Finite-time complex projective synchronization of fractional-order complex-valued uncertain multi-link network and its image encryption application
Yong-Bing Hu(胡永兵) Xiao-Min Yang(楊曉敏) Da-Wei Ding(丁大為) and Zong-Li Yang(楊宗立)
1School of Electronics and Information Engineering,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,China
2National Engineering Research Center for Agro-Ecological Big Data Analysis&Application,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,China
Multi-link networks are universal in the real world such as relationship networks,transportation networks,and communication networks. It is significant to investigate the synchronization of the network with multi-link. In this paper,considering the complex network with uncertain parameters,new adaptive controller and update laws are proposed to ensure that complex-valued multilink network realizes finite-time complex projective synchronization(FTCPS).In addition,based on fractional-order Lyapunov functional method and finite-time stability theory, the criteria of FTCPS are derived and synchronization time is given which is associated with fractional order and control parameters. Meanwhile,numerical example is given to verify the validity of proposed finite-time complex projection strategy and analyze the relationship between synchronization time and fractional order and control parameters.Finally,the network is applied to image encryption,and the security analysis is carried out to verify the correctness of this method.
Keywords: multi-links network, fractional order, complex-valued network, finite-time complex projective synchronization,image encryption
1. Introduction
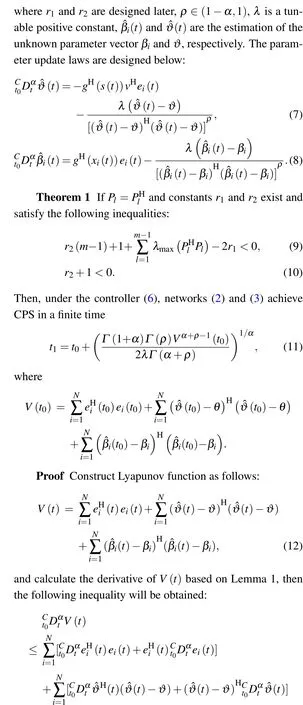
Complex networks (CNs) are effective system modeling tools in the real world, every network can be described in terms of nodes and edges, where each edge represents a connection between nodes. Multi-link networks[1–3]are the networks that have more than one connection between two nodes.There are numerous multilink networks in life, such as relationship networks, transportation networks, and communication networks.[4,5]For example, in the transportation networks, the speeds of transmission among highway network,railway network, and airline network are different from each other,which can be seen as that the connections of transportation network have different delays. In Refs.[6,7],the complex multi-link network is split into sub-networks with delay so as to describe the delay characteristics of multi-links network.As a special case of multi-link network, single-link network has been investigated by many researchers. Nevertheless, little attention has been paid to multi-link networks. Therefore,complex dynamic networks with multiple links have certain research value.[8,9]
Synchronization is an important research topic in CNs.Researchers have studied many synchronization methods,such as projective synchronization,[10]pinning synchronization,[11]and exponential synchronization.[12,13]Projective synchronization(PS)reflects the proportional relationship between synchronization states by introducing a scaling factor.In Ref.[14], Shaet al.used the control method based on uncertainty and disturbance estimation and linear feedback to accomplish PS in complex chaotic systems. As an extension of PS, complex projective synchronization (CPS) leads to synchronization complexity and diversity because its scale factor is a complex number. In Ref.[15],using the stability theorem of the fractional-order systems with multiple delays, Dinget al.achieved CPS in memristive neural network. The CPS occurs asymptotically and it has unbounded convergence time.In fact,the synchronization is often required to accomplish in a finite time. The finite-time control technology is made realize finite-time synchronization in CNs.[16,17]By using a functional scaling factor,Wanget al.investigated finite-time function projective synchronization for multi-link networks with time-varying delay.[18]In Ref. [19], Zhaoet al. realized the fixed-time synchronization and finite-time synchronization in CNs with multilink by using Lyapunov function and linear matrix inequality. In Ref. [20], Zhenget al. studied the decay synchronization of complex multi-link time-varying dynamic network.
