Entanglement of two distinguishable atoms in a rectangular waveguide:Linear approximation with single excitation?
Jing Li(李靜),Lijuan Hu(胡麗娟),Jing Lu(盧競),and Lan Zhou(周蘭),,?
1Affiliation Synergetic Innovation Center for Quantum Effects and Applications,Key Laboratory for Matter Microstructure and Function of Hunan Province,Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Structures and Quantum Control of the Ministry of Education,School of Physics and Electronics,Hunan Normal University,Changsha 410081,China
2College of Science,Hunan University of Science and Engineering,Yongzhou 425199,China
Keywords:entanglement,concurrence,two two-level systems,energy separations
1.Introduction
The principle of quantum superposition allows a system to be composed of multiple quantum systems that cannot be decomposed into the product of individual quantum states.This nonseparability,labeled as entanglement,is an important physical resource for applications of quantum information processing.Quantum network is essentially based on a scalable quantum information processing.[1]A quantum network consists of quantum channels and nodes.Two-level systems(TLSs)fixed at quantum nodes are called stationary qubits which generate,store,and process quantum information.It is essentially important to generate or keep the correlation among TLSs located at different positions for protecting quantum information.The bipartite entanglement involving two TLSs is of special interest.Spatially separated TLSs’talking to each other can be either mediated or destroyed via electromagnetic fields.[2–6]Complete disentanglement is achieved in finite time for two TLSs coupled individually to two vacuum cavities.[7,8]The entanglement exhibits revivals in time for two TLSs coupled collectively to a multimode vacuum field in free space.[9,10]
To build large scale quantum networks,an electromagnetic field in a one-dimensional(1D)waveguide is of special interest.The electromagnetic field is confined spatially in two dimensions and propagates along the remaining one,so it consists of infinite modes for right and left-going photons of continuous varying frequencies.Spontaneously emitted waves from the TLS will interfere with the incident wave.[11–26]The coupling of the electromagnetic field to a TLS can be increased by reducing the transverse size.A waveguide with a cross section has many guiding modes,e.g.,transverse-magnetic(TM)modes or transverse-electric(TE)ones.However,most work only consider TLSs interacting with one guiding mode of the waveguide,[14–33]which means that the transverse-size effect has been ignored.In this paper,we study the time evolution of entanglement measure for two uncoupled TLSs interacting with the electromagnetic field confined in a 1D rectangular hollow metallic waveguide.The TLSs share initially an excitation and the field is in vacuum.Such waveguide has many guiding modes.There is a continuous range of frequencies and a minimum frequency(called cutoff frequency)allowed in each guiding mode.[34]When the transitions of the TLSs are far away from the cutoff frequencies of guiding modes,the probability amplitudes of the TLSs is described by the delay differential equations by tracing out the continuum of bosonic modes in the waveguide.The influence on the time evolution of the concurrence of the TLSs are examined by inspecting the following identities:the difference of TLSs’energy separations characterized byδ,the inter-TLS distance d,and the number of the guiding modes.
This paper is organized as follows.In Section 2,we introduce the model and establish the notation.In Section 3,we derive the relevant equations describing the dynamics of the system for the case of the TLSs being initially sharing an excitation and the waveguide mode in the vacuum state.In Section 4,we analyze the behavior of the TLSs’concurrence when the TLSs interact resonantly with the electromagnetic field of one or two guiding modes.We make a conclusion in Section 5.
2.Two TLSs in a rectangular waveguide
The Hamiltonian of the TLSs interacting with the electromagnetic field of a rectangular waveguide consist of three parts
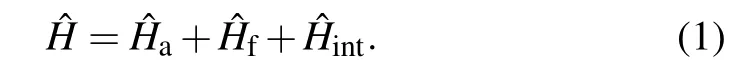
The fist part is the free Hamiltonian of the TLSs
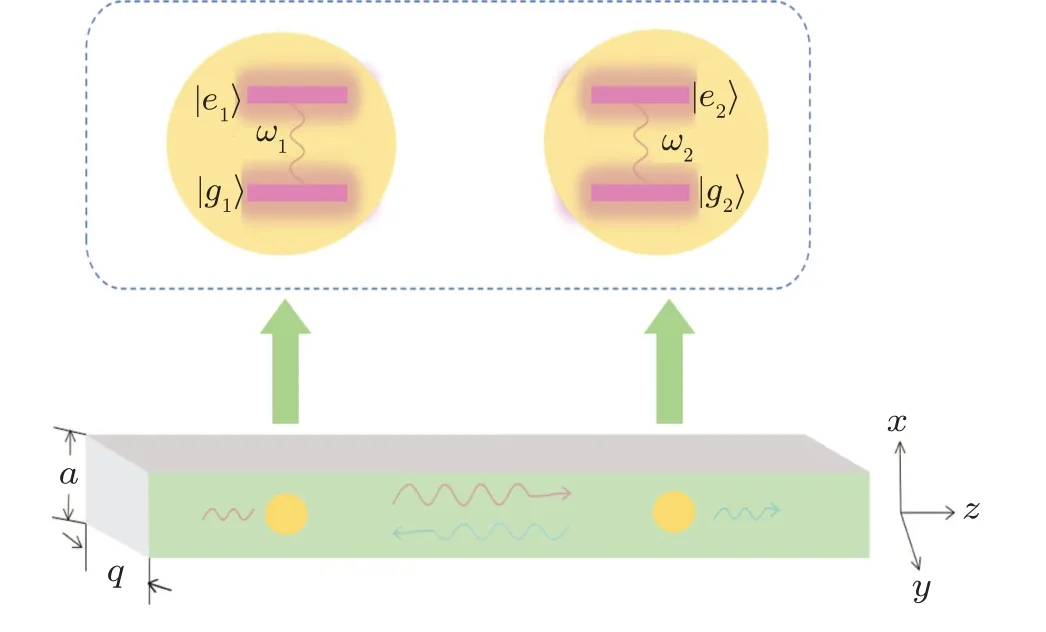
Fig.1.Schematic illustration for an infinite waveguide of rectangular cross section A=aq(a)coupling to two TLSs,(b)located at r1=(a/2,q/2,z)and r2=(a/2,q/2,z+d).
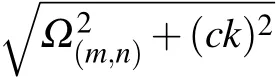
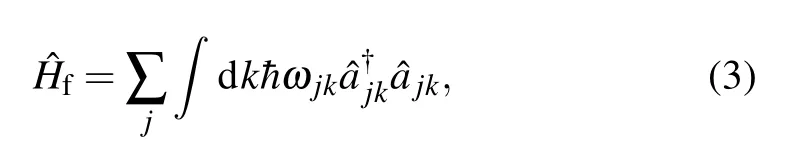

