Two bone blocks sandwich technique for horizontal reconstruction of severely atrophic alveolar ridge in anterior maxilla:A case report
Hai-Bin Xia,Yu-Feng Zhang,Bin Shi,Min Wang
Abstract
Key words: Horizontal bone resorption; Onlay bone graft; Sandwich; Dental implant;Esthetic; Case report
INTRODUCTION
Alveolar bone resorption is progressive and unavoidable following tooth loss[1,2].Particularly in the maxillary anterior esthetic zone,horizontal bone loss occurs faster than vertical bone loss to a great extent,which makes the installation of dental implants a major challenge[3].
In the past decades,various clinical approaches have been developed for horizontal alveolar reconstruction of the atrophic alveolar ridge,including onlay bone graft,alveolar ridge splitting,and guided bone regeneration[4-6].Onlay bone grafting with delayed implant placement is the preferred treatment option in severe atrophy of the alveolar ridge,when the available alveolar width is less than 4 mm[7,8].However,this treatment also has some complications,such as extended surgical time,cost,discomfort to patients,bone resorption and nerve damage or morbidity[9,10].Alveolar ridge splitting is an alternative treatment option for augmenting horizontal bone defects comprising triangular V-shaped crests with adequate bone height[6].The main complication of alveolar ridge splitting is fracture of the buccal plate,which forces the surgeon to use an onlay bone graft to finish the bone augmentation procedure[11].
In addition,the combination of bone substitute materials and titanium mesh could be an alternative treatment option for patients with severe maxillary anterior horizontal bone deficiency.However,the gingival tissues are prone to dehiscence and the titanium mesh is then exposed,especially in thin gingival biotype,which can lead to local infection and surgical failure[12,13].
A number of different materials used in bone augmentation,such as autogenous grafts,allografts,xenografts and alloplastic grafting materials,have been documented in the literature[4,14,15].Of these materials,autogenous bone graft harvested from intraor extraoral sites has been considered the “gold standard” for the augmentation of bone thickness[16],because it contains excellent osteoinductive,osteogenic and osteoconductive components and has a physical and chemical structure identical to that of host sites without any immunologic reactions[17].
This clinical report describes a two bone blocks sandwich technique (TBBS) to restore a missing right maxillary incisor with severe horizontal bone deficiency with available bone width of 3.1-4.0 mm.A schematic illustration of the procedure is shown in Figure 1.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 22-year-old female patient presented to the dental clinic at Wuhan University with a missing maxillary right central incisor (tooth 11).
History of present illness
The maxillary right central incisor in the patient was restored with a porcelain fused metal (PFM) crown after root canal treatment several years ago.The tooth was extracted 1 year ago due to restoration failure.

Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the two bone blocks sandwich technique.
History of past illness
The patient was in good condition,and she denied tobacco use.
Personal and family history
The patient denied personal or family history.
Physical examination upon admission
The patient’s blood pressure was 103/52 mmHg with a pulse rate of 78 beats per minutes (bpm).The level of the gingival margin of tooth 11 was lower than that of tooth 21 and a localized soft tissue collapse was observed from the occlusal view(Figure 2).The gingival margin of tooth 21 was red and swollen,and tooth 21 was restored with a PFM crown.
Laboratory examinations
The routine blood count and coagulation profile were within normal limits.
Imaging examinations
Examination by cone beam computer topography (CBCT) showed that the available bone height was 18.9 mm and the available bone width was 3.1-4.0 mm (3.1 mm at the marginal level,3.4 mm at 5 mm apically and 4.0 mm at 10 mm apically) (Figure 3).
1)農機裝備水平高。主要表現為裝備標準高,配套農具數量多;科技含量高,自動化、智能化、機電液一體化程度高。
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Maxillary dentition defect; gingivitis of tooth 21.
TREATMENT

Figure 2 Preoperative intraoral photos.
