A relativistic canonical symplectic particlein-cell method for energetic plasma analysis
Yulei WANG (王雨雷), Feng YUAN (袁豐) and Jian LIU (劉健)
1 Department of Engineering and Applied Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, People’s Republic of China
2 School of Mathematical Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026,People’s Republic of China
Abstract A relativistic canonical symplectic particle-in-cell (RCSPIC) method for simulating energetic plasma processes is established. By use of the Hamiltonian for the relativistic Vlasov–Maxwell system, we obtain a discrete relativistic canonical Hamiltonian dynamical system, based on which the RCSPIC method is constructed by applying the symplectic temporal discrete method.Through a 106-step numerical test, the RCSPIC method is proven to possess long-term energy stability. The ability to calculate energetic plasma processes is shown by simulations of the reflection processes of a high-energy laser (1×1020 W cm-2) on the plasma edge.
Keywords: canonical symplectic method, relativistic particle-in-cell, energetic plasma(Some figures may appear in colour only in the online journal)
1. Introduction
Plasmas are complex multi-body and multi-scale systems involving complex electromagnetic interactions. Theoretical methods, such as the guiding center theory, the magnetohydrodynamic theory, and the kinetic theory, have been established in recent years to explain plasma processes.Although analytical methods are vital for plasma analysis,numerical simulations are inevitable for the study of plasmas.Among all the numerical methods, the particle-in-cell (PIC)method plays an important role.Established based on the idea of a first principle,the PIC method has become the first choice for simulating particle-field interaction processes, such as nonlinear Landau damping [1], laser-plasma interactions [2],and magnetic reconnections in plasmas [3]. In the 1970s,Birdsal provided a systematic study of the PIC method [4].After that, many works have been done to improve the performance and the accuracy of the PIC method. With the progress in the technical development of high-performance computers, PIC simulations using thousands of processors have become possible for high-resolution studies of plasma processes.
Like other numerical methods, digital errors exist in PIC simulations,which can stimulate unreal phenomena in results,especially in cases of multi-scale nonlinear processes. To reveal an accurate picture in both large and small space/time scales, high space/time sampling rates as well as long-term consistent simulations are necessary, in which global errors might grow rapidly. Most of the traditional algorithms, such as the Newton method and the Runge–Kutta method are built based on dealing with a Fourier series, which can produce high-order schemes and decrease local numerical errors in a one-step map.However,global errors cannot be controlled by these algorithms. In recent years, scientists have found an elegant way to control global errors, namely, by developing discrete numerical schemes that preserve the geometric structures of continuous systems [1, 5–31]. Solving Vlasov–Maxwell equations,that describe collisionless plasmas,is the kernel consideration when constructing PIC algorithms. The Hamiltonian structures of the Vlasov–Maxwell systems were studied in the 1980s [32–34]. After these original works,many structure-preserving PIC methods have been established [1, 6–11, 24], which can limit the increase of global errors without artificial interventions.




