多孔硅膠鼻假體改善包膜形成的實驗研究
張駿 劉宸 聞可 劉佳 黃金龍



[摘要]目的:探討多孔硅膠鼻假體改善包膜形成的機制,為進一步臨床研究提供依據。方法:將多孔硅膠鼻假體及傳統無孔硅膠鼻假體分別置入兔背皮下,于置入后4周、8周、12周每次處死3只兔子并取出假體。觀察假體周圍組織愈合情況并取出假體切取包膜行Masson染色及I型膠原免疫組化染色,并對包膜中MMP9及TIMP1蛋白表達量行Western Blot檢測。結果:兩組假體均無異常移位、穿出及感染。肉眼可見實驗組多孔硅膠假體組包膜較對照組薄,包膜內可見規律突起組織長入假體空隙內。包膜切片Masson染色和I型膠原免疫組化染色提示多孔硅膠假體包膜的炎癥反應較對照組輕,且纖維組織結構更為纖細、排列更為齊整。Western Blot結果提示多孔硅膠假體包膜較對照組MMP9表達下調,而TIMP1表達上調。結論:多孔硅膠鼻假體較傳統無孔硅膠鼻假體包膜炎性反應輕,增強包膜膠原的降解和重塑,可能降低該假體臨床應用相關并發癥,值得推廣。
[關鍵詞]多孔硅膠鼻假體;假體包膜;包膜攣縮;隆鼻術;I型膠原
[中圖分類號]R622? ? [文獻標志碼]A? ? [文章編號]1008-6455(2022)03-0100-03
Experimental Study on Porous Silicone Nasal Implant Improving Capsule Formation
ZHANG Jun,LIU Chen,WEN Ke,LIU Jia,HUANG Jinlong
(Department of Plastic Surgery,Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine,Nanjing 210000,Jiangsu,China)
Abstract: Objective To evaluate the effect of porous silicone nasal implant on capsule formation and provide basis for further clinical research. Methods Porous silicone nasal implant and traditional non porous silicone nasal implant were transplanted under the skin of rabbit's back respectively. 3 rabbits were executed and impact removed at each time for 4 weeks, 8 weeks, and 12 weeks after transplatation.The healing of tissues around the implant was observed. The implant was removed, and the capsule was cut for Masson staining and type I collagen immunohistochemical staining. The expressions of MMP9 and TIMP1 protein in the capsule were detected by Western blot. Results There were no abnormal displacement, exposition and infection of implant in both groups. The capsule of porous silicon implant group is thinner than that of control implant, and regular protrusions can be seen in the capsule. Masson staining and type I collagen immunohistochemical staining showed that the inflammatory reaction of the capsule around the porous silicon implant was lighter than that of the control implant, and the fibrous tissue structure was more slender and arranged more neatly. Western blot showed that the expression of MMP9 was down-regulated and TIMP1 was up-regulated in porous silicon implant capsule compared with the control group. Conclusion Porous silicone nasal implant has less inflammatory reaction than traditional non porous silicone nasal implant, enhances the degradation and remodeling of capsule collagen, and may reduce the complications related to the clinical application of the implant, which is worthy of popularization.
