Facial and bilateral lower extremity edema due to drug-drug interactions in a patient with hepatitis C virus infection and benign prostate hypertrophy:A case report
Ya-Ping Li, Ying Yang, Mu-Qi Wang, Xin Zhang, Wen-Jun Wang, Mei Li, Feng-Ping Wu, Shuang-Suo Dang
Ya-Ping Li, Ying Yang, Mu-Qi Wang, Xin Zhang, Wen-Jun Wang, Mei Li, Feng-Ping Wu, Shuang-Suo Dang, Department of Infectious Diseases, Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China
Abstract
Key words:Direct-acting antivirals;Hepatitis C virus;Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir;Drug-drug interactions;Case report
INTRODUCTION
The emergence of second generation direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) has radically changed the landscape of treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.A once-daily, single-tablet, pange334notypic regimen comprising velpatasvir, a NS5A inhibitor of HCV viral ribonucleic acid replication and virion assembly, and sofosbuvir, a HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor, for 12 wk has proven highly effective and is well tolerated in all patients with chronic HCV genotype 1-6 infection[1].The single-tablet sofosbuvir/velpatasvir (Epclusa?) has well established pharmacological properties and achieves very high rates of sustained virological response at 12 wk post treatment in both treatment-na?ve and treatment-experienced individuals with chronic HCV genotype 1-6 infection[2].Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir is generally well tolerated and has low rates of adverse events.However, treatment of HCV infection in patients with comorbidities is a medical challenge.Evidence-based safety data are lacking regarding HCV treatment with DAAs and drugs for comorbidities.
In the current case report, we described the development of acute facial and bilateral lower edema in a patient with HCV infection and benign prostatic hypertrophy and a history of drug abuse who received sofosbuvir/velpatasvir,methadone and tamsulosin.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 46-year-old man with HCV infection and dysuria for 1 wk was referred to our department for HCV therapy assessment in September 2018.Genotyping revealed HCV 3b.Initial viral load was 5.8 lgIU/mL.Liver stiffness was 8.0 kPa by liver transient elastography (Fibroscan?).
History of present illness
At 8 wk later, the patient started taking oral tamsulosin hydrochloride (0.2 mg/d)because of dysuria.Forty-eight hours later, the patient complained of progressive bilateral lower extremity edema and facial edema, which did not change with posture.No redness or swelling was present, and there was no skin ulceration in the lower limbs.The patient did not complain of lower limb pain, and there was no limited range of motion of the lower limbs.High-resolution Doppler ultrasound of the arteries and veins of the lower limbs showed no flow alterations.
History of past illness
The patient had a history of intravenous drug abuse and received methadone maintenance therapy.He also took tamsulosin hydrochloride intermittently for benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH) during the past 3 years.
Physical examination
Physical examination at admission revealed no remarkable findings.
Laboratory examinations
The laboratory findings (Table 1) showed alanine aminotransferase at 118 IU/L(reference range <50 IU/L), aspartate aminotransferase at 66 IU/L (reference range <40 IU/L), gamma glutamyl transferase at 127 IU/L (reference range <60 IU/L) and creatinine at 53.26 μmol/L (reference range 57-111 μmol/L).Echocardiogram showed normal ejection fraction and diastolic function.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The final diagnosis of the presented case is chronic hepatitis C and benign prostatic hypertrophy.
TREATMENT
The patient was not contraindicated for methadone and sofosbuvir/velpatasvir and was started on antiviral therapy.Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir was administered at a fixeddose (100/400 mg) as a singlet tablet once daily for 12 wk.At week 1 of sofosbuvir/velpatasvir treatment, the viral load of the patient became negative.At week 8 of treatment (Figure 1), due to urination discomfort, the patient visited the urology department.Then, the patient was treated by tansoroxin hydrochloride, and antiviral treatment was continued.After 48 h of tamsolosin hydrochloride, edema appeared on the face and lower limbs of the patient.Tamsulosin hydrochloride was discontinued immediately.Oral furosemide (20 mg/d) and spironolactone (20 mg twice daily) were administered.The edema dissipated gradually after treatment and disappeared 10 d later.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
At 1 mo after antiviral treatment, his viral load was negative, and his liver function index improved (Table 1).He was re-started with tamsulosin hydrochloride after 12 wk antiviral treatment.No signs of edema were observed.
The current case report was approved by the local ethics committee of the authors’affiliated hospital (No.2018-1104).Patient data were anonymized in the report.
DISCUSSION
DAAs are highly effective and well tolerated and have radically improved the treatment of chronic HCV infection.However, each DAA has a unique metabolic profile and has an important potential for drug–drug interactions (DDIs).Chronic hepatitis C patients may have comorbidities and could receive multiple drugs along with DAAs and are therefore prone to potential DDIs[3].The current paper presents the first report of a potential DDI between DAAs and tamsulosin in a patient who developed edema of the lower limb following polypharmacy.
