L 2-CONVERGENCE TO NONLINEAR DIFFUSION WAVES FOR EULER EQUATIONS WITH TIME-DEPENDENT DAMPING?
Shifeng GENG()
School of Mathematics and Computational Science,Xiangtan University,Xiangtan 411105,China
E-mail:sfgeng@xtu.edu.cn
Feimin HUANG()
Academy of Mathematics and Systems Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China
E-mail:fhuang@amt.ac.cn
Xiaochun WU()?
School of Mathematics and Statistics,HNP-LAMA,Central South University,Changsha 410083,China
E-mail:xcwu22@csu.edu.cn
Abstract In this paper,we are concerned with theasymptotic behavior of L∞weak-entropy solutions to the compressible Euler equations with a vacuum and time-dependent damping Asλ∈(0,],we prove that the L∞weak-entropy solution converges to the nonlinear diffusion wave of the generalized porous media equation(GPME)in L 2(R).Asλ∈(,1),we prove that the L∞weak-entropy solution converges to an expansion around the nonlinear diffusion wave in L 2(R),which is the best asymptotic profi le.The proof is based on intensive entropy analysis and an energy method.
Key words L 2-convergence;compressible Euler Equations;time asymptotic expansion;time-dependent damping;relative entropy inequality
Dedicated to Professor Banghe LI on the occasion of his 80th birthday
1 Introduction
In this paper,we consider the compressible Euler equations with a vacuum and timedependent damping
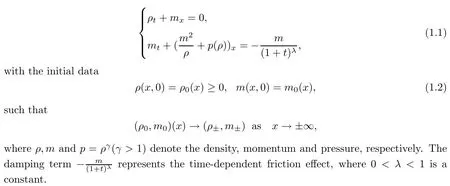
Whenλ=0,(1.1)becomes the compressible Euler equation with damping.For the case away from a vacuum,Hsiao-Liu [9]first rigorously proved that Darcy’s law is well suited to approximating the momentum equation in system(1.1),and they showed that the solution of(1.1)-(1.2)tends time-asymptotically to the diffusion wave of the porous media equation(PME)
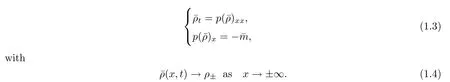
Since then,this problem has attracted considerable attention;see [9,10,22–26,35,36]and the references therein.However,when a vacuum occurs,the difficulty of the problem increases dramatically.In fact,Liu-Yang [20,21]showed that the local smooth solutions with a vacuum of(1.1)blow up in finite time,where the new singularity occurs due to the vacuum.Thus,theL∞global weak solution has to be considered.For the case without the damping term,i.e.,where the right hand side of(1.1)is zero,Diperna [5]first proved the global existence ofL∞entropy solutions with arbitrarily large initial data by the theory of compensated compactness forγ=with any integern≥2.Subsequently,Ding et al.