Thirty-day mortality of patients with hip fracture during COVID-19 pandemic and pre-pandemic periods: A systematic review and metaanalysis
Sujit Kumar Tripathy, Paulson Varghese, Sibasish Panigrahi, Bijnya Birajita Panda, Sandeep Velagada,Samrat Smrutiranjan Sahoo, Monappa A Naik, Sharath K Rao
Sujit Kumar Tripathy, Department of Orthopedics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar 751019, India
Paulson Varghese, Sibasish Panigrahi, Sandeep Velagada, Department of Orthopedics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar, Bhubaneswar 751019, India
Bijnya Birajita Panda, Department of Ophthalmology, SCB Medical College, Cuttack 753007, India
Samrat Smrutiranjan Sahoo, Department of Orthopedics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Nagpur 441108, India
Monappa A Naik, Department of Orthopedics, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Udupi, Karnataka 576104, India
Sharath K Rao, Department of Orthopedics, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Udupi, Karnataka, Manipal 576104, India
Abstract BACKGROUND Timely intervention in hip fracture is essential to decrease the risks of perioperative morbidity and mortality. However, limitations of the resources, risk of disease transmission and redirection of medical attention to a more severe infective health problem during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic period have affected the quality of care even in a surgical emergency.AIM To compare the 30-d mortality rate and complications of hip fracture patients treated during COVID-19 pandemic and pre-pandemic times.METHODS The search of electronic databases on 1st August 2020 revealed 45 studies related to mortality of hip fracture during the COVID-19 pandemic and pre-pandemic times. After careful screening, eight studies were eligible for quantitative and qualitative analysis of data.RESULTS The pooled data of eight studies (n = 1586) revealed no significant difference in 30-d mortality rate between the hip fracture patients treated during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods [9.63% vs 6.33%; odds ratio (OR), 0.62; 95%CI, 0.33, 1.17; P = 0.14]. Even the 30-d mortality rate was not different between COVID-19 non-infected patients who were treated during the pandemic time, and all hip fracture patients treated during the pre-pandemic period (OR, 1.03; 95%CI, 0.61, 1.75; P = 0.91). A significant difference in mortality rate was observed between COVID-19 positive and COVID-19 negative patients (OR, 6.99; 95%CI, 3.45, 14.16; P < 0.00001). There was no difference in the duration of hospital stay (OR, -1.52, 95%CI, -3.85, 0.81; P = 0.20), overall complications (OR, 1.62; P = 0.15) and incidence of pulmonary complications (OR, 1.46; P = 0.38) in these two-time frames. Nevertheless, the preoperative morbidity was more severe, and there was less use of general anesthesia during the pandemic time.CONCLUSION There was no difference in 30-d mortality rate between hip fracture patients treated during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods. However, the mortality risk was higher in COVID-19 positive patients compared to COVID-19 negative patients. There was no difference in time to surgery, complications and hospitalization time between these two time periods.
Key Words: Hip fracture; Femur neck fracture; Trochanter fracture; Mortality; Pandemic; COVID-19
INTRODUCTION
The health care delivery systems of most of the nations have been affected by the outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)[1]. In order to prevent the spread of the disease and to provide essential care to infected patients, many elective surgical procedures were postponed. Even emergency surgical procedures also got delayed because of the lack of human resources and operation theatre. Optimization of the patients before surgery also took a long time. Hip fracture is a surgical emergency. Despite mandatory lockdown during COVID-19 pandemic, hip fracture incidence has remained unaltered[2-5].
The most worrisome problem is that majority of these patients are elderly individuals with numerous comorbidities[6-10]. Management of such fractures in these vulnerable immunocompromised patients during COVID-19 pandemic time is a big challenge[11-29]. With the best possible care, the incidence of 30-d mortality in hip fracture has been reported between 9%-13% in the literature[14,15]. Those who survive usually have a poor functional outcome and quality of life[14,15]. During the pandemic time, when the entire medical services have focused on COVID-19 treatment, delaying of hip fracture surgery might cause increased complication and perioperative mortality. Although it was believed that COVID-19 infected patients with hip fracture might have more incidences of pulmonary complications, pneumonia and perioperative mortality, few studies reported similar mortality rates in both COVID-19 infected and non-infected patients[18,24]. The observational study by the Spanish HIPCOVID group reported a 10% incidence of in-hospital death among fracture patients who were negative for COVID-19[16]. Similar observations were reported by Kayaniet al[18], who had a similar incidence of mortality in hip fracture among the COVID-19 infected and non-infected patients. Several cohort studies reported no significant difference in delay in surgery, treatment methods, complications, and 30-d mortality in the hip fracture between the pandemic and the pre-pandemic period[24,27]. Because of the small cohort of hip fracture patients during the pandemic time, such conclusion should be interpreted judiciously as it seems there is no ill-effect of COVID-19 infectionper seon the patient and probably there is no severe consequence of slight treatment delay. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis were designed to look for: (1) The 30-d mortality in hip fracture during the pandemic timevsthe prepandemic time; and (2) the 30-d mortality rate between COVID-19 negative hip fracture patients and pre-pandemic era hip fracture patients. Similarly, delay in surgery, the length of hospital stay, and overall complication in the hip fracture patients in these two-time frames will be compared. We hypothesized that the 30-d mortality rate in hip fracture patients treated during the pandemic time is more than the pre-pandemic time.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The recommendations of Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Metaanalyses was followed for reporting this systematic review/meta-analysis[30](Figure 1). It was registered in PROSPERO (Regd. No.: CRD42020203581) before the data extraction and analysis.
Literature search strategy
A literature search was performed on 1stof August 2020 by two authors (Tripathy SK and Varghese P) to identify studies that have evaluated hip fractures during COVID-19 pandemic and pre-pandemic period. PubMed/Medline, Embase and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) databases were searched using the keywords “COVID”, “COVID-19”, “pandemic”, “hip fracture”, “trochanter fracture” and “femur neck fracture”. The Boolean operators “and” or “or” was used with different combinations of the keywords. The search was not time-bound but limited to the English literature and human being. The exact search strategy of Medline database has been provided in Table 1. The title and abstract of the retrieved articles were assessed carefully for possible inclusion in this review. The references of the relevant articles and reviews were also searched to get more studies related to the topic. The opinion of a third author (Panda BB) was sought when there was any disagreement/ discrepancy between the two authors (Figure 1).