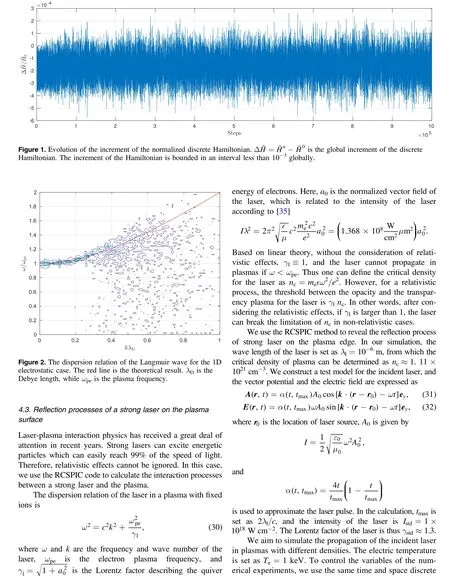

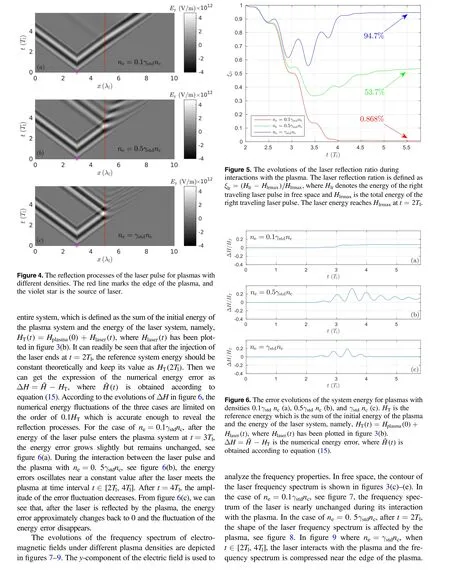
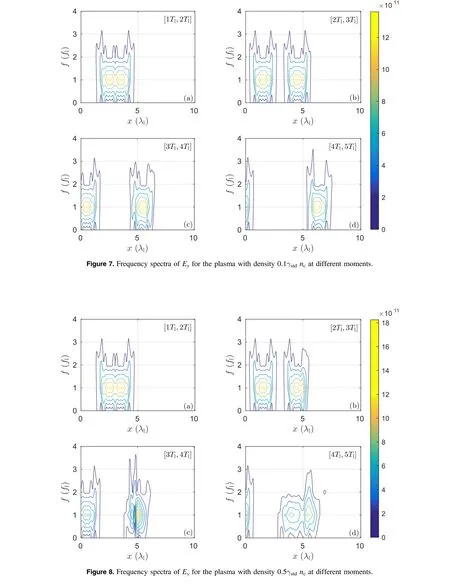
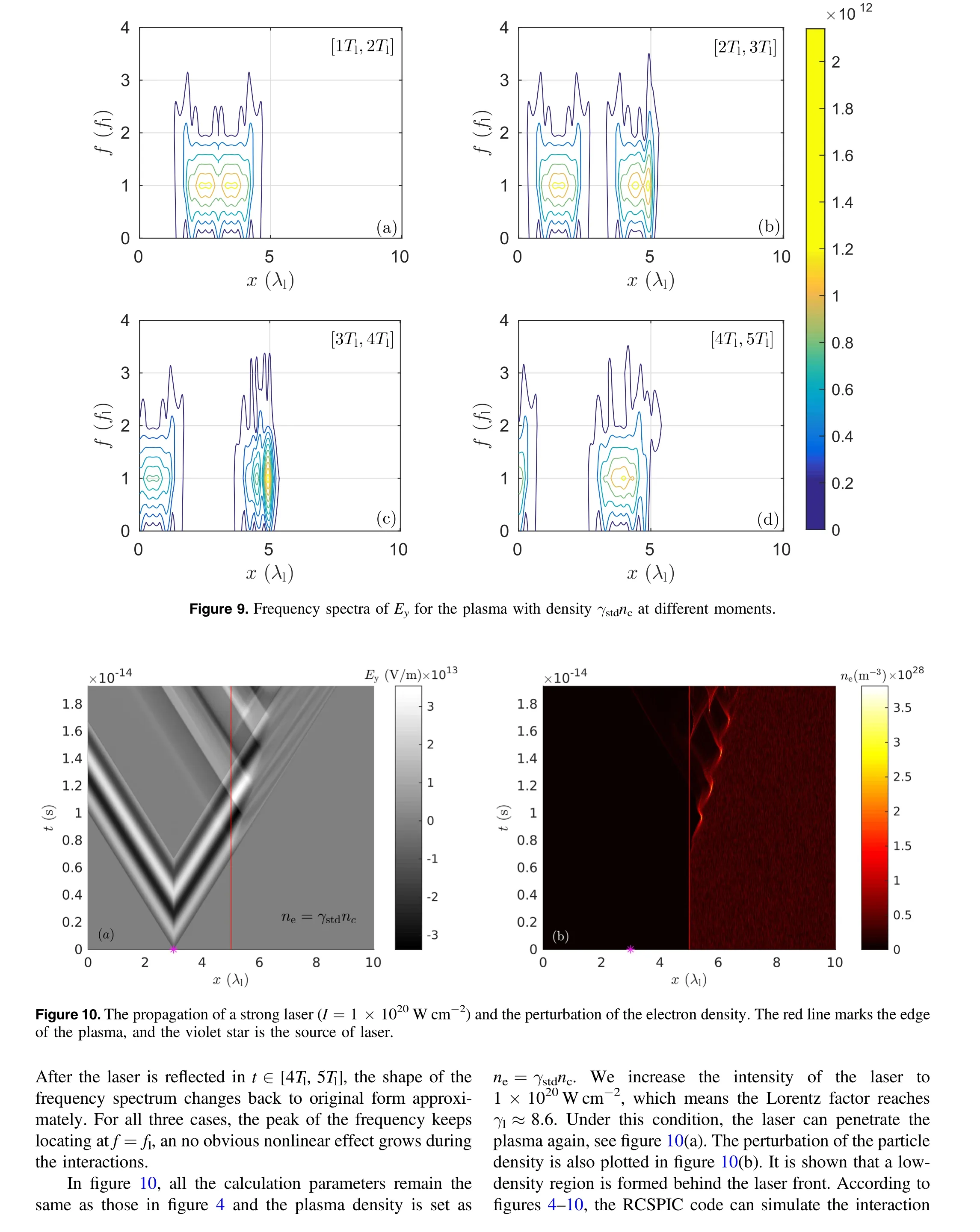
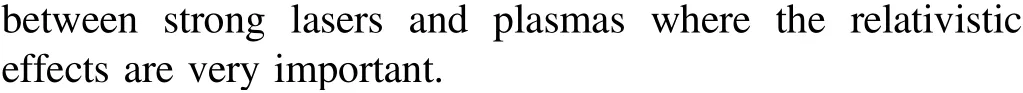
5. Conclusions
In this paper,we generalize the theory introduced by Qin et al[1] to the relativistic cases. The discrete Hamiltonian canonical dynamical equations for relativistic Vlasov–Maxwell systems are derived,based on which we obtain the relativistic canonical symplectic PIC algorithm. In mathematical derivations, we introduce all the physical constants to provide a clear picture of the discrete system. At the same time, we introduce some dimensionless variables, such as η, λ, to describe the relations between real charged particles and the sampling macro particles. We eliminate all the physical units through a normalization based on a set of standard units.The RCSPIC method then can be used directly to implement the PIC codes, see equations (26)–(29). A code based on the RCSPIC method is developed and tested by several symbolic processes. The secular energy stability is proven through a long-term plasma simulation that contains 106iterations. The dispersion relationship of the Langmuir wave in the electrostatic case is revealed correctly. The interactions between a strong laser (1×1018–1×1020W cm-2) and the plasma system is also simulated using the RCSPIC code. We also show that the density limitation of the laser and the reflection processes on the plasma edge can be simulated precisely,which proves the ability of calculating energetic plasma processes.
The structure-preserving algorithms have shown fantastic abilities in simulations of key basic plasma processes. The construction of the RCSPIC method modifies the canonical symplectic-preserving method of plasma kinetic theory to fit the relativistic simulations. The secular stability of energy is vital for simulations of nonlinear multi-scale processes.In the future, we will focus on the applications of the method in more physical areas, and improve the performance as well as the efficiency of the method at the same time.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(Nos.11805203,11775222,11575185),the National Magnetic Confinement Fusion Energy Research Project of China (2015GB111003), and the Key Research Program of Frontier Sciences CAS(QYZDB-SSW-SYS004).
Appendix
Here we provide the derivation of canonical relativistic Vlasov–Maxwell equation based on the Hamiltonian and canonical Poisson bracket given in equations(1)and(2).First,the functional derivatives of the Hamiltonian, i.e., equation (2),are
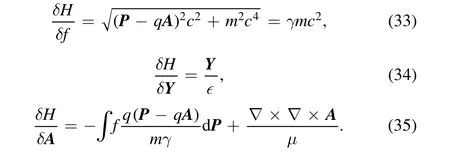
Equation (35) is obtained as follows. The variation of H in terms ofAis