[4]and Chen [1]successfully extended the result toγ∈(1,].Lions et al.,in [17]and [18],treated the caseγ >Huang-Wang [15]completed the proof of the global existence of theL∞entropy solutions for the case in whichγ=1.For the case with constant damping,i.e.,λ=0,Huang-Pan [13]proved the global existence ofL∞weak-entropy solutions forγ≥1.Furthermore,Huang-Pan [12]verified that theL∞weak-entropy solutions to(1.1)–(1.2)also tend to the nonlinear diffusion waves of(1.5)time-asymptotically in the form
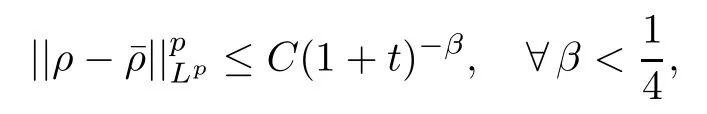
under the condition that the end-statesρ±are away from the vacuum.For more on weak solutions to(1.1)with a vacuum,we refer to [6,14,19,29,37].
For when 0<λ<1,Cui-Yin-Zhang-Zhu [3](seealso Li-Li-Mei-Zhang [16])showed that the global smooth solution away from a vacuum to(1.1)–(1.2)converges to the nonlinear diffusion waves to the generalized porous media equation(GPME)
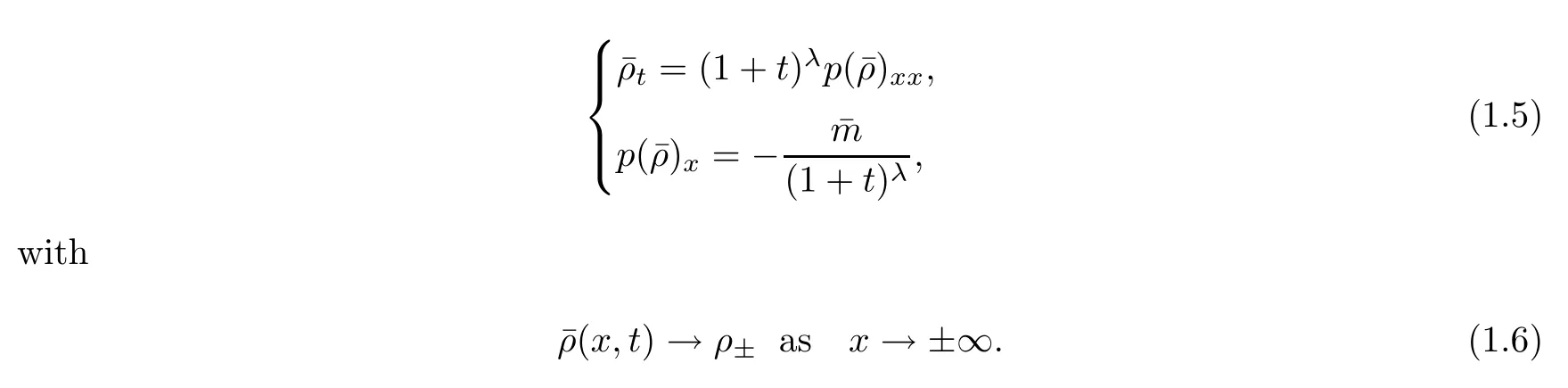
Similarly to the case whereλ=0,it is also important to study the large time behavior of an entropy solution of system(1.1)with a vacuum.We will try to obtain the asymptotic behavior of anyL∞weak entropy density of(1.1)–(1.2)forλ∈(0,1).For other interesting contributions to(1.1),we refer to [2,7,27,28,30–34].
Before stating our main results,let us first recall the definition of anL∞entropy solution of(1.1)–(1.2).
Definition 1.1We call(ρ,m)(x,t)∈L∞an entropy solution of(1.1)–(1.2)if,for any test functionφ∈D(R×R+),it holds that
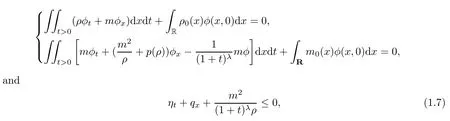
in the sense of distributions,where(η ,q)is the mechanical entropy-fl ux pair
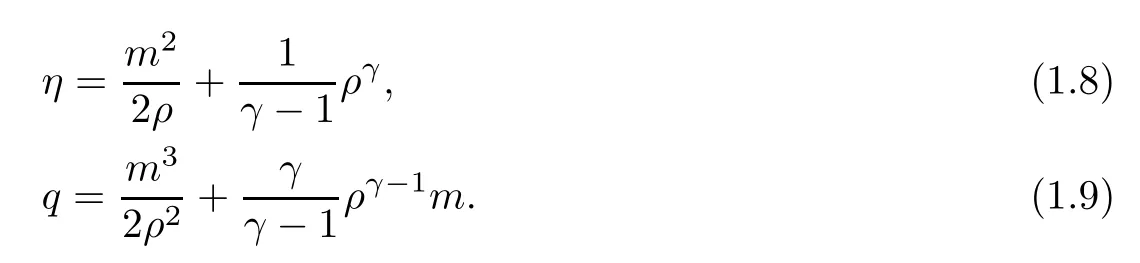
Following the argument in [13],it is straightforward to show that there exists aL∞entropy solution of the Cauchy problem(1.1),(1.2)withγ >1 if the initial data(ρ0,m0)(x)satisfies that
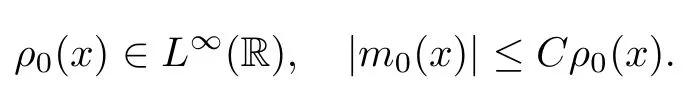
The details are omitted.Then our first result is stated as follows:
Theorem 1.2Let(ρ,m)be anyL∞entropy solution of the Cauchy problem(1.1),(1.2).If the initial data(y0,y1)(x)∈H1(R)×L2(R),where
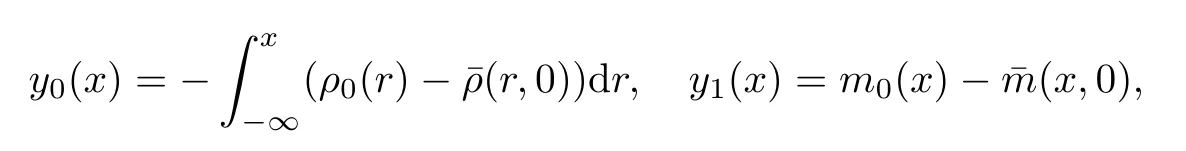
then it holds that

