基于GEO數據庫基因表達數據探索影響卵巢癌患者預后及臨床分期的基因
侯娟 蔣樹立 滕長財
【摘要】 目的 利用基因表達綜合征(gene expressed omnibus,GEO)公共數據庫篩選與卵巢癌分期相關的基因,并分析其臨床意義。
方法 從GEO數據庫的數據集GSE9891中篩選與臨床分期相關差異基因,通過DAVID數據庫對差異基因進行基因本體論(gene ontology,GO)和基因組百科全書(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)富集分析。并且通過腫瘤基因組圖譜(the cancer genome atlas,TCGA)對差異基因進行驗證。
結果 分析數據集GSE9891得到23個與臨床分期相關差異基因;GO富集分析發現有效靶基因參與膠原組織和細胞外基質合成;KEGG通路富集分析發現主要通過類固醇合成信號通路影響卵巢癌進展過程。臨床分期相關差異基因在TCGA數據庫中驗證得到LUM、COL11A1、IGF1、TIMP3、COL10A1、FAP、COL8A1、EPYC、SFRP2、FABP4與臨床分期相關(P<0.05,|log2FC|>1.5),其中COL8A1、COL11A1、COL10A1、FABP4和SFRP2等五個基因與卵巢癌的預后相關(P<0.05)。
結論 COL8A1、COL11A1、COL10A1、FABP4和SFRP2可能是影響卵巢癌進展的生物標志物。
【關鍵詞】 卵巢癌;臨床分期;基因本體論;通路富集分析;預后
中圖分類號:R715.5?? 文獻標志碼:A?? DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-1383.2022.03.003
Exploration on genes affecting the prognosis and clinical stage of patients with ovarian cancer based on expression data of GEO database gene
HOU Juan, JIANG Shuli, TENG Changcai▲
(Department of Clinical Laboratory, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256603, Shandong, China)
【Abstract】 Objective To screen genes related to ovarian cancer stage by gene expressed omnibus (GEO) public database, and to analyze their clinical significance.