Study selection
Any randomized controlled trial or observational prospective/retrospective study that mentioned the 30-d mortality rate of hip fracture patients (age > 18 years) in both pandemic and pre-pandemic periods were selected for this systematic review/metaanalysis. Studies that reported on open fracture or pathological fracture were not considered. If any study reported the 30-d mortality of hip fracture only for the pandemic period, it was excluded.
The hip fracture in this review included both intracapsular (neck femur fracture) and extracapsular fracture (intertrochanteric and subtrochanteric fracture). Patients who had clinical symptoms/signs of COVID-19 with reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction positive nose or throat swab for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) were considered as COVID-19 infected (COVID-19 +). Asymptomatic patient with negative throat and nose swabs were considered asCOVID-19 non-infected (COVID-19 ?). In cases where there was strong clinical suspicion, it was labelled as COVID suspect even though the swab tests were negative. For data analysis, all suspect patients were included in the COVID-19 + group. Similarly, patients who were not tested, and there was no clinical suspicion, were categorized as COVID-19 ?.

Table 1 Search strategy of Medline database
Data extraction
The data from the included studies were extracted by two authors (Tripathy SK and Varghese P). The details (author, year of publication, study design, demographic properties, surgical details, follow-up, 30-d mortality, and complications) were filled up in a Microsoft Excel sheet for subsequent analysis. The opinion of a third author (Panda BB) was sought in case of disagreement.
The primary objective of this study was to look for the 30-d mortality of hip fracture in COVID-19 pandemic period and pre-pandemic period. The secondary objective was to compare 30-d mortality of hip fracture among COVID-19 negative patients and prepandemic hip fracture patients. The duration of hospital stay, complications and preoperative morbidity among the hip fracture patients during these two-time frames were compared.
Methodological quality and risk of bias assessment
The methodological quality and risk of bias of the observational studies were evaluated by two authors (Tripathy SK and Varghese P) using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS)[31]. The NOS evaluates a study in three domains (8 items with maximum score 9): Study group selection, comparability of the groups, and determining the outcome of interest for case-control and cohort studies[31]. A score of more than six was considered as a high-quality study. In case of disagreement between the authors, the opinion of a third author (Naik MA) was sought.
Statistical analysis
The Review Manager (RevMan) V.5.3 was used for data analysis[32]. Few studies provided the median value and interquartile range (IQR). The mean and SD value was calculated from the median and IQR as per the recommendation of Luoet al[33]and Wanet al[34]. The study, providing the previous two years of data (pre-pandemic) were evaluated jointly, and the mean (SD) was calculated using the RevMan calculator. Whenever feasible, data were pooled for analysis. For the comparison of binary data, the odds ratio (OR) and a 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated. Similarly, the mean difference (MD) and 95%CI were estimated for continuous data. ThePvalue of < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. The heterogeneity among the cohort studies was evaluated by Cochrane's Q (χ2P< 0.10) and quantified byI2-Higgins test. TheI2value of 25%, 50% and 75% were considered as low, moderate, and high grade of heterogeneity, respectively[35,36]. The random-effects model was applied to address the high grade of heterogeneity (I2> 50%)[37].
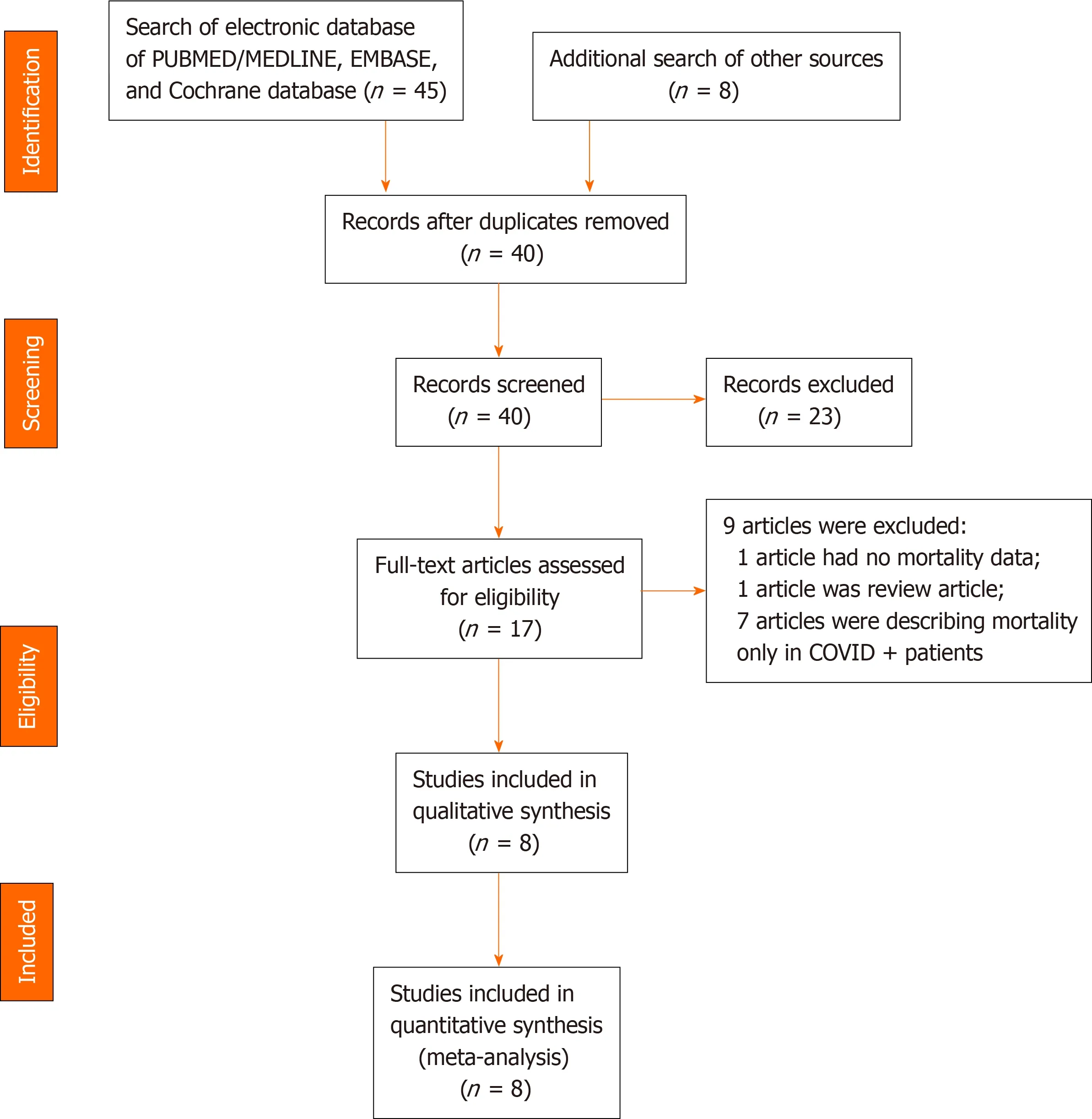
Figure 1 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses flow diagram showing methods of study recruitment.