for any small constant 0< ε?1.
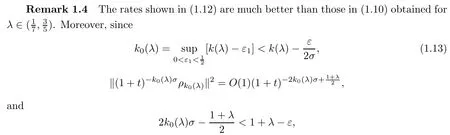

NotationsThroughout this paper,the symbolCwill be used to represent a generic constant which is independent ofxandt,and that may vary from line to line.TheL2-norm on R is simply denoted by‖·‖.In addition,forr,s∈N,we adopt the convention that

2 The Convergence to the Nonlinear Diffusion Wave
We first state some known results concerning with the self-similar solutions of the GPME,i.e.,

The following properties are due to [3],[16]:
Lemma 2.1It holds that
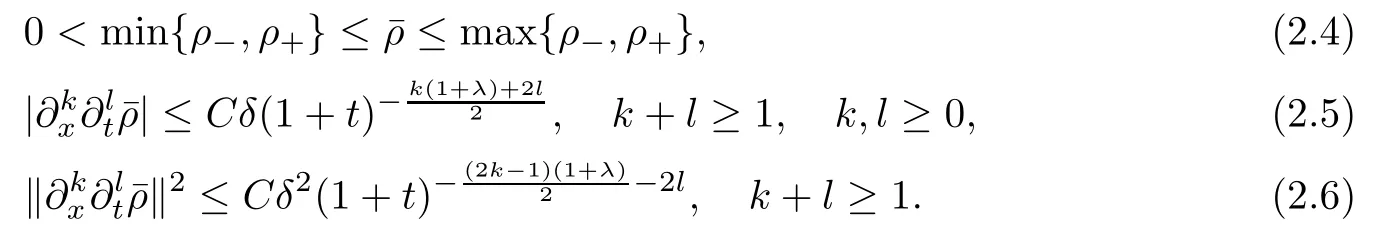
We give an invariant region theorem for theL∞entropy solution to(1.1),(1.2),(cf.[7],[14]).
Theorem 2.2Assume that(ρ0,u0)(x)∈L∞(R)satisfies that
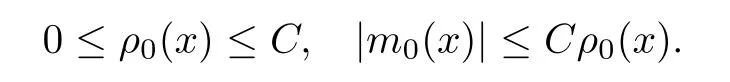
Let(ρ,u)∈L∞(R×[0,T])be theL∞entropy solution of the system(1.1),(1.2)withγ >1.Then(ρ,m)satisfies that

where the constantCdepends solely on the initial data.
Before we derive the basic energy estimates,we give some important inequalities which provide information on the pressure near the vacuum(cf.[11],[14]).
Lemma 2.3Letting 0≤ρ≤M<∞,0

As in [3,16],we introduce the auxiliary functions
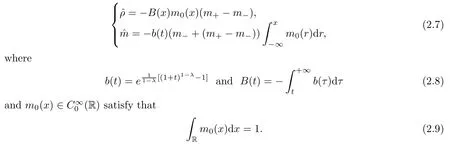
From(1.1),(2.1),we have that

Integrating the above equation with respect toxover R,we get that
This yields that
where the shiftx0is determined by
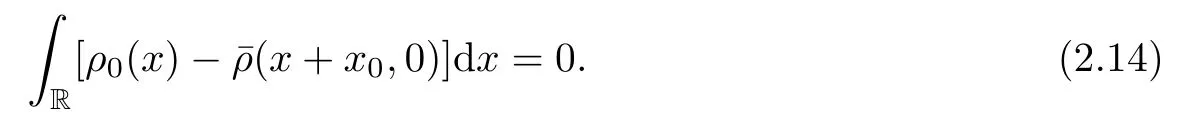
Define
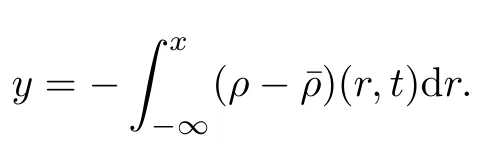
Then
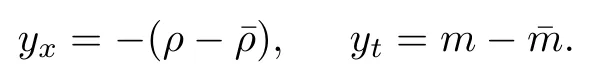
We can reduce the perturbation system of(1.1)and(2.1)to a quasilinear wave equation with a source term,degenerate at the vacuum:

Lemma 2.4Under the assumptions of Theorem 1.2,it holds that

where 0<β<λ.
ProofMultiplying(2.15)with(α+t)βy,integrating over R×[0,t]and integrating by parts,we have that

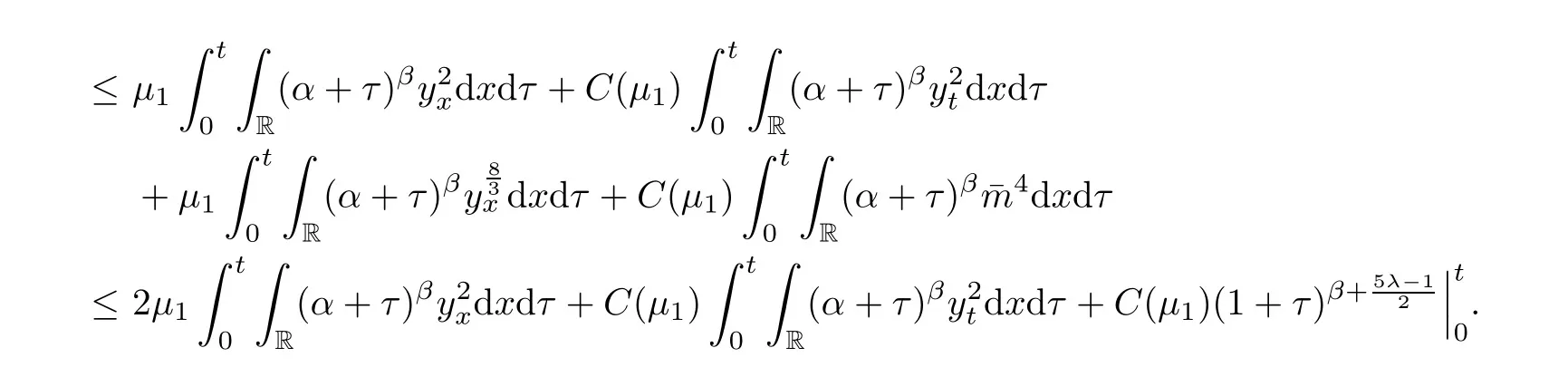
Substituting(2.18)–(2.20)and(2.22)into(2.17)and choosingμ1small enough yields that(2.16),directly.Thus,the proof of Lemma 2.4 is complete. □
To control the terms on the right hand side of(2.16),we denote that
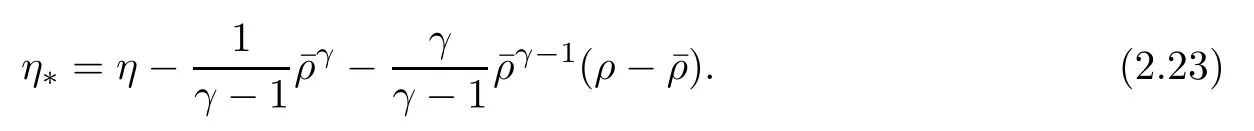
Then,it follows from(1.7)that

where we have used the fact that
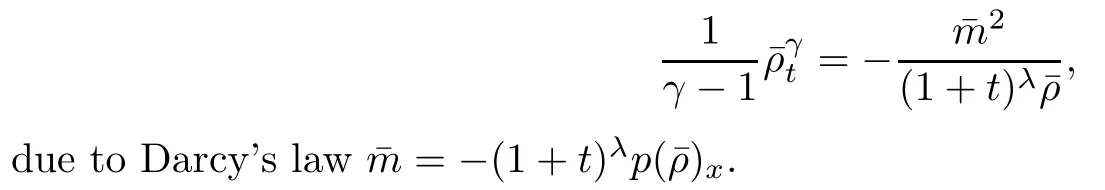
Lemma 2.5Under the assumptions of Theorem 1.2,it holds that

where 0<β<λ.
ProofMultiplying(2.24)by(α+t)λ+βand integrating the result over R×[0,t]gives that

