Insight into influence of thermodynamic coefficients on transient negative capacitance in Zr-doped HfO2 ferroelectric capacitors?
Yuan-Yuan Zhang(張?jiān)? Xiao-Qing Sun(孫曉清) Jun-Shuai Chai(柴俊帥)Hao Xu(徐昊) Xue-Li Ma(馬雪麗) Jin-Juan Xiang(項(xiàng)金娟)Kai Han(韓鍇) Xiao-Lei Wang(王曉磊) and Wen-Wu Wang(王文武)
1Key Laboratory of Microelectronics&Integrated Technology,Institute of Microelectronics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100029,China
2College of Microelectronics,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
3Department of Physics and Electronic Science,Weifang University,Weifang 261061,China
Keywords: transient negative capacitance(NC),ferroelectric,hafnium-zirconium oxide
1. Introduction
The power consumption of microprocessors has significantly increased with the improvement of computing power,due to the ongoing pursuit of Moore’s law.[1–4]Reducing the power consumption of devices is thus a key challenge in contemporary information industry.[5–8]However, a fundamental thermodynamic limit of 60 mV·dec?1at room temperature,which is known as Boltzmann limit, impedes the reducing of power consumption for conventional device.[9,10]In order to overcome this limit,the steep subthreshold swing devices are required.
Negative capacitance field effect transistor[11–22](NCFET) is a promising steep subthreshold swing device, which is expected to work at extremely low supply voltages.[23,24]It becomes thus a potential candidate for the next generation of low power transistors. So far,there are two types of NC (steady-state NC[25,26]and transient NC[27–33])that have been extensively reported. The steady-state NC has been indirectly demonstrated by total capacitance enhancement in ferroelectric-dielectric (FE-DE) superlattices and heterostructures.[34–37]It can be understood from the viewpoint of energy: the negative curvature region of ferroelectric Gibbs free energy landscape is stabilized by the superposition of ferroelectric and dielectric energy landscapes. However,the existence of the steady-state NC has a great controversy in recent years.[38–40]For the transient NC,it has been experimentally observed in the series circuit of resistor and ferroelectric capacitors(R-FEC)[27–31]and theoretically understood by the Landau–Ginzburg–Devonshire(L-G-D)theory.[41–44]The transient NC is caused by the mismatch between the ferroelectric polarization switching rate and the circuit current.[45–47]This means that transient NC cannot exist stably,and can only appear in the process of ferroelectric polarization switching.The previous studies have reported that the transient NC is affect by external resistors and viscosity coefficients.[45,48]However,the related studies on the influences of more intrinsic ferroelectric material parameters and extrinsic factors in theR-FEC circuit for transient NC are lacked and need to be clarified.
In this work,using the theoretical simulation based on the Landau–Khalatnikov(L-K)theory and experimental measurement of electrical properties,we systematically investigate the influence of thermodynamic coefficients on transient NC for the Zr-doped HfO2(HZO) ferroelectric capacitors in theRFEC circuit. Our results show that transient NC is not only related to series resistor and viscosity coefficient,but also thermodynamic coefficientsα,β, andγ. Moreover, we find that the smaller theαandβ,the more conducive to the appearance of the transient NC.In addition,we also find that the generally accepted viewpoint of Gibbs free energy minimization is not applicable to explain the transient NC effect of ferroelectric capacitors.
2. Experimental details and theoretical model
2.1. Experimental details
The metal–ferroelectric–metal (MFM) capacitors were fabricated with the top and bottom electrodes, as shown in Fig.1. Si substrate was cleaned by standard wet clean. Then,the bottom electrode (TiN), the 10-nm-thick Zr-doped HfO2(HZO)thin film and top electrode(TiN and W)were deposited by atomic layer deposition[49,50](ALD)in turn. The HZO thin films were crystallized in N2ambient and rapid thermal anneal (RTA) system of 550–650?C. The composition of the HZO thin film was changed by controlling the deposition ratio of HfO2and ZrO2to realize the adjustment of ferroelectric intrinsic parameters(thermodynamic coefficientsα,βandγ,etc)and form the ferroelectric capacitors with different Hf:Zr ratios. The range of ZrO2content is from 10% to 90%, as listed in Table 1.
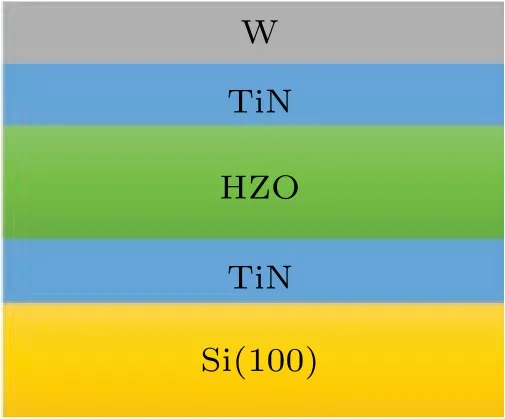
Fig.1. The schematic of TiN/HZO/TiN ferroelectric capacitor.

