差示掃描量熱法測定鈦合金的相變溫度
張業勤 丁小明 黃利軍 張文強
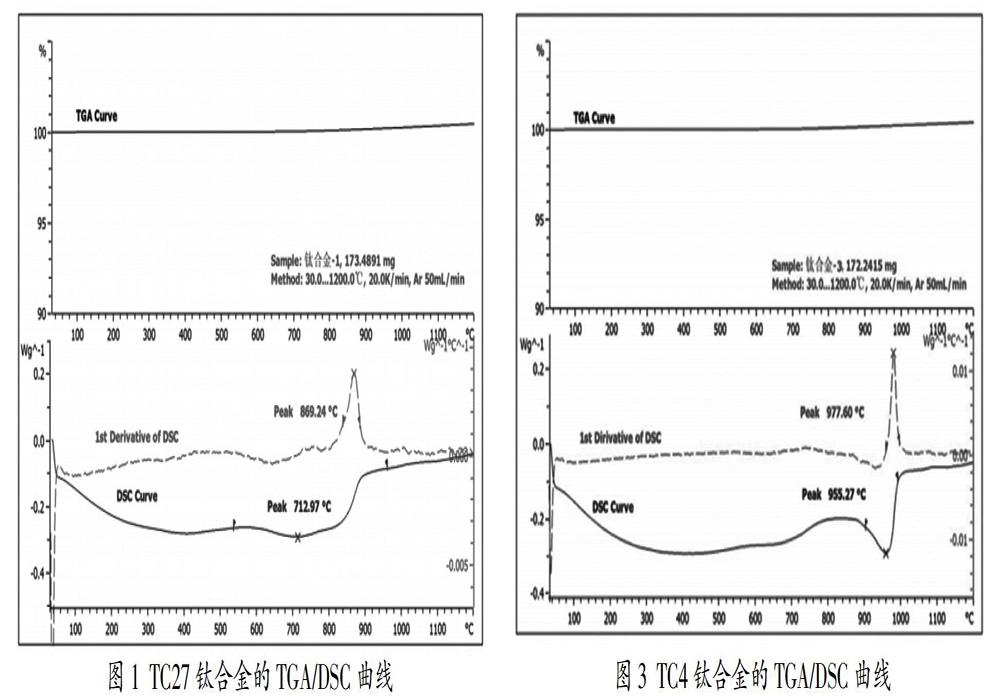
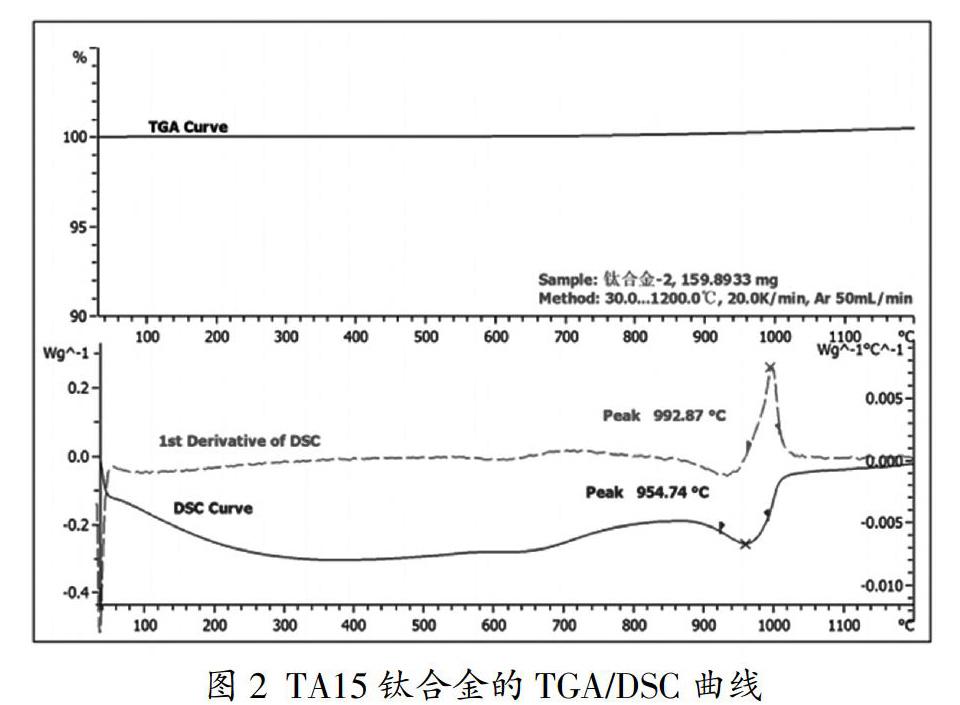
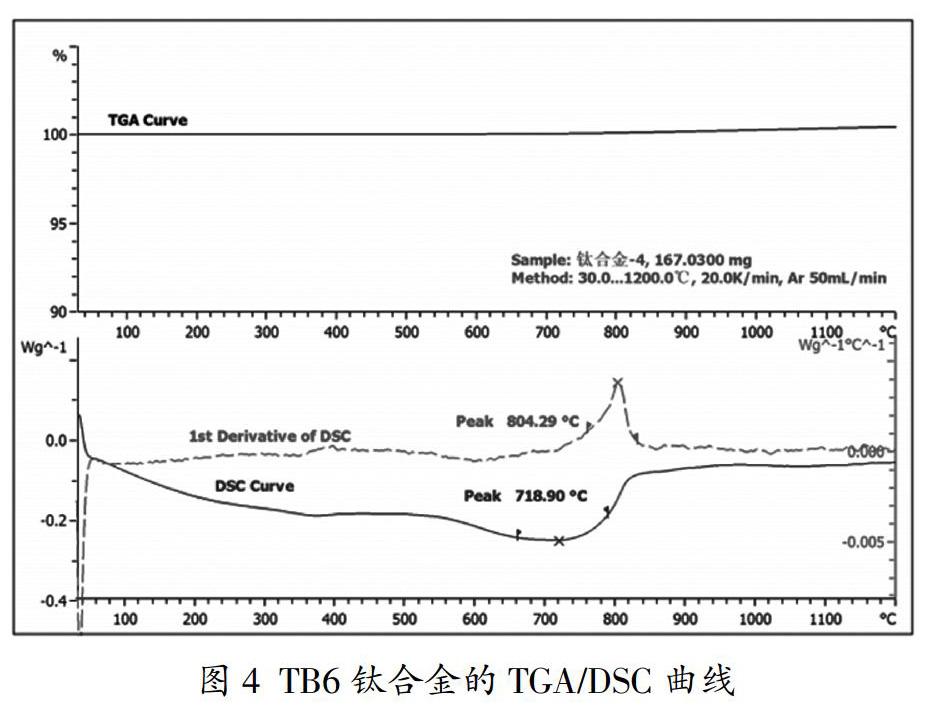
摘? 要:采用差示掃描量熱法測定了四種不同鈦合金TC27、TA15、TC4、TB6的?茁相變溫度。四種不同鈦合金的測試曲線體現出類似的規律,TG線一直保持不變說明升溫過程中沒有發生氧化反應,在500℃前由于釋放殘余應力呈現放熱現象,而在后向吸熱方向偏移,這個過程發生了相變。通過對DSC曲線求一階導數,其峰值即為?茁相變溫度。通過對比四種不同鈦合金差示掃描量熱法和金相法的測試結果,兩者相當接近,因此差示掃描量熱法也是一種有效的測試鈦合金?茁相變溫度的方法。
關鍵詞:差示掃描量熱法;鈦合金;?茁相變溫度;金相法
Abstract: The phase transition temperatures of four different titanium alloys TC27, TA15, TC4 and TB6 were measured by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The test curves of four different titanium alloys show a similar rule. The TG line remains constant all the time, which means that no oxidation reaction occurs during the heating process. Due to the exothermic phenomenon due to the release of residual stress before 500 ℃, it shifts backward