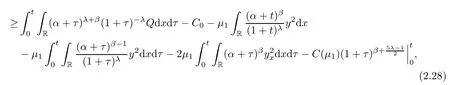
where we have used the fact that

In addition,by direct computation,we have that
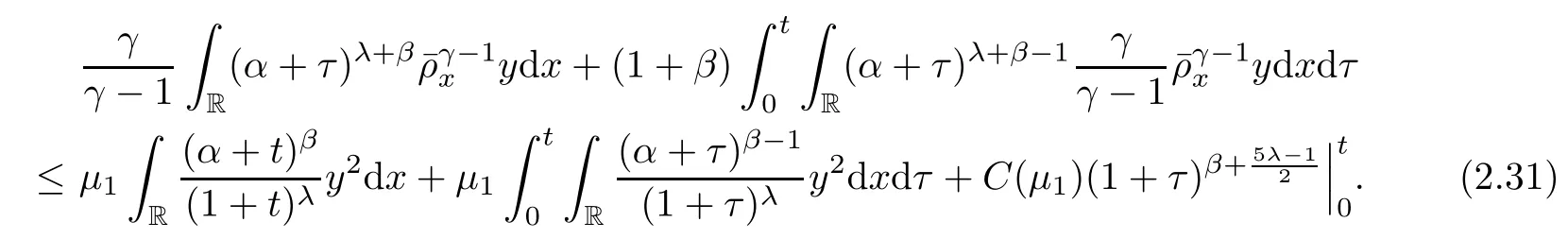
Substituting(2.28)and(2.30)–(2.31)into(2.26)and choosingμ1small andαlarge enough yields that
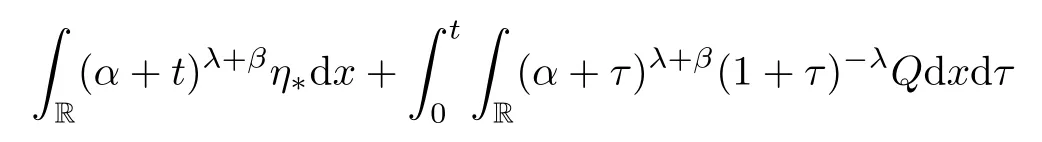

which implies(2.25),directly.Thus,the proof of Lemma 2.5 is complete. □
Based on the abovebasic estimatesobtained,wefurther adopt the relativeentropy inequality as in [6]to sharpen the decay rate.Defi ne