In the existing literature concerning multi-link networks,most of researches are based on integer-order multi-link networks. As a mathematical element that deals with integrals and derivatives in the form of non-integer order,fractional calculus not only has more degrees of freedom than integer calculus,but also possesses unique properties including heredity and infinite memory. At present, fractional calculus has been widely used in CNs which is called fractional order CNs. For example, in Ref.[21], Liet al.used hybrid impulsive control to investigate the global synchronization for two fractional order CNs with non-delayed and delayed coupling. Baoet al.achieved the synchronization of fractional order neural networks with output coupling on the basis of fractional-order Lyapunov function and linear matrix inequalities.[22]Nevertheless, as far as we know, the research results of fractional order multi-link networks are few until now. Therefore, it is significant to incorporate fractional calculus into multi-links networks.
Comparing with real-valued networks, the applications of complex-valued networks are more extensive. For example, there are more variables and transmitted information in complex-valued networks, and the security of transmitted information is also greatly enhanced. Furthermore,complex-valued networks show complex dynamic behaviors and can describe some physical phenomena such as electromagnetic field amplitude, and rotating fluid.[23,24]Yanget al. studied the quasi-projective synchronization of fractional order complex-valued neural networks via linear control strategy.[25]In Ref.[26],Xuet al.used complex function theory and combined Lyapunov method with graph theory to address finite-time synchronization for fractional order complexvalued multi-weighted dynamical networks.
Because the fluctuation of system parameters and the disturbance of external environment are always inevitable, they lead to the uncertainty of system parameters. When analyzing system dynamic characteristics, parameter uncertainties should be considered because they may have influence on the synchronization performance and system stability. Therefore,uncertain complex networks are valuable.[27–30]In Ref. [31],making use of the properties of fractional calculus, Liet al.accomplished finite-time synchronization for fractional order complex dynamical networks (FOCDNs) with unknown parameters and the parameters were identified. Duet al. investigated synchronization of all nodes in FOCDNs with uncertain parameters by adaptive control strategy.[32]Yanget al.designed two different controllers to study finite-time lag synchronization of uncertain complex networks with impulsive disturbance.[33]
In addition, synchronization can improve the security of image transmission and has great applications in secure communication. Considering the highly nonlinear nature of complex networks and non-locality of fractional order chaotic systems, fractional order complex networks are worth applying to image encryption.[34]Wang and Yang proposed a new encryption system algorithm for encrypting/decrypting color images.[35]The DNA encoding algorithm has advantages of high parallelism, high storage capacity and low power consumption in the field of image encryption.[36,37]Moreover,image encryption based on complex network and DNA approach has a good encryption effect.
From the above analysis,this paper is to address FTCPS of fractional order complex-valued multi-links network and applies it to the image encryption. The main difficulty is how to deal with the delay problem in fractional order multi-link networks. The synchronization is realized via adaptive controller.The criteria of FTCPS are obtained by using fractionalorder Lyapunov functional method and finite-time stability theory. Two examples are used to verify the validity of theoretical results. The main contributions are listed below. First,most of researches are based on integer-order multi-links networks,but we extend the integer-order multi-link networks to the fractional-order networks to make the results more general. Secondly,most of previous multi-link networks are realvalued,but this paper focuses on complex-valued field. Then,considering the uncertainty of network parameters, new update laws are designed and the control strategy of FTCPS is proposed. Compared with the infinite-time synchronization,this finite-time synchronization can improve convergence performance. Finally, the criteria of FTCPS are derived and the relationship between synchronization time and fractional order and control parameters is analyzed. Besides, the network is applied to image encryption and the security analysis is carried out.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows.In Section 2 some preliminaries and network description are introduced.In Section 3, the main results are demonstrated. Numerical example and image encryption application are provided in Section 4 to verify the validity of the proposed results. In Section 5 some conclusions are drawn from the researches of this paper.