Methods Differential genes related to clinical stage were screened from the data set (GSE9891) of the GEO database. Enrichment analysis of differential genes were performed by gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) through DAVID database. In addition, the differential genes were verified by the cancer genome atlas (TCGA).
Results By analyzing the data set GSE9891, 23 differential genes related to clinical stage were obtained, GO enrichment analysis found that effective target genes were involved in collagen tissue and extracellular matrix synthesis, and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was found to influence ovarian cancer progression mainly through the steroid synthesis signaling pathway. The differential genes related to clinical stage were verified in TCGA database that LUM, COL11A1, IGF1, TIMP3, COL10A1, FAP, COL8A1, EPYC, SFRP2 and FABP4 were related to clinical stage (P<0.05, |log2FC|>1.5), and five genes including COL8A1, COL11A1, COL10A1, FABP4 and SFRP2 were related to the prognosis of ovarian cancer (P<0.05).
Conclusion COL8A1, COL11A1, COL10A1, FABP4 and SFRP2 genes may be biomarkers affecting the progression of ovarian cancer.
【Key words】 ovarian cancer; clinical stage; gene ontology; pathway enrichment analysis; prognosis
卵巢癌是致死率最高的婦科腫瘤,在2019年的腫瘤統計資料中顯示全球新增卵巢癌患者22 240人,死亡14 170人[1]。卵巢癌患者的5年生存率只有45.6%,但是早期卵巢癌患者的5年生存率有70%,目前卵巢癌尚無令人滿意的早期診斷和治療的方法[2]。卵巢癌由早期向晚期的進展離不開多種基因的協同調控,而對于影響卵巢癌進展的基因的研究目前尚不明確。有研究顯示,CirPUM1、YTHDF1和miR-363-3p均可以通過調節不同基因表達影響卵巢癌的進展[3~4]。本文通過基因表達綜合征(gene expressed omnibus,GEO)公共數據庫中的數據集GSE9891篩選差異基因,對差異基因進行基因本體論(gene ontology,GO)和信號通路富集分析,為研究卵巢癌的進展和治療提供新的治療靶點和理論支持。同時用腫瘤基因組圖譜(the cancer genome atlas,TCGA)數據庫對差異基因進行驗證,發現與卵巢癌患者生存相關的差異基因。
1 材料與方法
1.1 資料來源
使用GEO2R(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/geo2r)分析GEO數據庫中GSE9891數據集中卵巢癌患者的基因表達數據,篩選閾值P<0.05和|log2FC|>1.5,卵巢癌患者相關TCGA數據由cBioPortal(http://www.cbioportal.org/)下載,根據性別、年齡、總生存(overall survival,OS)、腫瘤分級、臨床分期以及差異基因表達量數據篩選得到485例卵巢癌患者的數據。基因功能富集分析利用DAVID(database for annotation,visualization and integrated discovery,https://david.ncifcrf.gov/)在線工具對差異表達基因進行GO功能和基因組百科全書(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)通路富集分析,顯著的GO功能和KEGG通路篩選標準為P<0.05。
1.2 統計學方法
用IBM SPSS Statistics 19.0、Graph Pad Prism 8、Excel 2010對數據進行統計分析。采用K-M法分析相應基因表達量與OS和無進展生存(progression free survival,PFS)間的關系;早期組和晚期組的表達量差異分析采用獨立樣本t檢驗。檢驗水準:α=0.05。
2 結? 果
2.1 分析數據集獲取的差異表達基因
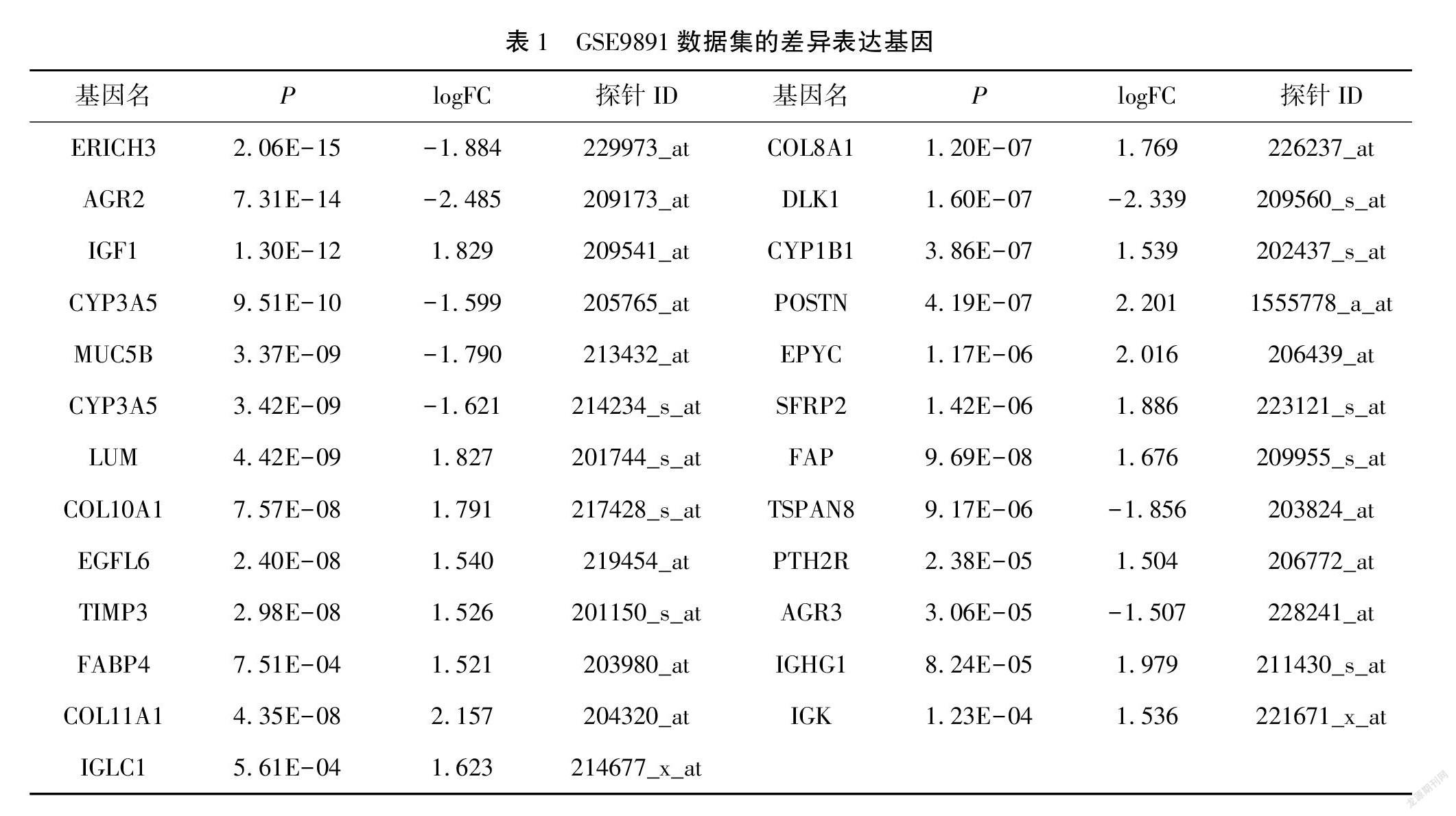
利用NCBI網站的在線分析工具GEO2R,分析數據集GSE9891獲取與卵巢癌患者分期相關的差異表達基因,共得到25個差異表達基因,其中8個基因表達下調和17個基因表達上調,|log2FC|>1.5,P<0.05。見表1。
2.2 差異基因功能富集分析和KEGG通路分析
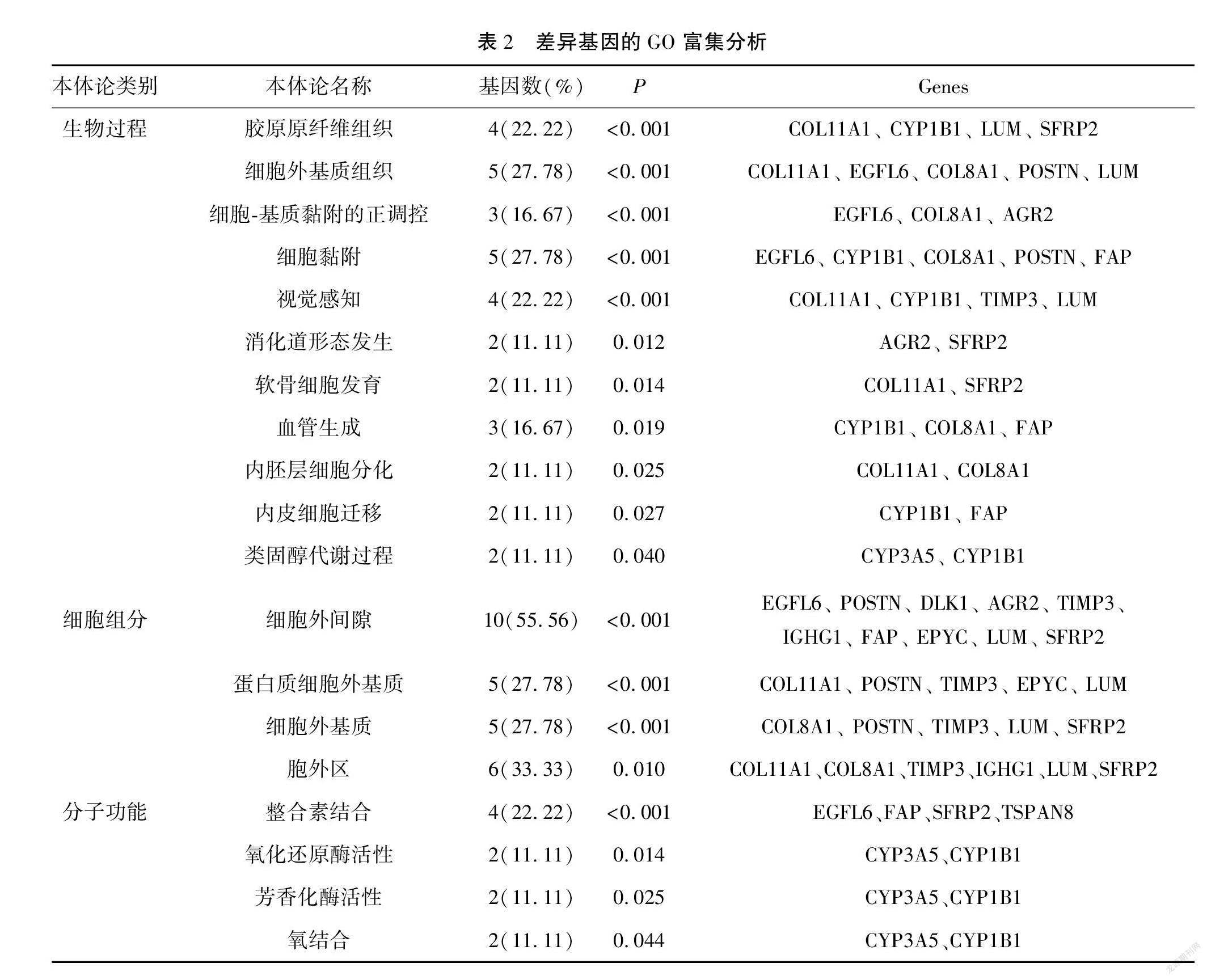
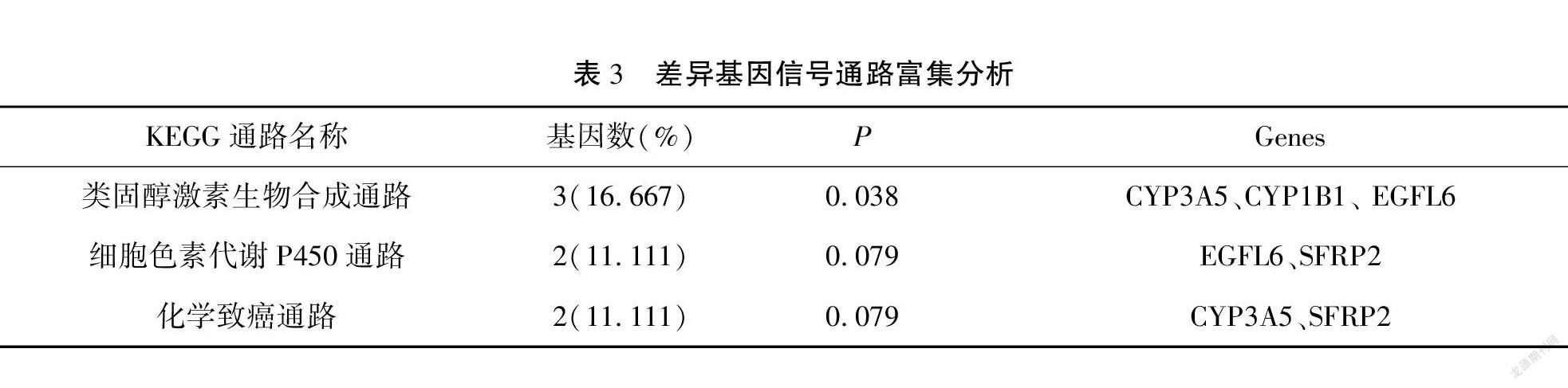
與卵巢癌分期相關的差異基因富集于19個GO terms中。見表2。另外,差異表達基因主要富集在類固醇激素生物合成(steroid hormone biosynthesis)的信號通路中,而卵巢癌患者激素水平的變化可能與卵巢癌進展相關(P<0.05)。見表3。
2.3 TCGA數據庫驗證差異基因及預后分析
