位置伺服永磁電機(jī)魯棒性無差拍預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速控制
王 政 溫從劍 朱辰雨 張子越 余開亮 程 明
位置伺服永磁電機(jī)魯棒性無差拍預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速控制
王 政 溫從劍 朱辰雨 張子越 余開亮 程 明
(東南大學(xué)電氣工程學(xué)院 南京 210096)
為了提高永磁同步電機(jī)位置伺服系統(tǒng)的控制性能,該文提出一種魯棒性無差拍預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速控制策略。首先,根據(jù)無差拍控制原理對速度環(huán)和電流環(huán)進(jìn)行設(shè)計。其次,采用增量模型消除了永磁磁鏈對電流預(yù)測的影響。再次,設(shè)計擴(kuò)展?fàn)顟B(tài)觀測器,對參數(shù)不匹配、負(fù)載和逆變器非線性造成的擾動進(jìn)行觀測。然后,根據(jù)位置伺服系統(tǒng)的特點(diǎn)提出一種補(bǔ)償策略。最后,通過實(shí)驗(yàn)對提出的控制策略進(jìn)行研究,實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果表明,該方法能提高系統(tǒng)的穩(wěn)態(tài)控制精度和動態(tài)響應(yīng)速度。
位置伺服系統(tǒng) 無差拍預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速控制 擴(kuò)展?fàn)顟B(tài)觀測器 補(bǔ)償策略
0 引言
永磁同步電機(jī)(Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor, PMSM)驅(qū)動系統(tǒng)[1-2]由于具有高功率密度、高效率和結(jié)構(gòu)緊湊等特點(diǎn),被廣泛地應(yīng)用于伺服系統(tǒng)中。磁場定向控制是PMSM驅(qū)動廣泛應(yīng)用的控制策略。在位置伺服系統(tǒng)中,為了獲得精確的穩(wěn)態(tài)跟蹤效果和快速的動態(tài)響應(yīng),傳統(tǒng)PI控制[3]是設(shè)計速度環(huán)和電流環(huán)時常用的方法。伺服電動機(jī)要求在各種工況、電機(jī)內(nèi)部參數(shù)變化和外部擾動的影響下都能保持理想的工作性能,因此對PI控制器的參數(shù)提出了更高的要求。
近些年,預(yù)測控制由于具有較好的自適應(yīng)能力和良好的動態(tài)性能,逐漸成為研究熱點(diǎn)[4-8]。預(yù)測控制主要可以分為兩類:模型預(yù)測控制(Model Predictive Control, MPC)[9-11]和無差拍預(yù)測控 制[12-13]。MPC利用電機(jī)離散模型預(yù)測未來的工作狀態(tài),進(jìn)而可以根據(jù)價值函數(shù)確定最優(yōu)的工作電壓矢量。文獻(xiàn)[10]提出了一種用于永磁同步電機(jī)的模型預(yù)測直接轉(zhuǎn)速控制(Model Predictive Direct Speed Control, MPDSC)方法。該方法結(jié)構(gòu)簡單,無需脈沖寬度調(diào)制(Pulse Width Modulation, PWM),但精確的預(yù)測需要較大的計算量,對硬件條件要求較高,限制了其在工業(yè)中的應(yīng)用。無差拍預(yù)測控制基于系統(tǒng)離散模型計算每個采樣周期的參考電壓矢量,通過PWM轉(zhuǎn)換為開關(guān)信號,能在較小的計算量下獲得相近的動態(tài)性能和更好的穩(wěn)態(tài)跟蹤效果。因此,無差拍預(yù)測電流控制(Deadbeat Predictive Current Control, DPCC)被應(yīng)用在很多工業(yè)領(lǐng)域。但是,目前很少有文獻(xiàn)提到速度環(huán)和電流環(huán)均采用基于離散模型設(shè)計的無差拍預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速控制(Deadbeat Predi- ctive Speed Control, DPSC)方法,因此將無差拍預(yù)測控制同時用于永磁同步電機(jī)電流環(huán)與速度環(huán),改善位置伺服電動機(jī)的性能還值得進(jìn)一步深入研究。
無論是MPDSC還是DPSC都需要精確的控制模型,包括電機(jī)的電氣參數(shù)、機(jī)械參數(shù)以及負(fù)載信息。一方面,電機(jī)的電氣參數(shù)會隨著運(yùn)行工況以及溫度的變化而發(fā)生變化,機(jī)械參數(shù)無法通過直接測量獲得,而負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩則需要通過額外的裝置進(jìn)行測量。另一方面,逆變器非線性會影響預(yù)測的精度從而降低系統(tǒng)的性能。可以采用電機(jī)在線參數(shù)辨識的方法來解決模型預(yù)測控制中的模型準(zhǔn)確度問題。文獻(xiàn)[14]中提出了一種基于模型參考自適應(yīng)系統(tǒng)(Model Reference Adaptive System, MRAS)的參數(shù)估計方法,為了解決欠秩問題,通過將一些參數(shù)作為已知的固定值來估計其他參數(shù)。但由于電機(jī)參數(shù)實(shí)時變化而無法固定,因此會導(dǎo)致MRAS得到參數(shù)辨識結(jié)果不準(zhǔn)確。文獻(xiàn)[15]提出了一種基于磁鏈注入的參數(shù)辨識方法,能夠?qū)崿F(xiàn)對電機(jī)電氣參數(shù)的辨識,但是額外的信號注入會影響系統(tǒng)正常的運(yùn)行狀態(tài)。文獻(xiàn)[16]提出了一種基于粒子群優(yōu)化算法的參數(shù)辨識方法,可以對電機(jī)參數(shù)以及逆變器非線性進(jìn)行全局辨識。但是該方法必須在空載情況下應(yīng)用,并且這種生物啟發(fā)式算法需要對大量數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行迭代尋優(yōu),難以應(yīng)用于實(shí)時數(shù)字處理器中。
另一種解決模型預(yù)測控制中模型準(zhǔn)確度問題的方法是采用擾動觀測器[17-18]進(jìn)行補(bǔ)償。文獻(xiàn)[17]基于滑模控制理論設(shè)計了一種全局參數(shù)擾動和負(fù)載觀測器,有效地提高了電機(jī)系統(tǒng)的魯棒性。但是滑模觀測器的效果依賴相關(guān)參數(shù)的合理選擇,目前尚未有相關(guān)文獻(xiàn)提出具體的選擇標(biāo)準(zhǔn)。文獻(xiàn)[18]提出了一種擴(kuò)展?fàn)顟B(tài)觀測器(Extended State Observer, ESO),可以對未知擾動進(jìn)行準(zhǔn)確觀測。ESO獨(dú)立于系統(tǒng)的數(shù)學(xué)模型,因此具有較強(qiáng)的魯棒性,但該文獻(xiàn)僅討論了其對電流環(huán)的性能改進(jìn),并沒有將其同時用于速度環(huán)和電流環(huán)預(yù)測控制中。文獻(xiàn)[19]采用無差拍控制策略來減小系統(tǒng)的動態(tài)響應(yīng)時間,提出一種指數(shù)ESO加快觀測狀態(tài)的收斂速度,提升了系統(tǒng)的擾動抑制性能。文獻(xiàn)[20]針對電機(jī)周期性轉(zhuǎn)矩波動問題,提出了一種模塊化ESO,將指定次轉(zhuǎn)矩紋波作為待觀測狀態(tài),有效減小周期性擾動對系統(tǒng)的影響。文獻(xiàn)[21]采用超螺旋滑模策略進(jìn)行速度控制,提出一種有限時間ESO用于對系統(tǒng)的集中擾動進(jìn)行觀測,從而進(jìn)行控制器補(bǔ)償。與傳統(tǒng)ESO相比,有限時間ESO通過非線性函數(shù)的引入具有更高的觀測速度與精度。
本文針對PMSM位置伺服系統(tǒng)提出了一種魯棒性DPSC策略。相比于之前相關(guān)文獻(xiàn),本文提出的控制策略具有如下特點(diǎn):①基于PMSM離散模型和無差拍控制原理,設(shè)計了速度環(huán)和電流環(huán),避免了級聯(lián)式PI控制器的設(shè)計,提高了系統(tǒng)的動態(tài)性能;②將ESO方法擴(kuò)展應(yīng)用至電流環(huán)與速度環(huán)同時采用預(yù)測控制的控制方法中,針對預(yù)測電流和預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速進(jìn)行實(shí)時補(bǔ)償,提高了系統(tǒng)的魯棒性,避免了復(fù)雜的全局參數(shù)辨識過程;③結(jié)合位置伺服系統(tǒng)的特點(diǎn),提出的控制方法采用位置跟隨補(bǔ)償策略,有效地提高了系統(tǒng)位置跟隨效果。
1 傳統(tǒng)無差拍轉(zhuǎn)速控制
本文研究對象為用于位置伺服的表貼式PMSM(Surface PMSM, SPMSM),d軸和q軸電感值相等,因此電磁轉(zhuǎn)矩和定子電壓可以表示為
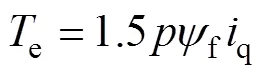