2. Preliminaries and network description
We introduce some definitions and lemmas in this section,which are helpful for our later research.
Definition 1[38]Caputo derivative of orderαfor a functionf(t)∈Cn([t0,+∞)R) (the set of alln-order continuous differentiable functions on[t0,+∞))is defined as

wheret≥t0,nis a positive integer,n-1<α <n.Γ(·)is the Gamma function. Particularly,when 0<α <1,

In this paper,we consider the fractional order complex-valued multi-links network with uncertain parameters, which is described by

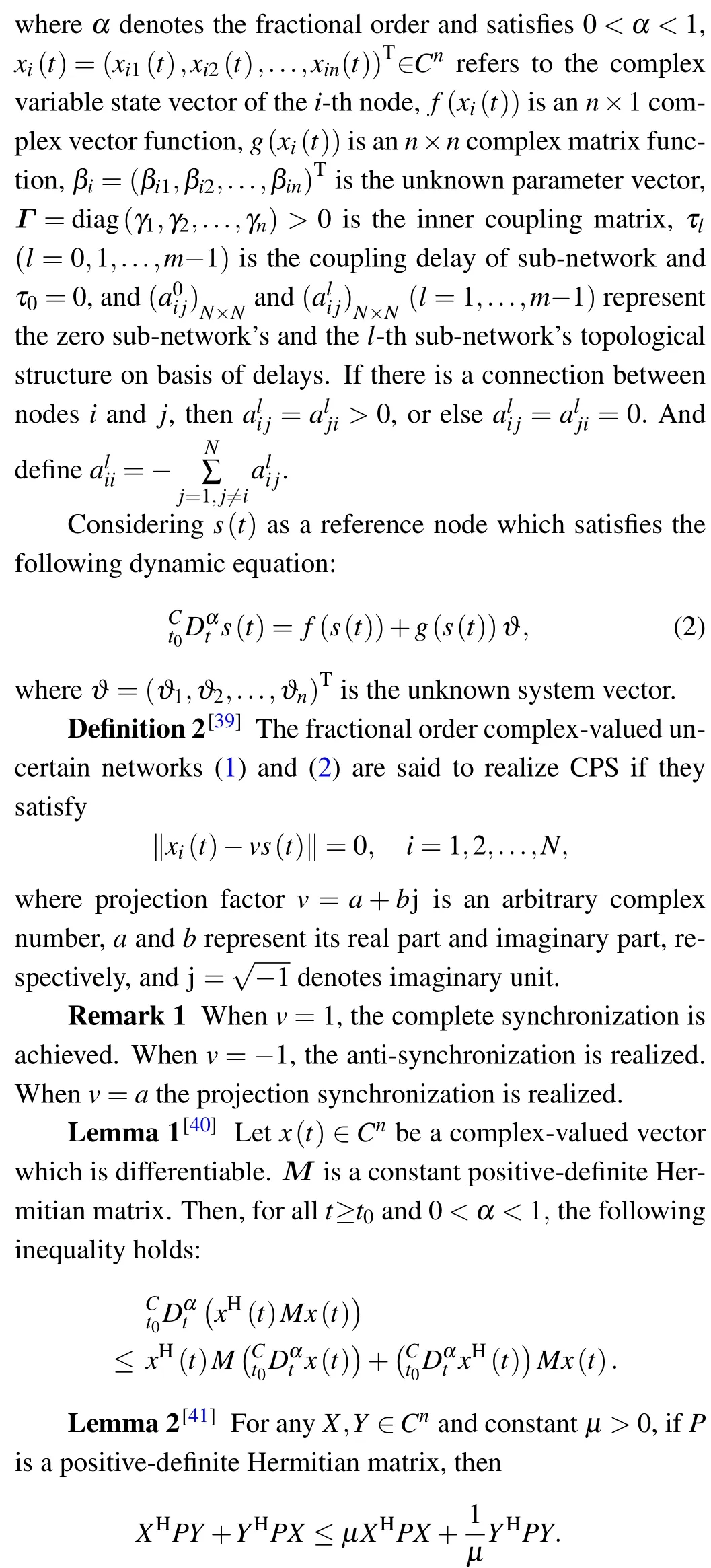
Lemma 3[42]Forδr≥0 withr=1,2,...,k, 0≤σ≤1,then