Many DAAs carry high DDI potential due to their metabolism by cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) or transport by P-glycoprotein (P-gp)[4].Velpatasvir is a pangenotypic HCV NS5A inhibitor and is administered in a fixed dose combination with sofosbuvir.Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir and methadone have different metabolic pathways[5,6].Sofosbuvir is a substrate of P-gp 14, and neither inhibits nor induces the CYP enzyme system, including inactive nucleoside metabolites of sofosbuvir.Velpatasvir is a substrate of P-gp, CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 and inhibits P-gp.Methadone is commonly used as an opioid substitute in patients with a history of drug abuse[7].Methadone binds to α1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) and is metabolized almost exclusively in the liver by type I cytochrome P450 enzymes, excluded mainly by P-gp[8].CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 are the main enzymes responsible for N-demethylation of methadone[9,10].The area under the curve for plasma velpatasvir is increased 30% when it is concurrently used with methadone[4].In addition, as an inhibitor of P-gp, velpatasvir may up-regulate effective concentration of methadone by restraining the transport of methadone[11].However, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir is safe and effective for HCV infection in patients who received methadone[12].Besides, there is no evidence that sofosbuvir/velpatasvir induces withdrawal syndrome.
Tamsulosin, an alpha-adrenoceptor blocker, is commonly used to treat BPH.Similar to methadone, tamsulosin binds to AAG and is extensively metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver[13].The metabolism of tamsulosin can be reduced when used together with methadone.Consequently, when two or more drugs that are metabolic substrates of the same CYP450 enzyme are administered concurrently, the drug that has the greater affinity for that cytochrome can inhibit the metabolism of the other drugs.Tamsulosin binds to AAG with higher affinity and could increase the effective concentration of methadone[14,15].
In the present case, facial and bilateral lower extremity edema emerged 48 h after concurrent treatment of tamsulosin with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir and methadone.Edema did not occur upon completion of antiviral treatment and continued tamsulosin therapy.Therefore, we have good reasons to speculate that edema was due to DDIs among sofosbuvir/velpatasvir, methadone and tamsulosin.A previous study reported systemic edema induced by methadone in a dose-dependent manner[16].Edema in this case could be the result of increased effective concentration of methadone by tamsulosin.
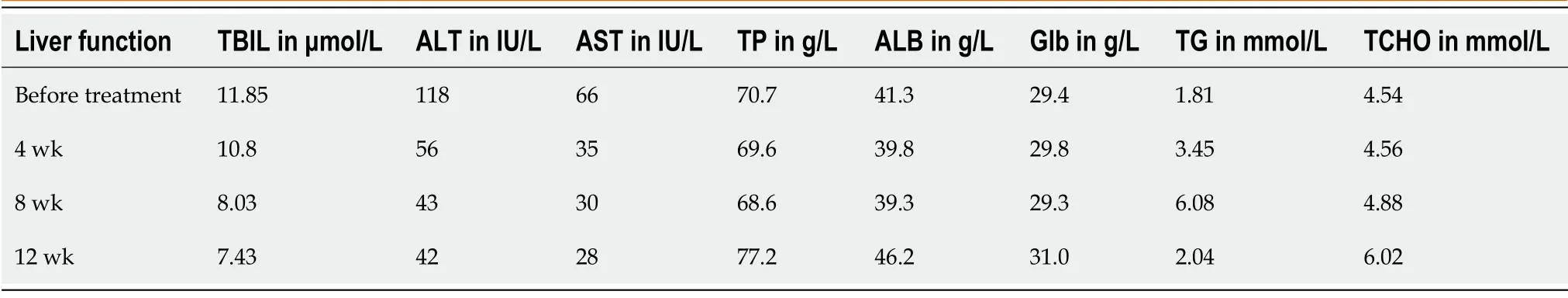
Table 1 Changes of liver function index before and after treatment
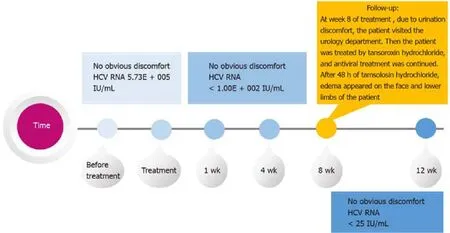
Figure 1 Timeline for the patient to develop symptoms and receive treatment.
CONCLUSION
This is the first case of acute bilateral lower extremity and facial edema in the course of treatment with DAAs, methadone and tamsulosin.These agents are useful in clinical management of patients with HCV infection, particularly in men with BPH.However,clinicians should be aware of potential DDIs in this subset of patients.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年15期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年15期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Total laparoscopic segmental gastrectomy for gastrointestinal stromal tumors:A case report
- COVID-19 with asthma:A case report
- Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and Fdeoxyglucose positron emission computed tomography/computed tomography findings of alveolar soft part sarcoma with calcification in the thigh:A case report
- Acute suppurative oesophagitis with fever and cough:A case report
- Coexistence of ovarian serous papillary cystadenofibroma and type A insulin resistance syndrome in a 14-year-old girl:A case report
- Imaging of hemorrhagic primary central nervous system lymphoma:A case report