in the electric dipole and rotating wave approximations,where

andμlis the magnitude of the dipole of the l-th TLS.We assume thatμlis real.If the dipolesμl=μ,the parameter gjlis independent of the subscript l and it becomes

whereε0is the permittivity of free space,and j=(1,1),(3,1),(5,1),...in the ascending order.
3.Time evolution of the TLSs
In the case of a single excitation present in the system,the state vector of the system can be written as

where|0〉is the vacuum state of the quantum field,bl(t),l=1,2 is the probability amplitude for TLS l being excited,bjk(t)is the probability amplitude for the excitation in a mode k of the TMjguiding mode.The initial state of the system is denoted by the amplitudes bjk(0)=0,b1(0),b2(0).The Schr¨odinger equation results in the following coupled equation of the amplitudes:

We introduce three new variables to remove the highfrequency effect
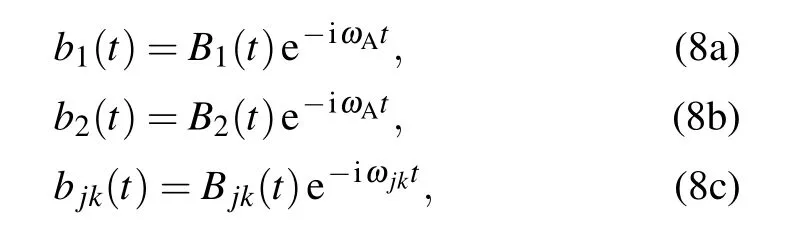

