?丁草胺在水稻及土壤鎘吸收富集中的作用?
王宇霖 羅惠莉 周靜如 賀曉美

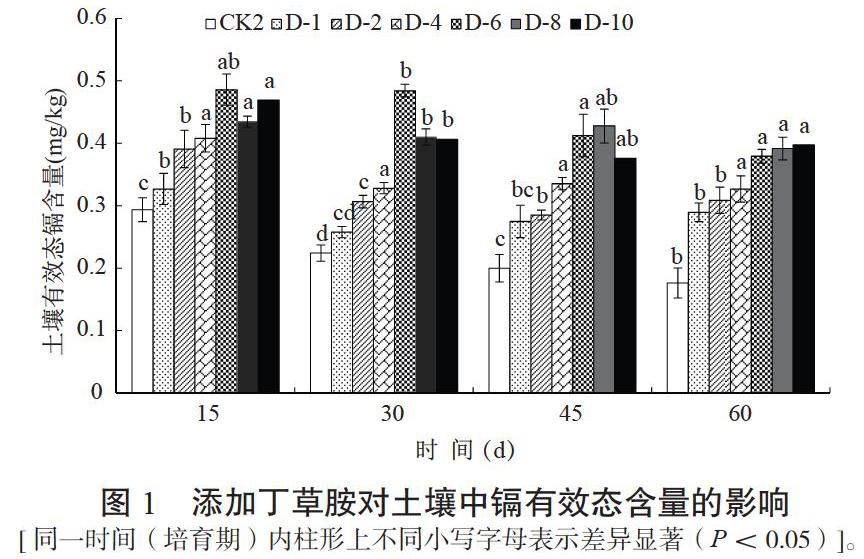

摘 要:以2種不同劑型丁草胺(乳油和水乳劑)為材料,通過(guò)土培盆栽試驗(yàn)?zāi)M田間種植水稻,研究了不同濃度丁草胺對(duì)土壤中鎘有效態(tài)、水稻生長(zhǎng)量及水稻植株吸收鎘的影響,旨在明確丁草胺在水稻及土壤鎘吸收富集過(guò)程中的作用。結(jié)果表明:丁草胺的施加可促進(jìn)土壤鎘的有效性,其中施加2、4、6 mg/kg的丁草胺后,土壤有效態(tài)鎘含量分別比未施加丁草胺的對(duì)照(CK2)增加33.14%、39.00%、65.50%,尤其是丁草胺濃度為6 mg/kg時(shí),土壤有效態(tài)鎘含量達(dá)到峰值(0.49 mg/kg),若施加濃度超過(guò)6 mg/kg丁草胺對(duì)土壤有效態(tài)鎘的促進(jìn)作用會(huì)減弱;施加丁草胺可抑制水稻生長(zhǎng),且施加濃度越高抑制作用越明顯,當(dāng)施加10 mg/kg丁草胺乳油時(shí),水稻的根長(zhǎng)、株高、葉綠素含量分別比CK2低69.55%、61.63%、41.26%;施加丁草胺對(duì)水稻鎘吸收有促進(jìn)作用,且使水稻吸收的鎘大多積累在根部,而隨丁草胺濃度的增加水稻地下部分鎘積累的增長(zhǎng)速度明顯快于地上部分,但丁草胺也能促進(jìn)水稻糙米對(duì)鎘的積累,且施加濃度越高促進(jìn)效果越明顯;2種劑型中,乳油型丁草胺的上述作用均強(qiáng)于水乳劑。
關(guān)鍵詞:丁草胺;土壤;水稻;鎘;吸收富集
中圖分類(lèi)號(hào):X53文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A文章編號(hào):1006-060X(2020)10-0062-05
Abstract:Two different formulations of butachlor (EC and EW) were used as materials to study the effects of butachlor on soil available cadmium, rice growth and cadmium uptake by rice plants through pot experiment in soil culture. The results showed that butachlor could promote the availability of soil cadmium; the content of available cadmium in soil increased by 33.14%, 39.00% and 65.50% respectively when butachlor was applied at 2, 4 and 6 mg/kg compared with the control without butachlor (CK2). When butachlor was applied at 6 mg/kg, the content of soil available cadmium reached the peak value (0.49 mg/kg). If the concentration of butachlor was more than 6 mg/kg, the promoting effect of butachlor on soil available cadmium would be weakened. Butachlor could inhibit the growth of rice, and the higher the concentration of butachlor, the more obvious the inhibition effect. When butachlor was applied at 10 mg/kg, the root length, plant height and chlorophyll content of rice decreased by 69.55%, 61.63% and 41.26%, respectively compared with CK2. Butachlor promoted the cadmium uptake of rice, and most of the cadmium absorbed by rice was accumulated in the root. With the increase of butachlor concentration, the growth rate of cadmium accumulation in underground part of rice was significantly faster than that in aboveground part. Butachlor also promoted the accumulation of cadmium in brown rice, and the higher the concentration, the more obvious the promotion effect. Among the two formulations, butachlor EC showed stronger effects than EW.
Key words: butachlor; soil; rice; cadmium; uptake and accumulation
土壤是環(huán)境乃至整個(gè)生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的必要成分,為植物、動(dòng)物和微生物提供了棲息場(chǎng)所,也是人類(lèi)農(nóng)業(yè)生產(chǎn)的基礎(chǔ)。隨著經(jīng)濟(jì)迅速發(fā)展,環(huán)境中大約90%的污染物會(huì)進(jìn)入土壤環(huán)境,從而造成嚴(yán)重污染[1]。重金屬污染具有持久性、毒性和生物富集作用,由此引起的環(huán)境污染對(duì)生物和人類(lèi)健康均會(huì)造成嚴(yán)重的危害[2-4]。……