which can directly give equation (35). In equation (36), the relation
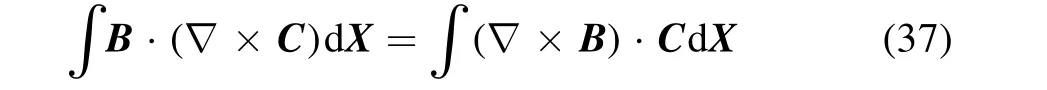
is used, which can be proven by

Here, ?ijkis the 3-dimensional Levi–Civita tensor.B X( ) andC X( ) are arbitrary vectors, and they vanish when →∞X∣ ∣ .
Using equation(1),equations(33)–(35),and considering thatδA(X′)δA(X) =δY(X′)δY(X) =δ(X′ -X), andδf(X′ ,P′)δf(X,P) =δ(X′ -X)δ(P′ -P),we can obtain the relativistic Vlasov–Maxwell equation,


 Plasma Science and Technology2020年6期
Plasma Science and Technology2020年6期
- Plasma Science and Technology的其它文章
- First-principles study on the mechanical properties and thermodynamic properties of Mo–Ta alloys
- Formation mechanism of Al2O3/MoS2 nanocomposite coating by plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO)
- Estimation of the sheath power dissipation induced by ion cyclotron resonance heating
- Influence of toroidal rotation on the tearing mode in tokamak plasmas
- Conversion between Vickers hardness and nanohardness by correcting projected area with sink-in and pile-up effects
- In-port-plug transmission line design of the ITER plasma position reflectometer