Table 1. HZO thin films with different ZrO2 contents.
2.2. Theoretical model
In order to investigate the transient NC effect of the ferroelectric HZO capacitors, we adopt the numerical simulation method. For the ferroelectric material, we use the L-K model,[51]which means that polarization switching obeys the energy minimization. In this model,the relationship ofP–VFEcan be expressed as

whereα,βandγrepresent the thermodynamic expansion coefficients.ρrepresents the viscosity coefficient and reflects the delay of polarizationP.EFErepresents the electric field across the ferroelectric material, anddFErepresents the ferroelectric material thickness.The L-K model describes the dynamic process of polarization with the time.
InR-FEC circuit(see Fig.2),the Kirchhoff’s rules can be written as

whereRrepresents the external resistance,Arepresents the ferroelectric material area, andVSrepresents the source voltage. The expression of electric displacement fieldDis

Kirchhoff’s rule describes the dynamic process of free charge with time. Combing with Eqs.(1)–(3),we can obtain the dynamic response of transient NC.
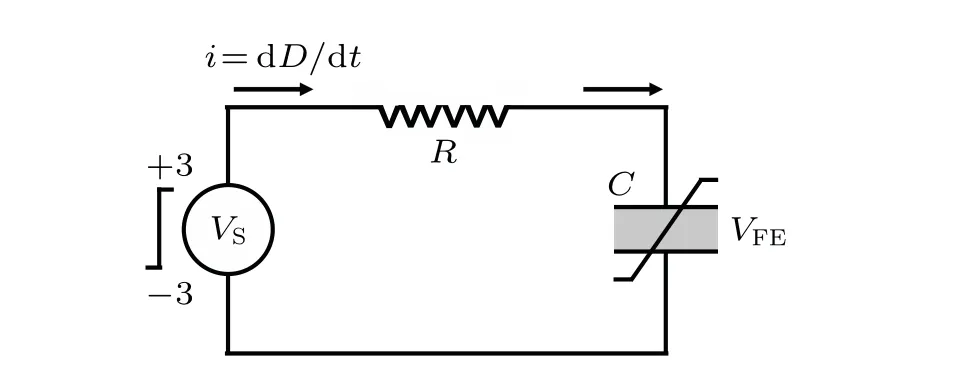
Fig.2. The schematic of an R-FEC circuit. C denotes the ferroelectric capacitor and R represents the external resistor. VFE and VS represent the voltage across the FE and the applied voltage,respectively.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Influence of thermodynamic coefficients on transient NC based on the theoretical derivation
We first investigate the affect factors of transient NC by rigorous theoretical derivation. Taking a derivation of Eq.(3)to timetyields

