Efficacy of haptic sutured in-the-bag intraocular lens for intraocular lens-capsule complex stability: a comparison of three insertion methods
INTRODUCTION
In eyes predisposed to intraocular lens (IOL) dislocation due to zonular insufficiency, devices such as standard and modified capsular tension rings (CTR) with transscleral fixation through the ciliary sulcus are used to add stability of IOL-capsule complex during cataract surgery
. Recently, late in-the-bag IOL subluxation or dislocation due to zonulolysis has been reported with increasing frequency and has been reported as 0.2% to 3%
.
Risk factors for postoperative IOL dislocation include pseudoexfoliation syndrome, prior vitreoretinal surgery, history of trauma, long axial length, uveitis, retinitis pigmentosa, and connective tissue disorders, such as Marfan syndrome
.Certain measures to prevent IOL-bag complex luxation have been proposed in these predisposing eyes: postoperative relaxing cuts of anterior capsulorhexis margin with Nd:YAG laser, intraoperatively, aspiration of cortex directed in a tangential fashion, and preference of a 3-piece hydrophobic acrylic IOL which may reduce continuous curvilinear capsulotomy (CCC) shrinkage through a combination of decreased anterior capsule fibrosis and greater haptic rigidity than a single piece IOL
.
The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the anatomical stability of IOL capsular bag complex; CCC area contracture, CCC shape and IOL tilt. And the secondary objective was to evaluate the resultant refractive stability,refractive change, and ACD.
據(jù)介紹,6月份,哈國(guó)家磷肥廠宣布投資80億堅(jiān)戈(約合2200萬(wàn)美元)用于現(xiàn)代化改造,預(yù)計(jì)到2020年擴(kuò)大磷肥產(chǎn)量至50萬(wàn)噸,遠(yuǎn)期目標(biāo)為100萬(wàn)噸。今年1~8月,該廠的產(chǎn)品主要銷往美國(guó)、中國(guó)、阿富汗、俄羅斯、烏克蘭、塔吉克斯坦和烏茲別克斯坦。同時(shí),哈產(chǎn)氮肥已開始向阿根廷、羅馬尼亞、捷克、保加利亞和伊朗出口。
At risk eyes with zonular insufficiency may require transscleral suture fixation which is utilized for both transscleral fixation of IOLs as well as endocapsular supporting devices, such as modified CTR and capsular anchoring devices
.
微網(wǎng)逆變器的VSG轉(zhuǎn)動(dòng)慣量和阻尼系數(shù)自適應(yīng)控制//溫春雪,陳丹,胡長(zhǎng)斌,樸政國(guó),周京華//(17):120
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Institutional Review Board (IRB)/Ethics Committee approval of St. Vincent’s Hospital was obtained(VC21RISI0078). All research was conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
A retrospective cohort study with 60 eyes was performed using records of 60 patients undergoing cataract surgery between January 2015 and May 2020 at St. Vincent’s Hospital. Surgeries were performed by one surgeon (Cho YK).Inclusion criteria for patients consisted of 50 or more years of age, clinically significant cataracts with zonular instability,less than 120° (4 clock hours) of zonulolysis, and over 1y of postoperative follow up results. Zonular instability was determined preoperatively by the presence of phacodonesis with or without visible zonular dehiscence in full mydriasis and intraoperatively by marked difficulty in performing the CCC due to lens movement with the presence of zonular dehiscence less than 4 clock hours detected under the operating microscope. Intraoperatively just before IOL insertion, the extent of zonulolysis in clock hours was measured with corneal radial marker with degree gauge. The eyes with phacodonesis in performing the CCC as well as eyes with visible anterior or posterior capsular wrinkling or centripetal movement of anterior capsular margin less than 120° were regarded as eyes with zonulolysis less than 4 clock hours.
The refractive change between 1mo and 1y for Group 1 was 0.71±0.02 D and showed significant hyperopic change compared to 0.37±0.15 D for Group 2 (
=0.009), and 0.05±0.05 D for Group 3 (
=0.007). There was no significant difference in refractive stability between Groups 2 and 3(Figure 6A).