A staged approach for implant insertion was planned following alveolar augmentation using an autogenous bone block.Her informed consent was obtained for treatment before surgery.Supragingival scaling was performed one week prior to surgery.The patient was instructed to take 2 g amoxicillin 1 h before surgery.On the day of surgery,the patient was asked to rinse her mouth with a chlorhexidine digluconate solution (0.12%) for 5 min.Local anesthesia was administered using local infiltration of articaine with adrenaline (1/100000).A midcrestal incision and two buccal vertical releasing incisions distal to the adjacent tooth were made.A full thickness mucoperiosteal flap was reflected to expose the whole alveolar ridge.The width of the alveolar ridge was approximately 3 mm measured by a periodontal probe.A small bone block (5 mm in depth) was harvested from the apical of tooth 11 with a 5.0 mm diameter trephine (Figure 4A).A large bone block (11 mm × 5 mm) was then prepared at the alveolar ridge of tooth 11 using Piezosurgery with copious saline irrigation (Figure 4A).The small bone block was placed at the alveolar ridge as a“sandwich” between the free large bone block and the residual palatal bone plate.The large bone block was gently fixed using a miniature titanium screw with a diameter of 1.5 mm (Figure 4B).Deproteinized cancellous bovine bone (Bio-Oss; Geistlich Pharma,Wolhusen,Switzerland) was wetted using blood.The grafting materials were then delivered into the gaps between the buccal and palatal bone plate and donor site.Resorbable collagen membrane (Bio-Gide; Geistlich Pharma,Wolhusen,Switzerland)was used to cover the bone blocks and the donor site.In addition,upper lip frenulum extension was performed.Postoperative instructions and antibiotics were given to the patient.
After 6 mo,the newly formed alveolar ridge dimension increased to 4.7-9.5 mm horizontally with total filling of the defect observed by CBCT (4.7 mm at the marginal level,7.8 mm at 5 mm apically and 9.5 mm at 10 mm apically) (Figure 5).The level of the gingival margin of tooth 11 was still lower than that of tooth 21.The contour of the soft tissue was full,and it was almost symmetrical to that of tooth 21 (Figure 6A).A surgical re-entry was performed with full thickness flap reflection.The osteogenesis outcome of the TBBS was obvious (Figure 6B).The micro titanium screw was removed.A dental implant (3.3 mm × 12 mm; SLActive,Straumann,Switzerland) was placed using the conventional two-stage approach.Periapical X-ray indicated that the implant was in the correct position (Figure 7A).
A second-stage surgery was performed 2 mo later,and a healing abutment was connected.The old PFM restoration of tooth 21 was removed and a final impression was taken simultaneously with tooth 11.All-ceramic cement-retained restorations were used.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
The implant was stable at the 1-year follow-up visit after restoration (Figure 8A and B).Periapical X-ray showed a stable bone level around the dental implant at the 1-year follow-up visit compared to the periapical X-ray after restoration (Figure 7B and C).According to the literature,the esthetic outcome of the soft tissues in the reconstructed zone was analyzed from clinical photography at the 1-year follow-up using a pink esthetic score (PES) scaling including 7 variables:(1) Formation of the mesial papilla; (2) Formation of the distal papilla; (3) Level of the gingival margin; (4)Form of the gingival margin; (5) Form of the alveolar process; (6) Contour of the keratinized mucosa/soft tissue; and (7) The soft tissue color[18].Also,the white esthetic score (WES) of the crown was analyzed according to the literature[19],the variables included:(1) Tooth form; (2) Tooth outline/volume; (3) Tooth color; (4) Tooth surface texture; and (5) Tooth translucency/characterization.The scores for PES and WES were 12 and 8,respectively.Fortunately,the smile line of this patient was moderate.The patient was very satisfied with the esthetic outcome.
DISCUSSION

Figure 3 Preoperative cone beam computer topography cross-sectional view of tooth 11.
Restoration of a missing maxillary incisor with severe horizontal bone deficiency is an esthetically challenging job,as rehabilitation of the anterior maxilla with dental implants demands not only a functional outcome but also a good esthetic result.Sufficient alveolar bone contour and volume are prerequisites for implant-supported esthetic restoration in the maxillary anterior region.Various clinical techniques have been used to increase the bone volume of the severe horizontal atrophic alveolar ridge to meet the demands of dental implantation.A previous study compared the increased bone width of autogenous onlay bone grafts and alveolar ridge splitting,and the results showed that the final bone width in the autogenous onlay bone graft group was significantly higher than that in alveolar ridge splitting group[20].According to the decision tree of horizontal bone augmentation,the alveolar bone width for the ridge splitting technique is more than 4 mm[3].