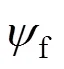
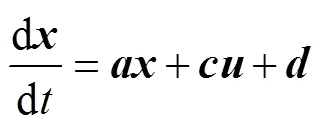
其中
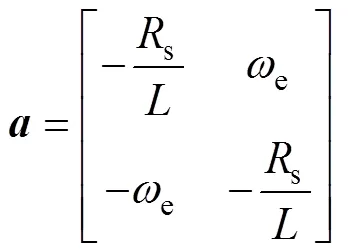
PMSM的機(jī)械方程可表示為

將式(1)代入式(4),機(jī)械方程可以改寫為
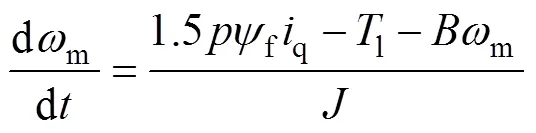
通過前向歐拉差分可得+1時刻預(yù)測的電機(jī)轉(zhuǎn)速為

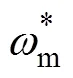

為實(shí)現(xiàn)電機(jī)電流環(huán)的無差拍控制,將電機(jī)電壓方程式(3)進(jìn)行離散化,根據(jù)時刻電壓、電流,可預(yù)測獲得+1時刻的電流為

其中


式中,s為電流采樣周期。根據(jù)式(8)可以推導(dǎo)出+1時刻的電壓方程為
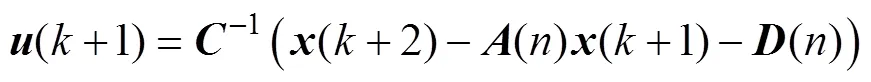
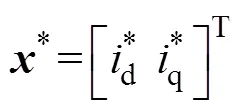