Surgical patients underwent one of three techniques for IOL (YA60BBR
, Hoya Corp., Tokyo, Japan) insertion(Figure 1) by surgeon’s preference according to the operative situation, such as patient’s cooperation including eye movement, hearing ability, availability of CTR, and reimbursement of medical insurance. Group 1 (IOL in the bag) utilized a three-piece IOL inserted in the bag with haptics oriented toward the areas of zonulolysis. Group 2(IOL with CTR in the bag) had a three-piece IOL inserted after injection of a 12 mm standard CTR (Ophtec, Groningen,The Netherlands). Group 3 (Haptic sutured IOL in the bag)received a three-piece IOL inserted in the bag with novel scleral suture fixation at optic-haptic junction.
下面我們將從國(guó)務(wù)院及其下屬部門,如國(guó)家發(fā)展和改革委員會(huì)、科技部、工業(yè)和信息化部、財(cái)政部、中國(guó)人力資源和社會(huì)保障部、自然資源部、生態(tài)環(huán)境部、水利部、農(nóng)業(yè)農(nóng)村部、商務(wù)部、國(guó)家衛(wèi)生健康委員會(huì)、國(guó)家市場(chǎng)監(jiān)督管理總局等各個(gè)部委發(fā)布的政策、新規(guī)、通知等方面來(lái)總結(jié)一下在2018年我國(guó)都出臺(tái)了哪些政策法規(guī)。
At postoperative 1mo and 1y follow-ups,refractive change, anterior chamber depth (ACD), IOL tilt, and CCC were obtained and compared between groups. Refractive changes (reported as spherical equivalent) were measured using an autorefractor keratometer (RK-F1, Canon, Japan).ACD was measured as the distance between the central corneal anterior surface and the anterior surface of the IOL using A-scan ultrasound (AVISO, Carl Zeiss Meditec Ag, France).Negative and positive values between that of preoperative and postoperative 1-year ACD results indicate forward or backward axial movement of the IOL.
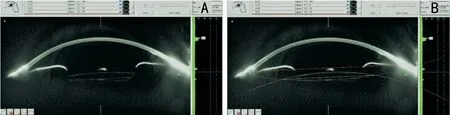
With sufficiently dilated pupils, IOL position was measured using the Oculus Pentacam (Oculus Optikger?te, Inc., Germany).These measurements were performed by an ophthalmic technician who was blinded to patient IOL insertion method.Two vertical Scheimpflug images of total 25 cross section of the target eye 90° apart were selected, and the mean value of tilt in perpendicular directions was recorded as IOL tilt.
山東威海海洋經(jīng)濟(jì)發(fā)展示范區(qū)的主要任務(wù)是發(fā)展遠(yuǎn)洋漁業(yè)和海洋牧場(chǎng),傳統(tǒng)海洋漁業(yè)轉(zhuǎn)型升級(jí)以及與海洋醫(yī)藥、生物制品業(yè)融合集聚發(fā)展模式創(chuàng)新。日照海洋經(jīng)濟(jì)發(fā)展示范區(qū)則是推動(dòng)國(guó)際物流與航運(yùn)服務(wù)創(chuàng)新發(fā)展,開展海洋生態(tài)文明建設(shè)示范。
The line between the anterior chamber angle (red line in Figure 2B) and the line between the IOL edges (yellow line in Figure 2B) were marked on imaging. The IOL tilt angle between red line and yellow line was measured using the reference line of Scheimpflug image (dotted line in Figure 2A and 2B).