Then we quote the more precise entropy inequality of [6]directly,without proof,as follows:
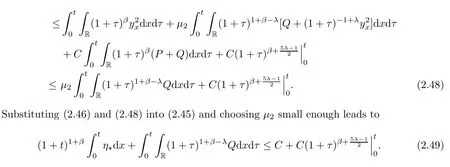
Then(2.44)follows from(2.47)and(2.49).Thus,the proof of Lemma 2.7 is complete. □
Proof of Theorem 1.2It follows from Lemmas 2.6 and 2.7 that
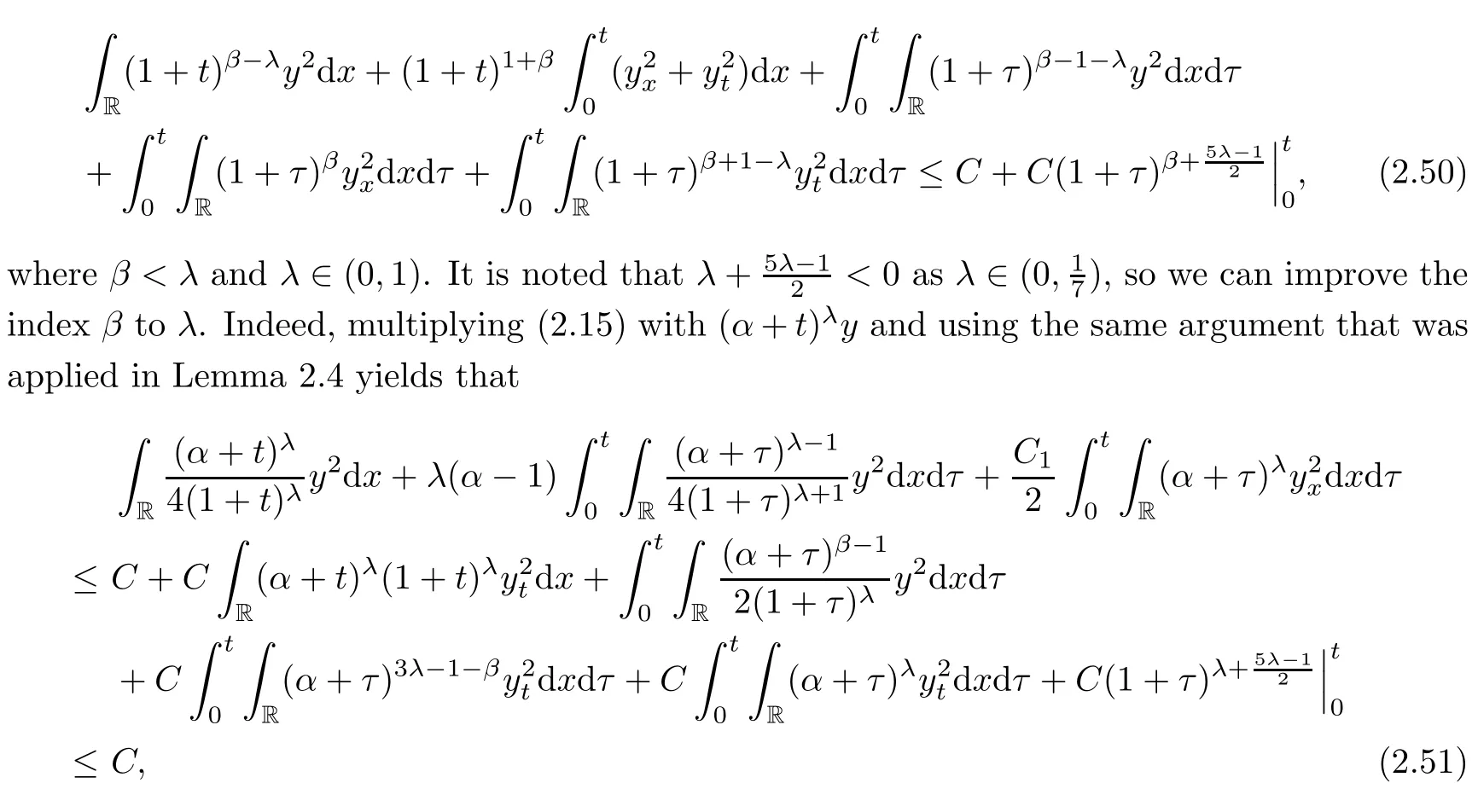
where in the last inequality we chooseβsatisfying that 2λ?1<β<λand use Lemmas 2.4 and 2.7.Furthermore,multiplying(2.41)by(1+t)1+λand using the same argument that was applied in Lemma 2.7,we have that
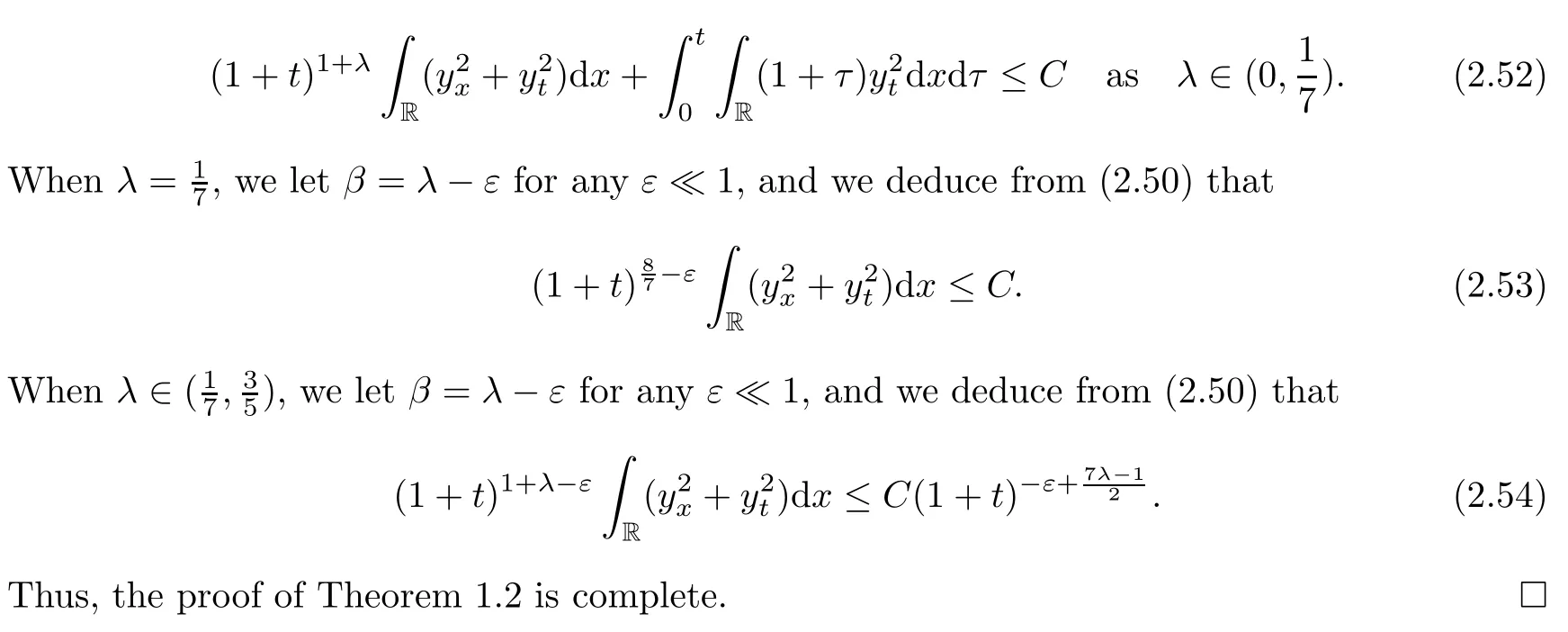
3 The Convergence to the Expansion Around the Nonlinear Diffusion Wave
In this section,we will show that the expansion around the solution of GPME is the best time-asymptotic profi le of the solution(ρ,m)of(1.1),(1.2),withλ∈(,1).As in [8],we write the time asymptotic expansion around the diffusion wavefor some nonnegative integerkas follows:

and herei=1,···,k,andhjare some explicit functions depending onandρlwithl∈{1,···,j?1}forj=2,···,k.
There exist solutions for the ODEs(3.4)in [8],and the existence is stated as follows:

Defi ne the source term as
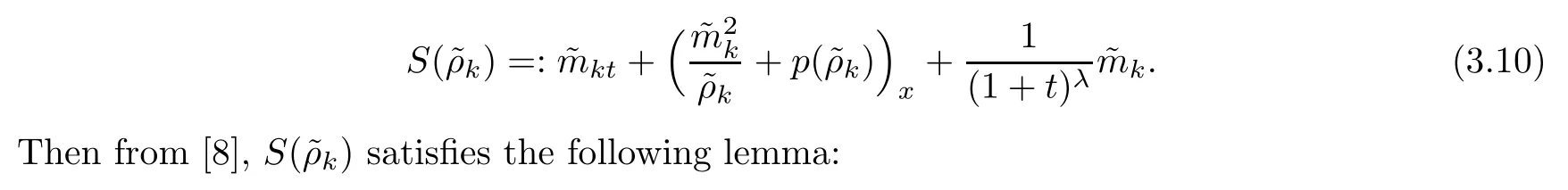
Lemma 3.2It holds that
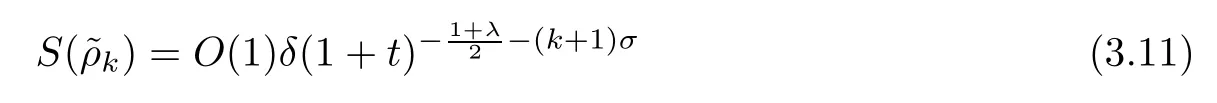
and
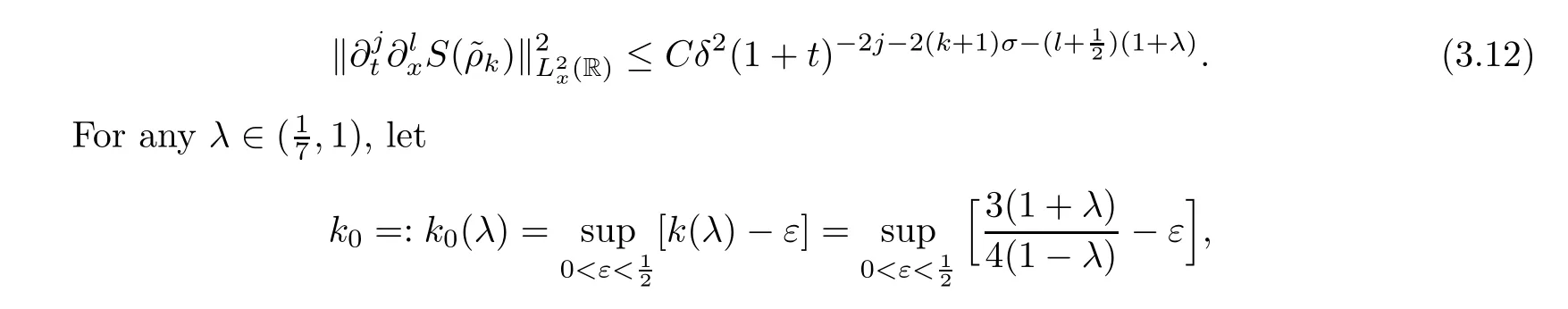
and the time asymptotic expansion is

