Study on the inflammatory response in the contralateral eye after phacoemulsification combined with intraocular lens implantation in the first eye
Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, phacoemulsification combined with intraocular lens implantation under topical anesthesia is the main surgical approach for the treatment of cataract[1-3]. Topical anesthesia significantly reduces the perceived pain at the time of making the clear corneal incision as compared with historical techniques such as retrobulbar anesthesia. However most ophthalmic surgeons performing a large number of cataract surgeries found that patients having cataract surgery under topical anesthesia often complain about increased pain in the fellow eye relative to the first surgery, despite the same operative and anesthetic conditions[4-10].
The above contradiction led a number of authors tocompare these consecutive procedures. In 2010, Mowattetal[4]reported that patients experienced more pain with 2ndeye surgery for the first time. In the next year, Urseaetal[5]also reported a statistically significant difference of pain perception between the first and second cataract surgeries, and they believed that it should be associated with decreased preoperative anxiety. In 2015, Zhuetal[7]found that MCP-1, an important factor resulting in pain, was increased significantly in the aqueous humor of patients undergoing second-eye cataract surgery compared to that in patients undergoing first-eye surgery which may help to explain why the second-eye phacoemulsification is often more painful.
Pain is a kind of unpleasant feeling and emotional experience caused by the actual or potential tissue damage of the body, and is generally considered to be a multi-process involving physical, emotional and perceptual integration, also as one of the primary function of self-defense when suffering injury. Pain as an essential sensation is known to be closely related to inflammation[11-14]. Pain-related inflammation cytokines, which contain reactive oxygen species, kinin and prostaglandins caused by tissue damage, substance P and neurokinin A secreted by sensory nerve endings, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α released by immune cells, as well as the Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 (MCP-1) secreted by monocytes and macrophages, can directly or indirectly sensitize the high-threshold small or medium - sized neurons Fiber and Aδ fibers as well as other pain sensors, thereby change the permeability and membrane excitability of the ion channel in sensory fiber membrane, result in the conduction of nerve impulses, finally integrate into pain perception[15].
For the phenomenon that patients complain about more pain during their second eye surgery, lots of surgeons did find statistically significant difference of pain perception between the first and second eye surgeries[5,8-10]. However, in most of the previous studies about this topic, pain was assessed using subjective responses or visual analog scale scores (VAS) instead of discussing the complex pathophysiological mechanisms. Accordingly, we performed the current study to determine whether there is an inflammatory response in the contralateral eye after cataract surgery in the first eye and try to provide more insight into the pathophysiological mechanisms of this phenomenon.
SUBJECTSANDMETHODS
The Institutional Review Board of Shanghai East Hospital of Tongji University approved this paired-sample study[Clinical Trials identifier EC.D (BG).016.03.1]. All recruits provided written informed consent before enrollment, and we ensured that all patients clearly understood the purpose, the content, the accidents, the benefits as well as the risks of this study, we informed all patients that he or she could voluntarily make decisions to participate or not to participate and voluntarily withdraw from the research. All procedures adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki and were conducted in accordance with the approved research protocol.
SubjectsThis paired-sample study was conducted in Shanghai East Hospital of Tongji University between May 2018 and Oct 2018. Aqueous humor samples from 37 bilateral age-related cataract patients were collected just before each cataract surgery. Samples collected during the first-eye cataract surgery were marked as Group A, samples collected during the second-eye cataract surgery were marked as Group B. All cataract surgeries were performed by the same surgeon (Cui HP), and all patients were screened from bilateral age-related cataract patients according to strict inclusion criteria (eyes with glaucoma, uveitis, previous trauma or surgery, fundus pathology, or diabetes-related disorders were excluded from the study). Postoperative medication was as follows: Levofloxacin drops 4 times a day, Tobramycin Dexamethasone eyedrops 4 times a day, Tobramycin Dexamethasone ointment 1 time every night. All the eyedrops and ointment should be used exactly for one month.
