黑土養分含量的航空高光譜遙感預測
楊越超,趙英俊,秦 凱,趙寧博,楊 晨,張東輝,崔 鑫
黑土養分含量的航空高光譜遙感預測
楊越超1,趙英俊1,秦 凱1,趙寧博1,楊 晨2,張東輝1,崔 鑫1
(1. 核工業北京地質研究院遙感信息與圖像分析技術國家級重點實驗室,北京 100029;2. 武漢大學城市設計學院,武漢 430072)
為監測黑龍江省黑土典型區土壤的養分元素含量,綜合利用統計理論與光譜分析方法,研究建三江農場黑土土壤的3類養分含量與土壤光譜之間的關系,建立土壤全氮、有效磷、速效鉀含量高光譜反演模型,實現土壤養分元素含量定量預測。對黑土土壤航空高光譜數據進行處理,應用偏最小二乘回歸(PLSR)和BP神經網絡方法分別建立土壤養分元素含量的高光譜定量反演模型,結果表明:全氮PLSR和BP神經網絡預測模型的RPIQ值(樣本觀測值第三和第一四分位數之差與均方根誤差的比值)分別為2.42和2.80;有效磷PLSR和BP神經網絡模預測型的RPIQ值分別為0.83和1.67;速效鉀PLSR和BP神經網絡模型的RPIQ值分別為2.00和2.33。試驗證明土壤全氮和速效鉀的光譜定量預測模型具備較好的精度和預測能力。但有效磷的預測效果不是特別理想,僅可達到近似定量預測的要求;全氮、有效磷和速效鉀的預測精度,BP神經網絡建模相比偏最小二乘建模有更好的精度和預測能力,預測精度分別提高6.5%、10.1%和6.6%。
土壤;遙感;模型;偏最小二乘法;BP神經網絡
0 引 言
土壤是植物生長養分的主要來源,尤其是土壤有機質、氮、磷、鉀元素對植物生長具有重要的作用[1]。植物需要大量的氮素合成蛋白質;磷能促進植物根系的形成和生長,鉀能夠促進光合作用。土壤中主要養分(全氮、有效磷和速效鉀)的含量是重要的農作物產量影響指標,是指導農業科學施肥的重要依據[2]。中國東北地區發育有全球非常重要的黑土地資源。黑土因土壤性狀好、肥力高,非常適合糧食作物生長。快速準確獲取黑土地土壤主要養分的含量,已然成為東北黑土區精準農業發展的必然需要[3]。
目前測量3類土壤養分主要采用實驗室化學方法,利用某些試劑溶液提取土壤中養分相對值加以測定[4],傳統方法工作量大、周期長,難以滿足現代農業快速發展的需要。隨著GIS及遙感技術的發展,多光譜影像解譯也在農業信息監測中得到了一定程度的應用,在具備現勢性強特點的同時,多光譜技術受制于譜段間隔較寬及環境干擾值的影響,一定程度上反演精度受限[5-6]。而通過高光譜技術反演土壤養分對于土壤信息快速測定具有重大意義[7]。國內外學者應用高光譜針對土壤礦物成分、水分及有機質等開展了一些定量研究,350~2 500 nm波段高光譜數據能映射一些土壤理化參數的微小差別,水分、有機質及鐵氧化物的含量與土壤反射率存在一定明顯的對應關系[8-10],可建立定量反演的預測模型[11]。綜合來看,氮、磷、鉀的高光譜分析預測研究相對較少,土壤中各類養分元素與光譜也存在較復雜的對應關系[10-11]。以往研究多數利用ASD FieldSpecPro地物光譜儀在室內或野外采集點狀數據研究光譜養分對應關系并建立估測模型[12-14],對于大面積土地光譜數據測量效率低,同時模型建立有較大的隨機性,不足以平衡局部和全局最優的問題,還需進一步挖掘土壤光譜信息[15-16]。
為提高黑土土壤養分信息定量預測的效率與精度,筆者將基于建三江地區航空高光譜遙感數據,在分析研究土壤光譜特征基礎上,利用偏最小二乘回歸和BP神經網絡分別建立黑土地土壤3類養分(全氮、有效磷和速效鉀)含量高光譜反演模型,探索快速測定黑土土壤養分的方法。
1 數據的獲取與處理
1.1 研究區概況
