Vitamin D supplementation for autoimmune hepatitis: A need for further investigation
Consolato M Sergi
Consolato M Sergi, Anatomic Pathology Division, Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario (CHEO), University of Ottawa, Ottawa K1H 8L1, ON, Canada
Consolato M Sergi, Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, University of Alberta, Edmonton T6G 2B7, AB, Canada
Abstract Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease harboring an autoimmune basis and progressive character.Despite still obscurity in etiology and pathogenesis, some evidence supports the importance of sustaining the immune system.Vitamin D is a lipo-soluble vitamin, which has been identified as decreased in our body.It is often due to the daily habit change and decrease of individual sun exposure due to the increase of the ultraviolet-induced potential melanocytic transformation.Here, we emphasize the importance of vitamin D supplementation in patients affected with liver disease.
Key Words: Vitamin D; Autoimmune hepatitis; Supplementation; Immunostimulants; Liver
TO THE EDITOR
We read with interest the article of Fanet al[1] on the pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) in one of the most recent issues of the journalWorld Journal of Hepatology[1].The authors summarize the evidence on this complex disease with evidence of the last five years.Although several autoimmune conditions may involve the liver, the three most common autoimmune hepatopathies are AIH, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and primary biliary cholangitis.These diseases may occurseriatimor as part of “overlap” syndromes.AIH is a chronic progressive liver disease whose, unfortunately, etiopathogenesis is still obscure.AIH has conventional features of autoimmune disorders, including antibodies generated by an organism in response to an element of its own tissues (autoantibodies), association with a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans (human leukocyte antigen genes or haplotypes) which encode proteins located on the cell surface and responsible for the regulation of the immune system, and a T-cell mediated necroinflammatory process.Histologically, a prominent inflammatory infiltrate consisting of both lymphocytes and plasma cells is seen.These inflammatory cells form clusters with accentuation at the edges of the portal tracts with striking periportal interface inflammatory activity at places (Figure 1).Genetic susceptibility, immunologic dysregulations, and environmental factors may play a role.In particular, viral infection and drugs may trigger a set of dysfunctions of the immune system.Currently, almost all patients require steroid hormones plus immunosuppressive maintenance therapy independently of age or genetic predisposition.However, long-term medication adverse effects, complications, and relapse after drug withdrawal are pretty variable.It has been suggested that we may need to do more in improving the satisfaction of our patients[2].
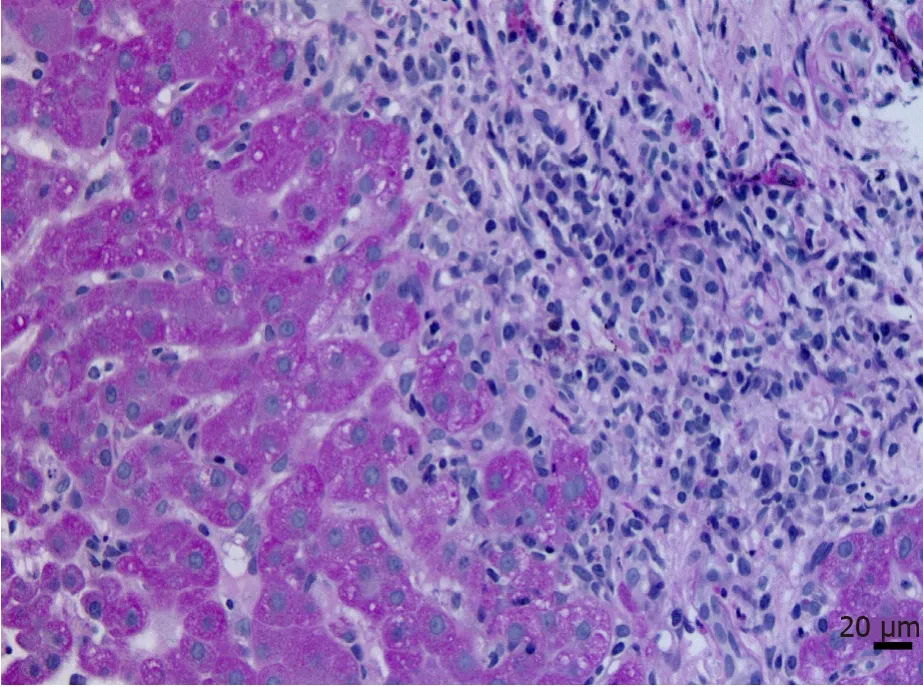
Figure 1 Autoimmune hepatitis.
Vitamin D can be successful in numerous diseases[3-5], and it is crucial to emphasize the role of vitamin D in AIH.After the turn of the last century, the interest in vitamin D increased enormously.Rickets has accompanied human civilization for centuries in both old and new continents.Still, despite supplementation of this vitamin in our diet, hypovitaminosis and child neglect cases have been diagnosed[6].Population surveys have indicated that important sectors of childhood and pregnant women will be affected by vitamin D inadequacy in their life.The change of the habits with indoor living, inadequate sunlight exposure, vitamin-deficient diets, and high rates of nutrition allergy are likely playing a significant role in growing the inadequacy of vitamin supplementation for some people worldwide.
Vitamin D is fat-soluble.It plays a leading role in calcium homeostasis[7,8].Vitamin D is tightly linked to immunity.It plays a remarkable role in inflammatory and cancer pathways[5,9,10].The immune system's cellular components possess vitamin D receptors (VDRs).These receptors can metabolize the active form of vitamin D or calcitriol, which is also labelled 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D, and abbreviated as 1,25(OH)2D.The storage form of vitamin D is 25-hydroxyvitamin D or 25(OH)D.It can be transformed by activated T and B lymphocytes to 1,25(OH)2Din vitro.In addition, 1,25(OH)2D acts on immunological cells in an obvious autocrine or paracrine fashion.This aspect has been considered crucial for several infections, as suggested in COVID-19 (coronavirus disease-2019), the infection caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), despite controversial data[11-13].