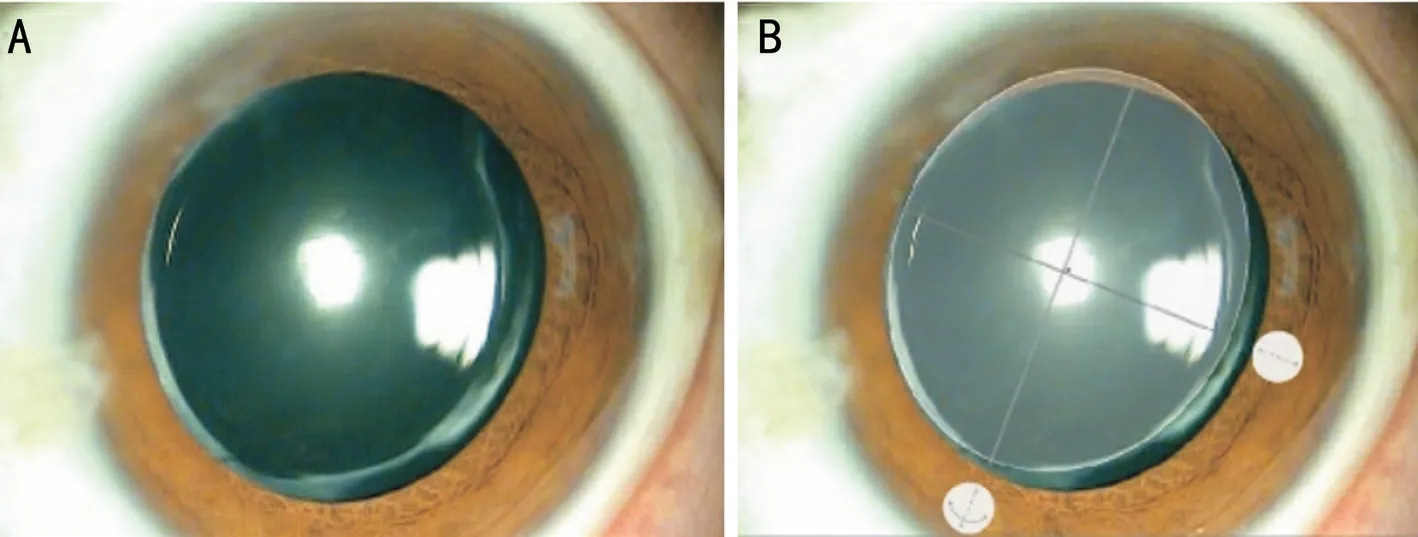
Two aspects of CCC contraction, shape and area, were measured. The shape was evaluated by calculating the CCC axis balance. An ellipse was drawn from the outer tangent lines of the CCC margin and the shortest axis (X axis) and the vertical, longest axis (Y axis) of the ellipse were measured. The axis balance of CCC was calculated (length of X axis ×100%/length of Y axis) and describes the similarity between axes as a percentage. A percentage of 100% denotes a perfect circle, and a smaller percentage nearing 0 denotes a flatter, ovoid shape due to CCC contraction (Figure 3).
從區(qū)域分布上看,內(nèi)蒙古地區(qū)“草原絲綢之路”可分為西部段和東部段兩部分。西部段以呼和浩特、烏蘭察布、包頭、鄂爾多斯為重要支點(diǎn),向西經(jīng)寧夏、青海與新疆絲綢之路相連;東部段由呼倫貝爾、通遼、赤峰等重要節(jié)點(diǎn)城市為依托,連接著俄羅斯、蒙古國(guó),是通往歐洲絲綢之路的重要通道。
SPSS Statistics for Windows software(version 11.5, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the statistical analysis. An analysis of variance test was applied to compare data between Groups, and a post hoc analysis was performed when statistical differences were noted between visits.To compare the causes of zonular dehiscence and postoperative 1-year PCO according to each group, the Chi-square test and Fisher exact test were used, respectively. In all cases, a
value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.

The cause of zonular dehiscence was determined by retrospective chart review including history taking, tonometry, slit lamp examination and visual field test.
Here, we describe a simple technique involving a modification to the IOL haptic suture fixation locations. The efficacy of this technique to maintain capsular bag stability was then compared with two other traditional methods, namely, in-thebag IOL insertion with haptics oriented toward areas of zonular dehiscence and in-the-bag IOL insertion with a standard CTR.
After local anesthetization (sub-tenon injection of lidocaine) and sterile draping, the procedure begins with an anterior CCC approximately 5.0-6.5 mm in diameter using a capsule forcep. In eyes with severe phacodoensis,capsular stability was maintained using disposable iris hook(Synergetics
O’Fallon, MO, USA) placed at the anterior capsular margins. Iris hooks were used in eyes with poor mydriasis. Next, routine phacoemulsification cataract surgery was performed and IOL insertion was accomplished by one of three methods. Group 1 receive a three-piece IOL alone with haptics oriented toward areas of zonulolysis, and Group 2 received CTR coimplantation. The novel method used in Group 3 was performed as follows: After irrigation and aspiration and injection of viscoelastics into the capsular bag and prior to IOL insertion, a 10-0 polypropylene double-armed suture was inserted at the 2 and 8 o’clock position (or the 4 and 10 o’clock position) according to the direction of zonulolysis,about 2 mm from the limbus, and docked in a 30-gauge needle in the anterior chamber. The 10-0 polypropylene suture was retrieved through the main incision and cut in half. Next, each end of the polypropylene suture was tied near the three-piece IOL optic-haptic junction. The IOL, now with both haptics tied with polypropylene sutures, was then inserted into the capsular bag. The opposite end of the polypropylene suture was placed through a trans-scleral tunnel, tied, and adjusted (Video 1,online supplementary).

