REVISITING A NON-DEGENERACY PROPERTY FOR EXTREMAL MAPPINGS*
Dedicated to the memory of Professor Jiarong YU
Xiaojun HUANG
Department of Mathematics, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ 08903, USA
Abstract We extend an earlier result obtained by the author in [7].
Key words non-degeneracy property; extremal mapping; pseudoconvex
1 Introduction
Let D be a bounded domain in Cwith n ≥1. An extremal map φ of D is a holomorphic map from the unit disk Δ:={ξ ∈C: |ξ|<1} into D such that the Kobayashi metric of D at φ(0)along the direction φ(0)is realized by φ. We say that φ is a complex geodesic if it realizes the Kobayashi distance between any two points in φ(Δ) ([1]).
Fundamental work on extremal maps and complex geodesics was done in the early 1980s by Lempert [9, 10], Poletsky [12], etc.. Among many other things, Lempert showed that extremal maps of a bounded strongly convex domain with a C-smooth boundary are complex geodesics.Poletsky[12]showed that extremal maps of a bounded pseudo-convex domain with a reasonably smooth boundary, say C-smooth, are almost proper. Both Lempert [9] and Poletsky [12]derived the Euler-Lagrange equations for extremal maps in their considerations. In his paper in the early 1990s,[6, 7],motivated by the Abate-Vensentini problem on establishing the Wolff-Denjoy iteration theory for bounded contractible strongly pseudo-convex domains, proved two localization theorems for extremal maps of pseudoconvex domains near a C-smooth strongly pseudoconvex point; these were then, used fundamentally, to resolve the Abate-Vensentini conjecture in[7]. These localization results later found many other applications,e.g.,in solving the homogeneous Monge-Amp′ere equations with a prescribed boundary singularity ([3, 4, 8]).The methods used in [7] also played an important role in establishing the regularities for CR mappings.



2 Proof of Theorem 1.1
We basically follow the argument presented in [7]. We include enough details to facilitate the reader’s understanding.






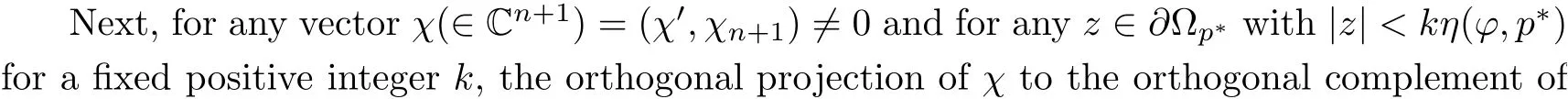

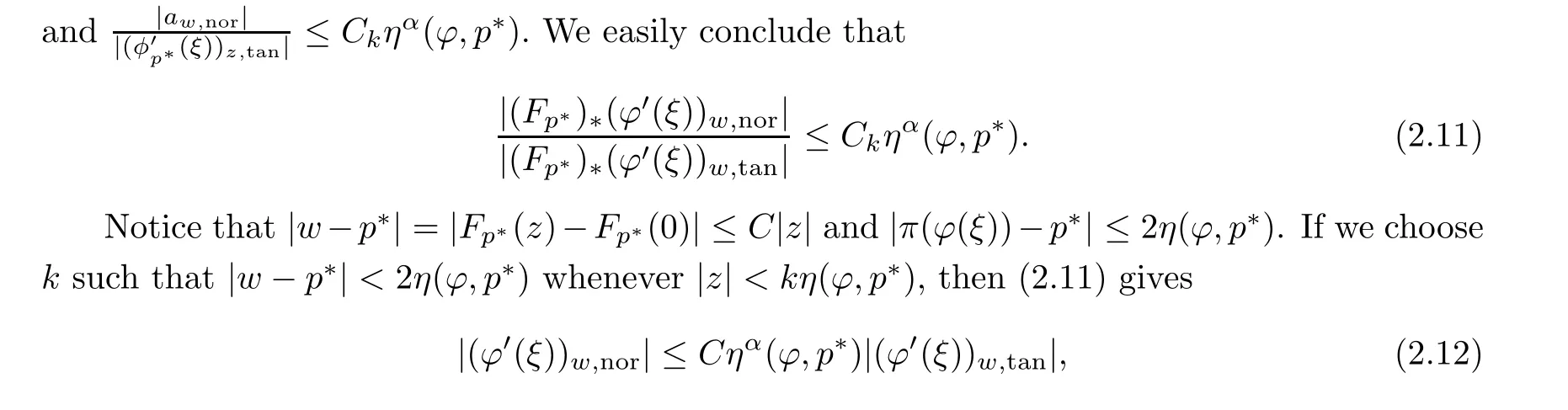
with C independent of pand φ, whenever pand φ are sufficiently close to p. This completes the proof of our theorem.□
Remark A By using the Lebesque covering lemma, we immediately see the following application of Theorem 1.1 and Corollary 1.2:
Corollary 2.2 Let Ω ?Cbe a bounded strongly pseudoconvex domain with a Csmooth boundary, where α ∈(0,1]. Then there is a sufficiently small positive number ε such that for any extremal map φ of D, when diam(φ)<?, it holds that