TCGA數據庫驗證得到的差異基因,發現10個與卵巢癌分期相關的基因。見表4。筆者對10個差異表達基因進行Cox生存分析,發現COL11A1、COL8A1、SFRP2和FABP4與卵巢癌患者的總生存和無進展生存相關,COL10A1只與卵巢癌患者的總生存相關,而FAP和EPYC只與卵巢癌患者的無進展生存相關(P<0.05)。見表5。
3 討 ?論
卵巢癌是一種以晚期為特征且預后極差的婦科腫瘤。卵巢癌患者具有較多的風險因素,比如哺乳期時間、服用避孕藥以及生產次數等均與卵巢癌相關[5]。研究顯示,卵巢癌的分期直接影響卵巢癌的預后,晚期卵巢癌患者的5年生存率只有45.6%,但是早期卵巢癌患者的5年生存率卻有70%[2],因此對于卵巢癌分期相關的分子機制研究十分重要。筆者利用生物信息學方法和工具,篩選出與卵巢癌分期相關的差異基因,對差異基因進行生存分析得到COL8A1、COL11A1、COL10A1、FABP4和SFRP2與卵巢癌的預后相關。研究顯示,COL8A1是細胞外基質的組成成分,可以促進平滑肌細胞和肝癌細胞的增殖和降低肝癌細胞對化療藥物的敏感性[6~7]。在乳腺癌和胃癌中也有類似報道,高表達COL8A1腫瘤患者預后較差[6,8~10],這與筆者的研究結果相一致,COL8A1是卵巢癌患者總生存和無進展生存的保護因素。COL11A1、COL10A1與COL8A1同屬于膠原蛋白家族,具有相似的生物學功能[4,11~12]。FABP4最初在脂肪細胞和巨噬細胞中表達,調節肥胖誘導的胰島素拮抗[13],在癌細胞與周圍細胞間質進行特異性雙向通訊進而影響腫瘤微環境的代謝[14]。SFRP2是褶皺蛋白家族成員,是典型的負反饋Wnt通路調節蛋白[15],SFRP2可以通過調節Wnt信號通路,抑制非小細胞肺癌的生存和轉移[15~16],同時,作為Wnt通路的拮抗蛋白可以導致β-catenin和MITF的降低,使氧化還原關鍵酶APE1失活,使其對靶向治療更具有抵抗力[17]。筆者對數據集GSE9891的分析發現,差異基因的信號通路富集于激素的生物合成通路,因此推斷激素的合成水平可能與卵巢癌的進展相關。目前,激素應用于乳腺癌和前列腺癌的治療已經有十余年,激素及類固醇類物質對癌癥的進展和治療均具有特殊作用。激素在生理狀態和病理狀態下均可以發揮作用,但其作用機制卻不同,仍需要進一步的機制研究。
綜上所述,本研究分析發現,COL8A1、COL11A1、COL10A1、FABP4和SFRP2這5個基因的表達水平與卵巢癌患者的分期有關,并且參與調節代謝,細胞凋亡和激素合成等多種生物過程。因此,當這些基因發生改變時,影響卵巢癌患者體內的激素水平,導致卵巢癌的發生和進展,進而對卵巢癌患者的生存率產生影響。因此及時注意觀測卵巢癌患者體內激素水平的變化十分重要,為激素治療卵巢癌提供了理論支持。
參 考 文 獻
[1] ?DESANTIS C E, MILLER K D, DALE W, et al. Cancer statistics for adults aged 85 years and older,2019[J].CA Cancer J Clin,2019,69(6):452-467.