Remark 2 Compared with the finite-time synchronization issue of integer-order systems,Lemma 4 has a wide range of applications, and the Lemma 4 can be used to study the finite-time stability or synchronization issue for fractionalorder systems or FOCDNs.
3. Main results
In this section,we put forward an adaptive controller for accomplishing FTCPS in the fractional-order complex-valued uncertain multi-links network.
Network(1)can be rewritten as follows:


then it will follow that
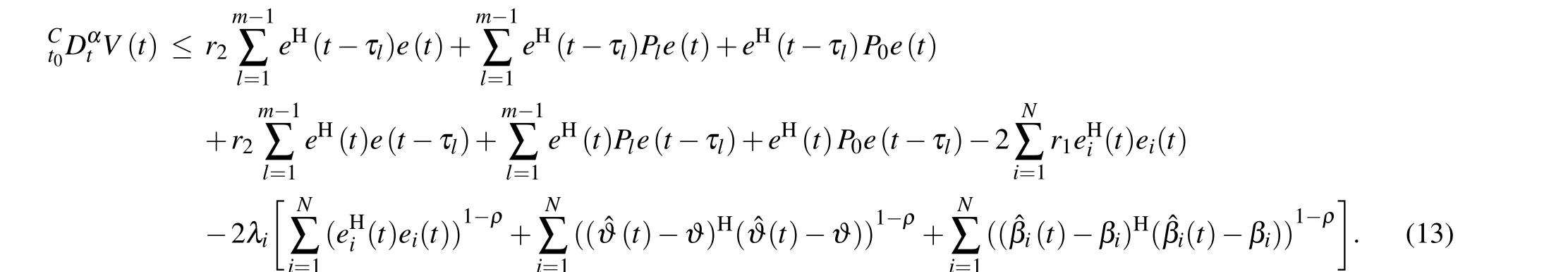
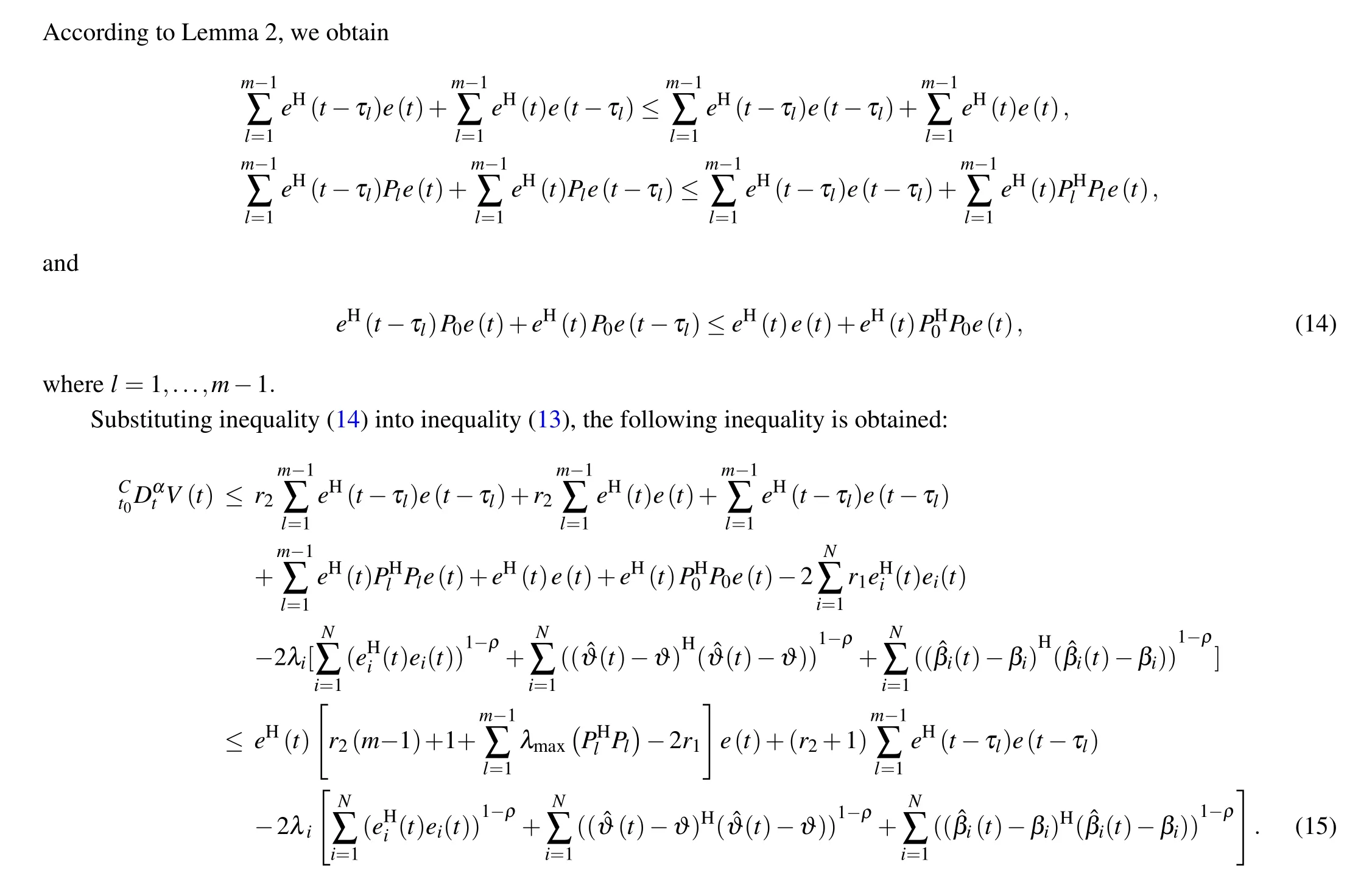
Using Lemma 3,it follows that