SampleCollectionandTestRoutine disinfection, exposure of surgery field. Made the clear corneal incision at 10 o’clock, sideport at 2 o’clock, then aspirated aqueous humor (100-200 μL) through the sideport with an 1 mL syringe just before OVD injection. Samples were immediately stored at -80℃. Aqueous humor samples collected during the first-eye cataract surgery were classified into Group A. Aqueous humor samples collected during the second-eye cataract surgery were classified into Group B. In addition, the samples were classified into five small groups according to different intervals between the first- and the second-eye cataract surgery: the binocular operation time interval one week was marked as 1wk (5 patients, 10 eyes), the binocular operation time interval two weeks was marked as 2wk (11 patients, 22 eyes), the binocular operation time interval three weeks was marked as 3wk (10 patients, 20 eyes), the binocular operation time interval four weeks was marked as 4wk (5 patients, 10 eyes), the binocular operation time interval two months was marked as 2mo (6 patients, 12 eyes). Finally the concentration of 13 selected cytokines (including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, CCL2/MCP-1, IL-6 Rα, IL-1 ra, MIP-1α, MIP-1d, CCL4, IL-2, CXCL9, TIMP-1, CCL11) in aqueous humor samples was detected by Luminex-200 (RnD) simultaneously in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
LuminexTechnologyLuminex uses proprietary techniques to internally color-code microspheres with various fluorescent dyes. Through precise concentrations of these dyes, up to 500 distinctly colored bead sets are created, each of which can be coupled with a reagent specific to a particular bioassay. After an analyte from the test sample is captured by the bead, a reporter molecule, labeled with a different fluorescent dye, is introduced to complete the reaction on the surface of each microsphere. Next, the microsphere’s internal dyes are excited by the laser identifying the microsphere set and thus identifying the marker of interest. A second laser excites the fluorescent dye on the reporter molecule. Finally, high-speed digital-signal processors identify each individual microsphere and quantify the result of its bioassay based on fluorescent reporter signals. Immunoassays based on Luminex technology enable simultaneous detection and quantitation of multiple secreted proteins (cytokines, chemokines, growth factors,etc.) Compared with the traditional clinical detection techniques, Luminex has advantages of high-throughput, high-sensitivity, high-reproducibility, wide detection range, especially for minimal sample volumes. This high-throughput technology produces results comparable to ELISA but with greater efficiency and speed. Simultaneous determination of multiple target molecules can greatly reduce the consumption of biological samples and make the analysis of the correlation between multiple target molecules more accurate.
StatisticalAnalysisAll data are Mean±SD. Theχ2test was used to examine differences in categorical variables. Paired-samplet-test was used to detect differences between the first- and second-eye surgery groups. ANOVA analysis was used to detect differences between different operation-interval groups.Pvalues <0.05 were considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using SPSS software version 11.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
DemographicDataDemographic characteristics of the patients are presented in Table1 and Table 2. There were no statistically differences among the five operation-interval groups in terms of age or sex (allP>0.05, Student’s test for age;χ2tests for sex).
As the results showed, standard deviations of all selected cytokines in both Group A and Group B are relatively great, which means interindividual differences are significant. So paired-samplet-test was necessary to evaluate differences between the first- and second-eye surgery groups, in order to eliminate the difference among people. Among the 13 selected cytokines, there wasstatistically difference between two eyes in concentration of IL-6, MIP-1α, CCL2/MCP-1, TNF-α, MIP-1d, IL-2 and TIMP-1 (P<0.05), and the levels of these 7 cytokines in the second eyes were all higher than those in the first eyes. In addition, the concentration of IL-6 and MIP-1a in the second eyes was significantly higher than that in the first eyes (P<0.001, paired-samplet-test). Compared with the first eyes, the concentrations of CCL4, CCL11, IL-6Rα, CXCL9, and IL-1ra in the second eyes only showed slightly increase, while IL-8 showed a slight decrease, all with no statistically difference (allP>0.05) (Figure 1).