RESULTS
Selection of the study, quality assessment, and patient demographics
A total of 45 studies were retrieved after the search of electronic databases using the keywords; of which, eight studies were eligible for review after screening[9,19,20,27-29,38,39](Figure 1). There were three prospective studies and five retrospective comparative studies. The inclusion and exclusion criteria were well defined in all studies. Assessment of quality of the studies using NOS revealed a low risk of bias in one study and moderate risk of bias in the remaining seven studies (Table 2). The data of 901 hip fracture patients who were treated during the pre-pandemic period (similar time in 2018 and 2019) was evaluated, and it was compared to 685 hip fracture patients treated during the pandemic period. There were 77 COVID-19 + patients and 608 COVID-19 ? patients (Table 2). The mean/median age of the patients in all studies was above 75 years during both pre-pandemic and pandemic periods. The female patients had more incidences of hip fracture during both the time periods. The study by Maceyet al[9]had age- and sex-matched hip fracture patient cohort from the pre-pandemic time. The body mass index and domicile status during both time periods have been provided in Table 2.
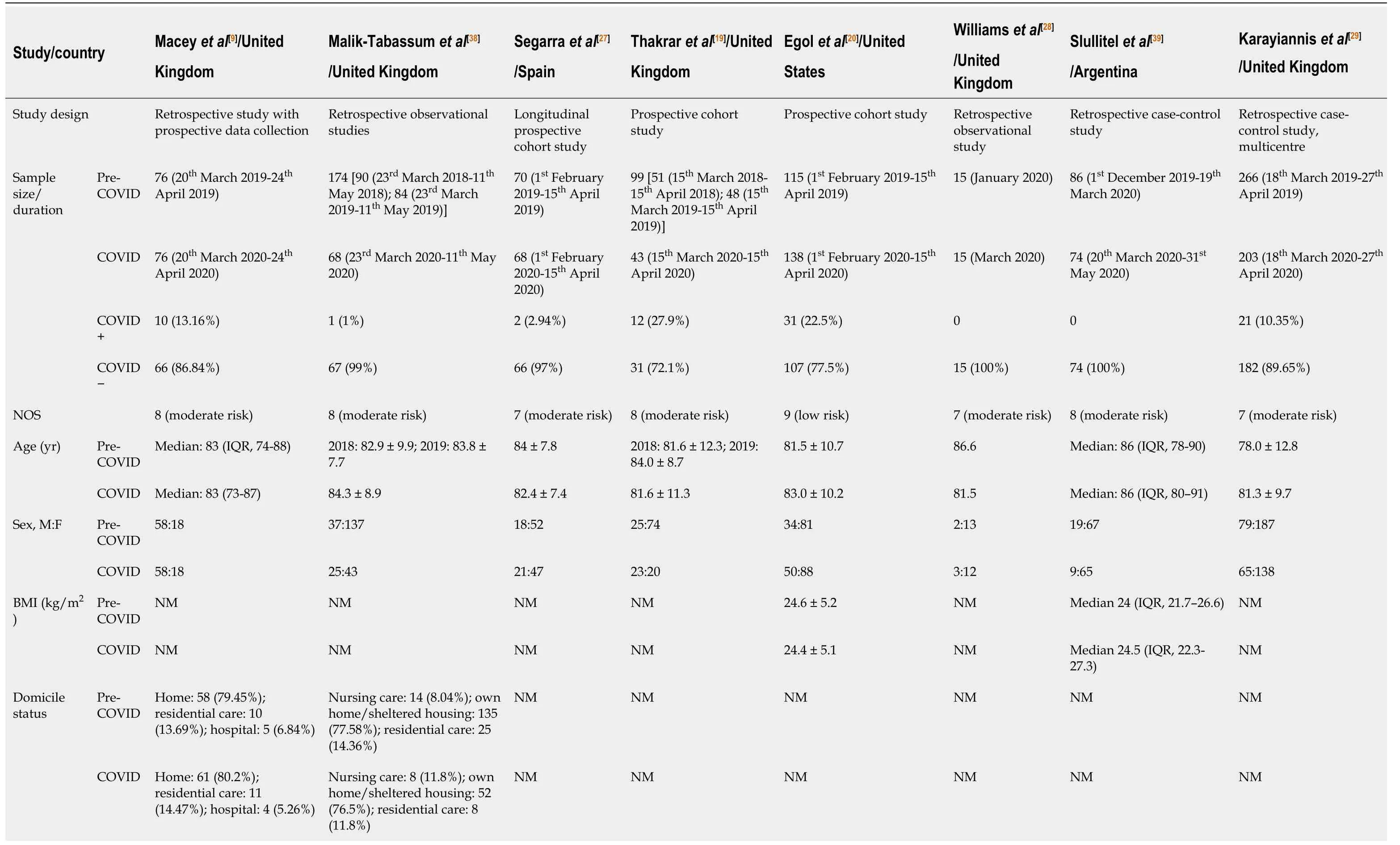
Table 2 Demographic properties, fracture type and surgical techniques in hip fractured patients treated during coronavirus disease 2019 and pre-coronavirus disease 2019 times (2020)
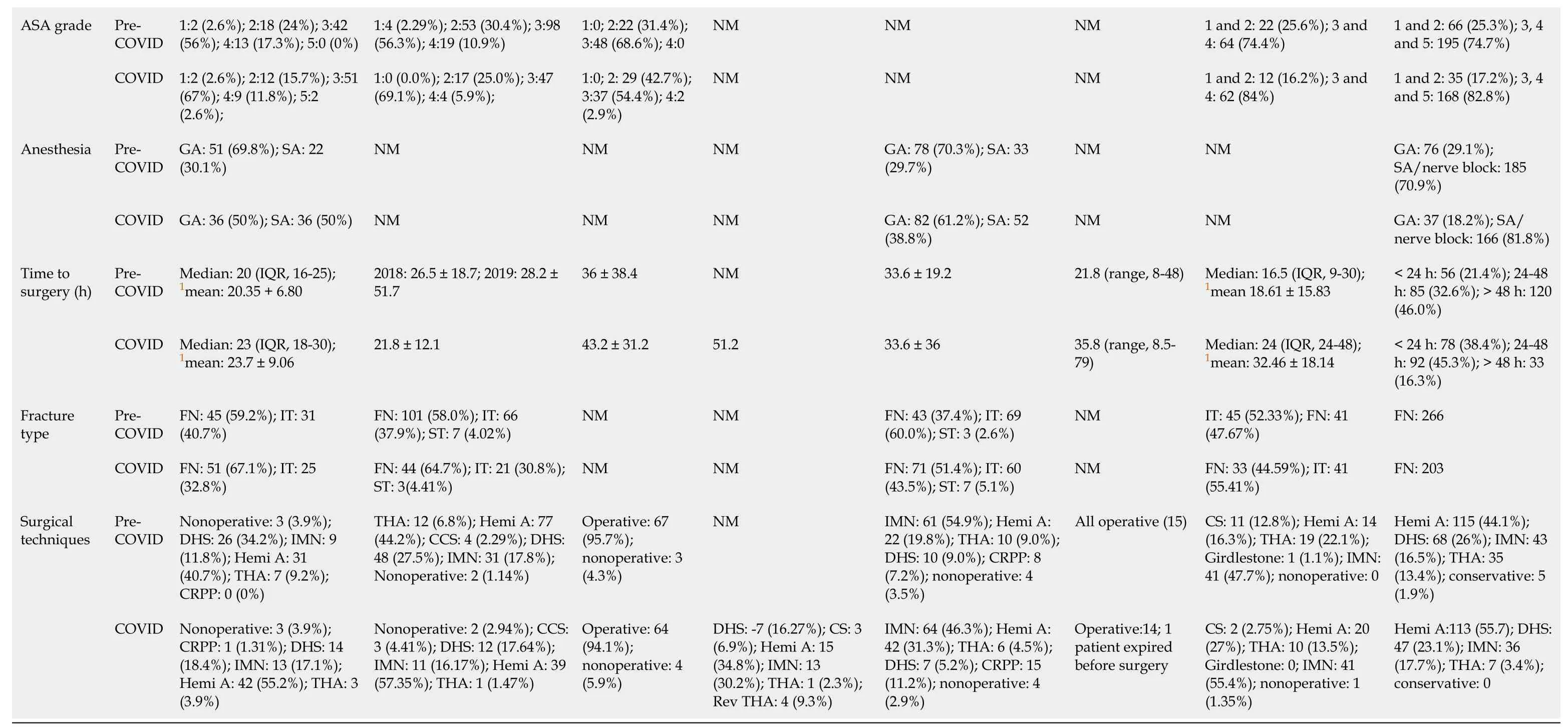