Key words: porous silicon nasal implant; implant capsule; capsular contracture; rhinoplasty; type I collagen
硅膠假體隆鼻術在美容外科已有近六十余年發展史。安全、穩定、價格合理是硅膠假體傳統優勢。但該術式仍存在多種并發癥,其中部分與假體周圍包膜的形成和攣縮有關,包括變形、顯形、移位、疼痛、周圍組織變薄等[1]。這些問題的產生與假體本身的生物學應力作用和由此帶來的慢性炎性反應相關[2]。改善硅膠鼻假體本身的特性,對于降低臨床使用并發癥具有重要價值。本文通過動物置入實驗研究一種新型多孔硅膠鼻假體的形態學及生物學性能,并著重觀察其與周圍包膜形成的關系,以期為硅膠鼻假體的進一步改進提供思路。
1? 材料和方法
1.1 實驗材料:實驗組多孔硅膠隆鼻假體:Transplus超體,深圳市大族三維科技有限公司。假體表面規律排列空隙,孔徑0.8~1 mm、孔深0.5~2.0 mm、孔間距0.5 mm。對照組普通無孔硅膠隆鼻假體:尺寸同實驗組,由深圳市大族三維科技有限公司提供。實驗動物:清潔級成年雌性新西蘭大耳白兔9只。
1.2 實驗主要試劑:Rabbit-anti-Collagen I(Novus Biologicals NB600-408);mouse-anti-Collagen I(Novus Biologicals NBP600-844);MaxVision試劑盒(兔/鼠)(福州邁新生物科技有限公司KIT-5010);Masson染色試劑盒(南京建成);mouse anti-TIMP-2(NOVUSBIO NBP2-53348);Rabbit-anti-MMP9(NOVUSBIO NBP2-13173);Rabbit-anti-GAPDH (10B8)(江蘇凱基生物)。
1.3 研究方法
