基于模型預測控制的智能車軌跡跟蹤控制研究
牛亞明 邵金菊 沈剛 李訓意 魏國

摘 要:為了完成智能車的軌跡跟蹤,提出一種基于模型預測控制的軌跡跟蹤方法,利用將運動學模型這個非線性系統線性化的方案,來獲得必須的線性時變系統,采取模型預測控制的三要素來設計控制器。并且基于MPC在控制過程中能增加多種約束的優點,建立基于車輛運動學模型的約束做軌跡跟蹤仿真實驗,最后,基于山東理工大學智能車平臺上GPS提供的定位信息,在校園中采集路線并對前提規劃好的的軌跡進行實車驗證。實驗結果表明:基于MPC算法所設計的控制器能快速且穩定地跟蹤期望軌跡。
關鍵詞:模型預測控制;線性化;軌跡跟蹤;定位
中圖分類號:U461 ?文獻標識碼:A ?文章編號:1671-7988(2020)06-34-03
Abstract: In order to complete the trajectory tracking of smart cars, a trajectory tracking method based on model predictive control is proposed. The linearization of the nonlinear system of the kinematic model is used to obtain the necessary linear time-varying system. The three elements of model predictive control are adopted. To design the controller. And based on the advantages that MPC can add a variety of constraints in the control process, a trajectory tracking simulation experiment is established based on the constraints of the vehicle kinematics model. Finally, based on the positioning information provided by the GPS on the intelligent vehicle platform of Shandong University of Technology, routes are collected on campus The real-world vehicle verification is performed on the trajectory planned in the premise. The experimental results show that the controller based on the MPC algorithm can track the desired trajectory quickly and stably.
Keywords: Model predictive control; Linearization; Trajectory tracking; Localization
CLC NO.: U461 ?Document Code: A ?Article ID: 1671-7988(2020)06-34-03
前言