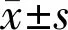
Table 1 Age analysis for patients of different operation-interval groups

Table 2 Gender analysis for patients of different operation-interval groups
To further explore the development of this inflammatory response,ANOVA analysis was used to detect significant differences of the seven cytokines (including IL-6, MIP-1α, CCL2/MCP-1, TNF-α, MIP-1d, IL-2 and TIMP-1) in different operation-interval groups. The results showed that the concentration differences of IL-6, MCP-1/CCL2, IL-2, MIP-1d between the first and second eyes were most obvious at the third week after PHACO+IOL in the first eye (Figure 2).
DISCUSSION
For the phenomenon that patients complain about more pain during their second eye surgery, lots of surgeons did find statistical difference of pain perception between the first and second eye phacoemulsifications[5,8-10]. As we referred above, most of the previous studies merely focused on subjective psychological mechanisms instead of the complex pathophysiological mechanisms.
Recent studies[7]which used the cytokine antibody array technique found that aqueous humor levels of MCP-1, a pain-related inflammatory chemokine, were significantly increased in patients undergoing cataract surgery on the secondaValues in boldface type indicate the cytokines that were found to be significantly different between the two groups (P<0.05).

Table 3 Actual concentrations of selected cytokines with Luminex-200 in the first eyes (Group A) and the second eyes (Group B)

Figure 1 Statistical difference (P Value) of different cytokines between the first eyes and second eyes (paired-sample t-test).

Figure 2 Cytokine level differences between the first and second eyes at different operation intervals (ANOVA analysis).
eye compared with those undergoing surgery on the first eye. However, they compared the first eye surgeries to the second eye procedures on separate groups of patients instead of sequential bilateral eyes, so inter-individual differences may have introduced a bias in the results. In our study, paired samples were used to compare the expression levels of multiple inflammatory cytokines, and the results showed that aqueous humor levels of IL-6, MIP-1α, CCL2/MCP-1, TNF-α, MIP-1d, IL-2 and TIMP-1 were increased in the second eyes compared with those in the first eyes. The results indicate that there may be an inflammatory response in the contralateral eye with changes of multiple cytokines in the aqueous humor after cataract surgery in the first eye. It was speculated that the disrupted integrity of the eye (blood-aqueous barrier damage, lens protein exposure,etc.) may lead to the exposure of intraocular antigens, causing immune response in the surgery eye as well as the contralateral eye after the first-eye cataract surgery, mimicking a sympathetic ophthalmia reaction, finally results in a more sensitive status in the contralateral eye.
Sympathetic ophthalmia (SO) is a rare, bilateral, non-necrotizing, granulomatous uveitis that occurs afterocular trauma or surgical procedures to one eye threatening sight in the fellow eye. The pathophysiology of SO is not clearly understood, but it appears that the disrupted integrity of the inciting eye leads to an autoimmune hypersensitivity reaction against the exposed ocular antigens in the injured eye as well as in the sympathizing eye[16-18]. Previous studies have shown that cellular immunity plays an important role in the development of sympathetic ophthalmia and autoimmune uveitis[16,19-20]. CD4+T cells (including Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg) and their secreted cytokines (including IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, TNF-α, INF-γ,etc.) play a significant role in the occurrence, development and the outcome of SO[21-22]. Th1 cells secrete cytokines including IL-2, TNF-α, INF-γ and IL-12, which mainly mediate cellular immunity and delayed type hypersensitivity, as well as participate in organ-specific autoimmune diseases[23]. Th2 cells secrete cytokines such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10 and IL-13, which promote the production of antibodies, participate in humoral immunity and typeⅠ hypersensitivity reactions.
The results of our study showed that there were statistical differences in the expression levels of IL-2, IL-6 and TNF-α between the first and second eyes (P=0.0170, 0.0007, 0.0064). Therefore, it is speculated that phacoemulsification combined with intraocular lens implantation (PHACO+IOL) may induce the Th cell-mediated autoimmune response in the contralateral eye due to the damage of the blood-aqueous barrier as well as the exposure of intraocular antigen. The elevation of a series of cytokines such as IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α may indicate an autoimmune uveal inflammatory response in the contralateral eye.