and define the mean frequency of the TLSs as well as the difference of the TLSs’frequencies Then,we formally integrate equation of Bjk(t),which is later inserted into the equations for B1(t),and B2(t).The probability amplitudes for one TLS being excited are determined by two coupled integro-differential equations.Assuming that the frequencyωAis far away from the cutoff frequenciesΩj,we can expandωjkaroundωAup to the linear term
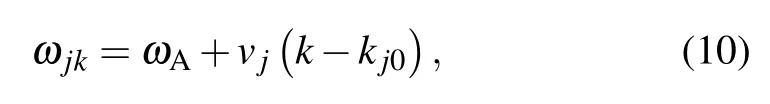
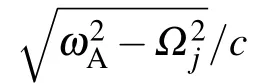
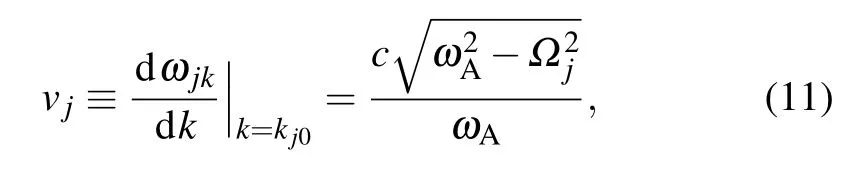
is different for different TMjguiding modes.Integrating over all wave vectors k gives rise to a linear combination of δ(t?τ?τj)andδ(t?τ),whereτj=d/vjis the delay time that the emitted photon travels from one TLS to the other TLS in the given transverse mode j.The dynamics of two TLSs is governed by the differential equations[35–39]
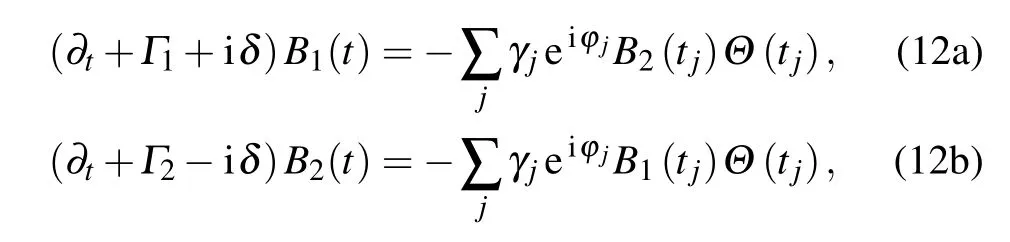

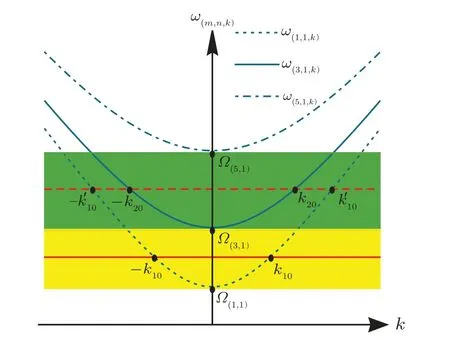
Fig.2.Dispersion relation of the TMj guiding modes of the waveguide.Ω(m,n)=+(nπ/q)2,Ω(m,n)is the cutoff frequency.ωA≈(Ω(1,1)+Ω(3,1))/2(red solid line)andωA≈(Ω(3,1)+Ω(5,1))/2(red dashed line).Photons with different frequencies can propagate in different modes with wave numbers k=k10,,k20,....
4.Entanglement dynamics of the TLSs
To measure the amount of the entanglement,we use concurrence as the quantifier.[40]By taking a partial trace over the degrees of freedom of the waveguide,the density matrix of the two TLSs is of an X-form in the two-qubit standard basis{|gg〉,|eg〉,|ge〉,|ee〉}.The concurrence for this type of state can be calculated easily as
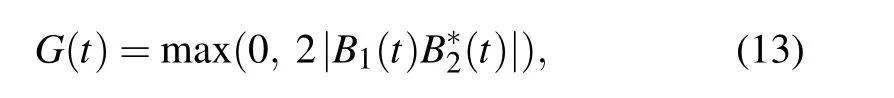
for TLSs initially sharing single excitation.
4.1.Single transverse mode
A TLS in its excited state radiates waves into the continua of the modes which are resonant with the TLS.If all TLSs’energy separations lie within the frequency band betweenΩ(1,1)andΩ(3,1)and are far away from the cutoff frequenciesΩ(1,1)andΩ(3,1),they only emit photons into the TM(1,1)(j=1)guiding mode.The equations for the amplitudes of the TLSs read