圖1 基于DPSC策略的SPMSM位置伺服系統(tǒng)控制框圖
2 魯棒性無差拍轉(zhuǎn)速控制
為了提高DPSC的魯棒性,本文采用增量模型消除電流預(yù)測模型中永磁磁鏈的影響,并且設(shè)計了ESO對SPMSM其他參數(shù)不匹配、負(fù)載擾動以及逆變器非線性造成的擾動進(jìn)行補(bǔ)償。
2.1 增量模型
由于電機(jī)機(jī)械時間常數(shù)遠(yuǎn)大于電氣時間常數(shù),可近似認(rèn)為相鄰電流采樣周期中電機(jī)轉(zhuǎn)速不變,因此時刻的電壓方程中參數(shù)矩陣()與()不變。根據(jù)式(9)可得時刻的電壓為

將式(9)與式(11)相減,可得增量模型為
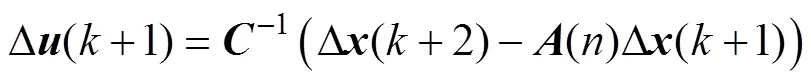
其中
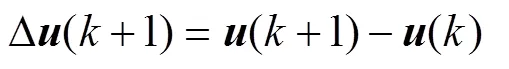
2.2 擴(kuò)展?fàn)顟B(tài)觀測器
考慮到系統(tǒng)參數(shù)不匹配、負(fù)載擾動以及逆變器非線性等擾動時,電機(jī)定子電壓和轉(zhuǎn)速分別為
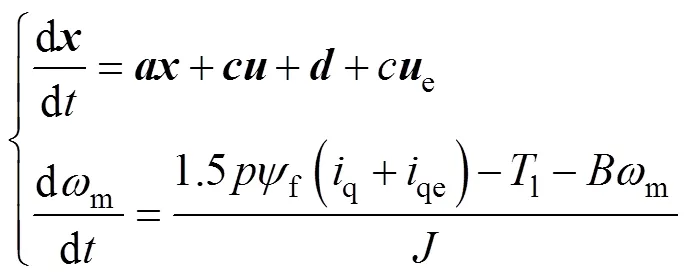
其中
式中,e和qe分別為電壓誤差和電流誤差。電壓和電流誤差可以擴(kuò)展為ESO中的新狀態(tài),通過ESO可以對電壓和電流誤差進(jìn)行估算,在此基礎(chǔ)上可以針對預(yù)測電流和轉(zhuǎn)速進(jìn)行實(shí)時補(bǔ)償。根據(jù)式(13),ESO可設(shè)計為

將式(14)進(jìn)行離散化,并在電流預(yù)測中采用增量模型,可得d、q軸電流和轉(zhuǎn)速預(yù)測方程分別為

式中,為單位矩陣。
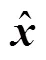




由式(16)可知,q軸電流參考值和電壓參考值計算依賴ESO得到的轉(zhuǎn)速、電流估計值以及電流、電壓誤差估計值,所以ESO是整個系統(tǒng)穩(wěn)定的基礎(chǔ)。式(13)可以變?yōu)?/p>
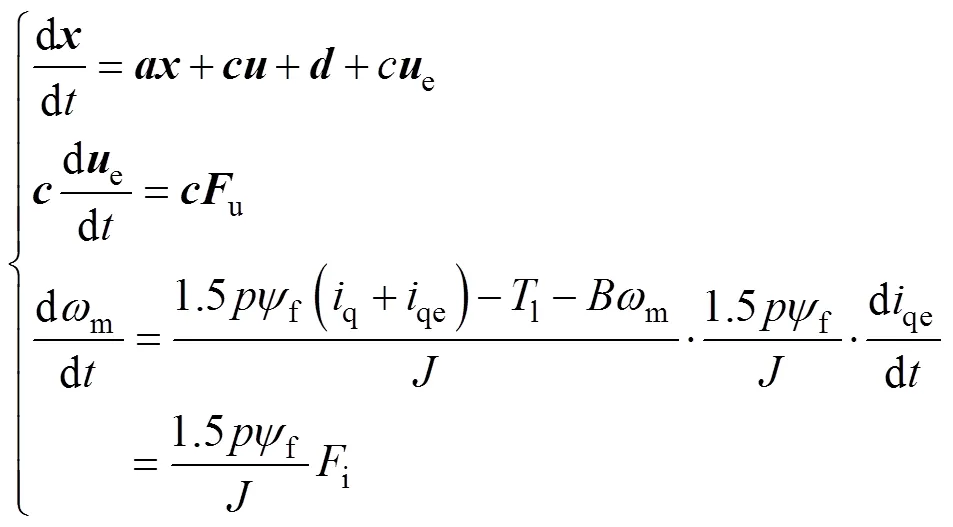
式中,u和i分別為e和qe的變化率。
然后,根據(jù)式(14)和式(19),可得