The current study also revealed that MCP-1 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1) was highly expressed in the contralateral eye after the first-eye cataract surgery (P=0.0013). This is consistent with previous studies. Zhuetal[7]analyzed the aqueous samples from 15 first-eye and 15 second-eye cataract patients by human cytokine antibody array. In their study, the expression of MCP-1 was increased significantly in the aqueous humor of patients undergoing second-eye cataract surgery compared to that in patients undergoing first-eye surgery (P=0.0067). MCP-1, also known as monocyte chemotactic and activating factor (MCAF) or chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2), is one of the pain-related inflammatory chemokines.MCP-1 can be produced by many cell types, especially monocytes and macrophages. It was the first C-C chemokine to be discovered and was perhaps the most extensively studied[24]. MCP-1 can exert various biological functions, such as recruiting monocytes, basophils and T cells to the site of inflammation, and inducing cells to express IL- 1, IL-6 and other cytokines, MCP-1 can also stimulate the release of histamine from basophils, playing an important role in the development of inflammatory diseases such as uveitis and neovascularization[7]. Studies have found that TNF-α, IFN-γ, MCP-1 and other inflammatory cytokines in patients with active Behcet disease abnormally increased, indicating that it may be closely related to the occurrence and development of autoimmune uveitis[24]. Therefore, it is suspected that MCP-1 may have a certain correlation with the uveal inflammatory response of the contralateral eye after the first-eye cataract surgery.
MIP-1α/CCL3 (macrophage inflammatory protein-1α) was a chemokine found in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage culture supernatants. MIP-1α is derived from a variety of cells, including monocyte macrophages, neutrophils, mastocytes, lymphocytes, and certain tumor cells. The biological activity of MIP-1α is very complex, mainly including the following aspects: chemotaxis of various inflammatory cells through the vascular endothelium into the site of inflammation; activation of cells, promoting their production of TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6,etc; stimulating eosinophil degranulation, basophils, mastocytes and plasma cells release histamine and inducing Th cell differentiation[16,25-27]. A recent study showed that MIP-1α/CCL3 may be associated with the occurrence of uveitis[22]. The results of our study showed that MIP-1α can be detected in both eyes, and there was significant difference in the concentration of MIP-1α between the first and second eyes (P=0.0008). Therefore, it is speculated that MIP-1α is related to intraocular inflammation and plays an inflammatory role in the contralateral eye after the first-eye cataract surgery.
As we referred, a large number of previous studies have shown that IL-2, MIP-1α, IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α and other cytokines are closely related to T lymphocyte-mediated autoimmune response or autoimmune uveitis, and these cytokines may interact in some way in the development of inflammatory response as well as pain perception. In connection with our study, a series of cytokines including IL-6, MIP-1α, CCL2/MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-2 were highly expressed in the contralateral eye after PHACO+IOL in the first eye, it was speculated that after the first-eye cataract surgery, the integrity of the eye was destroyed, leading to intraocular antigen exposure, causing slight autoimmune reaction in the surgery eye as well as contralateral eye, resulting in the contralateral eye being more sensitive to painful stimuli.
In addition, this study also showed that the concentration differences of IL-6, MCP-1/CCL2, MIP-1d, IL-2 between the first and the second eyes were most obvious at the third week after phacoemulsification combined with intraocular lens implantation (PHACO+IOL) in the first eye, which indicated that the inflammatory response in the second eye appears to be most significant at the third week after the first-eye cataract surgery.
In conclusion, considering the phenomenon thatpatients complain about more pain during their second eye cataract surgery, our current study indicates that there may be an inflammatory response in the contralateral eye after cataract surgery in the first eye, and this inflammatory response appeared to be most significant at the third week after phacoemulsification combined with intraocular lens implantation in the first eye.