whereP0andE0are the polarization and electric field across the ferroelectric at a given timet0, respectively. Equation(5)indicates that the transient NC depends on not onlyVSandR,but alsoα,β,γandρ. The parametersVSandRare related to the extrinsic characteristics of theR-FEC circuit,while parametersα,β,γandρa(bǔ)re the intrinsic parameters of ferroelectric material and determined by the material itself. This means that transient NC depends not only on extrinsic factors in theR-FEC circuit, but also on the ferroelectric material itself. Therefore,it is possible to realize that the change of polarization with time is greater than that of free charge change with time by adjusting the intrinsic parametersα,β, andγ,resulting in the appearance of transient NC.
3.2. Influence of thermodynamic coefficients on transient NC based on experimental measurement
3.2.1. Ferroelectricity
We next characterize electrical properties of the fabricated TiN/HZO/TiN capacitors to discuss the influence of different ratios of hafnium and zirconium on ferroelectricity. The measuredP–Ecurves of the TiN/HZO/TiN capacitors with the ZrO2content of 0.1–0.9 are plotted in Fig.3. At the low ZrO2content of 0.1 in Fig.3(a),theP–Ecurve almost presents the linear distribution, meaning that the sample has the dielectric property. When the ZrO2content is changed from 0.25 to 0.5 in Figs. 3(b)–3(d), theP–Ecurves present a hysteresis loop,and the hysteresis gradually becomes larger. This mean that these samples have the ferroelectricity,and ferroelectricity enhances with the increase of the ZrO2content.At the high ZrO2content of 0.6–0.9 in Figs.3(e)–3(g), theP–Ecurves present a double hysteresis loop, which means that the samples have the antiferroelectricity. These results indicate that the sample shows the phase transition from dielectric to ferroelectric to antiferroelectric as the ZrO2content increases from 0.1 to 0.9.This can be attributed to the structural phase transition of HZO from monoclinic to orthorhombic to tetragonal phase.[52,53]In addition, in Figs. 3(d) and 3(e), the hysteresis curves are not closed, which is caused by leakage current, charge injection,back injection,and defects of the material itself.
Figure 4 shows the remnant polarization of the HZO thin films as a function of ZrO2content. It can be seen that the remnant polarization increases first and then decreases as the ZrO2content increases from 0.1 to 0.9, and the sample with the same Hf and Zr contents (sample Hf0.5Zr0.5O2) has the largest remnant polarization of 18μC/cm2,which corresponds to the strongest ferroelectricity in Fig.3(d).

Fig.3. The P–E curves of TiN/HZO/TiN capacitors with different ZrO2 contents.

Fig. 4. The remnant polarization of HZO capacitors as a function of ZrO2 content.
3.2.2. Thermodynamic coefficients
We choose the samples of Hf0.5Zr0.5O2,Hf0.6Zr0.4O2and Hf0.75Zr0.25O2with ferroelectricity to investigate the influence of intrinsic ferroelectric parameters on transient NC.Based on the L-G-D theory,the“S”-shapedP–Ecurves of these samples are simulated to the corresponding measuredP–Ehysteresis loops, as shown in Fig. 5. It can be seen that the simulated S-shapedP–Ecurve of sample Hf0.5Zr0.5O2is similar to that of Hf0.6Zr0.4O2, while they are obviously different from the S-shapedP–Ecurve of sample Hf0.75Zr0.25O2. This indicate that the negative slope of the S-shapedP–Ecurve for the HZO ferroelectric material is related to ZrO2contents.
The thermodynamic coefficientsα,β, andγare further extracted from the simulated S-shapedP–Ecurves, listed in Table 2. It shows that the coefficientsαandβfor samples Hf0.5Zr0.5O2and Hf0.6Zr0.4O2are similar, which are clearly smaller than that of Hf0.75Zr0.25O2, especially forα. This causes the difference of the S-shapedP–Ecurves for these samples in Fig.5. The thermodynamic coefficientsγfor these three samples are assumed as zero. These results indicate that the thermodynamic coefficientsαandβare related to the ferroelectric material itself.
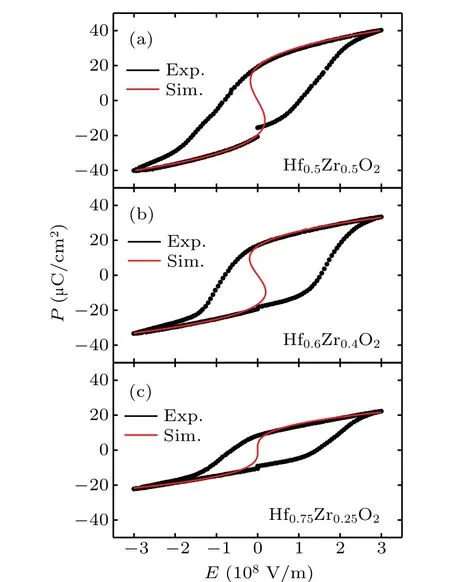
Fig.5. The measured P–E hysteresis curves(black lines)and the simulated S-shape P–E curves(red lines).