In this case report,the TBBS technique was used to restore severe horizontal bone deficiency.The TBBS technique refers to two autogenous bone blocks harvested from alveolar bone in the maxillary anterior edentulous region,including one small bone block and one large bone block.The large bone block is derived from the labial cortical bone of the edentulous area with a mesial-distal interval of 5-6 mm.The small bone block with a diameter of 5 mm is harvested from the apical zone of the large bone block,and it is sandwiched between the large bone block and the palatal bone plate.The small bone block is placed at the ridge of alveolar bone to increase the width and prevent soft tissue from collapsing.In addition,the free large bone block is overlaid on part of the small bone block and part of the apical cortical bone,as shown in Figure 1.One miniature titanium screw with a diameter of 1.5 mm is then used to gently fix the large bone block.The diameter of the miniature titanium screw is much narrower than those of the two grafted bone blocks; therefore,the grafted bone blocks are not vulnerable to breaking with insertion of the miniature titanium screw.In addition,the small bone block plays a supportive role in fixation of the large bone block,so only one miniature screw was used in this case without any micromovement of the large bone block.Compared to the traditional autogenous onlay bone graft,the TBBS technique had several advantages.First,there was no donor injury.Second,the operation time was shortened.Third,no risk of nerve injury or morbidity occurred with this technique.In addition,the postoperative reaction in the patient was moderate.This TBBS technique conformed to the principle of minimally invasive surgery.
A previous study indicated that one of the main disadvantages of a horizontal augmentation using an autogenous bone block graft was significant bone resorption during bone healing[10].The mean volume of resorption ranged from 35% to 51%[21].The use of bovine bone particles together with a resorbable membrane was suggested to minimize resorption of the autogenous bone block graft[5,22].Therefore,TBBS combined with Bio-Oss bone substitute and resorbable collagen membrane was used in this case to offset the bone resorption.In addition,many marrow cavities were open after removal of the large bone block.Bone marrow stromal cells and precursor osteoblasts were exposed.Various cytokines and growth factors were released by rich blood to facilitate bone formation.Greenberget al[23]applied an intraoral autogenous bone block in the atrophic anterior maxilla,and the mean alveolar width gained at the margin and 7 mm apically were 4.16 mm and 5.25 mm,respectively.Monjeet al[5]used a mandibular ramus bone block to augment a severely atrophic maxillary anterior ridge and a mean gain of 3.23 mm in bone width was obtained.Another clinical study using iliac crest showed that the horizontal bone gained was 2.7 mm at the marginal level and 5.0 mm at 5 mm apically[8].In this case after 6 mo healing,the CBCT images showed that the horizontal bone gained was 1.6 mm at the marginal level,4.4 mm at 5 mm apically and 5.5 mm at 10 mm apically.These results are consistent with previous clinical studies.In addition,the soft tissue contour of tooth 11 was almost symmetrical to that of tooth 21 due to a sufficient alveolar bone contour and volume after TBBS bone augmentation.

Figure 4 The two bone blocks sandwich technique surgical procedure.
The profile of the soft tissue around dental implants was determined by the morphology of the alveolar bone[8].The morphology of bone deficiency in this case was only a horizontal defect without a vertical defect.Moreover,the soft tissue levels of tooth 11 before and after bone augmentation were lower than tooth 21,which was beneficial to the soft tissue closure of the bone augmentation and the final PES outcome.The PES and WES scores in this case were 12 and 8,respectively.This was a satisfactory result according to Cosynet al[24],who set the thresholds for clinical acceptance at a value of 8/14 for PES and 6/10 for WES.
To our knowledge,this is the first clinical report using the TBBS technique for reconstruction of a severely atrophic anterior maxilla.However,the TBBS technique cannot be used in all severe horizontal bone defects as it is a highly sensitive technique.The following conditions should be met in order to use this technique:Firstly,horizontal bone resorption occurs after tooth loss without vertical bone resorption in the maxillary anterior region; secondly,the available bone height is sufficient,and the available bone width is more than 3 mm with cancellous bone;thirdly,the mesial-distal interval is more than 6 mm; fourthly,the two bone blocks must be fixed appropriately and the fixation cannot be too tight; finally,the soft tissue should be closed without tension.Only based on these prerequisites can the best outcome be achieved using the TBBS technique.