1Indicates that the mean has been calculated from the median value and interquartile range/range. NOS: Newcastle-Ottawa scale; M: Male; F: Female; ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists Classification; COVID: Coronavirus disease 2019; IQR: Interquartile range; NM: Not mentioned; GA: General anesthesia; SA: Spinal anesthesia; FN: Femoral neck fracture; IT: Intertrochanteric fracture; DHS: Dynamic hip screw; IMN: Intramedullary nail; Hemi A: Hemiarthroplasty; THA: Total hip arthroplasty; CRPP: Closed reduction percutaneous pinning; ST: Subtrochanteric fracture; CS: Cannulated screw; CCS: Cannulated compression screw; Rev THA: Revision total hip Arthroplasty.
Preoperative morbidity, time to surgery and type of anesthesia
The preoperative morbidity status of the patients in both pandemic and pre-pandemic periods were compared using the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) classification. Pooled analysis of five studies (n= 1159) revealed significantly increased number of severely morbid (ASA grade > 3) hip fracture patients who were treated during the pandemic period (OR, 1.43; 95%CI, 1.08, 1.89;P= 0.01)[9,27,29,38,39]. Egolet al[20](2020) did not observe a significant difference in preoperative morbidity using the Charlson Co-morbidity index between 2020 hip fracture cohort and 2019 hip fracture cohort.
After pooling of the data from five studies[9,20,27,38,39], it was observed that there was no difference in time to surgery following the injury (MD, 6.57; 95%CI, ?0.25, 13.39;P= 0.06). The high grade of heterogeneity (I2= 88%) among the studies was addressed by the random effect model (Figure 2).