The posterior capsular opacity (PCO) at postoperative 1-year follow up were measured using slit lamp microscopic examination according to the grading by Congdon
as follows: absent (Grade 0), no opacity or opacity limited to the peripheral capsule; Grade 1, any wrinkling or opacity of the capsule affecting a circle 4 mm in diameter and centered on the visual axis ; Grade 2, central/paracentral opacity as described above sufficient to degrade details of the macula slightly;Grade 3, central/paracentral opacity as defined above, but sufficient to make ascertainment of the cup/disc ratio difficult;Grade 4, central/paracentral opacity as defined above, but sufficient to make visualization of fundus details difficult or impossible.
RESULTS
Table 1 shows the preoperative demographics of three groups.At postoperative 1mo, there was no difference between groups in comparison of IOL tilt, axis balance of anterior capsulotomy area and the percentage area of anterior capsulotomy compared with total corneal area (Figure 5).
Exclusion criteria were congenital zonular laxity (
, Marfan syndrome), previous ocular surgery, intraoperative posterior capsule rupture, greater than 2.00 D of corneal cylinder by keratometry, abnormal corneal topographic patterns, and extreme axial length (less than 21.0 mm or longer than 25.0 mm).
For ACD changes between 1mo and 1y, Group 1 (0.40±0.05 mm) showed a significant ACD increase compared to Group 3 (-0.04±0.01 mm,
=0.005). There was no significant difference in ACD change between Group 2 (-0.07±0.01 mm)and Group 3 (Figure 6B).
As for IOL tilt, Group 2 (2.66°±0.11°) showed significantly less IOL tilting than Group 1 (6.35°±0.28°,
=0.005) and Group 3 (3.47°±0.11°,
=0.006). Group 3 showed significantly less tilt than the Group 1 (
=0.007; Figure 6C).
Comparing of shapes of CCC, Group 2 (93.13%±1.00%)showed the largest axis balance (the least disparity), and Group 3 (64.13%±0.55%) showed the largest disparity between X and Y axis (Figure 6D). For change in area due to CCC contraction,Group 1 (21.62%±1.06%) showed significant CCC contraction compared to the Group 2 (1.00%±0.52%,
=0.005) and Group 3 (6.32%±1.36%,
=0.007). Group 2 showed less CCC contraction than Group 3 (
=0.010; Figure 6E).
Comparing of PCO, there was no eye with PCO Grade 3 or above. There was no difference of PCO incidence between groups (Table 2).
As a result, Group 3 showed the superior anatomical (CCC area, IOL tilt) and refractive stability (ACD, refraction) to Group 1 and showed superior anatomical stability (CCC area,CCC shape, and IOL tilt) to Group 2.
DISCUSSION
Given the rising prevalence of pseudophakia due to increased life expectancy and earlier surgical intervention for cataracts,the incidence of late in-the-bag IOL dislocation may increase over time
. Surgeons need to consider preoperative risk factors and various surgical techniques to prevent this dangerous complication.
大部分國(guó)家和地區(qū)的教師開展教學(xué)活動(dòng)時(shí),比較依賴教材的探究活動(dòng)。……
 International Journal of Ophthalmology
2022年9期
International Journal of Ophthalmology
2022年9期
- International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- What can we learn from negative results in clinical trials for proliferative vitreoretinopathy?
- Suggestions on gut-eye cross-talk: about the chalazion
- A novel mutation of RPGR in a Chinese family with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa
- Novel technique of penetrating keratoplasty in high-risk grafts with significant corneal neovascularization
- COVlD-19 infection with keratitis as the first clinical manifestation
- Corneal histomorphology and electron microscopic observation of R124L mutated corneal dystrophy in a relapsed pedigree
