社團結構對一個SIR模型的基本再生數的影響
李金仙 劉雅楠


摘 要: 重點研究了社團結構對基本再生數的影響.通過邊的斷開和重新連接,一個隨機的配置網絡演變成了一系列具有相同的總度分布和不同的社團結構的網絡.除此之外,推導出了在這些網絡中的一個SIR(susceptible-infectious-recovered)模型的基本再生數,并且發現它在整個過程中并沒有改變.
關鍵詞: SIR(susceptible-infectious-recovered)傳染病; 基本再生數; 網絡; 度分布; 社團結構
1 Introduction
Community structure is universal in real contact networks.It is the division of network nodes into groups within which the connections are dense,but between which the connections are sparse.At present,the research on the structure of the community includes? the community detection[1-3],the community growth model[4] and the epidemic model in a network with communities[5-8].We are also interested in the third point.In 2008,VOLZ[9] built a susceptible-infectious-recovered (SIR) epidemic model in a complex network with generating function.Then,it was simplified? to a one-dimensional problem by MILLER[10].In 2013,KOCH et al.[11] extended the MILLER network SIR model[10] to model the spread of disease in complex two-community networks in the special case of independence between the inter- and intra-community degrees.And in the same year,the same model was extended by MILLER et al[12] to model disease spread in complex networks with n communities and an arbitrary joint degree distribution (a 2-community network yielded a 4-dimensional model).KOCH et al.[11]? have? proved that random edge removal,from either within a group or between the groups,always decreases the basic reproduction number.MILLER et al.[12] have? proved that for the same distribution of two populations,variation of the correlations of the within-group and between-group partnerships will alter the course of an epidemic.Recently,LI et al.[13] extended the VOLZ network SIR model[9] to study disease spreading in two-community complex networks with an arbitrary joint degree distribution and discussed the effect of the community structure on the? final cumulative epidemic incidence.However,the disease threshold? obtained in [13] is not critical.
The basic reproduction number is an important parameter for characterizations of disease invasion.It is the average number of secondary infections caused by a typical infectious individual during the whole course of infection in a completely susceptible population.If it is more than 1,then the disease will invade.As far as we know,there is no? literature on the basic reproduction number of epidemic dynamics in a complex network with community structure except [11].However edge removal alters not only the community structure but also the total degree.Therefore,they cannot see whether their dynamical behaviors are altered by changing the total degree distribution or by changing the community structure.It is still a question to know the behavior of the basic reproduction number when the community structure of the network is altered.
In this paper,we focus on the effect of the community structure on the basic reproduction number.By? disconnecting and reconnecting edges,we can change the community structure by adjusting the ratio of the inside and outside edges of the community and keep the total degree invariant.Then,the influence of community structure on the basic reproduction number is studied under the evolutionary mechanism introduced in Section 2.2.The conclusion shows that the basic reproduction number is not changed when the community structure is strengthened.
2.2 Evolutionary mechanism