1.3.1 兔假體置入模型建立:耳緣靜脈麻醉后,于兔背部旁正中切開皮膚,分離腔隙,于淺筋膜層與肌層之間,左側置入實驗組假體,右側置入對照組假體,逐層縫合皮膚,見圖1。術畢動物常規飼養觀察。術后隔日換藥,術后7 d拆線。分別于置入后4周、8周、12周后每次處死3只兔子,取假體樣本進行相關檢測。
1.3.2 假體周圍組織愈合情況觀察:術后4周、8周、12周觀察切口附近的皮膚愈合情況,是否有假體外露及移位。
1.3.3 假體包膜膠原增生程度評估:術后固定檢測點取出假體,完整切取包膜,觀察形態。取出假體包膜,標記包膜囊內外面,制作石蠟包塊并切片,根據染色試劑盒步驟行Masson染色,同時行I型膠原免疫組化染色,通過Image J軟件計算膠原容積率來綜合評估包膜內膠原厚度及纖維粗細程度。術后4周、12周取出的包膜樣本提取總蛋白,Western Bolt檢測膠原合成及降解相關蛋白MMP9、TIMP1的表達。
1.4 統計學分析:圖片分析通過Image pro6.0軟件分析組織染色差異。定量資料通過SPSS 15.0進行方差分析,P<0.05表示差別有統計學意義。
2? 結果
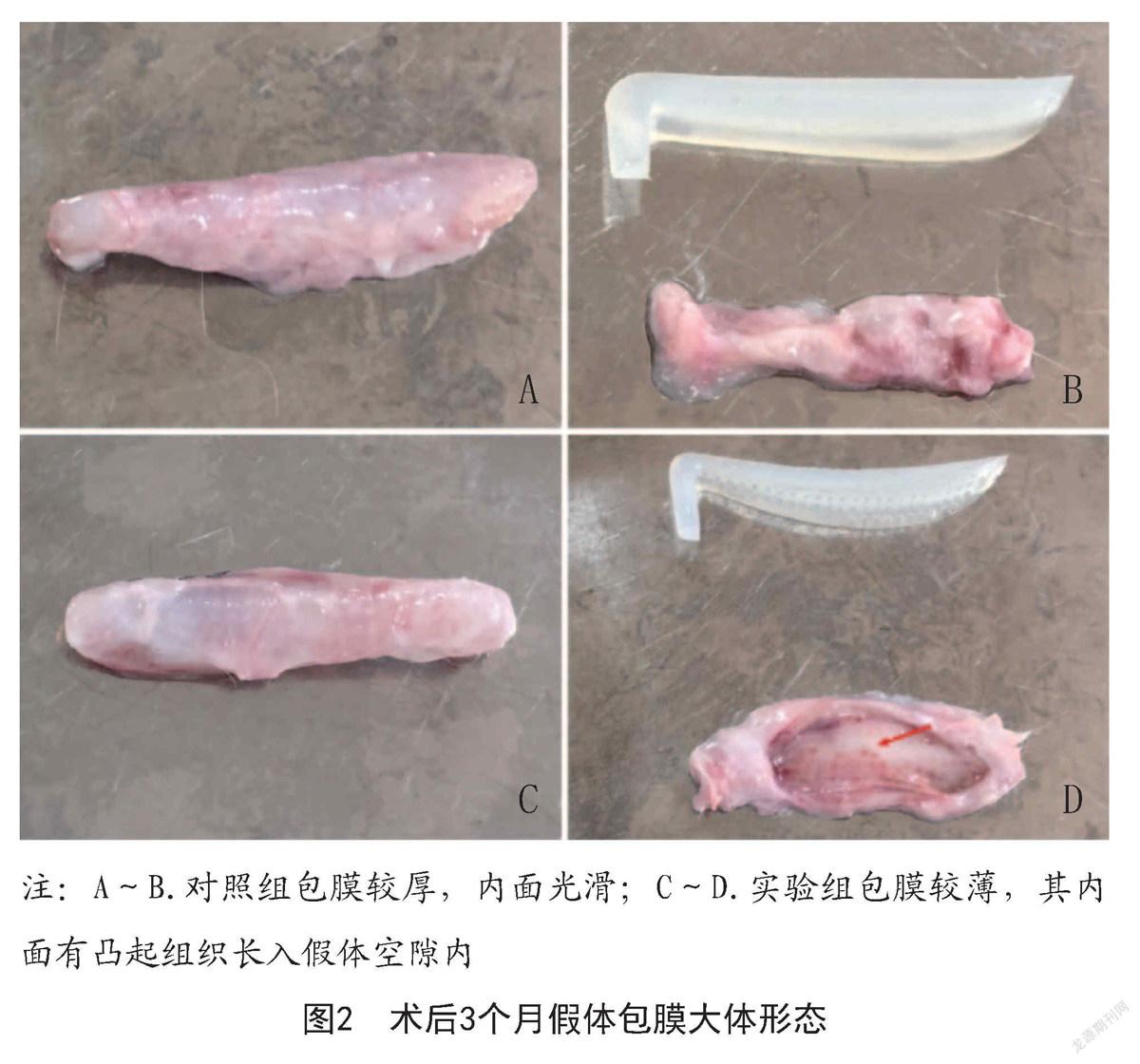
2.1 假體周圍組織愈合情況:術后7 d兩組手術切口愈合良好時拆線。術后4、8、12周觀察假體附近的皮膚無紅腫、破潰,假體無明顯移位、無外露;定期取出假體過程順利,無周圍正常組織副損傷。實驗組包膜與假體貼合緊密,包膜無鈣化,包膜內面可見規律突起組織長入假體孔隙內,假體無扭曲變形,見圖2C~D;對照組假體與包膜貼合較松弛,包膜內面較光滑,見圖2A~B。
2.2 假體包膜膠原增生評估
2.2.1 術后4、8、12周包膜切片Masson染色提示隨著時間延長,假體周圍包膜細胞含量逐漸減少,膠原含量逐漸增多,膠原排列逐漸從紊亂向規則過渡。相較于對照組,實驗組膠原纖維結構更為纖細,膠原沉積厚度更小。通過Image J軟件計算膠原容積率,對照組為0.72±0.0 016,實驗組為0.43±0.0 023,兩組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見圖3。
