川西高寒地區(qū)不同海拔高度土壤酶活性特征研究
周琳 艾應偉
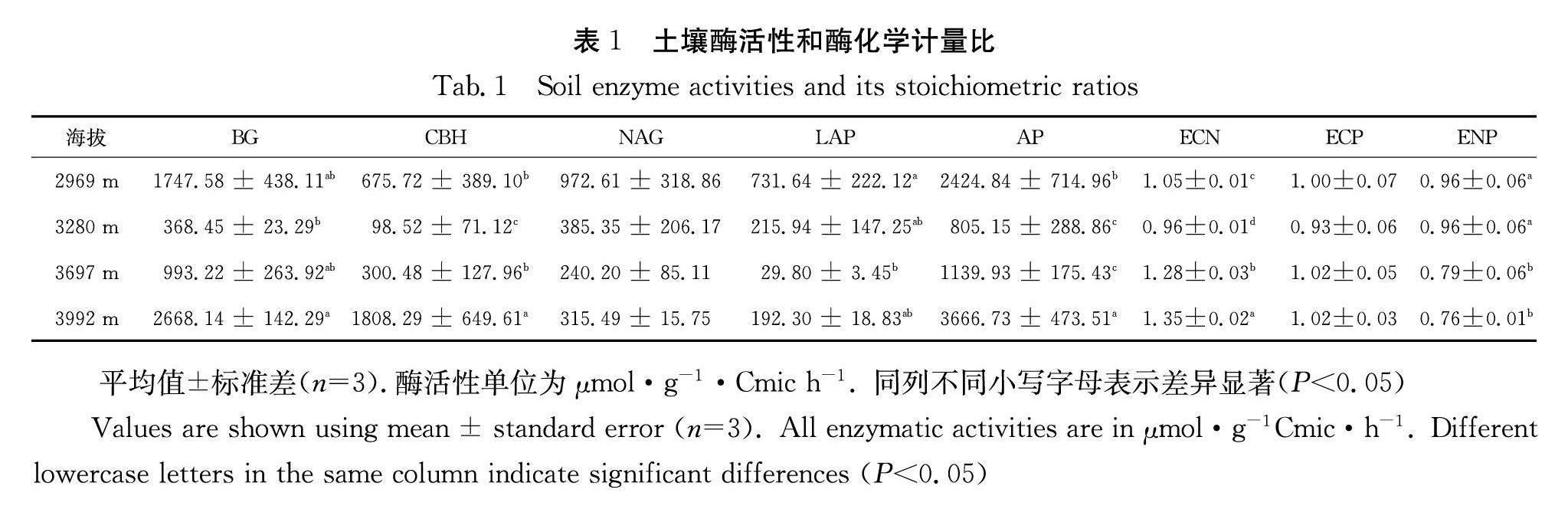

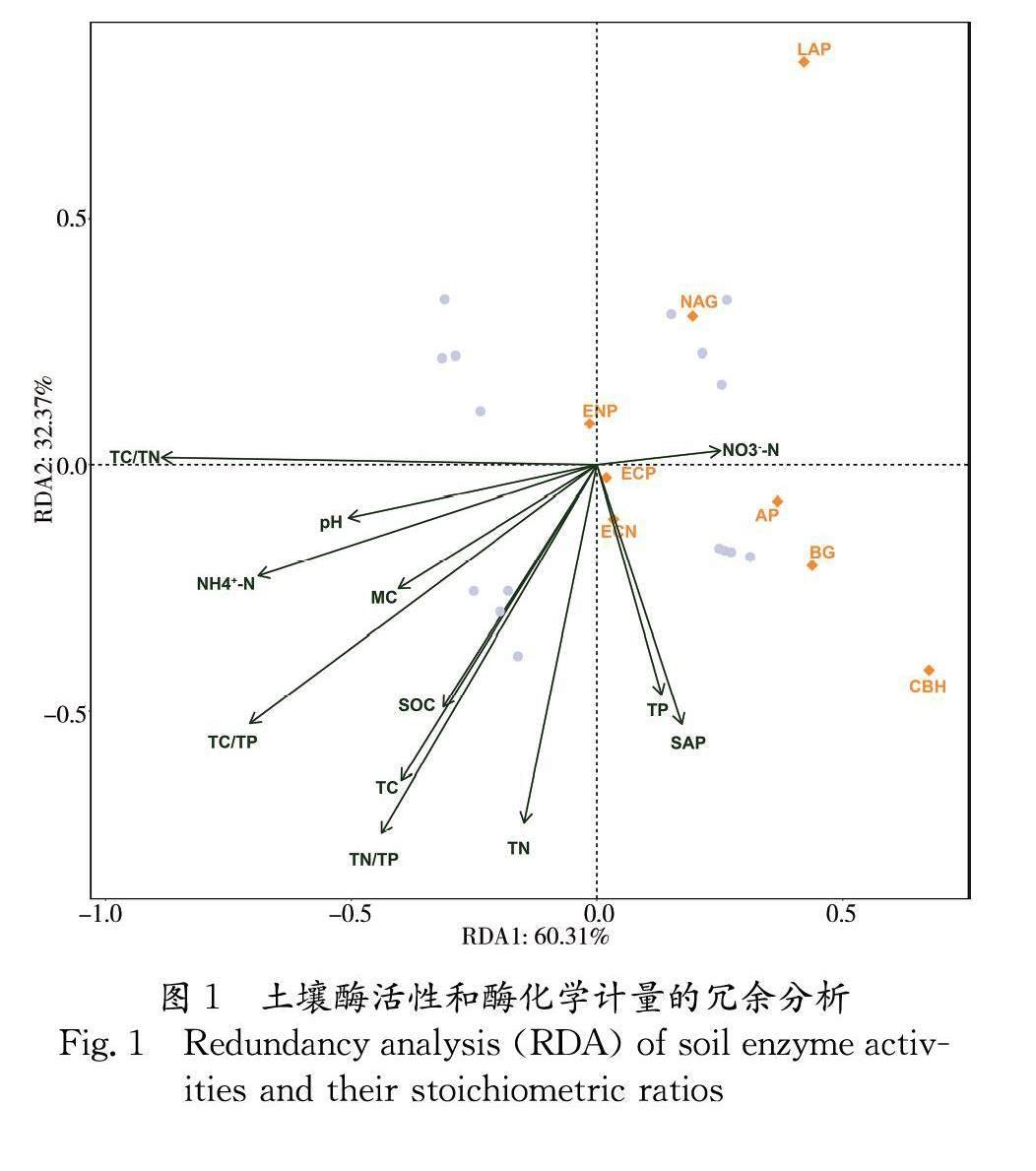
為增進對川西高寒地區(qū)土壤微生物的能量和養(yǎng)分限制狀況的了解,以川西地區(qū)不同海拔高度(2969 m,3280 m,3697 m和3992 m)的土壤為研究對象,通過測定土壤的酶活性和相關理化性質,探討了川西地區(qū)土壤酶活性和酶化學計量沿海拔的分布規(guī)律及其影響因素.結果表明:(1)土壤的β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶(BG)、纖維二糖水解酶(CBH)、β-1,4-N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖苷酶(NAG)、亮氨酸氨基肽酶(LAP)和酸性磷酸酶(AP)活性隨著海拔的增加,呈現出先減小后增大的分布模式.具體表現為土壤BG、CBH和AP酶活性在海拔3992 m處最大,在海拔3280 m處最小.土壤NAG和LAP酶活性在海拔2969 m處最大,在海拔3697 m處最小.(2)海拔3280 m的土壤微生物相對受氮、磷限制,而其余三個海拔的土壤微生物相對受碳、磷限制.(3)銨態(tài)氮、全氮、全碳和土壤養(yǎng)分的化學計量是驅動土壤酶活性及酶化學計量沿海拔變化的關鍵因素.從結果可知本研究區(qū)域的土壤酶活性特征與環(huán)境資源的可用性相關.
海拔梯度; 土壤酶活性; 酶化學計量
S158.2A2023.036003
收稿日期: 2022-04-14
基金項目: 國家自然科學基金面上項目(41971056); 國家重點研發(fā)計劃課題(2017YFC0504903)
作者簡介: 周琳(1992-), 女, 四川遂寧人, 碩士研究生, 研究方向為修復生態(tài)學.E-mail: 463375399@qq.com
通訊作者: 艾應偉. E-mail: aiyw99@sohu.com
Study on soil enzyme activity characteristics at different altitudes in the alpine region of Western Sichuan
ZHOU Lin, AI Ying-Wei
(Key Laboratory of Bio-Resources and Eco-Environment of Ministry of Education, College of Life Sciences, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
In order to improve the understanding of the energy and nutrient limitation of soil microorganisms in the alpine region of western Sichuan, the soils at different altitudes (2969 m, 3280 m, 3697 m and 3992 m) in the alpine region of western Sichuan were used as the research object. By