研究區位于黑龍江省佳木斯市建三江管理局七星農場(見圖1)。地處47°01′~47°10′ N,132°43′~133°02′ E,面積約380 km2;位于黑龍江、松花江和烏蘇里江交匯河間地帶,水資源豐富。區內分布著黑鈣土、黑土、沼澤土、草甸土和水稻土等。土壤成土母質主要為黃土狀粉質黏土、淤泥質粉質黏土[17]。隸屬中溫帶大陸性季風氣候。平均海拔50 m,耕地集中成片,地勢平坦,適宜現代農業規模化經營。

圖1 研究區地理位置及采樣點示意圖
1.2 航空高光譜數據采集及處理
野外航空高光譜數據采集使用CASI-1500和SASI-600線陣推掃型成像光譜儀器,空間分辨率分別為1.5和3.75 m,總視場角40°,每行像元數1470,絕對輻射精度小于<2%。波段范圍分別為380~1 058 nm和950~2 450 nm,波段數分別為72和100,光譜分辨率分別為9.3和15 nm[18]。地面鋪設黑白布,采用ASD FieldSpecPro光譜儀獲取定標光譜,其光譜范圍為350~2 500 nm,光譜分辨率為1 nm。
將航空高光譜原始輻射數據進行定標、大氣輻射校正,利用POS 510系統進行幾何校正。經過光譜去噪、重采樣、歸一化和包絡線去除等預處理,獲得地表反射率數據。進一步對光譜應用Savitzky-Golay方法選取3個像元為窗口進行平滑濾波,并進行一階微分、對數變換和去連續統處理,突出分離光譜變化趨勢和光譜吸收谷。
1.3 土壤樣品采集
野外土壤樣品采樣深度5~15 cm,選取耕地地塊中心,土壤裸露區域,清除表層雜草、礫石等雜質。為增加樣本代表性,采樣時以采樣點為中心原點,周圍15 m范圍內多點采集3~5個子樣進行組合,混合后留取1.5 kg,共采集96組。經過風干、拌勻、研磨后,過200目篩后用于實驗室測試。元素含量采用NaOH擴散法(N)、NaHCO3浸提-鉬藍比色法(P2O5)和NH4OAC浸提-火焰光度法(K2O)測定,參考Kennard-Stone法選取72組代表性樣品作為養分元素預測的建模樣品,24組為模型預測樣品[19]。其各元素統計特征描述見表1。
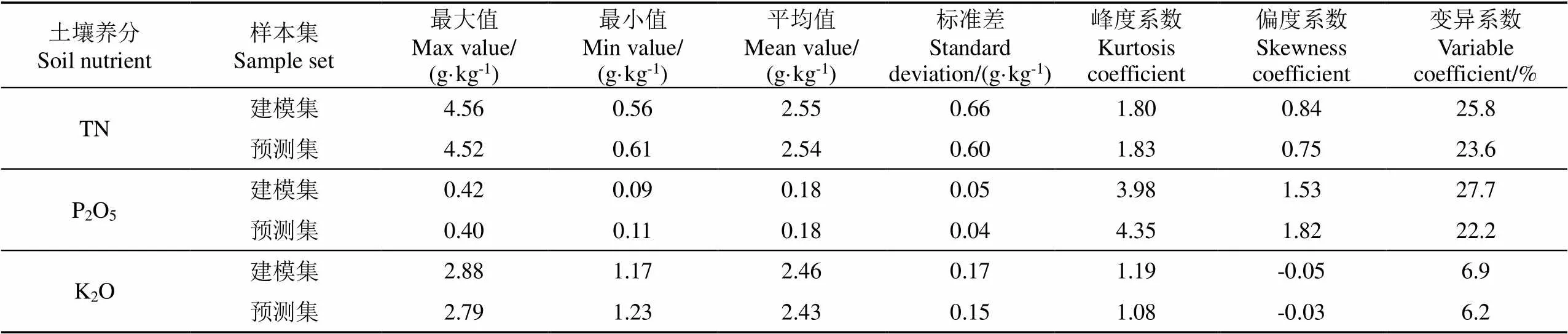
表1 土壤樣品3類養分含量信息
1.4 不同含量黑土養分光譜特征分析
將96組樣本按養分含量大小排序,對比在可見光-近紅外波段范圍內光譜變化規律[20]。
1)每個養分含量區間取2條光譜進行分析,得出全氮變化規律是隨含量增高,反射率逐漸降低(圖2a)。其中3號樣品全氮質量分數為4.56g/kg,反射率顯著低于其他樣品。而22號和68號樣品全氮含量在0.60g/kg左右,其反射率相對高于總體光譜均值。變化規律與有機質光譜曲線類似[21]。但當全氮含量較低時受土壤含水量及混合像元干擾,此規律會逐漸減弱至不顯著。(2)有效磷含量在此波段范圍內無顯著規律(圖2b)。黑土中有效磷含量相對較低,在光譜曲線上特征不明顯。(3)速效鉀在此波段范圍內無顯著規律(圖2c)。黑土中速效鉀含量相對較低,在光譜曲線上特征不明顯。

圖2 不同養分含量黑土光譜特征
1.5 相關性分析
針對3類養分元素進行相關性分析(表2),各光譜變換的相關性不同,其中顯著相關性出現在一階微分光譜變換中[22-23]。挑選其中5個較為代表性波段列出,如580 nm一階微分光譜與TN含量呈顯著相關,相關系數為?0.43;與P2O5含量相關系數為?0.36。1 730~2 200 nm一階微分光譜與K2O呈顯著相關,相關系數最大為?0.31。以TN為例,對比原始光譜波形,一階微分與三種養分含量間的相關系數波動變化、正負交差相對劇烈,峰值系數點較多[24](圖3)。對數一階微分變換與包絡線去除變換光譜與養分元素含量相關性相對不高。