4. Numerical simulation and application to image encryption
4.1. Numerical examples
In this section,the Lorenz system and application to image encryption are used to verify the validity of the proposed theorem.Example 1 Consider complex Lorenz system as the node dynamic system of network with five nodes as follows:
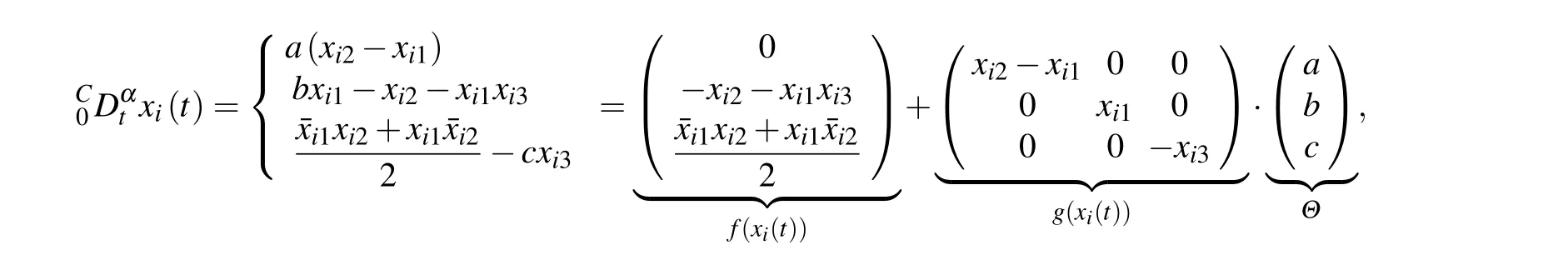
whereα=0.95,Θ=(a,b,c)T=(10,28,8/3)T,xi1,xi2∈Cn,xi3∈Rn,i=1,2,...5. Chaotic behavior of fractional order complex Lorenz system is exhibited in Fig.1.

Fig.1. Chaotic behavior of fractional order complex Lorenz system.
Consider the multi-link network with two different subnetworks,each with five nodes. The weight configuration matrixesA0andA1are respectively chosen as
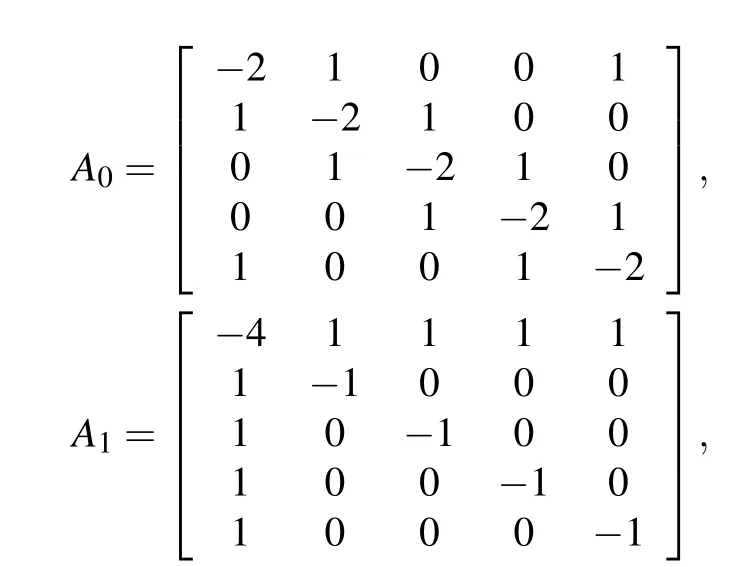
whereA0has no time-delay. Figure 2 shows the topological structures of two weighted subgraphsA0andA1respectively.