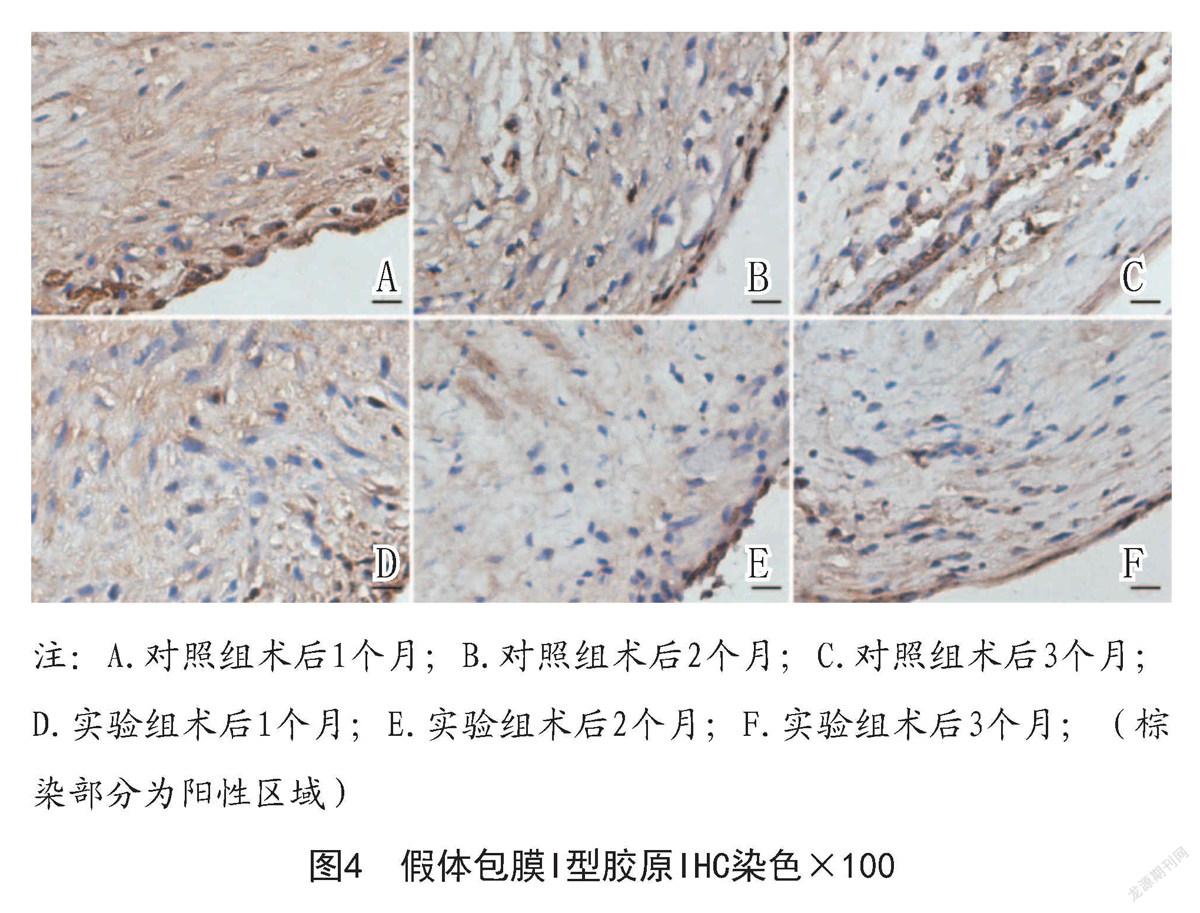
2.2.2 組織切片I型膠原免疫組化染色可見包膜組織內棕褐色陽性區,術后1個月染色區域比較紊亂,隨時間延長,陽性染色區域逐漸匯聚成粗索條狀;術后3個月對照組染色陽性區域明顯強于實驗組,其趨勢與Masson染色結果相似,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見圖4。
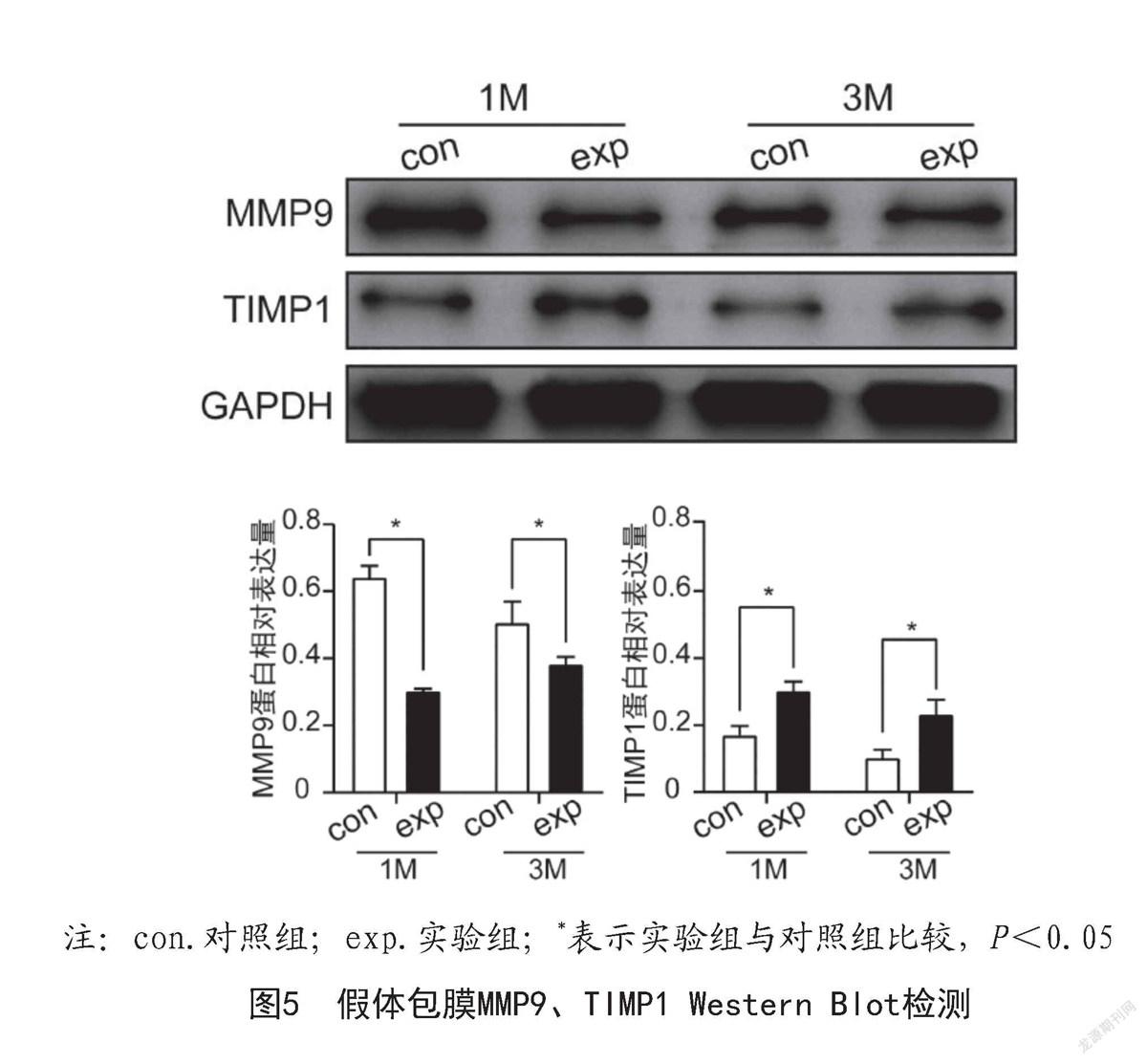
2.2.3 包膜組織總蛋白Western Blot檢測提示:術后1個月及3個月,對照組MMP9表達高于實驗組,TIMP1的表達低于實驗組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),見圖5。
3? 討論
傳統隆鼻術中硅膠鼻假體的表面光滑堅硬,組織無法有效長入固定假體,造成假體在包膜內的滑動和移位,容易帶來炎癥反應,刺激機體形成較厚的包膜[2-3]。而富含膠原纖維的包膜會進一步攣縮,提高假體的顯形、移位、穿出和感染發生的概率,是臨床常見的不良反應[4]。已有研究表明假體包膜的形成與炎癥免疫反應有著較強的相關性[2,5],事實上包膜的形成與機體對于異物的識別和兼容有關。膨體相對于硅膠假體而言包膜的形成要減輕,其中原因與其多孔結構有密切關系,孔隙性結構有助于組織的長入,可以緩解周圍組織為固定假體所承受的生物應力,而應力正是炎癥反應和刺激組織增生及瘢痕纖維化的關鍵[6-7]。將膨體材料的部分優勢復制于硅膠假體可以進一步提高硅膠假體的臨床適用性,進一步降低并發癥。