模型預測控制(MPC)可以對系統輸出量進行反饋矯正,使誤差最小化來提高系統的魯棒性。本文率先建立了車輛的運動學模型,之后對其進行線性化得到相應的線性模型,再利用模型預測控制三要素預測方程建立、滾動優化以及反饋校正來設計控制器;實驗設計是以山東理工大學的哈佛H7改裝智能車為平臺處理的,最后試驗仿真及行車試驗,驗證控制效果。
1 車輛運動學模型的建立
在建立車輛運動學模型之前,要率先簡化汽車運動,以使得模型簡單易用,且能基本屬實的反映車輛特點和性能,為此自行車模型是首選。
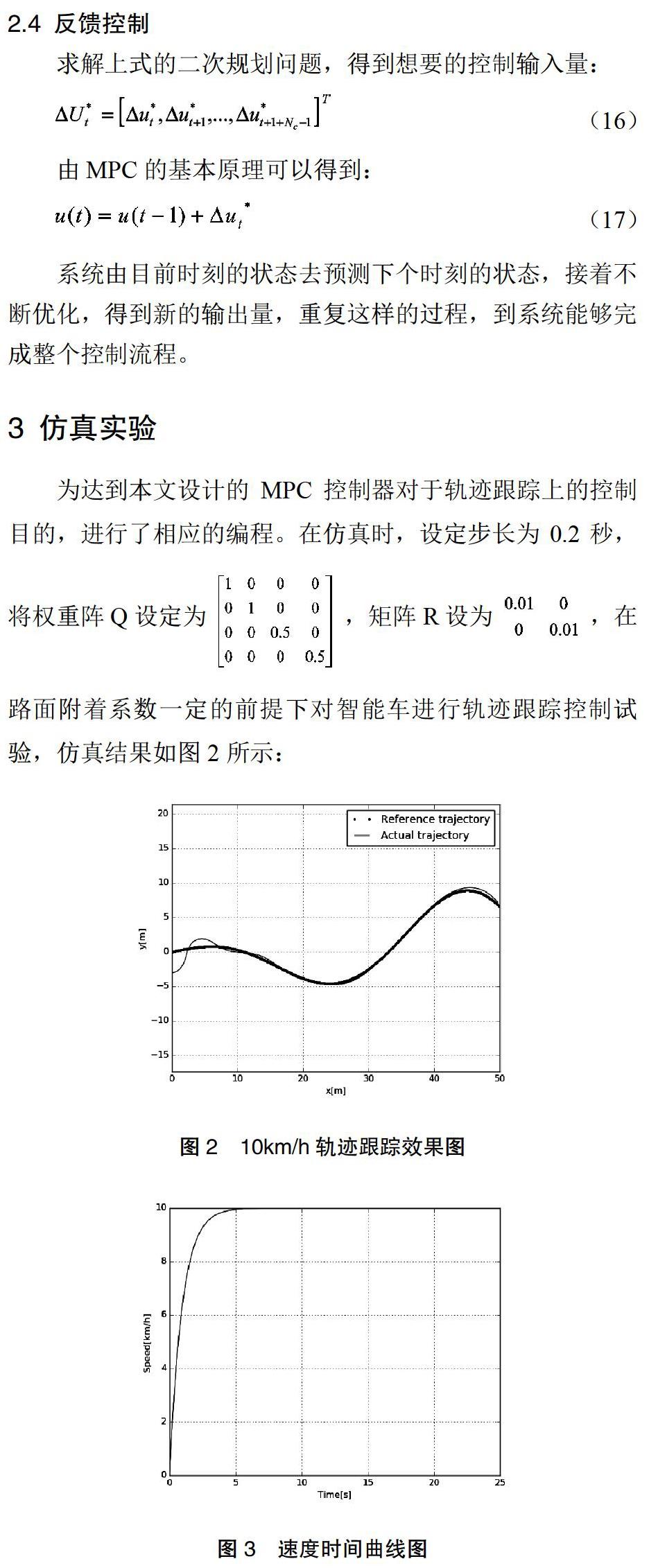
在仿真中,設置的汽車速度為10km/h,其中圖3中紅色的線段是智能車跟蹤的參考軌跡,也叫做期望軌跡,藍色線段是汽車實際在跟蹤過程中行駛軌跡;圖6是速度時間變化曲線,從圖中可看出,汽車速度從0開始加速,一直加速到10km/h,之后不再變化。
從仿真結果可知,智能車在模型預測控制器的作用下能夠能夠在低速運動時比較快速且很準確的跟蹤上期望軌跡。
4 結論
實驗證明,本文所設計的模型預測控制器使得車輛在中低速時可以具有良好的魯棒性,很好的實現了在校園規定路徑下的軌跡跟蹤實驗。
參考文獻
[1] 車輛起步MPC控制器設計及FPGA實現[J].許月亭,陳虹,季冬冬,許芳.控制工程. 2015(05).
[2] Linear time-Varying Model Predictive Control and its Application to Active Steering Systems: Stability Analysis and Experimental Validation[J].P.Falcone,F.Borrelli,H.Multi-Objective Control Synthe -sis: an Application to 4WS Passenger Vehicles[J].S.-S. You,Y.-H. Chai. Mechatronics . 1999 (4).
[3] 基于模型預測控制的無人駕駛車輛軌跡跟蹤控制算法研究[D]. 孫銀健.北京理工大學,2015.
[4] Optimal Synchronous Trajectory Tracking Control of Wafer and Reticle Stages[J].王春洪,胡金春,朱煜,尹文生.Tsinghua Science and Technology. 2009(03).
[5] 趙潔.智能車輛的路徑跟蹤及底層控制研究[D].吉林大學,2018.
[6] 王藝,蔡英鳳,陳龍,王海,何友國,李健.基于模型預測控制的智能網聯汽車路徑跟蹤控制器設計[J/OL].機械工程學報.
[7] 段建民,田曉生,夏天,宋志雪.基于模型預測控制的智能汽車目標路徑跟蹤方法研究[J].汽車技術,2017(08):6-11.
[8] 焦巍,劉光斌.非線性模型預測控制的智能算法綜述[J].系統仿真學報.
[9] Gong P, Yang J, Ma C, et al. Research on Multi-Point Monitoring Anti-Collision System for Vehicle Auxiliary Driving[J].Optik- Inter -national Journal for Light and Electron Optics, 2016, 127(18):7121 -7127.
[10] 模型預測控制[M].科學出版社,陳虹,2013.