CONCLUSION
Within the limitations of the present case,the TBBS technique may be an alternative treatment option in augmenting severe horizontal bone deficiency of the anterior maxilla.
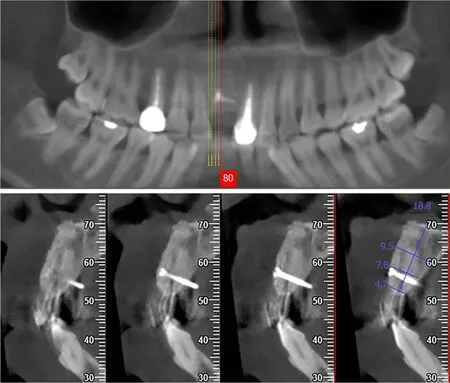
Figure 5 Cone beam computer topography cross-sectional view at 6 mo after the two bone blocks sandwich technique.

Figure 7 Periapical image at different times.
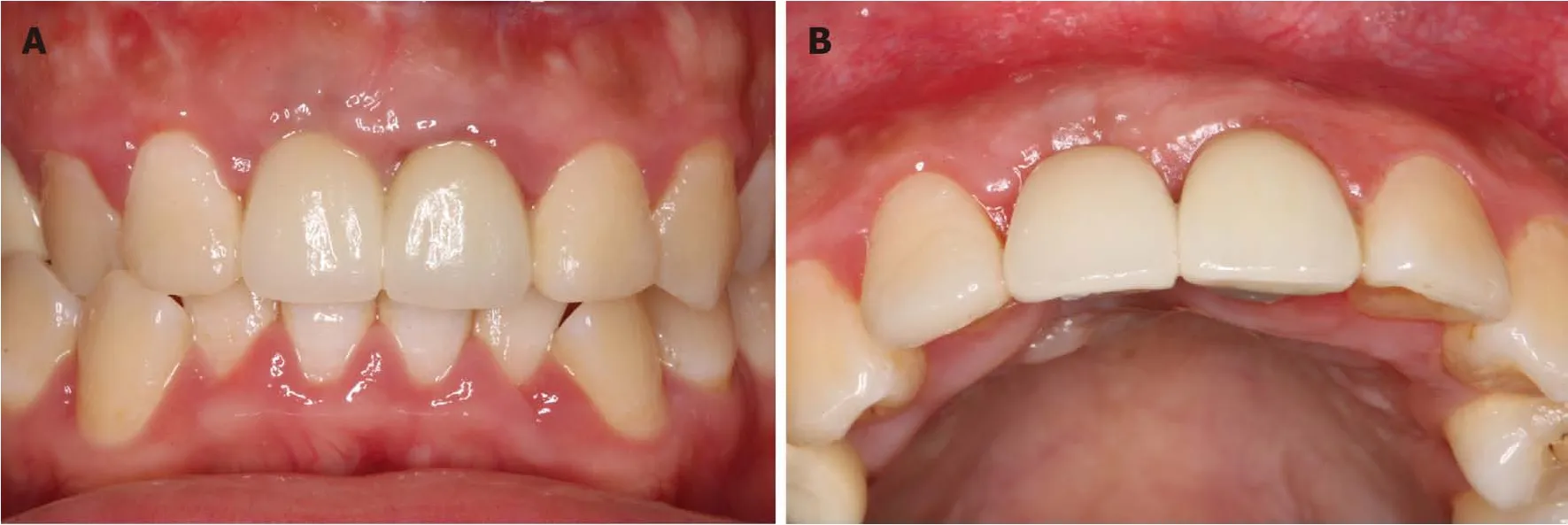
Figure 8 lntraoral photos at 1-year follow-up.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年6期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年6期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Late-onset multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency with cardiac syncope:A case report
- Misdiagnosis of primary intimal sarcoma of the pulmonary artery as chronic pulmonary embolism:A case report
- Anomalous retinal artery associated with branch retinal artery occlusion and neovascular glaucoma:A case report
- Muscular involvement of extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma misdiagnosed as polymyositis:A case report and review of literature
- Total endovascular repair of an intraoperative stent-graft deployed in the false lumen of Stanford type A aortic dissection:A case report
- Extrapontine myelinolysis caused by rapid correction of pituitrin-induced severe hyponatremia:A case report