相較于傳統硅膠鼻假體,Trans plus超體是一種新型硅膠鼻假體,它在原有硅膠性能的基礎上增加了規則排列的孔隙,利于組織長入,減輕移植假體移位和假體包膜攣縮導致的假體變形[8]。可有效減輕包膜形成環境中的組織免疫反應[9]。本實驗從形態學角度證明了多孔硅膠鼻假體上的孔隙可有效固定假體,同時可減輕包膜組織的形成。包膜的組織學切片經Masson染色進一步證實了多孔硅膠鼻假體相較于傳統硅膠假體,可以減輕局部炎性細胞浸潤和粗大膠原纖維的形成,且隨著置入時間的延長可持續發揮作用。假體包膜的形成本質上是瘢痕形成、增生及逐漸軟化的過程。從兩組假體包膜免疫組化結果可以看出隨著移植時間的延長,包膜內成纖維細胞逐漸減少,分泌的膠原也在不斷的改造塑形。移植后3個月對照組包膜內膠原沉積為較為粗大的深染索條狀,而實驗組膠原分布較為稀疏規則。這與包膜大體觀對照組較厚而實驗組較薄相符合。瘢痕增生分泌的膠原主要為I型膠原,其合成增加往往伴有MMP9的表達上調[10-11]。而膠原合成增加的同時往往也伴有膠原分解的增加,其標志是TIMP1表達的上調[12]。Western Blot結果提示對照組MMP9表達高于實驗組,TIMP1表達低于實驗組,實驗組相較于對照組其膠原更多趨向于分解,這與免疫組化及Masson染色結果相一致。以上實驗結果進一步證實了多孔硅膠鼻假體經由調整局部組織的炎性反應強弱,增強膠原重塑期的降解水平,從而減輕包膜纖維的形成,避免遠期的攣縮等不良影響[13-15]。
綜上所述,多孔硅膠鼻假體可以更好促進周圍組織有效長入,緩解局部組織的炎性反應并增強包膜膠原的降解和重塑。預期其在臨床上具有良好的應用前景,值得進一步臨床研究。
[參考文獻]
[1]Kim I S.Augmentation rhinoplasty using silicone implants[J].Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am,2018,26(3):285-293.