Only three studies (n= 874) had provided details about the type anesthesia (regionalvsgeneral anesthesia) used during surgery[9,20,29]. There was significantly less use of general anesthesia during the pandemic period (37.17%vs44.86%; OR, 0.57; 95%CI, 0.42, 0.77;P= 0.0003) (Figure 2).
Mortality, length of hospital stay, complications
Pooled analysis of 30-d mortality from the eight studies (n= 1586) revealed a significantly increased death among hip fracture patients during the pandemic time (9.63%vs6.33%; OR, 0.62; 95%CI, 0.33, 1.17;P= 0.14) (Table 3, Figure 3)[9,19,20,27-29,38,39]. There was no difference in 30-d mortality rate between COVID-19 negative patients who were treated during the pandemic time and all hip fractured patients treated during the pre-pandemic period (6.44%vs5.74%; OR, 1.03; 95%CI, 0.61, 1.75;P= 0.91)[9,19,20,29,38]. However, a significant difference in mortality rate was observed between COVID-19 + and COVID-19 ? patients with an OR of 6.99 (29.33%vs5.73%; 95%CI, 3.45, 14.16;P< 0.00001) (Table 3, Figure 3)[9,19,20,29,38].
There was no difference in length of hospital stay among hip fracture patients treated during pandemic and pre-pandemic periods (OR, ?1.52; 95%CI, ?3.85, 0.81;P= 0.20)[9,20,38,39]. Similarly, major complications (17.98%vs10.64%; OR, 1.62;P= 0.15) and the incidence of pulmonary complications (9.09%vs6.78%; OR, 1.46;P= 0.38) among the hip fracture patients during these two-time frames were not different (Table 3, Figure 4)[9,20,38,39].
DISCUSSION
The main finding of the meta-analysis was that there was no difference in 30-d mortality in hip fracture patients between the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods. Even, the mortality risk was not different among the COVID-19 ? patients of pandemic time and all hip fracture patients of pre-pandemic time. However, significantly increased 30-d mortality rate was observed in COVID-19 + patients. There was less use of general anesthesia during the pandemic period and patients with hip fracture treated during this time were severely morbid.
Early intervention in hip fracture reduces morbidity and mortality. A shorter hospital stay and minimal respiratory complications have been reported if the hip fracture surgery is stabilized within 24 h of admission[40,41]. During the pandemic, there was difficulty in treating these patients within the stipulated time[42,43]. Accordingly, a high incidence of 30-d mortality was expected, but the pooled analysis of the studies did not observe a significant difference in mortality among the hip fracture patients treated during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods. However, the difference in the mortality was limited to the COVID-19 + patients as the analysis failed to notice a difference between COVID-19 ? patients and pre-pandemic hip fracture patients. The respiratory compromise because of the COVID-19 infection in the perioperative period acts as a second hit phenomenon as the cytokines are already flared up by the traumatic hip fracture[18,20,24]. Prolonged recumbency, poor immunity and multiple comorbidities in the elderly individuals are also detrimental[43,44]. Nevertheless, asymptomatic COVID-19 ? patients are not different from the typical elderly cohort. Accordingly, segregations of the hip fracture patients into the COVID-19 positive site or the negative site will minimize cross-infection, and it will help in early delivery of medical care to the non-infected patients[24,27]. The patient may be temporarily held up in a transition zone till COVID-19 test result is available.
The importance of patient segregation into two different sites has been evaluated by Chuiet al[24]and Segarraet al[27]. Chui and his associate did not notice a significant difference in mortality between COVID-19 infected and non-infected patients as they could operate 61% of hip fractured patients within 36 h[24]. It has been reported that the respiratory symptoms have improved after femur fracture stabilization[23]. Catellaniet al[23]advocated that the patients could be mobilized after surgery with general patient comfort, and there was an improvement in physiological ventilation. Few studies reported a slight delay (48-72 h) in providing care to the COVID-19 infected compared to non-infected patients because of the need for medical optimization ofthese patients[18,20,24]. Whether this delay was responsible for increased mortality in the COVID-19 positive patients is unknown. Overall, there was no significant delay in time to surgery during this epidemic. It indicates the promptness of medical health care professionals in understanding the timely delivery of emergency care. Despite understanding the risk of disease transmission, the orthopedic surgeons have given priority to the patients’ health and safety. In order to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 infection in the hip fracture patients, the mortality rate of these patients was compared with the national average mortality rate of the corresponding country that has been related to COVID-19 infection. The national statistics bulletin report of United Kingdom stated that 13.7% of all deaths that occurred in England (45439 deaths) between January and July 2020 was COVID-19 related and it was 10.8% in Wales (2274 deaths) for the same period. The age-standardized mortality rates for deaths due to COVID-19, per 100000 persons, in England for March, April and May 2020 (for the period under consideration in this meta-analysis), were 33.8, 623.2 and 244.8 respectively[45,46]. It is quite apparent that the death rate of hip fracture patients with the SARS-CoV-2 infection is very high (29.33% as per the current meta-analysis) compared to the national average death due to COVID-19 infection (13.7%, five studies are from the United Kingdom).