因此選取一階微分變換光譜中于養分相關性較高的波段(N:456~600,809~856,1 025~1 190,1 355~1 415,1 685~1 805,2 195~2 285 nm;P2O5:447~495,562~580,819~886,1 085~1 145,1 715~1 790,1 910~1 955,2 195~2 300 nm;K2O:467~485,542~571,886~933,1 250~1 295,1 355~1 430,1 685~1 805,1 920~2 360 nm)應用于研究,波段數共計為86個。

表2 土壤TN、P2O5、K2O含量與部分波段的相關系數
注:*在0.05水平(雙側)上顯著相關。
Note: Significant correlation at *0.05 level (bilateral).

圖3 TN含量與不同變換形式的光譜相關系數圖
2 反演與驗證方法
2.1 偏最小二乘回歸
偏最小二乘(PLSR)是一種多對多回歸建模的算法[24]。建模流程中融合了主成分分析、典型相關性分析和線性回歸的方法優點,同時克服主成分分析對自變量解釋較強,因變量解釋不夠的缺點。本次研究應用偏最小二乘回歸模型,以土壤養分含量為因變量針對光譜特征波段多自變量進行回歸。
2.2 BP神經網絡
BP神經網絡較為適用于預測、分類及評價等方面。由輸入層、隱含層、輸出層構成,采用誤差反向傳播算法進行學習,逐層傳播數據,連接權值逐層向前修正,層層之間全部互相連接,同層單元之間不存在相互連接,每一層神經元只針對下一層神經元有影響。若輸出層未能達到期望輸出,便轉入誤差逆向傳播階段,依據誤差信號修改每個單元權值。學習過程將持續到誤差減小到可接受范圍或預定訓練次數為止。為防止學習速度過快或過擬合造成的模型誤差,BP神經網絡建模的過程分為訓練建模和測試校正兩個步驟,達到一定測試精度即可確定為模型[25-29]。
2.3 模型驗證
反演模型精度驗證由模型穩定性和預測能力決定[30-31]。決定系數(2)、均方根誤差(RMSE)和RPIQ值分別衡量模型的穩定性和精度。建模集決定系數2 c越大,均方根RMSEC誤差越小,說明模型越穩定,精度越好。預測集決定系數2 p越大,均方根誤差RMSEP越小,說明預測效果越好。RPIQ(樣本觀測值第三四分位數Q3和第一四分位數Q1的差IQ與RMSE的比值)對于非正態分布土壤數據的光譜預測模型精度評價更為客觀,其值越大,說明預測效果越好。
3 結果與分析
3.1 偏最小二乘回歸模型
應用Unsramble 9.7建立最小二乘回歸模型,將建模集樣品進行土壤TN、P2O5和K2O含量預測建模。建模中變量投影重要性指標VIPj值所指示變量集合與相關性較高的波段對應,證明其對應波段在解釋因變量集合即養分元素時具有重要作用[32-35]。建模集TN和K2O的模型決定系數2 c分別為0.891和0.816,RMSEC為0.23 g/kg和0.06 g/kg均小于樣本平均值的10%,預測集決定系數2 p對比建模集也較為穩定,分別為0.851 2和0.808 6,RMSEP分別為0.29 g/kg和0.07 g/kg,RPIQ值分別為2.42和2.00,模型具備較好的精度和預測能力。P2O5的模型決定系數2 c=0.693,RMSEC為0.03 g/kg,預測集決定系數2 p=0.707 5,RMSEP為0.06 g/kg,RPIQ值為0.83,表明P2O5的預測效果不是特別理想,僅可達到近似定量預測的精度要求。三類養分的回歸系數與回歸方程均能通過顯著性檢驗(<0.01),回歸方程如下:
(TN)=31.57723?46.55943+15.43950+11.2011730?