Fig.2. Topological structures of two weighted subgraphs,showing(a)topological structures of weighted subgraph A0 and (b) topological structure of weighted subgraph A1.
The fractional-order complex-valued uncertain multilinks network containing five nodes is expressed as achieve CPS with Eq. (18) within the limited time, and we obtain the estimationt1


Figure 3 shows the trajectories of synchronization errorei(t)(i=1,2,...,5)We can see thatei(t)=0(i=1,2,...,5)whent ≥1.3087, which denotes that the networks (17) and(18) can accomplish CPS in a finite time. Figure 4 displays the trajectories of uncertain parameters. Moreover, we observe from Fig. 4 that?1→10 andβi2→28 within a finite time interval,which indicates that the uncertain parameters are successfully identified.

Fig.3. Synchronization errors ei(t)(i=1,2,...,5)of networks(17)and(18),showing[(a),(c),and(e)]real part of synchronization error,and[(b),(d),and(f)]imaginary part of synchronization error.

Fig.4. Uncertain parameters of the networks(17)and(18): (a)estimation of ?1 (b)estimation of βi2.
In the following Figs. 5–10, we display the relations between the estimatedt1and the fractional-order parameterαand the control parametersρandλ. From Fig.5,we can observe that the estimatedt1increases with the growth of the the fractional-orderα. From Fig.6,we can observe that the estimatedt1firstly decreases as the control parameterρincreases,then it increases as theρincreases. From Fig. 7, we can see that the estimatedt1decreases with the control parameterλincreasing.

Fig.5. Relations between estimated t1 and α.
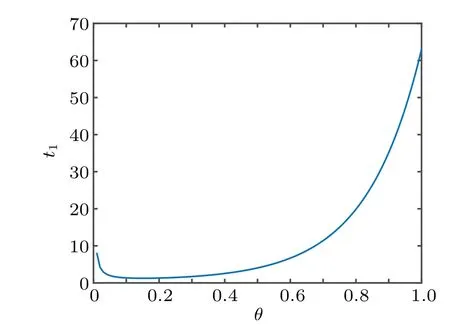
Fig.6. Relations between estimated t1 and ρ.

Fig.7. Relation between estimated t1 and λ.

Fig.8. Relations between estimated t1 and α,λ.

