR-9-5p leading to the up-regulation of RHOA.Further experimental evidence on miR-9-5p-targeted regulation of RHOA is needed.
Authors’ contribution
Yunjing Jia: experimental design and practical work, data collation and statistical analysis, paper writing and revision; Chenyu Li:experimental operation assistant; Yanwu Ling, Bin Zhong, Juefang Gan, Chunrong Lian, Shasha Li: research supervision, paper revision, financial support.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年14期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年14期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on key genes of vitamin D signaling pathway
- Research progress on the influence of local hemodynamics on carotid atherosclerosis
- Copy number variation sequencing for diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection based low?depth whole?genome sequencing technology in fetus: Three cases and literature review
- Exploration of the molecular mechanism of Qishen decoction in regulating miR-495/FTO pathway mediated macrophage polarization to improve insulin resistance therapy of type 2 diabetes
- Intervention of Xuduan Zhongzi Formula on spermatogenesis epididymal morphological changes in a mice model of oligospermia
- miR-483-5p regulates osteoclast generation by targeting Timp2