34.5602 105+25.6302 120?48.0702 180+
86.822 195?40.672 210+2.879 1 (1)
(P2O5)=31.55950?47.59965?6.613980+19.6995?
37.611 295+43.441 310+45.282 090?
10.272 105+63.752 120?25.162 135+
65.022 195?50.072 210+5.4512 225?
3.5242 435+1.6812 450+0.949 6 (2)
(K2O)=0.764933+0.865943+0.898950?1.0051100?
1.0481 115?1.0131 130+0.5231 355+0.6921 430+
0.6821 445+2.0861 760+0.9912 015?2.3592 210?
2.522 375+1.7242 435?0.4072 450+2.49 (3)
運用PLSR模型對黑土土壤樣本進行養分含量預測,3類養分的實測與預測值散點擬合對比結果見圖4。TN預測值范圍為1.35~3.45 g/kg,平均值為2.37 g/kg,標準差為0.03 g/kg。P2O5預測值范圍為0.13~0.27 g/kg,平均值為0.18 g/kg,標準差為0.04 g/kg;K2O預測值范圍為2.34~2.56 g/kg,平均值為2.45 g/kg,標準差為0.05 g/kg。

圖4 黑土養分樣本實測值與PLSR預測值對比圖
3.2 BP神經網絡擬合
利用MATLAB編程實現神經網絡的設計、訓練及仿真函數實現BP神經網絡建立模型,采用三層BP網絡,將相關性較高的特征波段提取的8個主成分分量作為神經網絡的訓練輸入節點,其主成分累計方差貢獻率達99.96%。隱含層為tansig傳遞函數,節點數經測試為5。輸出層采用purelin傳遞函數,輸出節點分別為三類土壤養分含量。訓練函數為trainlm,訓練次數為1 000次,期望誤差為0.000 1。以全氮為例,其BP神經網絡訓練的誤差性能變化及數據訓練回歸情況如圖5,經過訓練的網絡誤差為0.001 279 3,相關系數達到0.998,模型擬合程度較高。
BP神經網絡擬合的TN預測模型決定系數2 p= 0.906 5,P2O5預測模型決定系數2 p=0.7786,K2O預測模型決定系數2 p=0.862 2。RMSEP分別為0.25、0.03和0.06 g/kg,RPD值分別為2.39、1.34和2.49。模型具備較好的精度和預測能力。三類黑土土壤養分的實測與預測值散點擬合對比結果見圖6。TN預測值范圍為1.33~3.65 g/kg,平均值為2.29 g/kg,標準差為0.53 g/kg;P2O5預測值范圍為0.12~0.28 g/kg,平均值為0.18 g/kg,標準差為0.04 g/kg;K2O預測值范圍為2.37~2.67 g/kg,平均值為2.47 g/kg;標準差為0.07 g/kg。

圖5 全氮BP神經網絡訓練情況

圖6 黑土養分樣本實測值與BP神經網絡預測值對比圖
3.3 結果對比
針對黑土土壤的可見光-近紅外航空高光譜數據,將全氮、有效磷和速效鉀3類土壤養分分別應用偏最小二乘和BP神經網絡建模預測,模型精度對比見表3。結果表明,在全氮定量預測方面,偏最小二乘法與BP神經網絡均展現了較高的擬合精度,BP神經網絡有較高的2 p和較小的相對誤差值,兩種方法均可用于全氮定量預測,但BP神經網絡有著更高的精度,2值提高了0.053 3,預測平均相對誤差提高了1.76%,RPIQ提高至2.80。在有效磷定量預測方面,偏最小二乘法擬合精度較低,BP神經網絡相比偏最小二乘法2 p提高了0.071 1,預測平均相對誤差提高了1.61%,RPIQ提高至1.67。速效鉀的定量預測中BP神經網絡相比偏最小二乘法2 p提高了 0.053 6,預測平均相對誤差提高了0.26%,RPIQ提高至2.33。在實測與預測值對比情況中,全氮、有效磷和速效鉀的定量預測中BP神經網絡相比偏最小二乘法具備更高的精度,2 p分別提高6.5%、10.1%和6.6%。將其應用到3類養分的定量預測,得到黑土養分含量的空間預測分布情況(圖7)。

表3 預測模型精度對比

圖7 黑土3類養分含量航空高光譜定量提取圖
4 結 論