ESO穩(wěn)定性和系數(shù)矩陣c及w有關(guān),相應(yīng)特征方程為

根據(jù)Routh-Hurwitz判據(jù),當(dāng)式(22)中系數(shù)均為非負(fù),即i1>0、i2>0、w1>0、w2>0時,ESO是穩(wěn)定的。式(23)以期望觀測帶寬形式給出了ESO參數(shù)整定方法[22],有
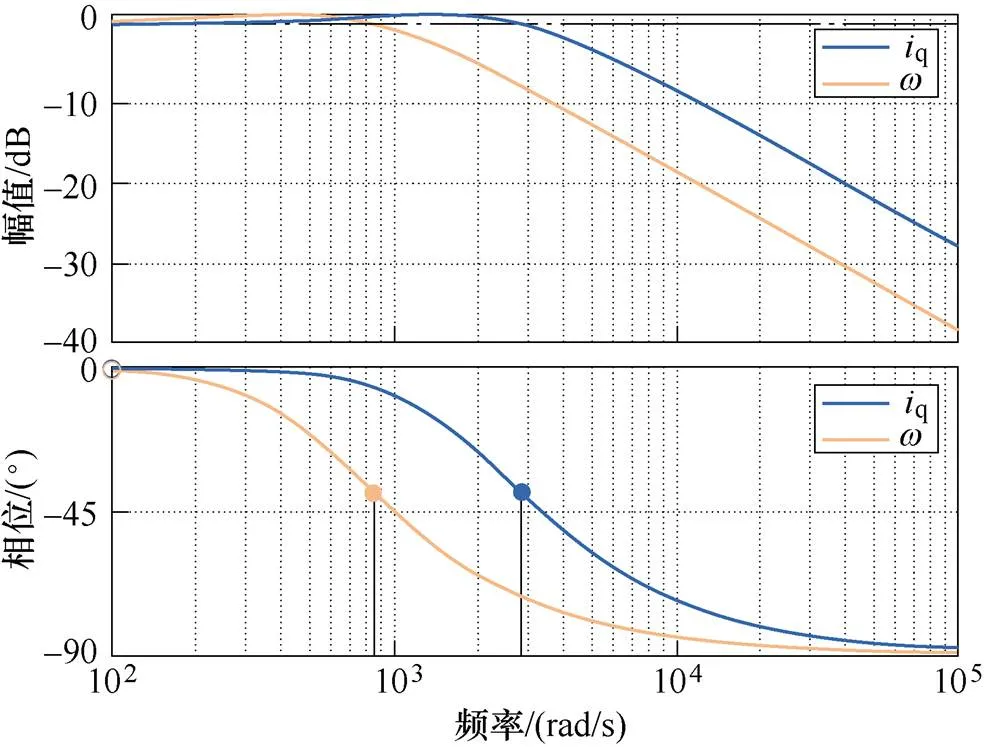
圖2 擴(kuò)張狀態(tài)觀測器伯德圖
2.3 補(bǔ)償策略