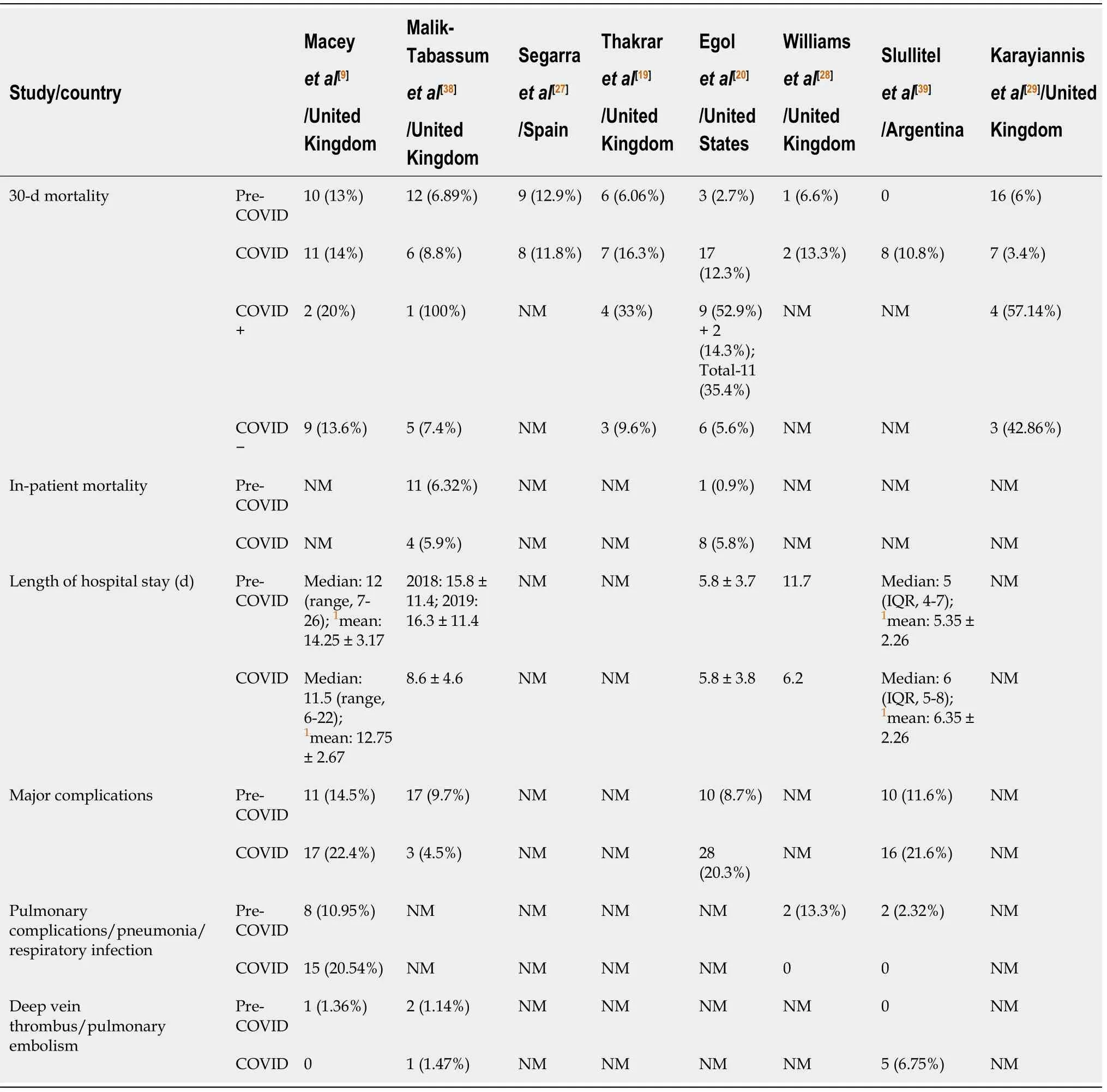
Table 3 Mortality and complications in hip-fractured patients treated during coronavirus disease 2019 and pre-coronavirus disease 2019 times (2020)
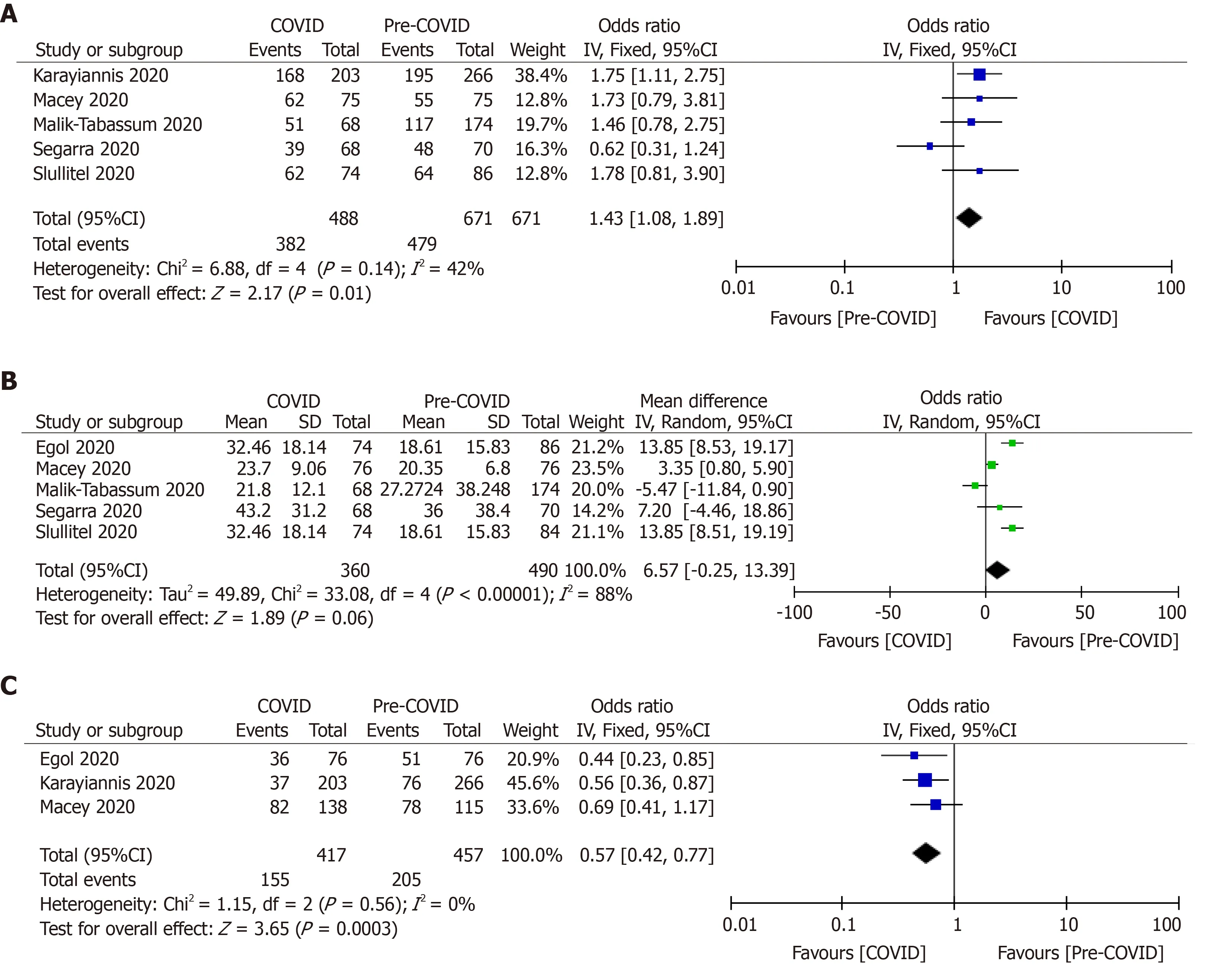
Figure 2 Forest-plot diagram showing preoperative morbidity, time to surgery and use of general anesthesia among hip-fractured patients during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods.