航空高光譜遙感為土壤養分元素含量預測提供了一種高效的數據獲取手段,面狀全區光譜測量相對點狀測量在養分元素含量預測上避免了插值方法帶來的二次誤差,反演效果得到提高。將偏最小二乘法及BP神經網絡模型應用于航空高光譜黑土養分信息提取,結果表明:1)全氮含量的光譜特征較為明顯,因此兩種方法模型預測精度均較高。2)BP神經網絡比偏最小二乘法建模的預測效果更佳,黑土土壤光譜反射率與土壤養分含量之間,受其他物質因素影響存在一定的非線性關系,采用BP神經網絡回歸建模能較好的處理這種關系,可以更好地實現對土壤全氮和速效鉀的含量預測,預測精度分別提高6.5%和6.6%。3)兩種方法的有效磷的預測效果不是特別理想,其含量與光譜特征走勢規律不明顯,含量標準差也較低僅為0.04 g/kg,導致較難得到較高精度的回歸模型,僅可達到近似定量預測的要求。
[1] 史舟. 土壤地面高光譜遙感原理與方法[M]. 北京:科學出版社,2014.
[2] Bendor E, Banin A. Near-infrared analysis as a rapid method to simultaneously evaluate several soil properties[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1995, 59(2): 364-372.
[3] Bendor E, Chabrillat S, Demattê J A M, et al. Using imaging spectroscopy to study soil properties[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2009, 113(1): S38-S55.
[4] 陳頌超,彭杰,紀文君,等. 水稻土可見-近紅外-中紅外光譜特性與有機質預測研究[J].光譜學與光譜分析,2016,36(6):1712-1716. Chen Songchao, Peng Jie, Ji Wenjun, et al. Study on the characteristics and organic matter prediction of rice soil visible-near infrared - mid-Infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(6): 1712-1716. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 王銳,蔡朕. 基于多光譜遙感的耕地土壤有機質定量反演[J]. 農業工程,2018,8(11):85-89. Wang Rui, Cai zhen. Quantitative inversion of cultivated soil organic matter based on multispectral remote sensing[J]. Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 8(11): 85-89. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 夏楠,塔西甫拉提·特依拜,丁建麗,等. 基于多光譜數據的荒漠礦區土壤有機質估算模型[J]. 農業工程學報,2016,32(6):263-267. Xia Nan, Taxipulati Teyibai, Ding Jianli, et al. Estimation model of soil organic matter in desert mining area based on multi-spectral data [J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(6): 263-267. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Daniel ?í?ala, Tereza Zádorová, Ji?í Kapi?ka. Assessment of soil degradation by erosion based on analysis of soil properties using aerial hyperspectral images and ancillary data[J]. Remote Sense, 2017, 9(1): 28-40.