Notice that the above conjecture follows from[5,Proposition 4]when the domain is strongly convex.
Remark B We recall the Lempert existence and uniqueness (up to an automorphism of the unit disk) result of a complex geodesic ([9, 11]) through an interior given point and a given complex direction for a C-smoothly bounded strongly convex domain. Once Theorem 1.1 is proved, the existence part of [7, Theorem 3] can be proved in the same way for when the domain D is just assumed to be C-smooth for α ∈(0,1). However, the uniqueness part,which was only discussed much later in [8], only holds for the bounded strongly convex domain D being Csmooth for α >1/2.
We mention that [6, Theorem 1, pp284] holds for p ∈?D being only a Cstrongly pseudoconvex point though it was only stated there under the C-smoothness assumption. The reason is as follows:
By examining the proofs of[9, Lemma 12,Propositions 13-16],all these results of Lempert[9]also hold when the domain D is a bounded C-smooth strongly convex domain. Indeed,all the arguments there also hold for a C-smoothly bounded strongly convex D, if the following two crucial geometric properties used in [9] hold for D: there are a small δ>0 and a large positive R >0 such that for any z ∈D with dist(z,?D) <δ, the closed ball centered at z with radius dist(z,?D) only intersects ?D at pwith |p-w| = dist(w,?D) for any w in the diameter of the ball through p; and for any q ∈?D there is a closed ball whose radius is R such that it contains D{p}, and is tangential to ?D at q. These facts are classical and can be easily proven to be true even when D is C-smooth.
Based on these observations,the same argument in[6]shows that[6,Lemma 4,pp 289]also holds for a C-smoothly bounded strongly convex domain D. Notice that the local Fornaess embedding theorem, proven in [6, Lemma 5], only needs C-smoothness near the point under study. Exactly the same proof as in [6] shows that [6, Theorem 1] holds for a C-smoothly bounded strongly convex domain D.
With the above observation and Theorem 1.1, exactly the same proof as that used in [7]shows that [7, Theorem 1, pp 399] holds for any C-smoothly bounded contractible strongly pseudoconvex domain D. However,it remains an open problem as to whether or not[7,Theorem 1, pp 399] holds for a C-smoothly bounded contractible strongly pseudoconvex domain D.
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2021年6期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2021年6期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- PREFACE
- PENALIZED LEAST SQUARE IN SPARSE SETTING WITH CONVEX PENALTY AND NON GAUSSIAN ERRORS*
- ENTROPICAL OPTIMAL TRANSPORT,SCHR¨ODINGER’S SYSTEM AND ALGORITHMS*
- NOTES ON REAL INTERPOLATION OF OPERATOR Lp-SPACES*
- HANDEL’S FIXED POINT THEOREM: A MORSE THEORETICAL POINT OF VIEW*
- Some questions regarding verification of Carleson measures