Previous literature revealed that COVID-19 patients with multiple associated comorbidities had an increased risk of death when admitted to the critical care service[18,20,24,45]. Denget al[47]compared the clinical characteristics, blood parameters and morbidity of 109 COVID-19 + patients who died during hospitalization with 116 recovered patients. The risk of mortality increased from 41.5% to 72.5% (P< 0.01) in patients with associated pre-existing comorbidities[45]. The national statistics bulletin of England and Wales reported 50335 deaths involving COVID-19 between March and June 2020. About 91% of these patients had at least one pre-existing disease, and the remaining 9% had no associated comorbidity[45,46]. The average number of comorbidities for COVID-19 related death was 2.1 for patients of 0-69 years of age, and it was 2.3 for patients aged > 70 years[45,46]. Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported that 8 out of 10 COVID-19 deaths in the United States have been in the older individuals of age > 65 years[48]. Poor immunological status and multiple chronic preexisting disease conditions such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus and chronic cardiorespiratory disorders were attributed for this high death rate[18,20,24,47,48]. The preoperative comorbidities, as reported using ASA grading system, showed increased premorbid patients during the pandemic time in this review. These patients had probably poor systemic baseline function and their physiological capability to endure the surgical procedure was limited[18,20,24]. The concomitant use of angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors that up-regulates the expression of ACE-2 receptors hypothetically might have increased the virus-cell binding and thereby increased the virus transmission into the cell in the COVID-19 patients. The resultant increased viral load explains the increased rate of mortality[49]. Regarding the increased numbers of premorbid patients during the pandemic time, we believe that most of these old patients had not performed their regular check-up for chronic illnesses because of lockdown, and restriction of medical service for regular care. Despite the poorly controlled chronic disease conditions among all hip fracture patients, the increased mortality was selectively observed in the COVID-19 + patients.
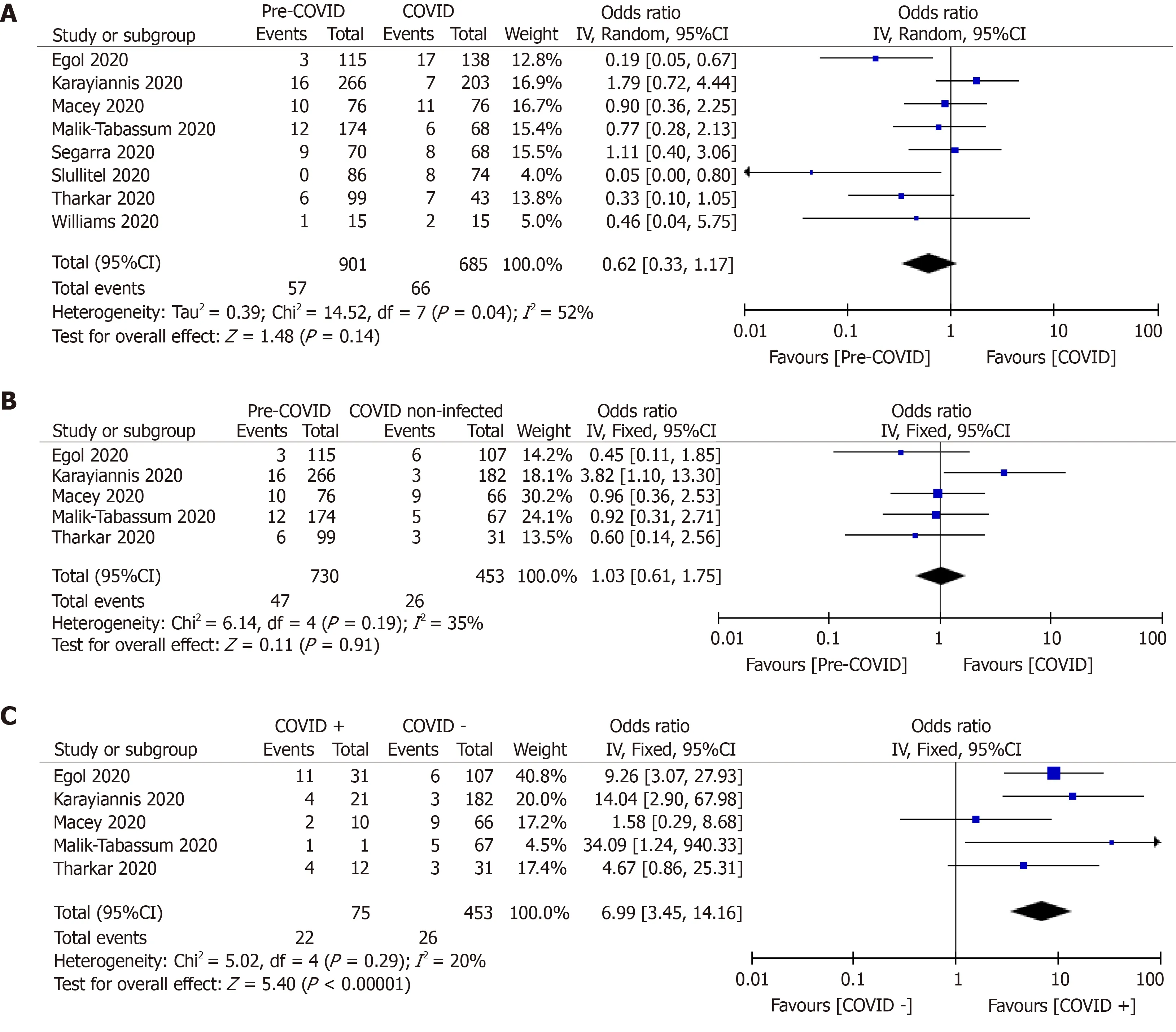
Figure 3 Forest-plot diagram showing 30-d mortality among hip-fractured patients in these two time frames.