measuring soil physicochemical properties and extracellular enzyme activities, the distribution law of soil enzyme activity and enzyme stoichiometry along the altitude and its influencing factors were discussed. The results showed that: (1) The activities of β-1,4-glucosidase (BG), Cellobiohydrolase (CBH), β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG), Leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) and Acid phosphatases (AP) showed a distribution pattern of first decreasing and then increasing with the increase of altitude. Specifically, the activities of carbon and phosphorus acquisition enzymes were the highest at 3992 m, and the lowest at 3280 m. The highest nitrogen-acquisition enzyme activity was at 2969 m, and the lowest was at 3697 m. (2) Soil microorganisms at 3280 m were relatively limited by N and P, while those at the other three altitudes were relatively limited by C and P. (3) Soil ammonium nitrogen (NH+4-N), total nitrogen (TN), soil total carbon (TC), and soil nutrient stoichiometry were the key factors driving the changes in soil enzyme activities and their stoichiometry along the altitude. According to the results, the characteristics of soil enzyme activities in this study area were related to the availability of environmental resources.
Altitude gradient; Soil enzyme activity; Enzyme stoichiometry
1 引 言
土壤酶是一類具有催化作用的生物活性物質.它在催化有機物分解和驅動生物地球化學循環(huán)過程中起到重要作用,常被用作微生物對養(yǎng)分需求的指標.其中,參與催化分解環(huán)境中資源最豐富的有機碳、氮和磷的土壤酶被研究得最為廣泛,如β-1,4-葡萄糖苷酶、纖維二糖……
