東部沿海地區(qū)秋冬季空氣PM2.5污染時(shí)空變化特征
陳亞慧 葛躍
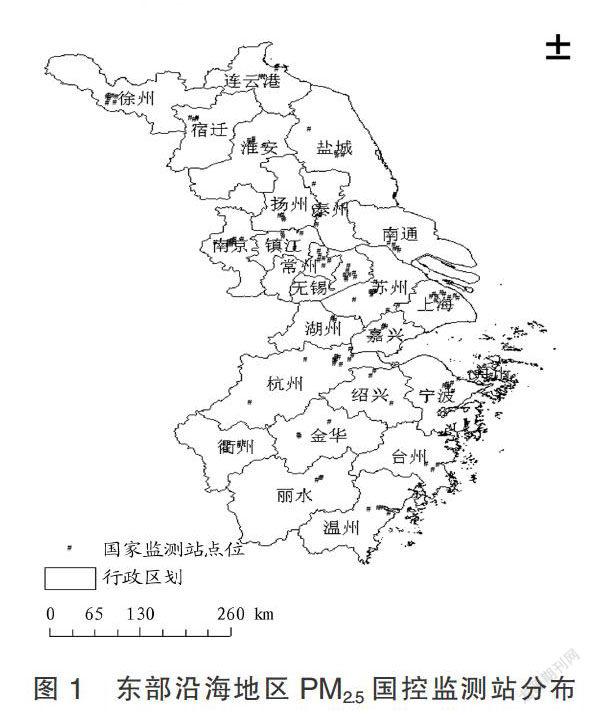

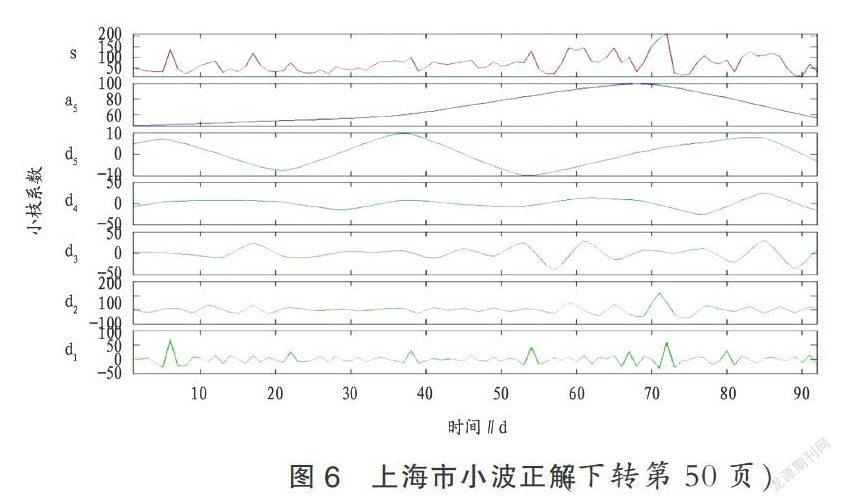
摘要? 利用東部沿海地區(qū)2014年11月到2015年1月的ρ(PM2.5)逐時(shí)數(shù)據(jù),分析研究PM2.5的時(shí)空分布特征。結(jié)果表明,ρ(PM2.5)的基底效應(yīng)值在0.08~0.40,以結(jié)構(gòu)性變異為主,空間自相關(guān)程度分別為強(qiáng)、中等,研究時(shí)段內(nèi)PM2.5與空間結(jié)構(gòu)和人類活動(dòng)都存在關(guān)系;對(duì)典型城市秋冬交替時(shí)間段內(nèi)的逐日ρ(PM2.5)時(shí)間序列進(jìn)行小波分析,發(fā)現(xiàn)ρ(PM2.5)在不同時(shí)間尺度上具有不同的“高-低”交替變化規(guī)律,從秋季到冬季ρ(PM2.5)污染逐漸惡化。總體上,東部沿海地區(qū)秋冬季PM2.5污染情況存在一定的空間自相關(guān)性和周期性,應(yīng)針對(duì)其時(shí)空特征進(jìn)行聯(lián)防聯(lián)控和統(tǒng)籌治理。
關(guān)鍵詞 PM2.5;東部沿海;地統(tǒng)計(jì)分析;小波分析
中圖分類號(hào):X513 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A 文章編號(hào):2095-3305(2019)01-053-04
DOI: 10.19383/j.cnki.nyzhyj.2019.01.020
Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of PM2.5 Pollution in Au tumn and Winter in East ern Coastal Areas
CHEN Ya-hui? et al(Hefei Environmental Monitoring Center, Hefei, Anhui 230031)
Abstract Using the hourly ρ(PM2.5) data of the eastern coastal areas from November 2014 to January 2015, the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of PM2.5 were analyzed. The substrate effect value of ρ(PM2.5) was 0.08-0.40, the type of ρ(PM2.5) variation was mainly structural variation,and the degree of spatial autocorrelation was strong and moderate, respectively. There was a relationship between PM2.5 and spatial structure, human activities during the studied time period. The wavelet analysis showed that ρ(PM2.5) had different change rule of high and low alternations in different time scale, and PM2.5 pollution was gradually serious from autumn to winter. In general, there was a certain spatial autocorrelation and periodicity of PM2.5 pollution in autumn and winter in the eastern coastal areas, so joint prevention and control and overall treatment should be carried out according to its spatial and temporal characteristics.
Key words? ?PM2.5; Eastern coastal areas; Geo-statistical analysis; Wavelet analysis
我國東部沿海地區(qū)自然資源豐富,區(qū)位優(yōu)勢突出,是我國城市化高度發(fā)達(dá)和經(jīng)濟(jì)發(fā)展水平最高的地區(qū),與此同時(shí),城市的高速發(fā)展也帶來了日趨嚴(yán)重的大氣污染問題,國內(nèi)外許多學(xué)者針對(duì)PM2.5污染特征方面開展了許多研究[1-5],但大部分研究空間尺度較小,監(jiān)測點(diǎn)數(shù)量較少,監(jiān)測頻次較低,而且主要分析PM2.5含量的動(dòng)態(tài)變化特征和區(qū)域差異及其影響因素,較少關(guān)注PM2.5污染的時(shí)間尺度特征和空間自相關(guān)性。自2012年12月起,京津冀、東部沿海和珠三角以及省會(huì)城市建立了PM2.5監(jiān)測網(wǎng)絡(luò),充分利用該監(jiān)測網(wǎng)絡(luò)豐富的數(shù)據(jù)資源開展PM2.5的時(shí)空變異特征[6],有利于掌握城市群PM2.5的時(shí)空分布規(guī)律,為區(qū)域PM2.5的削減及聯(lián)防聯(lián)控提供基礎(chǔ)研究數(shù)據(jù)。
筆者采用地統(tǒng)計(jì)和小波統(tǒng)計(jì),以東部沿海地區(qū)為研究對(duì)象,對(duì)PM2.5進(jìn)行動(dòng)態(tài)變化和空間差異分析,揭示其動(dòng)態(tài)變化的時(shí)間尺度特征和空間自相關(guān)性,旨在為東部沿海地區(qū)霧霾污染防治提供科學(xué)依據(jù)和決策參考。……