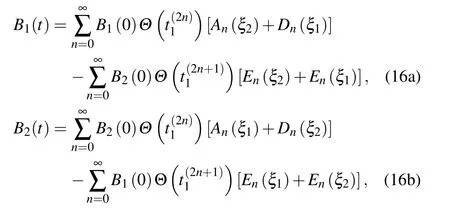
where the functions are defined as


with subscripts k,l∈{1,2}and k/=l.The TLSs show different behaviors depending on the retardation times nτ1required for light to travel between two TLSs located at a finite distance,the phaseφ1,the differenceδof the TLSs’frequencies and the differenceγ11?γ21of the decaying factors.For t∈[0,τ1],only one term appears
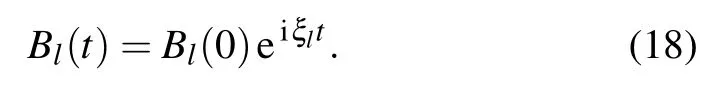
Two TLSs decays as if they are isolated in the waveguide,so the concurrence decay from|B1(0)B2(0)|with a rateγ11+γ21.As long as(γ11+γ21)τ1?1,two TLSs emit photons independently,the photon travels along the waveguide for timeτ1,then the part toward the other TLS will be absorbed,and the TLSs is partially excited,later TLSs re-emit the photon again,the whole process of emission and absorption was repeated as time goes on,however no interference occurs,so the phaseφ1has no effect on the entanglement.Equation(18)is also the solution of Eq.(14)withτ1→∞.If the TLSs decay slowly so that(γ11+γ21)τ1is smaller than or equal to 1,it is possible for a TLS to be aware of the other very soon,interference can be produced by multiple re-emissions and re-absorptions of light,which leads to an oscillatory energy exchange between the TLSs.It can be easily seen that the atomic upper state population contains two terms for t∈[τ1,2τ1]



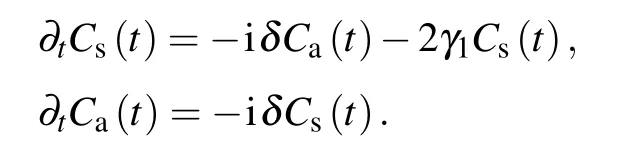


Fig.3.The concurrence between the TLSs as functions of the dimensionless time t/τ1 with the TLSs initially in the antisymmetry state|a〉for a difference energy separationδ=0(green dot-dashed line),δ=γ(blue dotted line),δ=2γ(black solid line),δ=5γ(red dashed line)in(a)τ1v1/λ1=1.0×109,(b)τ1v1/λ1=8.0×109,(c)τ1v1/λ1=8.0×1010.We have set the following parameters:a=2q,ωA=(Ω(1,1)+Ω(3,1))/2,γ1λ1/v1=1.5×10?10,φ1=2πτ1v1/λ1.
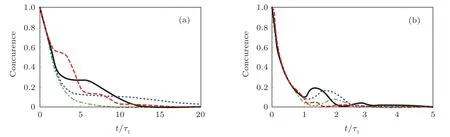
Fig.4.The concurrence between the TLSs as functions of the dimensionless time t/τ1 with the TLSs initially in the symmetry state|s〉for a difference energy separationδ=0(green dot-dashed line),δ=γ(blue dotted line),δ=2γ(black solid line),δ=5γ(red dashed line)in(a)τ1v1/λ1=1.0×109,(b)τ1v1/λ1=8.0×109.Other parameters are the same as those in Fig.3.
4.2.Two transverse modes
As the energy splitting of both TLS increases so that they are much larger than the cutoff frequencyΩ(3,1)and much smaller thanΩ(5,1),the TLSs interacts with the field of both TM(1,1)and TM(3,1)guiding modes.For dipolesμl=μ,the equations for the amplitudes of the symmetry and antisymmetry states reads


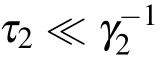

This equation can also explain the exponential decay of panel(d)of Fig.5 in the time interval[0,τ1].Actually,equation(21)also describes the dynamics of TLSs when the delay timeτ1→∞,it indicates that two TLSs emit photons independently,and the emitted photon travels along the waveguide and is never absorbed by the TLSs.For two TLSs far apart as shown in Fig.5(d),the phaseφjdo not make sense,and the increase ofδlowers the magnitude of the concurrence.Although the emitted photon could be absorbed by the TLS resulting the birth of entanglement,but the revival time becomes pτ1+qτ2with p,q are integer,which can be obtained by performing the Laplace transformation on Eq.(12)with j=1,2.