to the endothermic direction. This process has undergone a phase transition. By calculating the first derivative of the DSC curve, the peak value is the phase transition temperature. By comparing the test results of differential scanning calorimetry and metallographic method of four different titanium alloys, the two methods are quite similar, so differential scanning calorimetry is also an effective method to measure the phase transformation temperature of titanium alloys.
鈦合金相變溫度是指在平衡狀態下α相剛好完全轉變為β相的溫度[1]。精確測定鈦合金的相變溫度對鈦及鈦合金加工和熱處理具有非常重要的意義,是制定最佳的材料熱加工變形參數和熱處理規范的依據[2]。差示掃描量熱法[3,4]可以記錄加熱或冷卻過程中熱流的變化,通過熱流變化分析出鈦合金的相變溫度。它是一種有效測試鈦合金相變溫度的方法[5],具有快速、高效、易于操作等特點。常規的DSC一般最高使用溫度在700℃左右,而近些年高靈敏度高溫DSC的發展及應用使得高溫測試鈦合金相變溫度成為可能,并使其測得的準確性得到大幅提高。
1 實驗
實驗所用的儀器為METTLER公司的TGA/DSC3/1600LF至尊型同步熱分析儀,可使用溫度范圍為:室溫~1600℃。實驗所用的樣品是分別從四種不同鈦合金TC27、TA15、TC4、TB6棒材上切取φ6mm×1~2mm的小圓柱。樣品編號及相變溫度如表1所示。……