式中,Pos*和Pos分別為系統(tǒng)給定位置和實(shí)際位置;Pos1為設(shè)定的給定位置和實(shí)際位置差值絕對值的閾值,本文選取Pos1=80脈沖;cnt為計數(shù)值;max為最大計數(shù)值。
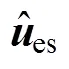
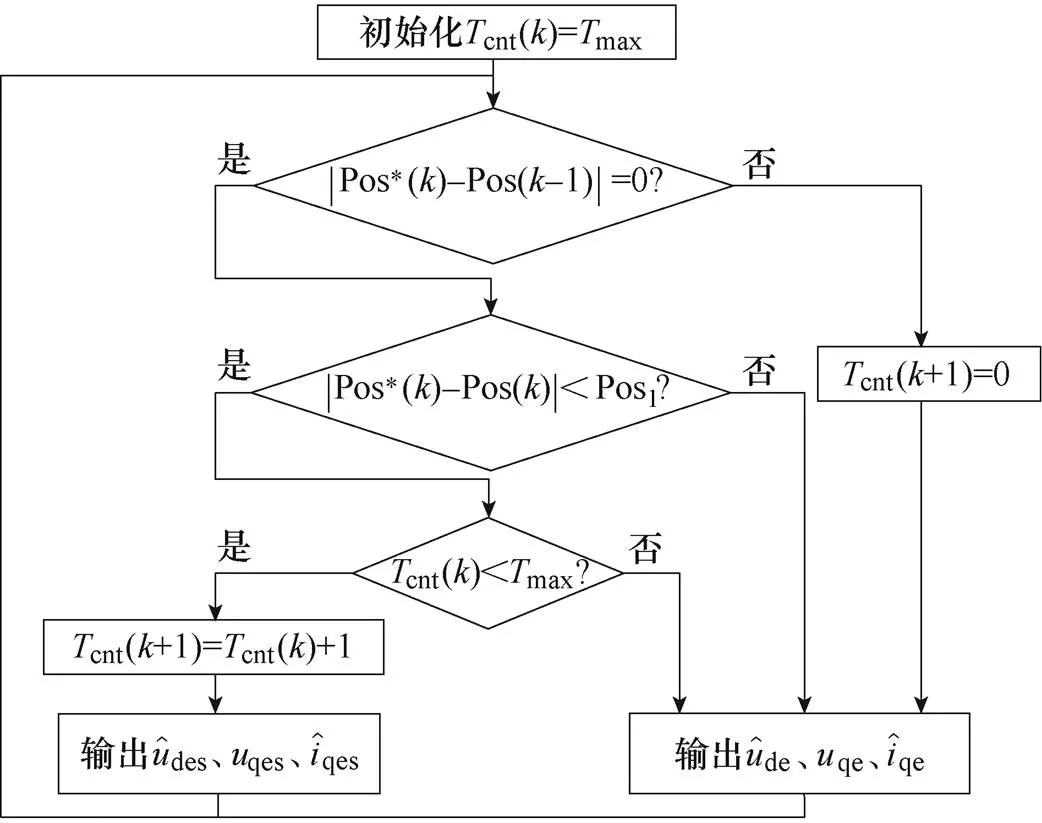
圖3 預(yù)測誤差補(bǔ)償策略流程
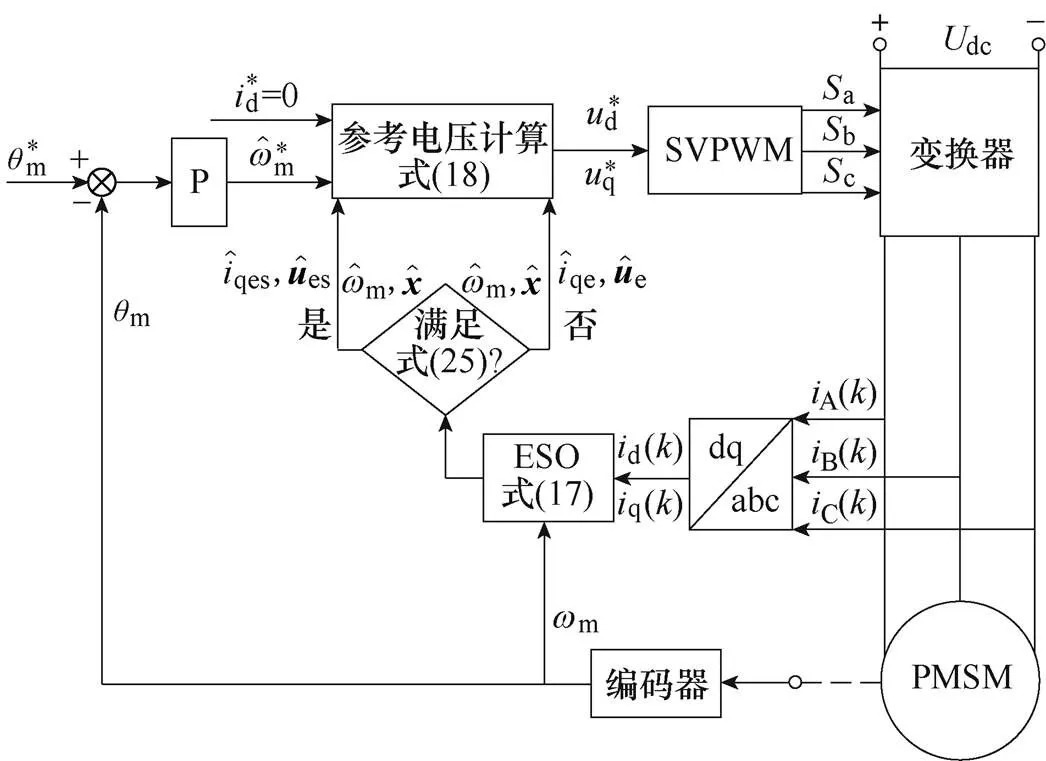
圖4 基于PR-DPSC策略的PMSM位置伺服系統(tǒng)控制框圖
3 實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果
為了驗(yàn)證本文所提出的控制策略,搭建了兩電平三相PMSM實(shí)驗(yàn)平臺,控制器為TMS320F28346,負(fù)載電機(jī)工作在恒轉(zhuǎn)矩模式。伺服系統(tǒng)的實(shí)驗(yàn)參數(shù)見表1,均選取了電機(jī)銘牌標(biāo)定值,負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩采用人為給定方式。
圖5所示為采用DPSC策略時的實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果,當(dāng)控制程序參數(shù)以及負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩值和實(shí)際值一致時,可以看出穩(wěn)態(tài)情況下實(shí)際位置與給定位置之間沒有誤差。當(dāng)控制程序參數(shù)設(shè)置為額定值的兩倍、負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩值設(shè)置為0 N·m時,由于程序控制參數(shù)以及負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩值和實(shí)際負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩值不一致,穩(wěn)態(tài)情況下實(shí)際位置與給定位置之間出現(xiàn)了誤差,如圖5b所示。
表1 實(shí)驗(yàn)參數(shù)

Tab.1 Experimental parameters

圖5 采用DPSC策略時給定階躍信號的實(shí)驗(yàn)波形
圖6所示為在參數(shù)和負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩值設(shè)置與實(shí)際值不匹配的情況下采用魯棒-無差拍預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速控制(Robust-DPSC, R-DPSC)策略時的實(shí)驗(yàn)波形。由于ESO的作用,穩(wěn)態(tài)情況下實(shí)際位置與給定位置之間的誤差得到了消除,并且電流可以控制在最大電流范圍之內(nèi)。由2.3節(jié)中的分析可知,因?yàn)閷φ`差的估計是一個積分過程,在實(shí)際位置接近給定位置時系統(tǒng)會出現(xiàn)振蕩,到達(dá)給定位置的時間也由圖5a中所示的70 ms增加到84 ms。
圖7為采用預(yù)測誤差補(bǔ)償魯棒-無差拍預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)速控制(PR-DPSC)策略的實(shí)驗(yàn)波形。控制信號電平高低表示采用不同補(bǔ)償量的切換過程,式(25)中,max的值可以根據(jù)位置振蕩過程具體時間來選取。