Fig.9. Relations between estimated t1 and ρ,α.
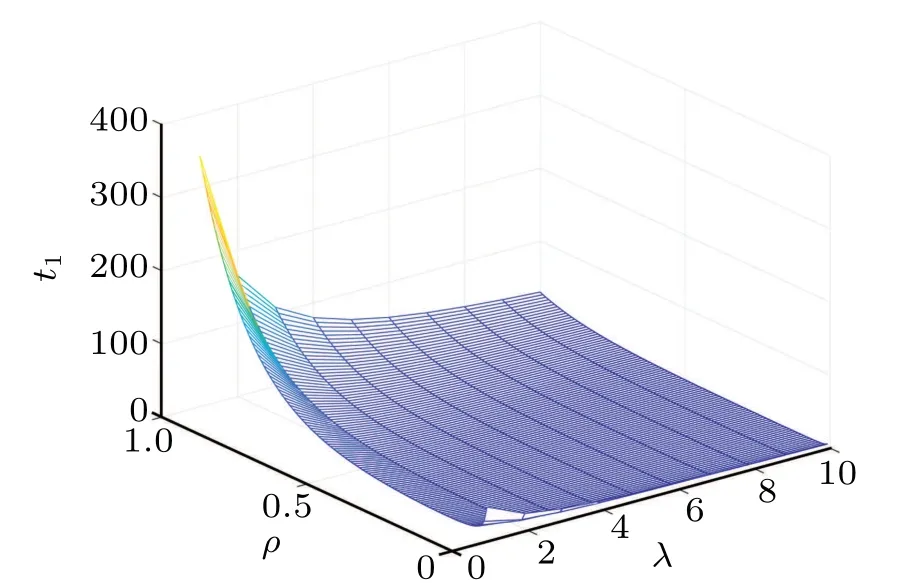
Fig.10. Relations between estimated t1 and ρ,λ.
Example 2 Based on synchronization results derived in Example 1, we apply them to image encryption. We take the network (17) as the encryption chaotic sequences to realize the image encryption and the synchronous node (18) as the decryption chaotic sequences to realize image decryption.
Here,we use the image encryption scheme on DNA coding. The DNA sequence consists of A(adenine),G(guanine),C (cytosine), and T (thymine), where A and T, G and C are two complementary base pairs. Owing to 0 and 1 being complementary in binary,we can encode four nucleic acids A,C,G and T with 00, 01, 10, and 11. Table 1 gives 8 kinds of encoding combinations which satisfy the Watson-Crick complement rule. Table 2 show the addition,subtraction and XOR operations of DNA sequences.
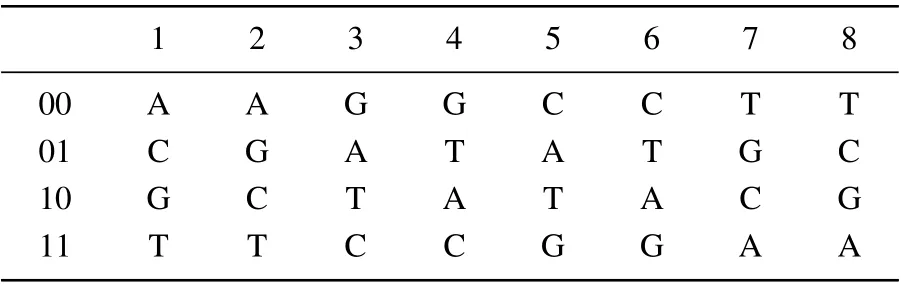
Table 1. Rules of DNA coding.

Table 2. Operations of DNA sequences.
4.2. Processes of image encryption and decryption
We use the fractional order complex-valued uncertain multi-links network to generate chaotic sequences to disturb the pixels of original image. The encryption flowchart is shown in Fig.11,which includes the generation of chaotic sequence and encryption of image by DNA coding and chaotic sequence.
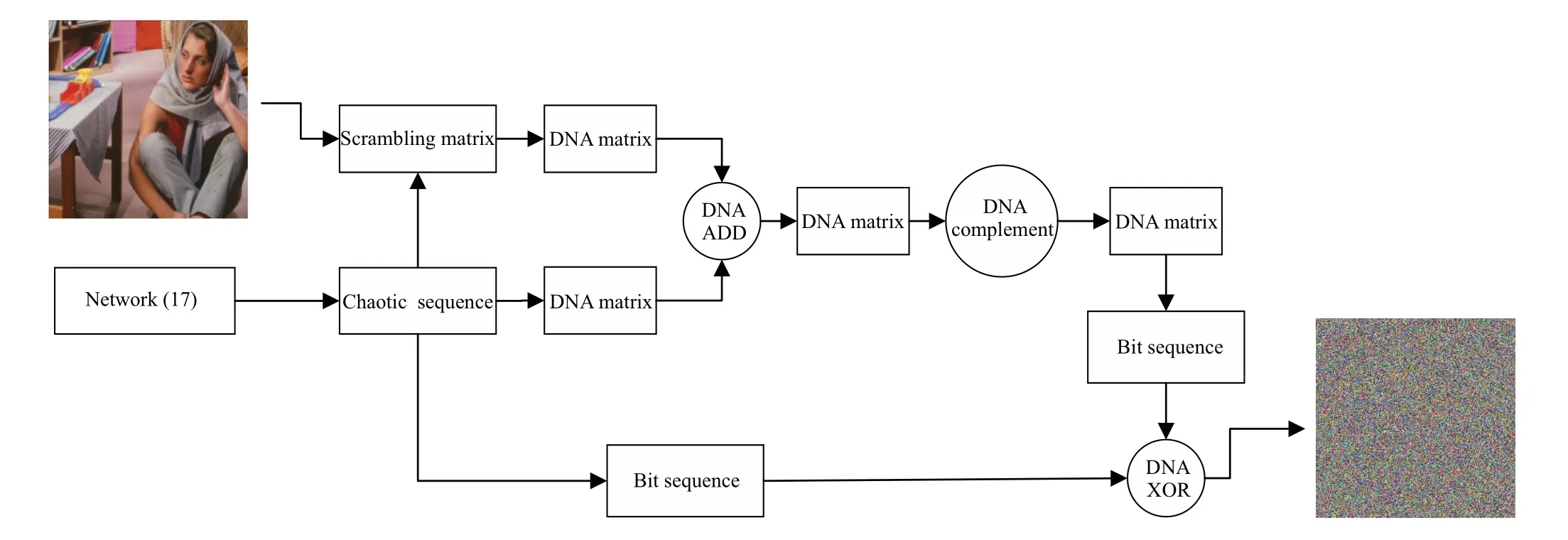
Fig.11. Flowchart of encryption.
4.2.1. Generate chaotic sequence
Step 1 The fractional order complex-valued uncertain multi-links network is iteratedN0+mntimes, and the lastmniterations are regarded as valid data,then the four state valuesxi(1),xi(2),xi(3),andxi(1)+xi(2),i=1,2,3,...,mnare obtained.
Step 2 Four state values are used to generate sequencess(i,j)∈[0,255],s′(i,j)∈[0,255],j=1,2,3,4.The calculation formulas are as follows:



4.3. Simulation results and security analyses
We select the color image with the size of 256×256×3 as the original image, which is depicted in Fig. 12(a). Using the encryption algorithm, we obtain the encrypted image in Fig. 12(b). It has no trace of the original image. The decrypted-image is shown in Fig.12(c).
As for encrypted image,it must be secure and can resist different security attacks. For this,we analyze the security from the histogram distributions and correlation coefficients.
4.3.1. Histograms test
The distribution of image pixel intensity values can be evaluated by histogram. We can see that the histograms of the encrypted image are equally distributed which can protect the original image information and resist the statistical attack. Figures 13(a)–13(f)display the histograms of the original image and encrypted image in the R,G,and B channels,respectively.

Fig.13. Histograms of[(a)–(c)]original images and[(d)–(f)]encrypted images.
4.3.2. Correlation coefficient analysis
The correlation of adjacent pixels reflects the correlation degree of pixel values at the adjacent positions of images.
Generally,we calculate the correlations of adjacent pixels in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions from the following formula:

wherexandyare the pixel values of two adjacent pixels,NdenotesNpairs of adjacent pixels selected,and

From Fig. 14 and Table 3, we can observe that correlations of adjacent pixels in the original image are high, but in the encrypted image, the correlations are efficiently reduced,which indicates that the encrypted image can effectively hide the information about original image.

Fig.14. Correlation of adjacent pixels in horizontal directions,showing[(a)–(c)]original images and[(d)–(f)]encrypted images.

Table 3. Correlation coefficients of adjacent pixels in original images and encrypted images.
5. Conclusions
This paper addresses FTCPS problem of fractional order complex-valued uncertain multi-link networks. Considering the uncertain parameters, the adaptive controller and parameter update laws are designed. On the basis of fractionalorder Lyapunov functional method and finite-time stability theory, the criteria of FTCPS in fractional-order complexvalued multi-link network are derived. In addition, the relationship between synchronization time and fractional order and control parameters are analyzed. Finally, simulation example and image encryption application are provided to verify the correctness of the obtained results. In the future, we will study the finite-time function projective synchronization in fractional order complex multi-links networks with timevarying delay.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Microwave absorption properties regulation and bandwidth formula of oriented Y2Fe17N3-δ@SiO2/PU composite synthesized by reduction–diffusion method
- Amplitude modulation excitation for cancellous bone evaluation using a portable ultrasonic backscatter instrumentation
- Laser-modified luminescence for optical data storage
- Electron delocalization enhances the thermoelectric performance of misfit layer compound(Sn1-xBixS)1.2(TiS2)2
- TiO2/SnO2 electron transport double layers with ultrathin SnO2 for efficient planar perovskite solar cells
- Sputtered SnO2 as an interlayer for efficient semitransparent perovskite solar cells