[2]Kook W S,Yang C E,Lew D H.Removal of nasal silicone implant and the Impact of subsequent capsulectomy[J].Plast Reconstr Surg,2019,144(4):575e-585e.
[3]Ho O Y M,Ku P K M,Tong M C F.Rhinoplasty outcomes and trends[J].Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg,2019,27(4):280-286.
[4]Na H G,Jang Y J.Use of nasal implants and dorsal modification when treating the east asian nose[J].Otolaryngol Clin North Am,2020,53(2):255-266.
[5]田甜,楊天榮.硅膠假體隆鼻術后包膜攣縮的臨床分級及防治[J].中國美容醫學,2018,27(8):154-157.
[6]杜春曉,張晨,陳偉妍,等.帶有孔隙硅膠鼻假體對兔包膜形態的影響[J].中華醫學美學美容雜志,2020,26(5):389-391.
[7]Kim Y K,Shin S,Kang N H,et al.Contracted nose after silicone implantation: a new classification system and treatment algorithm[J].Arch Plast Surg,2017,44(1):59-64.
[8]田甜.硅膠假體隆鼻術后包膜攣縮的臨床分級及防治[J].中國美容醫學,2018,27(8):154-157.
[9]Safakogullari H,Yalcinozan E T,Tinazli R,et al.Extrusion of alloplastic septal silicone implant: 25 years after rhinoplasty[J].J Craniofac Surg,2019,30(5):e464-e465.
[10]Zhang Q,Guo B,Hui Q,et al.miR-137 Inhibits Proliferation and Metastasis of Hypertrophic Scar Fibroblasts via Targeting Pleiotrophin[J].Cell Physiol Biochem,2018,49(3):985-995.
[11]Lin P T,Xue X D,Zhao Z D,et al.Necrostatin-1,RIP1/RIP3 inhibitor,relieves transforming growth factor beta-induced wound-healing process in formation of hypertrophic scars[J].J Cosmet Dermatol.2021,20(8):2612-2618.
[12]Aoki M,Matsumoto N M,Dohi T,et al.Direct delivery of apatite nanoparticle-encapsulated sirna targeting timp-1 for intractable abnormal scars[J].Mol Ther Nucleic Acids,2020,22:50-61.
[13]Possiedi R D,Khoo L S,Mazzarone F,et al.Expression of NF-κB-p65 and α-SMA in the study of capsules formed by surface textured implants versus foam covered silicone implants in a rat model[J].World J Plast Surg,2021,10(3):34-45.
[14]Govindaraju P,Todd L,Shetye S,et al.CD44-dependent inflammation,fibrogenesis,and collagenolysis regulates extracellular matrix remodeling and tensile strength during cutaneous wound healing[J].Matrix Biol,2019,75-76:314-330.
[15]Hallab N J,Samelko L,Hammond D.Particulate debris released from breast implant surfaces is highly dependent on implant type[J].Aesthet Surg J,2021,41(7): 782-793.
[收稿日期]2021-08-05
本文引用格式:張駿,劉宸,聞可,等.多孔硅膠鼻假體改善包膜形成的實驗研究[J].中國美容醫學,2022,31(3):100-102,159.