Fig.5.The concurrence of the TLSs as functions of the dimensionless time t/τ1 with the TLSs initially in the antisymmetry state|a〉and a=2q,ωA=(Ω(3,1)+Ω(5,1))/2,γ1λ1/v1=1.1×10?11,andφ1=2πτ1v1/λ1.Panel(a):τ1v1/λ1=0,δ=0 for dash–dotted green line,δ=2γ2 for dotted blue line,δ=2(γ1+γ2)for black solid line,δ=5(γ1+γ2)for dashed red line.In panels(b)–(d),δ=0 for dotted blue line,δ=1.5γ1+2γ2 for solid black line,δ=5(γ1+γ2)for dashed red line,and the phases are different:τ1v1/λ1=3.1×109 in panel(b),τ1v1/λ1=2.3×1010 in panel(c),τ1v1/λ1=1.8×1012 in panel(d).
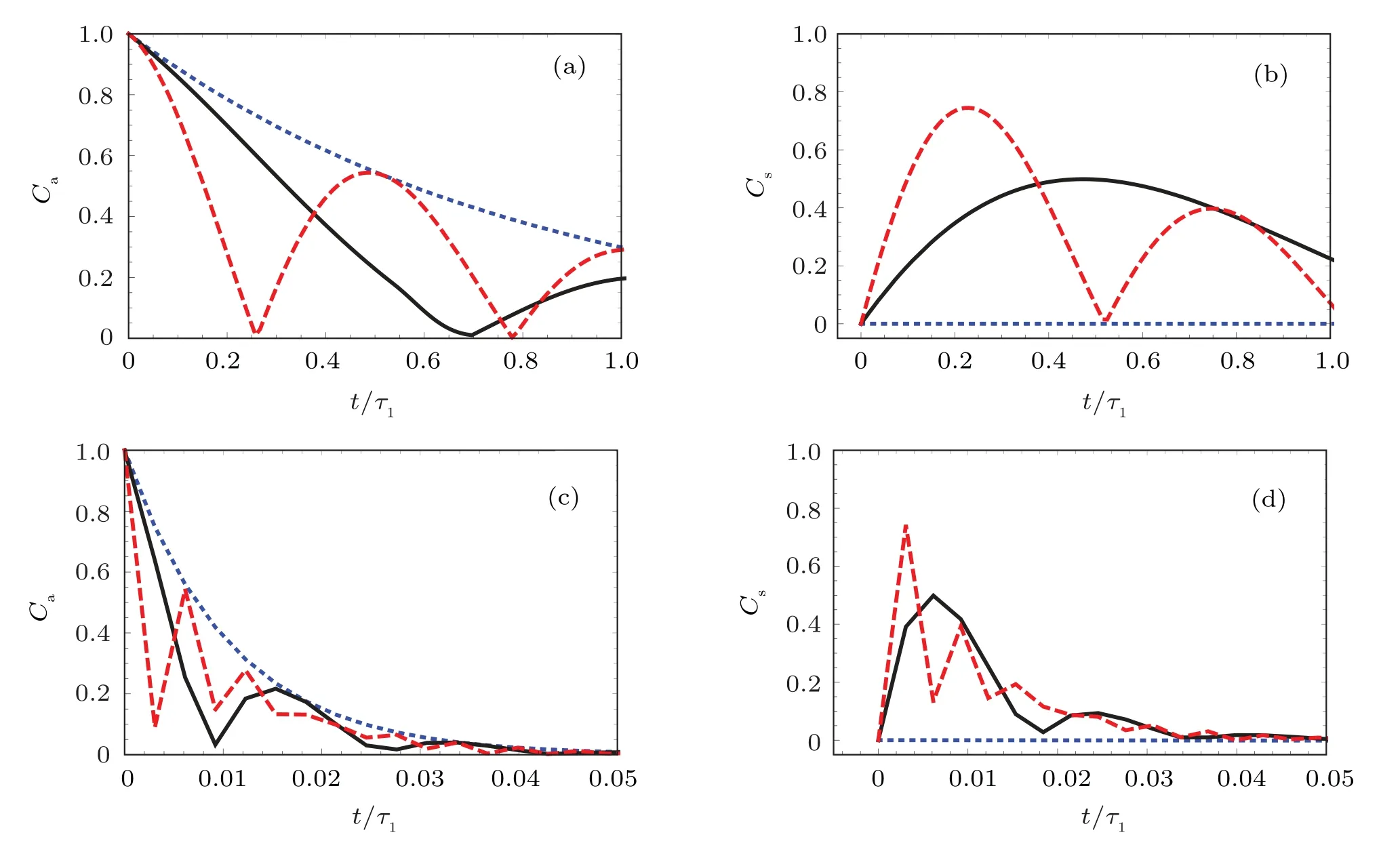
Fig.6.The populations of the symmetry and antisymmetry states in the time interval[0,τ1]of Figs.5(c)and 5(d).Here,δ=0 for dotted blue line,δ=1.5γ1+2γ2 for solid black line,δ=5(γ1+γ2)for dashed red line,andφ1=2πτ1v1/λ1;τ1v1/λ1=2.3×1010 in panels(a)and(b),τ1v1/λ1=1.8×1012 in panels(c)and(d).
5.Conclusion
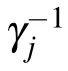
- Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Origin of anomalous enhancement of the absorption coefficient in a PN junction?
- Protection of isolated and active regions in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs using selective laser annealing?
- First-principles study of plasmons in doped graphene nanostructures?
- Probing thermal properties of vanadium dioxide thin films by time-domain thermoreflectance without metal film?
- An improved model of damage depth of shock-melted metal in microspall under triangular wave loading?
- Signal-to-noise ratio of Raman signal measured by multichannel detectors?