圖6 采用R-DPSC策略時給定階躍信號的實(shí)驗(yàn)波形

圖7 采用PR-DPSC策略時給定階躍信號的實(shí)驗(yàn)波形
同樣地,在控制參數(shù)以及負(fù)載轉(zhuǎn)矩值設(shè)置與實(shí)際值不匹配的情況下,可以看出采用所提出的補(bǔ)償策略后,穩(wěn)態(tài)情況下實(shí)際位置與給定位置之間沒有誤差,并且實(shí)際位置接近給定位置時振蕩現(xiàn)象得到消除,系統(tǒng)到達(dá)給定位置的時間也由84 ms減少到了62 ms。
為了進(jìn)一步評估所提出的PR-DPSC策略控制性能,在相同的實(shí)驗(yàn)條件下,分別采用PI控制和DPCC策略進(jìn)行了相關(guān)實(shí)驗(yàn)比較。如圖8、圖9所示,PI控制的速度環(huán)和電流環(huán)以及DPCC策略的速度環(huán)均已調(diào)至最優(yōu),可以看出采用PI控制和DPCC策略時,系統(tǒng)到達(dá)給定位置的時間分別為94 ms和86 ms。通過三種不同控制方法實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果的比較,可以證明PR-DPSC策略具有更好的控制效果。
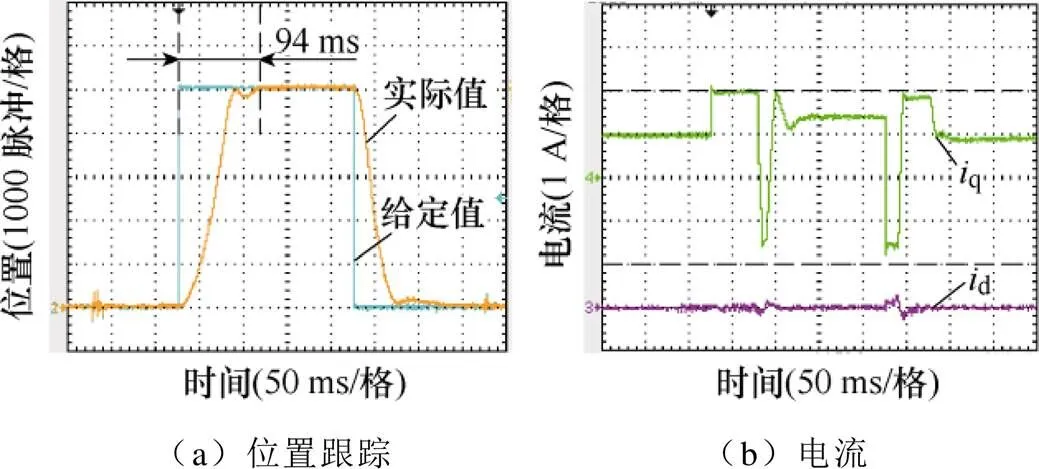
圖8 采用PI控制時給定階躍信號的實(shí)驗(yàn)波形
圖10為采用不同預(yù)測控制策略時系統(tǒng)抗擾動性能實(shí)驗(yàn)波形對比。由于在負(fù)載突變時系統(tǒng)給定位置沒有發(fā)生變化,此時R-DPSC與PR-DPSC是等價的,因此僅給出了PR-DPSC和DPSC的對比結(jié)果。
采用DPCC策略時,系統(tǒng)在負(fù)載突變時實(shí)際位置偏離給定位置的最大誤差為122脈沖,75 ms后實(shí)際位置與給定位置間的誤差得到消除。采用PR- DPSC時,系統(tǒng)在負(fù)載突變情況下實(shí)際位置偏離給定位置的最大誤差為70脈沖,55 ms后實(shí)際位置與給定位置間的誤差得到消除。可以看出,相比DPCC策略,所提出的PR-DPSC策略具有更好的抗擾動性能。
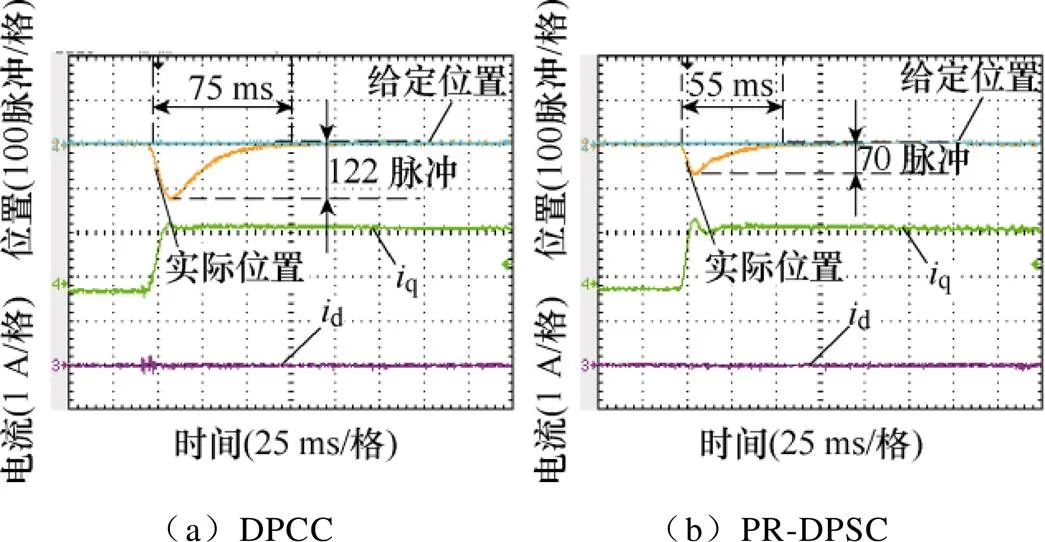
圖10 負(fù)載突變情況下采用DPCC策略和 PR-DPSC策略時的實(shí)驗(yàn)波形
4 結(jié)論
本文研究了基于DPSC策略的魯棒性位置伺服PMSM系統(tǒng),研究結(jié)論如下:
1)提出的DPSC策略提高了系統(tǒng)的動態(tài)響應(yīng),使得系統(tǒng)能更快到達(dá)給定位置。
2)設(shè)計的ESO能對參數(shù)不匹配、負(fù)載和逆變器非線性造成的擾動進(jìn)行觀測,結(jié)合提出的補(bǔ)償策略,消除了系統(tǒng)到達(dá)給定位置時的振蕩現(xiàn)象,提高了控制精度和動態(tài)性能。
通過實(shí)驗(yàn)驗(yàn)證了本文提出的基于DPSC魯棒性位置伺服永磁電機(jī)控制器具有較好的位置跟隨效果和魯棒性。
[1] 付興賀, 江政龍, 呂鴻飛, 等. 電勵磁同步電機(jī)無刷勵磁與轉(zhuǎn)矩密度提升技術(shù)發(fā)展綜述[J]. 電工技術(shù)學(xué)報, 2022, 37(7): 1689-1702.
Fu Xinghe, Jiang Zhenglong, Lü Hongfei, et al. Review of the blushless excitation and torque density improvement in wound field synchronous motors[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(7): 1689-1702.
[2] 王一波, 王政, 溫從劍, 等. 多通道三電平風(fēng)力發(fā)電系統(tǒng)協(xié)同控制策略研究[J]. 中國電機(jī)工程學(xué)報, 2019, 39(2): 366-375, 634.
Wang Yibo, Wang Zheng, Wen Congjian, et al. Collaborative control strategies for multi-channel three-level wind energy conversion system[J]. Pro- ceedings of the CSEE, 2019, 39(2): 366-375, 634.
[3] Kazmierkowski M P, Malesani L. Current control techniques for three-phase voltage-source PWM con- verters: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1998, 45(5): 691-703.
[4] 李祥林, 薛志偉, 閻學(xué)雨, 等. 基于電壓矢量快速篩選的永磁同步電機(jī)三矢量模型預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)矩控制[J]. 電工技術(shù)學(xué)報, 2022, 37(7): 1666-1678.
Li Xianglin, Xue Zhiwei, Yan Xueyu, et al. Voltage vector rapid screening-based three-vector model predictive torque control for permanent magnet syn- chronous motor[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2022, 37(7): 1666-1678.
[5] 郭磊磊, 王朋帥, 李琰琰, 等. 不同代價函數(shù)下永磁同步電機(jī)模型預(yù)測控制參數(shù)失配可視化分析[J]. 電工技術(shù)學(xué)報, 2023, 38(4): 903-914.
Guo Leilei, Wang Pengshuai, Li Yanyan, et al. Visual analysis of parameters mismatch in model predictive control for permanent magnet synchronous motor under different cost functions[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(4): 903-914.
[6] 章回炫, 范濤, 邊元均, 等. 永磁同步電機(jī)高性能電流預(yù)測控制[J]. 電工技術(shù)學(xué)報, 2022, 37(17): 4335-4345.
Zhang Huixuan, Fan Tao, Bian Yuanjun, et al. Predictive current control strategy of permanent magnet synchronous motors with high performance[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2022, 37(17): 4335-4345.
[7] 李昱, 郭宏, 平朝春, 等. 基于電流源變流器的永磁同步電機(jī)驅(qū)動系統(tǒng)全狀態(tài)變量預(yù)測轉(zhuǎn)矩控制[J]. 電工技術(shù)學(xué)報, 2021, 36(1): 15-26.
Li Yu, Guo Hong, Ping Zhaochun, et al. A full-state variable predictive torque control of current source converter fed permanent magnet synchronous motor drives[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2021, 36(1): 15-26.
[8] 谷鑫, 魯金月, 王志強(qiáng), 等. 基于無差拍電流預(yù)測控制的永磁同步電機(jī)諧波電流抑制策略[J]. 電工技術(shù)學(xué)報, 2022, 37(24): 6345-6356.
Gu Xin, Lu Jinyue, Wang Zhiqiang, et al. Harmonic current suppression strategy for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on deadbeat current predi- ction control[J]. Transactions of China Electro- technical Society, 2022, 37(24): 6345-6356.
