適用于強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí)慣性環(huán)境的分?jǐn)?shù)階改進(jìn)OU噪聲
王濤 張衛(wèi)華 蒲亦非


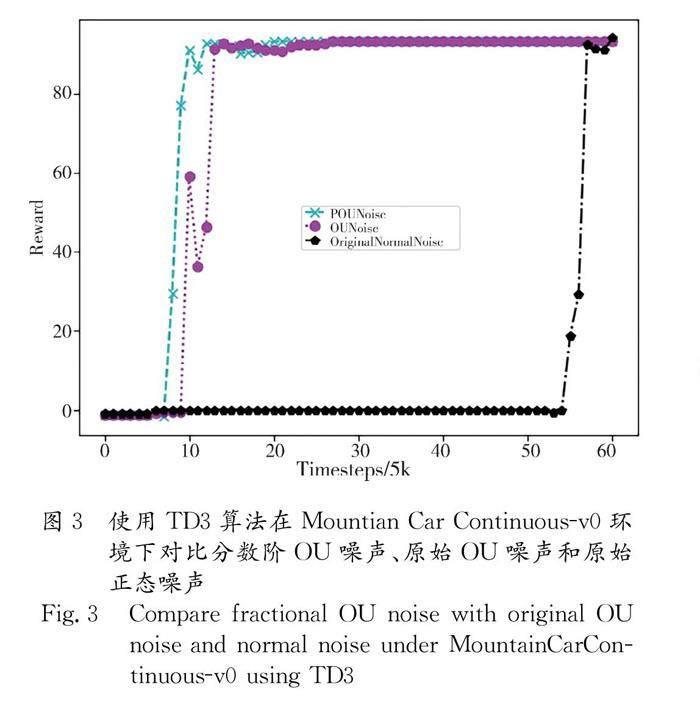
本文將DDPG算法中使用的Ornstein-Uhlenbeck (OU) 噪聲整數(shù)階微分模型推廣為分?jǐn)?shù)階OU噪聲模型,使得噪聲的產(chǎn)生不僅和前一步的噪聲有關(guān)而且和前K步產(chǎn)生的噪聲都有關(guān)聯(lián).通過(guò)在gym慣性環(huán)境下對(duì)比基于分?jǐn)?shù)階OU噪聲的DDPG和TD3算法和原始的DDPG和TD3算法,我們發(fā)現(xiàn)基于分?jǐn)?shù)階微積分的OU噪聲相比于原始的OU噪聲能在更大范圍內(nèi)震蕩,使用分?jǐn)?shù)階OU噪聲的算法在慣性環(huán)境下具有更好的探索能力,收斂得更快.
DDPG算法; TD3算法; 分?jǐn)?shù)階微積分; OU噪聲; 強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí)
TP39A2023.022001
收稿日期: 2022-03-26
基金項(xiàng)目: 四川省科技計(jì)劃(2022YFQ0047)
作者簡(jiǎn)介: 王濤(1997-), 男,? 碩士研究生, 四川資陽(yáng)人, 研究方向?yàn)榉謹(jǐn)?shù)階微積分與強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí). E-mail: 2647877536@qq.com
通訊作者: 張衛(wèi)華. E-mail: zhangweihua@scu.edu.cn
An improved Ornstein-Uhlenbeck exploration noise based on fractional order calculus for reinforcement learning environments with momentum
WANG Tao, ZHANG Wei-Hua, PU Yi-Fei
(College of Computer Science, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065, China)
In this paper, the integer-order Ornstein-Uhlenbeck (OU) noise model used in the deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) algorithm is extended to the fractional-order OU noise model, and the generated noise is not only related to the noise of the previous step but also related to the noise generated in the previous K steps in the proposed model.The DDPG algorithm and twin delayed deep deterministic(TD3) algorithm using the fractional-order OU noise model were compared with the original DDPG algorithm and TD3 algorithm in the gym inertial environment. We found that, compared with the original OU noise, the fractional-order OU noise can oscillate in a wider range, and the algorithm using the fractional-order OU noise had better exploration ability and faster convergence in inertial environment.
Deep deterministic policy gradient; Twin delayed deep deterministic; Fractional calculus; Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process; Reinforcement learning
1 引 言
深度Q網(wǎng)絡(luò)(DQN)[1]的提出開(kāi)創(chuàng)了深度學(xué)習(xí)和強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí)結(jié)合的先例,DQN算法直接使用了深度神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)來(lái)擬合強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí)中的Q(s,a) 函數(shù),并根據(jù)貪心策略選擇下一步需要執(zhí)行的動(dòng)作,這一工作使得算法在Atari游戲上達(dá)到了近似人類玩家的水平.
基于DQN的工作,后續(xù)還有人還提出了DDQN[2],Dueling DQN[3],Rainbow DQN[4]等工作,這些工作極大地改進(jìn)了基于值函數(shù)估計(jì)類算法的效果.不過(guò),這些工作的動(dòng)作空間都是離散的,智能體每次只能選擇有限的幾個(gè)動(dòng)作.然而,在實(shí)際的應(yīng)用場(chǎng)景下,更多的是需要強(qiáng)化學(xué)習(xí)算法處理連續(xù)控制任務(wù).比如無(wú)人機(jī)追逃控制[5],飛行器高度控制[6],機(jī)械臂軌跡規(guī)劃[7,8],無(wú)人機(jī)航跡規(guī)劃[9]等.
對(duì)于連續(xù)控制任務(wù)則無(wú)法直接使用DQN系列的算法,研究人員參考DQN系列算法值函數(shù)估計(jì)的思想,提出了DDPG算法[10],在……