In this section,we discuss the community structure and its effect on the epidemic dynamics.In order to get the network with the same degree distribution and different community structure,we use the following process to reconstruct the network:
I.The N nodes are randomly divided into two groups,which are recorded as community 1 with N1 nodes and community 2 with N2 nodes,respectively.
II.In one unit time,an edge? is randomly chosen in each community for disconnection,then reconnects these four keys randomly.
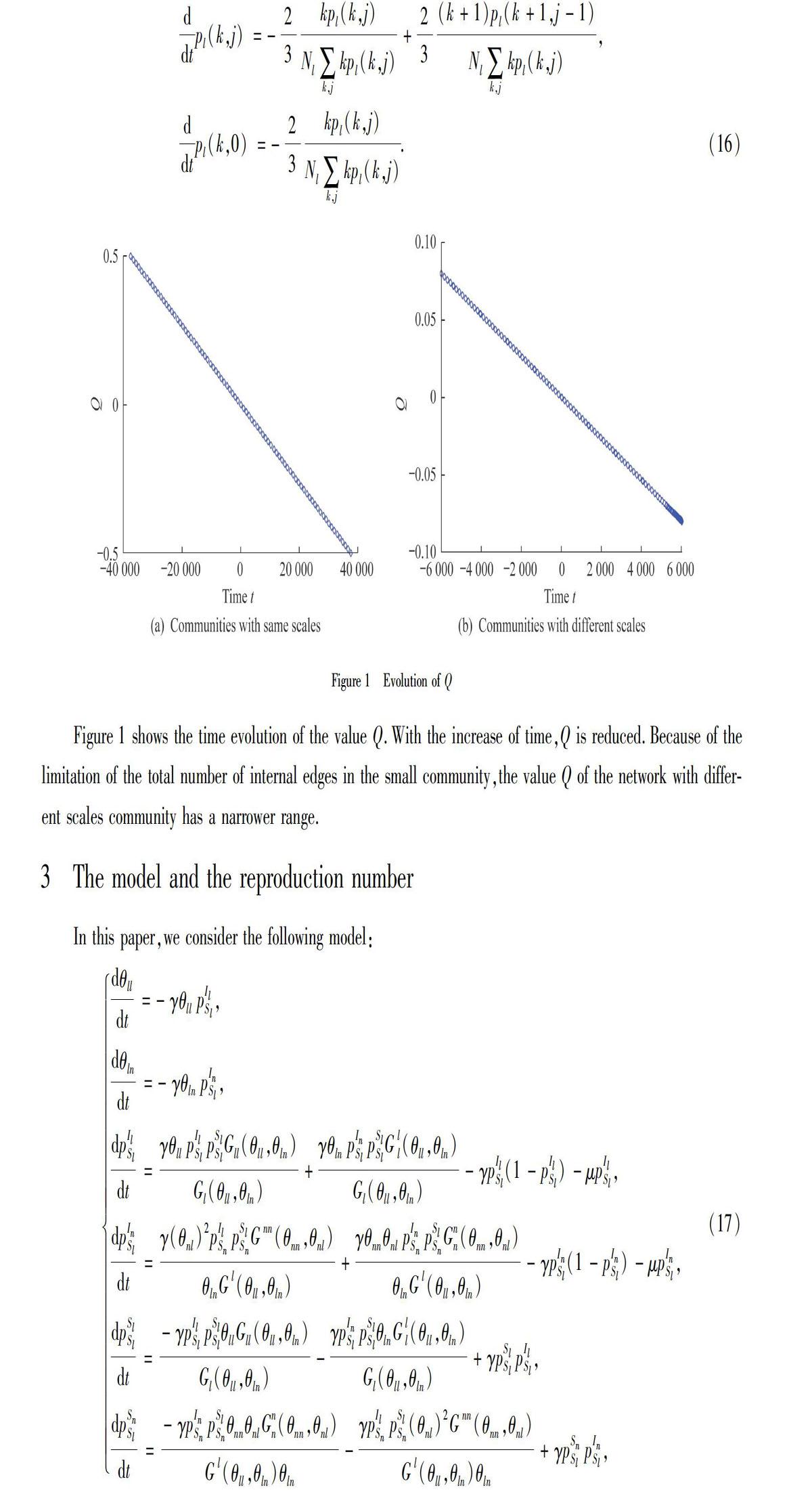
From the above evolutionary mechanism,we conclude that the total degree distribution is invariant in this process.From t=0,the community structure is strengthened along the negative axis and the network goes to show more features similar to the bipartite network? along the positive axis.
The above equation shows that the basic reproduction number is not changed in the whole evolution process of the networks.Since the community structure is changed,it? has no obvious effect on the basic reproduction number in this evolution process.
References:
[1] TRAUD A,KELSIC E,MUCHA P,et al.Community structure in online collegiate social networks [J].APS March Meeting,2009,53(3):526-543.
[2] ZACHARY W W.An information flow model for conflict and fission in small groups [J].Journal of Anthropological Research,1977,33(4):452-473.
[3] NEWMAN M E J,GIRVAN M.Finding and evaluating community struture in networks [J].Physical Review E:Statistical Nonlinear and Soft Matter Physics,2004,69(2):026113.
[4] JIN E M,GIRVAN M,NEWMAN M E J.Structure of growing social networks [J].Physical Review E:Statistical Nonlinear and Soft Matter Physics,2001,64(2):322-333.
[5] PENG X L,SMALL M,XU X J,et al.Temporal prediction of epidemic patterns in community networks [J].New Journal of Physics,2013,15(11):17161-17175.
[6] TUNC I,SHAW L B.Effects of community structure on epidemic spread in an adaptive network [J].Physical Review E:Statistical Nonlinear and Soft Matter Physics,2014,90(2):022801.
[7] WU X Y,LIU Z H.How community structure influences epidemic spread in social networks [J].Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications,2008,387(2):623-630.
[8] YAN G,FU Z Q,REN J,et al.Collective synchronization induced by epidemic dynamics on complex networks with communities [J].Physical Review E:Statistical Nonlinear and Soft Matter Physics,2007,75:112-118.
[9] VOLZ E.SIR dynamics in random networks with heterogeneous connectivity [J].Journal of Mathematical Biology,2008,56(3):293-310.
[10] MILLER J C.A note on a paper by Erik Volz:SIR dynamics in random networks [J].Journal of Mathematical Biology,2011,62(3):349-358.
[11] KOCH D,ILLNER R,MA J L.Edge removal in random contact networks and the basic reproduction number [J].Journal of Mathematical? Biology,2013,67(2):217-238.
[12] MILLER J C,VOLZ E M.Incorporating disease and population structure into models of SIR disease in contact networks [J].PLoS One,2013,8(8):1-14.
[13] LI J X,WANG J,JIN Z.SIR dynamics in random networks with communities [J].Journal of Mathematical Biology,2018(2):1-35.
[14] NEWMAN M E J.Mixing patterns in networks [J].Physical Review E:Statistical Nonlinear and Soft Matter Physics,2003,67(2):241-251.
[15] van den DRIESSCHE P,WATMOUGH J.Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission [J].Mathematical Biosciences,2002,180(1/2):29-48.
(責任編輯:馮珍珍)