[8] 何挺,王靜,林宗堅,等. 土壤有機質光譜特征研究[J]. 武漢大學學報:信息科學版,2006,31(11):975-979. He Ting, Wang Jing, Lin Zongjian, et al. Spectral features of soil organic matter[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2006, 31(11): 975-979. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 劉煥軍,潘越,竇欣,等. 黑土區田塊尺度土壤有機質含量遙感反演模型[J]. 農業工程學報,2018,34(1):127-133. Liu Huanjun, Pan Yue, Dou Xin, et al. Soil organic matter content inversion model with remote sensing image in field scale of black soil area[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(1): 127-133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李焱,王讓會,管延龍,等. 基于高光譜反射特性的土壤全氮含量預測分析[J]. 遙感技術與應用,2017,32(1):173-179. Li Yan, Wang Ranghui, Guan Yanlong, et al. Prediction of total nitrogen content in soil based on high spectral reflectance[J]. Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2017, 32(1): 173-179. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 祁亞琴,呂新,邵玉林,等. 基于高光譜數據提取土壤養分信息的研究進展[J]. 中國農學通報,2014,30(12):28-31. Qi Yaqin, Lü Xin, Shao Yulin, et al. Research progress of soil nutrient information extraction based on hyperspectral data[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014, 30(12): 28-31. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 邱壑,陳瀚閱,邢世和,等.基于Hyperion數據的耕地土壤有機質含量遙感反演[J]. 福建農林大學學報:自然版,2017,46(4):460-467. Qiu He, Chen Hanyue, Xing Shihe, et al. Soil organic matter estimation models based on hyperion data[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University: Natural Science, 2017, 46(4): 460-467. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李雪瑩,范萍萍,侯廣利,等,可見-近紅外光譜的土壤養分快速檢測[J]. 光譜學與光譜分析,2017,37(11):3562-3566. Li Xueying, Fan Pingping, Hou Guangli, et al. Visible–near infrared spectrum of soil nutrient rapid detection[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(11): 3562-3566. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 史舟,梁宗正,楊媛媛,等,農業遙感研究現狀與展望[J]. 農業機械學報,2015,46(2):247-260. Shi Zhou, Liang Zongzheng, Yang Yuanyuan, et al. Current situation and prospect of agricultural remotesensing research[J]. Transactions of The Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(2): 247-260. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 周鼎浩,薛利紅,李穎,等. 基于可見–近紅外光譜的水稻土全磷反演研究[J]. 土壤,2014,46(1):47-52. Zhou Dinghao, Xue Lihong, Li Ying, et al. Visible–near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for prediction of total phosphorus content in paddy soil[J]. Soil, 2014, 46(1): 47-52. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王人潮,蘇海萍,王深法. 浙江省主要土壤光譜反射特性及其模糊分類在土壤分類中的應用研究[J]. 浙江大學學報:農業與生命科學版,1986,12(4):464-471. Wang Renchao, Su Haiping, Wang Shenfa. Spectral reflectance characteristics of main soils in zhejiang province and Its fuzzy classification applied to soil classification[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 1986, 12(4): 464-471. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 吳嵩. 典型黑土區土壤有機質含量反演研究[D]. 長春:吉林大學,2016. Wu Song. Research of Soil Organic Matter Content Inversion in Typical Black Soil Area[D]. Changchun:Jilin university, 2016.
[18] 葉發旺,劉德長,趙英俊. CASI/SASI航空高光譜遙感測量系統及其在鈾礦勘查中的初步應用[J]. 世界核地質科學,2011,28(4):231-236. Ye Fawang, Liu Dechang, Zhao Yingjun. Airborne hyper-spectral survey system CASI/SASI and its preliminary application in uranium exploration[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2011, 28(4): 231-236. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 張瑤,李民贊,鄭立華,等. 基于近紅外光譜分析的土壤分層氮素含量預測[J].農業工程學報,2015,31(9):121-126. Zhang Yao, Li Minzan, Zheng Lihua, et al. Prediction of nitrogen content in soil based on near infrared spectrum analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(9): 121-126. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 張俊華,馬天成,賈科利. 典型龜裂堿土土壤光譜特征影響因素研究[J]. 農業工程學報,2014,30(23):158-165. Zhang Junhua, Ma Tiancheng, Jia Keli. Factors affecting spectral characteristics of typical takyr solonetzs[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(23): 158-165. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 劉煥軍,張柏,趙軍,等. 黑土有機質含量高光譜模型研究[J]. 土壤學報,2007,44(1):27-32. Liu Huanjun, Zhang Bai, Zhao Jun, et al. Spectral models for prediction of organic matter in black soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(1): 27-32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Nour-Omid B, Parlett B N, Ericsson T, et al. How to implement the spectral transformation[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1987, 48(178): 663-663.
[23] Du P J, Chen Y H, Fang T, et al. Study on the extraction and applications of spectral features in hyperspectral remote sensing[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2003, 32(5): 500-504.