Thus the system(1.1)can be rewritten as a quasilinear wave equation forzwith a source term as follows:
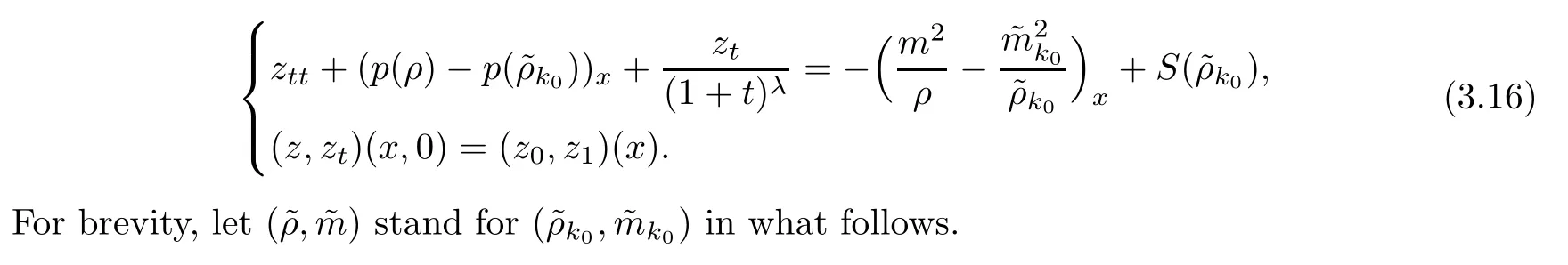
Lemma 3.3Ifδis small,then it holds that
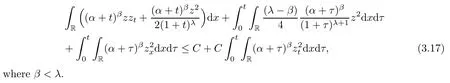
ProofMultiplying(3.16)with(α+t)βzand integrating the result over R×[0,t],the same argument as to that in Lemma 2.4 gives that
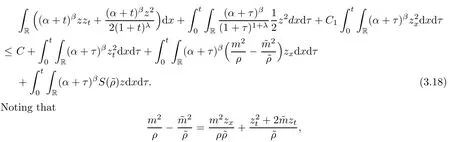
we use Theorem 2.2 and the smallness ofδto get that

whereμ1is small enough.Moreover,it follows from the estimates in(3.12)that
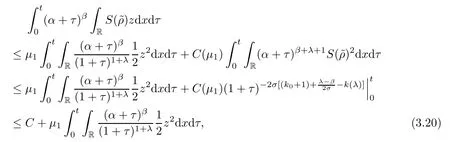
where we have used the facts thatβ<λand

Next,we will use the relative entropy inequality to close the estimates(3.17).Similarly to(2.40),define that
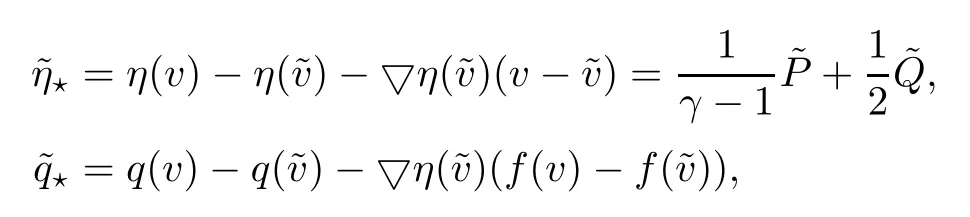


Proof of Theorem 1.3Letβ=λ?εwithε?1.Then(1.12)follows from Lemma 3.4 directly.Thus,the proof of Theorem 1.3 is complete. □
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2022年6期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2022年6期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- GLOBAL WELL-POSEDNESS OF A PRANDTL MODEL FROMMHD IN GEVREY FUNCTION SPACES?
- SYMBOLIC COMPUTATION FOR THE QUALITATIVE THEORY OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS?
- OPINION DYNAMICS ON SOCIAL NETWORKS?
- ON ACTION-MINIMIZING SOLUTIONS OF THE TWO-CENTER PROBLEM?
- SOME RESULTS ON HEEGAARD SPLITTING?
- GENERIC NEWTON POLYGON OF THE L-FUNCTION OF n VARIABLES OF THE LAURENT POLYNOMIAL I?