General anesthesia increases the risk of aerosol exposure among health care workers and hence increases the chance of infection in them[16,18,20]. Besides, the general anesthesia also augments an inflammatory reaction within the lung parenchyma of the patients. Consequently, there was significantly less use of general anesthesia during the pandemic time compared to the pre-pandemic period. Despite the recommendation of regional anesthesia, Kayaniet al[18]noted no difference in types of anesthesia between COVID-19 infected and non-infected patients in their series.
Many researchers reported increased early mortality, increased length of hospital stay, a higher incidence of major complications, and a greater incidence of respiratory complications in COVID-19 infected compared to the non-infected patients[16,18,20]. However, this meta-analysis did not perceive a significant difference in major complications, length of hospital stay and respiratory complication among hip fracture patients managed during the pandemic and pre-pandemic times. Probably the higher proportion of COVID-19 ? patients (89%) in the evaluation controlled the result or, most of the COVID-19 + patients were probably asymptomatic or minimally affected by the infection.

Figure 4 Forest-plot diagram showing length of hospital stay, overall complications, and respiratory complications among hip-fractured patients during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods.
There were certain limitations to this meta-analysis. All these studies are from developed nations where the health care sectors are streamlined and protocol-based; hence it cannot be generalized to all nations. Only 30-d follow up has been studied in this review, so the outcome after one month is unknown. The retrospective study design and small patient cohort are also the main limitations for this meta-analysis. Despite that, this meta-analysis is first of its kind comparing the mortality and morbidity among hip fracture patients during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods.
CONCLUSION
To conclude, there was no difference in 30-d mortality rate among hip fracture patients treated during the COVID-19 pandemic and pre-pandemic periods. The mortality risk was significantly high among COVID-19 + patients as compared to non-infected patients. With the development of better drug and better treatment protocol of COVID-19, the interpretation of this meta-analysis might change.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic time, the attention of the whole of the medical fraternity was diverted to the infective viral severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection. There was a huge risk of infection among the medical staffs and patients coming to the hospital for other serious problems. Limitations of the operation theatre and medical staff were other hurdles in tackling life-threatening emergency surgeries. Although the mandatory lockdown policy might have reduced the incidence of the road traffic accident, the incidence of fragility fractures remained unaltered. Hip fracture is a surgical emergency and needs urgent surgical intervention to reduce morbidity and mortality. The impact of the COVID-19 infection on hip fracture management has been studied by a few researchers.
Research motivation
This systematic review and meta-analysis were designed to look for the impact of COVID-19 infection on hip fracture management and outcome.
Research objectives
The objectives of this meta-analysis were to compare the 30-d mortality and complications of hip fracture management during COVID-19 pandemic time and prepandemic time.
Research methods
The search of electronic databases was performed to retrieve studies related to hip fracture management during COVID-19 pandemic and pre-pandemic times. A total of 45 studies were identified, of which eight studies were eligible for quantitative and qualitative analysis of data.
Research results
The pooled data of eight studies with 1586 patients showed no significant difference in 30-d mortality rate between the hip fracture patients treated during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods [9.63%vs6.33%; odds ratio (OR), 0.62; 95%CI, 0.33, 1.17;P= 0.14]. Even there was no difference in the 30-d mortality rate between COVID-19 ? patients managed during the pandemic timevsall hip fracture patients managed during the pre-pandemic period (OR, 1.03; 95%CI, 0.61, 1.75;P= 0.91). A significant difference in mortality rate was observed between COVID-19 positive and COVID-19 negative patients (OR, 6.99; 95%CI, 3.45, 14.16;P< 0.00001). There was no difference in the duration of hospital stay (OR, ?1.52; 95%CI, ?3.85, 0.81;P= 0.20), overall complications (OR, 1.62;P= 0.15) and pulmonary complications (OR, 1.46;P= 0.38) in these two-time frames. Nevertheless, the preoperative morbidity was more severe, and there was less use of general anesthesia during the pandemic time.
Research conclusions
There was no difference in 30-d mortality rate between hip fracture patients treated during the pandemic and pre-pandemic periods. However, the mortality risk was higher in COVID-19 positive patients compared to COVID-19 negative patients. There was no difference in time to surgery, complications and hospitalization time between these two time periods.
Research perspectives
This meta-analysis showed that the COVID-19 infected patients with a hip fracture had a higher mortality rate, but the non-infected patients received the same level of care and they had similar mortality to that of hip fracture patient managed during the pre-pandemic period. The orthopedic trauma surgeons have learnt the ways to tackle the orthopedic emergency during the epidemic time.
 World Journal of Orthopedics2021年1期
World Journal of Orthopedics2021年1期
- World Journal of Orthopedics的其它文章
- Anterior glenohumeral instability: Current review with technical pearls and pitfalls of arthroscopic soft-tissue stabilization
- Hallux rigidus treated with adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells:A case report
- Hello, can you hear me? Orthopaedic clinic telephone consultations in the COVID-19 era- a patient and clinician perspective
- Ceramic-on-ceramic vs ceramic-on-polyethylene, a comparative study with 10-year follow-up