[24] 王昶,黃馳超,徐光輝,等. 近紅外光譜結合偏最小二乘法快速評估土壤質量[J]. 土壤學報,2013,50(5):36-45. Wang Chuang, Huang Chichao, Xu Guanghui, et al. Rapid evaluation of soil quality through a near infrared-partial least squares (NIR-PLS) method[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2013, 50(5): 36-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李碩,汪善勤,張美琴,等. 基于可見長丘紅外光譜比較主成分回歸、偏最小二乘回歸和反向傳播神經網絡對土壤氮的預測研究[J]. 光學學報,2012,32(8):0830001-0830005. Li Shuo, Wang Shanqin, Zhang Meiqin, et al. Comparison among principal component regression,partial least squares regression and back propagation neural network for prediction of soil nitrogen with visible-near infrared spectroscopy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2012, 32(8): 0830001-0830005. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] Zhang P, Li Y. Study on the comparisons of the establishment of two mathematical modeling methods for soil organic matter content based on spectral reflectance[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(3): 903-910.
[27] Doustfatemeh I, Baleghi Y. Comprehensive urban area extraction from multispectral medium spatial resolution remote-sensing imagery based on a novel structural feature[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 37(18): 4225-4242.
[28] Andreas Steinberg, Sabine Chabrillat, Antoine Stevens, et al. Prediction of common surface soil properties based on Vis-NIR airborne and simulated EnMAP imaging spectroscopy data: Prediction Accuracy and Influence of Spatial Resolution[J]. Remote Sense, 2016, 8(7): 613-627.
[29] 鄭立華,李民贊,潘孌,等. 基于近紅外光譜技術的土壤參數BP神經網絡預測[J]. 光譜學與光譜分析,2008(5):1160-1164. Zheng Lihua, Li Minzan, Pan Luan, et al. Prediction of soil parameters BP neural network based on near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2008(5): 1160-1164 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 薛利紅,周鼎號,李穎,等. 不同利用方式下土壤有機質和全磷的可見近紅外高光譜反演[J]. 土壤學報,2014,51(5):993-1001. Xue Lihong, Zhou Dinghao, Li Ying, et al. Prediction of soil organic matter and total phosphorus with vis-nir hyperspectral inversion relative to land use[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2014, 51(5): 993-1001. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 徐永明,藺啟忠,王璐,等. 基于高分辨率反射光譜的土壤營養元素估算模型[J]. 土壤學報,2006,43(5):709-716. Xu Yongming, Lin Qizhong, Wang Lu, et al. Model for estimating soil nutrient elements based on high resolution reflectance spectra[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2006, 43(5): 709-716. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 高燈州,曾從盛,章文龍,等. 閩江口濕地土壤全氮含量的高光譜遙感估算[J]. 生態學雜志,2016,35(4):952-959. Gao Dengzhou, Zeng Congsheng, Zhang Wenlong, et al. Estimating of soil total nitrogen concentration based on hyperspectral remote sensing data in Minjiang River estuarine wetland[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2016, 35(4): 952-959. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 張東輝,趙英俊,秦凱. 一種新的光譜參量預測黑土養分含量模型[J]. 光譜學與光譜分析,2018,38(9):1-5. Zhang Donghui, Zhao Yingjun, Qin Kai. A new model for predicting black soil nutrient content by spectral parameters[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(9): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[34] 李晨,張國偉,周治國,等. 濱海鹽土土壤水分的高光譜參數及估測模型[J]. 應用生態學報,2016,27(2):525-531. Li Chen,Zhang Guowei,Zhou Zhiguo,et al. Hyperspectral parameters and prediction model of soil moisture in coastal saline[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2016, 27(2): 525-531. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 程先鋒,宋婷婷,陳玉,等. 滇西蘭坪鉛鋅礦區土壤重金屬含量的高光譜反演分析[J]. 巖石礦物學雜志,2017,36(1):60-69. Cheng Xianfeng, Song Tingting, Chen Yu, et al. Retrieval and analysis of heavy metal content in soil based on measured spectra in the Lanping Zn-Pb mining area, western Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica ET Mineralogica, 2017, 36(1): 60-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Prediction of black soil nutrient content based on airborne hyperspectral remote sensing
Yang Yuechao1, Zhao Yingjun1, Qin Kai1, Zhao Ningbo1, Yang Chen2, Zhang Donghui1, Cui Xin1
(1.,,100029,; 2.,,430072,)