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells harbor VDR, supporting vitamin D's notable role in regulating the immune system.Other than activity on the cells of the immune system, vitamin D increases the absorption of calcium from the small intestine and participates in cilia movements[14].Nicolaysenet al[15] and Haavaldsenet al[16,17] also observed that animals, which were kept for determined set of the experiments on a low calcium diet, exhibited much greater calcium absorption competence than experimental animals kept on a diet with an adequate amount of calcium.Calmodulin, an intermediate calcium-binding messenger protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells, is localized in the hamster's ciliated cells.Indeed, calcium is prominent for cilia's bioenergetic activity and the bile canaliculus[18-21].
Vitamin D is crucial in maintaining innate immunity[22-29].Various studies have demonstrated that it also behaves as an essential regulator of immnunologic system and host defense.It includes exquisitely respiratory host defense.Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) decreases the host defense of epithelial cells by altering the vitamin D-reconciled expression of host defense peptides and proteins[30].When primary CD4+ T cells from healthy donors were obtained and cultured in specific and well detailed Th17-polarizing requirements, vitamin D lowered the expression of Th17 markers.Subsequently, there was also a decrease in the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines.It involved interleukin 17A (IL-17A) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) predominantly.It induced an expansion of the CD4+ T cell subset expressing the highest levels of CD25 cells.It also upregulated their expression of CTLA-4 (cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4) and Foxp3 (forkhead box P3) regulatory markers.It seems that vitamin D supplements regulate the microbiome by increasing the abundance of beneficial bacterial strains.
Moreover, vitamin D improves glucocorticoids[31,32], increases the production of glutathione[33], and inhibits hepatic stellate cells[34].Vitamin D may influence the histological severity of AIH and advanced liver fibrosis, and the need for liver transplantation.A recent systematic review summarized the importance of vitamin D supplementation for AIH[31].A substantial scientific background supports the use of vitamin D in AIH, showing that circulating concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D are less than 30 ng/mL or 75 nmol/L (1 nmol/L = 0.4 ng/mL 25-hydroxyvitamin D, and 1 ng/mL = 2.5 nmol/L 25-hydroxyvitamin D) in more than four fifths (81%) of Turkish patients with AIH, matched to about two fifths (44%) of healthy individuals[35].These patients have clearly demonstrated a higher frequency rate of non-response to steroids (glucocorticoid therapy) than patients exhibiting no identifiable vitamin D deficiency (P= 0.04).In AIH, severe interface inflammatory activity of the liver or interface hepatitis, higher stages of hepatic fibrosis, and therapy failure have been linked with 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels in serum of less than 10 ng/mL.Several international hepatologists have suggested that vitamin D deficiency should be proposed as a prognostic biomarker in AIH[35].
Most people are satisfactorily protected against vitamin D deficiency, but others may show a level of susceptibility.In addition, some individuals may develop such deficiency, which may target several critical functions of the body.Therefore, the National Institutes for Health recommends supplementation of vitamin D for some categories.They include breastfed infants, individuals living in cold climatic conditions, or subjects working night shifts, adults harboring a body mass index of 30 or over, and individuals who underwent gastric bypass surgery, suffer from inflammatory bowel disease, or cover continuously their skin for religious reasons.Infants should receive 400 international units (IU) of vitamin Dperday until weaning.It equals 10 micrograms (mcg or μg) considering that the mass that gives 1 IU is dependent on the rate or potency of the compound and varies obviously from compound to compound depending on what is being measured.In the case of vitamin D, 1 IU is the biological equivalent of 0.025 mcg ergocalciferol or cholecalciferol.After infancy and up to the 70thyear of age, the dosage of vitamin D supplementation should be 600 IU (15 mcg).Individuals older than 70 years should receive 800 IU (20 mcg) of vitamin D.Skin exposure for 5-30 min at least twiceperweek may be sufficient for most individuals.However, underlying conditions may still require an increase in vitamin D supplementation.
In conclusion, vitamin D is not a new miraculous drug but a compound discovered more than half a century ago.It has immunoregulatory, anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and anti-fibrotic effects, affecting remarkably the occurrence and outcome of immune-mediated diseases.Vitamin D may influence the histological severity of AIH, liver fibrosis, and the need for liver transplantation.Thus, the supplementation of this vitamin in these patients is potentially critical in reducing the interface hepatitis.There are still several unexplored fields for vitamin D, and the study of how genetic variants ofVDRgenes can affect the susceptibility of individuals to chronic autoimmune liver diseases should be at the forefront of the developments in hepatology.Still, independently from theVDRhaplotype, it seems that patients affected with AIH will benefit from vitamin D supplementation, and an advocacy for its use may be critical in internal medicine.
 World Journal of Hepatology2022年1期
World Journal of Hepatology2022年1期
- World Journal of Hepatology的其它文章
- Current highlights on solid pseudopapillary neoplasm of the pancreas
- Is there a role of lipid-lowering therapies in the management of fatty liver disease?
- Acute liver failure secondary to acute antibody mediated rejection after compatible liver transplant: A case report
- COVID-19 emergency: Changes in quality of life perception in patients with chronic liver disease-An Italian single-centre study
- Correlation of hepatitis B surface antigen expression with clinicopathological and biochemical parameters in liver biopsies: A comprehensive study
- Can the computed tomography texture analysis of colorectal liver metastases predict the response to first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy?