Table 2. The thermodynamic coefficients of HZO capacitors.
3.2.3. Transient NC
We finally simulate the transient responses ofR-FEC circuit for different ferroelectric HZO capacitors. The input step voltage pulseVSis?3 V→+3 V→?3 V, and the external resistance and the viscosity coefficient are set to 50 k? and 500 m·sec/F, respectively. Figure 6 shows the voltageVFEacross ferroelectric capacitors as a function of time. It can be seen from Figs. 6(a) and 6(b) that for samples Hf0.5Zr0.5O2and Hf0.6Zr0.4O2, when the voltage pulse changes from?3 V→+3 V,as the evolution of time,theVFEincreases first,then decreases,then increases again,and finally reaches a stable state. When the voltage pulse changes from+3 V→?3 V,theVFEdecreases first,then increases,then decreases again, and finally reaches a stable state. This process is opposite to the case of input voltage pulse of?3 V→+3 V.We also plot the free charge on metal plates as a function of time in Fig. 6. It shows that with the evolution of time, the free charge increases first and then reaches a stable state under the voltage pulse of?3 V→+3 V, which is opposite to the change of free charge under+3 V→?3 V.The above results mean that,there are two regions,where with the increase(decrease) of free charge, the voltage across the ferroelectric capacitor decreases (increases), that is, dQ/dVFE<0. This indicates that transient NC occurs in these two regions.

Fig.6. The input step voltage(black lines),voltage across ferroelectric capacitors (red lines) and free charge on metal plates (blue lines) as a function of time.

Fig.7. The Gibbs free energy profiles as a function of polarization P.
For sample Hf0.75Zr0.25O2in Fig.6(c), both theVFEand free charge increase (decrease) with the time under voltage pulse, indicating that there is no transient NC phenomenon.This is because the ferroelectricity of sample Hf0.75Zr0.25O2is significantly weak,and its thermodynamic coefficientsαandβare obviously larger than those of samples Hf0.5Zr0.5O2and Hf0.6Zr0.4O2, especially forα(sample Hf0.75Zr0.25O2is one order of magnitude larger than other two samples).
In addition, we simulate the distributions of Gibbs free energyGof samples Hf0.5Zr0.5O2and Hf0.6Zr0.4O2,as shown in Fig.7. It can be seen that the distribution ofGpresents the“M” shape. As the polarization increases,Gfirst increases,then decreases,then increases,and finally decreases. This indicates that the thermodynamic process of transient NC does not follow the generally accepted viewpoint of the minimization ofG.
4. Conclusion
The influence of thermodynamic coefficients on transient NC for Zr-doped HfO2thin film is systemically investigated.Our results show that the HZO thin film undergoes the ferroelectric phase transition from dielectric to ferroelectric to antiferroelectric under the induction of different ZrO2contents.Moreover, we find that transient NC effect depends not only on series resistor and viscosity coefficients, but also on thermodynamic coefficientsα,βandγ. The smaller coefficientsαandβ,the more significant the transient NC effect. In addition, we also find the the well known Gibbs free energy minimization is not applicable to understand the thermodynamic process of the transient NC.This work provides a comprehensive understanding of the affect factors on transient NC in the ferroelectric capacitors.
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Modeling the dynamics of firms’technological impact?
- Sensitivity to external optical feedback of circular-side hexagonal resonator microcavity laser?
- Controlling chaos and supressing chimeras in a fractional-order discrete phase-locked loop using impulse control?
- Proton loss of inner radiation belt during geomagnetic storm of 2018 based on CSES satellite observation?
- Embedding any desired number of coexisting attractors in memristive system?
- Thermal and mechanical properties and micro-mechanism of SiO2/epoxy nanodielectrics?