[9] Gu Minrui, Wang Zheng, Yu Kailiang, et al. Inter- leaved model predictive control for three-level neutral- point-clamped dual three-phase PMSM drives with low switching frequencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(10): 11618-11630.
[10] Kawai H, Zhang Zhenbin, Kennel R, et al. Direct speed control based on finite control set model predictive control with voltage smoother[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(3): 2363-2372.
[11] Gu Minrui, Wang Zheng, Wen Congjian, et al. Collaborative mid-point voltage regulation in low- switching-frequency MPC for three-level NPC inver- ters fed dual three-phase PMSM drives[J]. IEEE Open Journal of Power Electronics, 2021, 2: 673-682.
[12] Yu Kailiang, Wang Zheng, Hua Wei, et al. Robust cascaded deadbeat predictive control for dual three- phase variable-flux PMSM considering intrinsic delay in speed loop[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(12): 12107-12118.
[13] Yu Kailiang, Wang Zheng. Improved deadbeat predi- ctive current control of dual three-phase variable-flux PMSM drives with composite disturbance observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(7): 8310-8321.
[14] Kim H S, Lee K. Model predictive current control with online parameter estimation for synchronous reluctance machine controlled by high-frequency signal injection position-sensorless[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 25267-25277.
[15] Wang Kang, Lorenz R D, Baloch N A. Enhanced methodology for injection-based real-time parameter estimation to improve back EMF self-sensing in induction machine deadbeat-direct torque and flux control drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2018, 54(6): 6071-6080.
[16] Liu Zhaohua, Wei Hualiang, Li Xiaohua, et al. Global identification of electrical and mechanical parameters in PMSM drive based on dynamic self-learning PSO[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 33(12): 10858-10871.
[17] Zhang Xiaoguang, Cheng Yu, Zhao Zhihao, et al. Robust model predictive direct speed control for SPMSM drives based on full parameter disturbances and load observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2020, 35(8): 8361-8373.
[18] Yang Ming, Lang Xiaoyu, Long Jiang, et al. Flux immunity robust predictive current control with incremental model and extended state observer for PMSM drive[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Elec- tronics, 2017, 32(12): 9267-9279.
[19] Wang Fengxiang, Ke Dongliang, Yu Xinhong, et al. Enhanced predictive model based deadbeat control for PMSM drives using exponential extended state observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Elec- tronics, 2022, 69(3): 2357-2369.
[20] Hu Mingjin, Hua Wei, Wang Zuo, et al. Selective periodic disturbance elimination using extended harmonic state observer for smooth speed control in PMSM drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2022, 37(11): 13288-13298.
[21] Hou Qiankang, Ding Shihong. Finite-time extended state observer-based super-twisting sliding mode controller for PMSM drives with inertia identi- fication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2022, 8(2): 1918-1929.
[22] Zhang Yongchang, Jin Jialin, Huang Lanlan. Model- free predictive current control of PMSM drives based on extended state observer using ultralocal model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(2): 993-1003.
Deadbeat Predictive Control for Position Servo Permanent Magnet Motor
(School of Electrical Engineering Southeast University Nanjing 210096 China)