In order to improve the efficiency and accuracy of the quantitative prediction of soil nutrient content in black soil of Heilongjiang province, in this paper, we utilized statistical theory and spectral analysis method, researched the relationship of three kinds of soil nutrient content and soil spectrum to established hyperspectral inversion model of soil total nitrogen, available phosphorus, available kalium content. We acquired the aerial hyperspectral data by using CASI-1500 and SASI-600 linear array push-broom imaging spectrometers. Preprocessing of calibration and atmospheric radiation correction of Airborne Hyperspectral raw radiation data was studied. 96 samples were evenly sampled. In order to increase the representativeness of samples, 96 groups of samples were collected from 3-5 samples collected from 15 meters around the sampling point, and 1.5 kg was retained after mixing. After air-drying, mixing and grindingetc, it is used for the contents of total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available kalium were obtained through laboratory tests. The content of total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available kalium was determined by NaOH diffusion method, NaHCO3extraction-molybdenum blue colorimetry and NH4OAC extraction-flame photometry. Referring to Kennard-Stone method, 72 groups of representative samples were selected as model samples for nutrient content prediction, and 24 groups were model prediction samples. 96 black soil samples were sorted according to nutrient content, and the spectral transformation in the visible near red range was analyzed. The change rule of total nitrogen is that the reflectance decreases with the increase of content. The first order differential spectra at 580 nm were significantly correlated with total nitrogen and available phosphorus content, with a correlation coefficient of -0.43 and -0.36, respectively. The first-order differential spectra at 1 730-2 200 nm were significantly correlated with K2O, and the maximum correlation coefficient was -0.31. Compared with the original spectral waveform, the correlation coefficient between the first derivative and three nutrient contents fluctuated sharply, and the positive and negative cross-sections were relatively sharp, with more peak coefficients .After spectral contrast analysis and correlation coefficient calculation, 86 bands with higher correlation coefficient were selected for the study under the first order differential variation. On black soil airborne hyperspectral data processing, the application of partial least squares regression (PLSR) and BP neural network method respectively establish soil nutrient content of high spectral quantitative inversion model. The results showed that RPIQ values (Difference between the third and the first quartile of sample observations ratio to RMSE) of total nitrogen PLSR and BP neural network prediction model were 2.42 and 2.80, respectively. The RPIQ values of effective phosphorus PLSR and BP neural network model were 0.83 and 1.67 respectively. The RPIQ values of the available kalium PLSR and BP neural network models were 2.00 and 2.33 respectively. Experiments showed that the spectral quantitative prediction model of soil total nitrogen and available kalium has good accuracy and prediction ability. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and the spatial distribution of nutrient content in black soil were obtained. However, the prediction effect of effective Phosphorus was not particularly ideal, which could only meet the requirements of approximate quantitative prediction. At the same time, the BP neural network modeling has better accuracy and prediction ability than the partial least square modeling, and the prediction accuracy increased by 6.5%, 10.1% and 6.6% respectively. Due to the limitation of soil samples and other conditions, more samples are needed to verify the universality of the model. More data mining methods are expected to establish more robust prediction models, which will provide more reliable information for the prediction and evaluation of black soil quality information.
soils; remote sensing; models; partial least squares method; BP neural network
楊越超,趙英俊,秦 凱,趙寧博,楊 晨,張東輝,崔 鑫. 黑土養分含量的航空高光譜遙感預測[J]. 農業工程學報,2019,35(20):94-101.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.20.012 http://www.tcsae.org
Yang Yuechao, Zhao Yingjun, Qin Kai, Zhao Ningbo, Yang Chen, Zhang Donghui, Cui Xin. Prediction of black soil nutrient content based on airborne hyperspectral remote sensing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(20): 94-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.20.012 http://www.tcsae.org
2019-06-05
2019-10-07
國家自然科學基金項目(41602333);東北黑土地1:25萬土地質量地球化學調查(DD20160316);遙感信息與圖像分析技術國家級重點實驗室基金項目(ZJ2019-1)
楊越超,工程師,主要從事高光譜遙感及GIS的科研工作。Email:ycyangcug@qq.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.20.012
S15
A
1002-6819(2019)-20-0094-08