[2] ?CHANDRA A, PIUS C, NABEEL M, et al.Ovarian cancer:current status and strategies for improving therapeutic outcomes[J].Cancer Med,2019,8(16):7018-7031.
[3] ?GU S Q, LUO J H, YAO W X. The regulation of miR-139-5p on the biological characteristics of breast cancer cells by targeting COL11A1[J].Math Biosci Eng,2019,17(2):1428-1441.
[4] ?LI C S, SHAO T, BAO G C, et al. Identification of potential core genes in metastatic renal cell carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis[J].Am J Transl Res,2019,11(11):6812-6825.
[5] ?ORONSKY B, RAY C M, SPIRA A I, et al.A brief review of the management of platinum-resistant-platinum-refractory ovarian cancer[J].Med Oncol,2017,34(6):103.
[6] ?ZHOU J, SONG Y N, GAN W, et al. Upregulation of COL8A1 indicates poor prognosis across human cancer types and promotes the proliferation of gastric cancer cells[J].Oncol Lett,2020,20(4):34.
[7] LI X F, WANG Z, TONG H L, et al. Effects of COL8A1 on the proliferation of muscle-derived satellite cells[J].Cell Biol Int,2018,42(9):1132-1140.
[8] ?MA Z H, MA J H, JIA L, et al. Effect of enhanced expression of COL8A1 on lymphatic metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in mice[J].Exp Ther Med,2012,4(4):621-626.
[9] ?ZHAO Y F, JIA L, MAO X Y, et al. siRNA-targeted COL8A1 inhibits proliferation,reduces invasion and enhances sensitivity to D-limonence treatment in hepatocarcinoma cells[J].IUBMB Life,2009,61(1):74-79.
[10] ?PENG W, LI J D, ZENG J J, et al. Clinical value and potential mechanisms of COL8A1 upregulation in breast cancer:a comprehensive analysis[J].Cancer Cell Int,2020,20:392.
[11] ?LI A Q, LI J, LIN J P, et al. COL11A1 is overexpressed in gastric cancer tissues and regulates proliferation,migration and invasion of HGC-27 gastric cancer cells in vitro[J].Oncol Rep,2017,37(1):333-340.
[12] WU Y H, CHANG T H, HUANG Y F, et al. COL11A1 promotes tumor progression and predicts poor clinical outcome in ovarian cancer[J].Oncogene,2014,33(26):3432-3440.
[13] ?MUKHERJEE A, CHIANG C Y, DAIFOTIS H A, et al. Adipocyte-induced FABP4 expression in ovarian cancer cells promotes metastasis and mediates carboplatin resistance[J].Cancer Res,2020,80(8):1748-1761.
[14] ?ZHANG Y Q, ZHAO X T, DENG L L, et al. High expression of FABP4 and FABP6 in patients with colorectal cancer[J].World J Surg Oncol,2019,17(1):171.
[15] ?LIN H, ANGELI M, CHUNG K J, et al. sFRP2 activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cardiac fibroblasts:differential roles in cell growth,energy metabolism,and extracellular matrix remodeling[J].Am J Physiol Cell Physiol,2016,311(5):C710-C719.
[16] ?LIU X Y, FU J M, BI H R, et al. DNA methylation of SFRP1,SFRP2,and WIF1 and prognosis of postoperative colorectal cancer patients[J].BMC Cancer,2019,19(1):1212.
[17] ?KAUR A, WEBSTER M R, MARCHBANK K, et al. sFRP2 in the aged microenvironment drives melanoma metastasis and therapy resistance[J].Nature,2016,532(7598):250-254.
(收稿日期:2021-07-04 修回日期:2022-02-09)
(編輯:潘明志)