For the predictive control strategy of the permanent magnet synchronous motor position servo system, both model predictive direct speed control (MPDSC) and deadbeat predictive speed control (DPSC) depend on an accurate control system model. However, in practical applications, the motor parameters are changing and challenging to measure, which makes the control performance worse. Moreover, the nonlinearity of the inverter will also affect the prediction accuracy and reduce the performance of the control system. Recently, some methods have been proposed to solve the issues of parameter inaccuracy, but most are computationally expensive and hard to implement in practice. This paper proposes a robust deadbeat predictive speed control (R-DPSC) strategy to improve the control performance of the permanent magnet synchronous motor position servo system by incorporating the deadbeat control and the disturbance observer.
Firstly, according to the mathematical model of PMSM in the synchronous coordinate frame and the deadbeat control principle, the current and speed loops are designed for the servo drive. A proportional controller is used to design the position loop. Then, according to the discrete-state model of the motor, the reference voltages are predicted and converted into the switching signals of the inverter by space vector pulse-width modulation (SVPWM). In this paper, the incremental model is adopted to predict the current without the permanent-magnet flux value, and an extended state observer (ESO) is designed with the incremental model to estimate and compensate for the prediction errors caused by inaccurate parameters and load disturbance. The R-DPSC strategy combined with ESO can accurately track the desired position in the case of inaccurate parameters and external disturbance in load. In order to reduce the oscillation caused by the observer when the system approaches the given position reference, a prediction error compensation method is proposed, which uses different compensation quantities according to different working states of the system. The R-DPSC strategy with prediction error compensation method (PR-DPSC) can improve the robustness of the system and maintain the good dynamic performance of the DPSC strategy. Thus, the system can achieve better position-tracking performance.
The experimental results show that when the control parameters and the load torque settings do not match the actual values, the position tracking error is eliminated by the R-DPSC strategy. After adopting the PR-DPSC strategy, the position tracking error can be eliminated, and the oscillation phenomenon disappears when the actual position is close to the given position. Furthermore, the time for the system to reach the given position is reduced. Under the same experimental conditions, comparative experiments were carried out for different control schemes, which proved that the PR-DPSC strategy has faster position tracking speed and better anti-disturbance performance.
The research conclusions are as follows: (1) The proposed DPSC strategy improves the dynamic response of the system, enabling the system to reach a given position faster; (2) The designed ESO can observe the disturbance caused by parameter mismatch, load, and inverter nonlinearity. The proposed compensation strategy eliminates the oscillation phenomenon when the system reaches a given position, and the control accuracy and dynamic performance are improved.
Position servo system, deadbeat predictive speed control, extended state observer, compensation strategy
10.19595/j.cnki.1000-6753.tces.221921
TM383.4
2022-10-09
2023-03-24
王 政 男,1979年生,教授,博士生導(dǎo)師,研究方向?yàn)殡姍C(jī)驅(qū)動及控制、新能源與分布式發(fā)電。E-mail: zwang@seu.edu.cn(通信作者)
溫從劍 男,1995年生,碩士研究生,研究方向?yàn)殡姍C(jī)驅(qū)動及控制。E-mail: wcj19951026@163.com
(編輯 崔文靜)
- 電工技術(shù)學(xué)報的其它文章
- 混合疊壓圓筒型永磁直線振蕩電機(jī)電磁特性分析
- A Novel Vibration-Noise Calculation Method by Coupling Finite Element Analysis and Optimized Meshless Method for Dual-Stator Electric Machine
- 國產(chǎn)特高壓大噸位懸式瓷絕緣子機(jī)電性能提升與工藝優(yōu)化方法
- 基于直接判據(jù)提取方式的直軸電流補(bǔ)償型IPMSM最大轉(zhuǎn)矩電流比控制算法
- 受控電壓/電流源型變流器混合多機(jī)暫態(tài)電壓支撐策略
- 基于直流側(cè)混合電壓諧波注入的低諧波串聯(lián)36脈波整流器

