Detection of androgen receptor(AR)and AR-V7 in small cell prostate carcinoma:Diagnostic and therapeutic implications
Pei Zho,Yezi Zhu,Ling Cheng*,Jun Luo,*
aDepartment of Urology,Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine,Baltimore,MD,USA
bDepartment of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine,Indiana University School of Medicine,Indianapolis,IN,USA
KEYWORDS Small cell prostate carcinoma;Androgen receptor;Androgen receptor splice variant-7;Immunohistochemistry
Abstract Objective:Small cell prostate carcinoma(SCPC)is a rare and highly malignant subtype of prostate cancer.SCPC frequently lacks androgen receptor(AR)and prostate-specific antigen(PSA)expression,and often responds poorly to androgen deprivation therapy(ADT).AR splice variant-7(AR-V7)is a truncated AR protein implicated in resistance to AR-targeting therapies.AR-V7 expression in castration-resistant prostate cancers has been evaluated extensively,and blood-based detection of AR-V7 has been associated with lack of response to abiraterone and enzalutamide.However,whether AR-V7 is expressed in SCPC is not known.Methods:Using validated antibodies,we performed immunohistochemistry(IHC)assay for the full-length AR(AR-FL)and(AR-V7)on post-ADT surgical SCPC specimens.Results:Seventy- five percent(9/12)of the specimens showed positive staining for the AR-FL with various intensities.Thirty-three percent(4/12)of the specimens showed positive staining for AR-V7.Among the specimens with positive AR-V7 staining,two samples displayed very weak staining,one sample showed weak-to-moderate staining,and one sample showed strong staining.All positive specimens displayed a heterogeneous pattern of AR-FL/AR-V7 staining.All specimens positive for AR-V7 were also positive for AR-FL.Conclusion:The study findings support the existence of measurable AR-FL and AR-V7 proteins in SCPC specimens.The results also have implications in detection of AR-V7 in specimens obtained through systemic sampling approaches such as circulating tumor cells.A positive AR-V7 finding by blood-based tests is not impossible in patients with SCPC who often demonstrate low PSA values.
1.Introduction
Small cell prostate carcinoma(SCPC)is a rare and highly malignant subtype of prostate cancer.SCPC only accounts for 0.5%-2%of untreated primary prostate cancer at initial diagnosis[1,2],but can present in up to 25%metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer(CRPC)autopsies[3].SCPC frequently lacks expression of androgen receptor(AR)and AR downstream target genes such as prostate-specific antigen(PSA),and often responds poorly to androgen deprivation therapy(ADT)[2].The widespread application of potent next-generation hormonal therapies such as enzalutamide and abiraterone may also lead to increased occurrences of treatment related SCPC[4].
Resistance to ADT in prostate cancer is often associated with aberrant androgen receptor(AR)activities mediated by AR protein overexpression,AR gene amplification,mutation and emergence of constitutively active AR variants such as AR splice variant-7(AR-V7)[5-7].However,detailed expression pattern of different AR isoforms in primary SCPC patients who received prior ADT remains poorly characterized.In this study,we have developed and validated antibodies for immunohistochemistry(IHC)assays suitable for evaluation of full length AR(AR-FL)and AR-V7 in primary SCPC specimens.The expression of AR-FL and AR-V7 protein were determined in post-ADT radical prostatectomy(RP)or transurethral resection of the prostate(TURP)samples from 12 SCPC patients.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Patients and tissue samples
This research was approved by the Institutional Review Board(IU IRB 1808872882).SCPC specimens were collected surgically via RP or TURP.All the patients were previously treated with hormonal therapy.The patients’age ranged from 43 to 87 years old(mean,70 years).Eleven cases were from TURP and one from RP(SC-06).
2.2.IHC assays
For AR C-terminus IHC,the antigen retrieval was done by placing the de-paraffinized slides in Antigen Unmasking Solution,Tris-Based High pH(H-3301;Vector Lab,Burlingame,CA,USA)at 95°C for 40 min.The slides were incubated with the rabbit monoclonal anti-human AR C-terminus antibody(1:200;Sigma-Aldrich,Saint Louis,MO,USA,catalog number:SAB5500007)for 1 h at room temperature.The secondary antibody was a ready-to-use antirabbit poly HRP IgG(PowerVision,PV6118;Leica Biosystems,Buffalo Grove,IL,USA)and was incubated with the slides for 30 min at room temperature.
For AR-V7 IHC,the antigen retrieval was done by placing the de-paraffinized slides in Antigen Unmasking Solution,Tris-Based High pH(H-3301)at 95°C for 20 min.The slides were incubated with the rabbit monoclonal anti-human AR-V7 antibody(1:200,RevMAb Biosciences,South San Francisco,CA,USA,catalog number:31-1109-00)for 70 min at room temperature.The secondary antibody was a ready-to-use anti-rabbit poly HRP IgG (PowerVision,PV6118)and it was incubated with the slides for 30 min at room temperature.
All the stained slides were scanned by Leica Biosystems Aperio AT2 Digital Pathology scanner(Leica Biosystems Imaging,Buffalo Grove,IL,USA)at 40×magnification.The IHC staining nuclear RGB intensity value was determined by Aperio ImageScope(Leica Biosystems Imaging,Buffalo Grove,IL,USA)using algorithm developed by Johns Hopkins University.The nuclear AR-FL staining intensity was classified as negative(nuclear RGB intensity value 220-250)and positive(nuclear RGB intensity value≤219).The AR-FL positive nuclear staining was further classified as weak(nuclear RGB intensity value 200-219),moderate(nuclear RGB intensity value 180-199)and strong(nuclear RGB intensity 155-179).The nuclear AR-V7 staining intensity was classified as negative (nuclear RGB intensity value 220-250)and positive(nuclear RGB intensity value≤219).Positive AR-V7 nuclear staining was further classified as weak(nuclear RGB intensity value 210-220),moderate(nuclear RGB intensity value 188-209)and strong(nuclear RGB intensity value 162-187).The total number of cells were determined by hematoxylin staining using Aperio ImageScope(Leica Biosystems Imaging,Vista,CA,USA).The percentage of positive tumor cells was calculated as number of cells with positive AR-FL or AR-V7 nuclear staining divided by total number of cells in the tissue.Samples were defined as AR-FL or AR-V7 positive if the total number of AR-FL or AR-V7 positive tumor cells were above 0.5%in the tissue.
3.Results
3.1.Validation of AR-FL and AR-V7 IHC assays
The antibodies targeting AR-FL and AR-V7 were validated using prostate cancer cell lines with known AR profiles.Both antibodies were tested in LNCaP95 cells,which express both AR-FL and AR-V7,and the AR-negative PC3 cells[8].The Western blot for the AR-V7 antibody(RevMab,South San Francisco,CA,USA)was examined and demonstrated in a previous publication from our group[9].The Western blot for the AR-C-terminal domain(AR-CTD)antibody(Sigma,Saint Louis,MO,USA)only showed a single specific band for AR-FL as shown in Fig.1,along with the IHC results.In LNCaP95 cells,both AR-V7 and AR-FL were detected predominantly in the nuclei,consistent with the expected expression pattern in this cell line.The antibodies showed good specificity to the corresponding antigens given lack of IHC staining in the AR-negative PC3 cell line.
3.2.AR-FL and AR-V7 protein expression in post-ADT SCPC cases
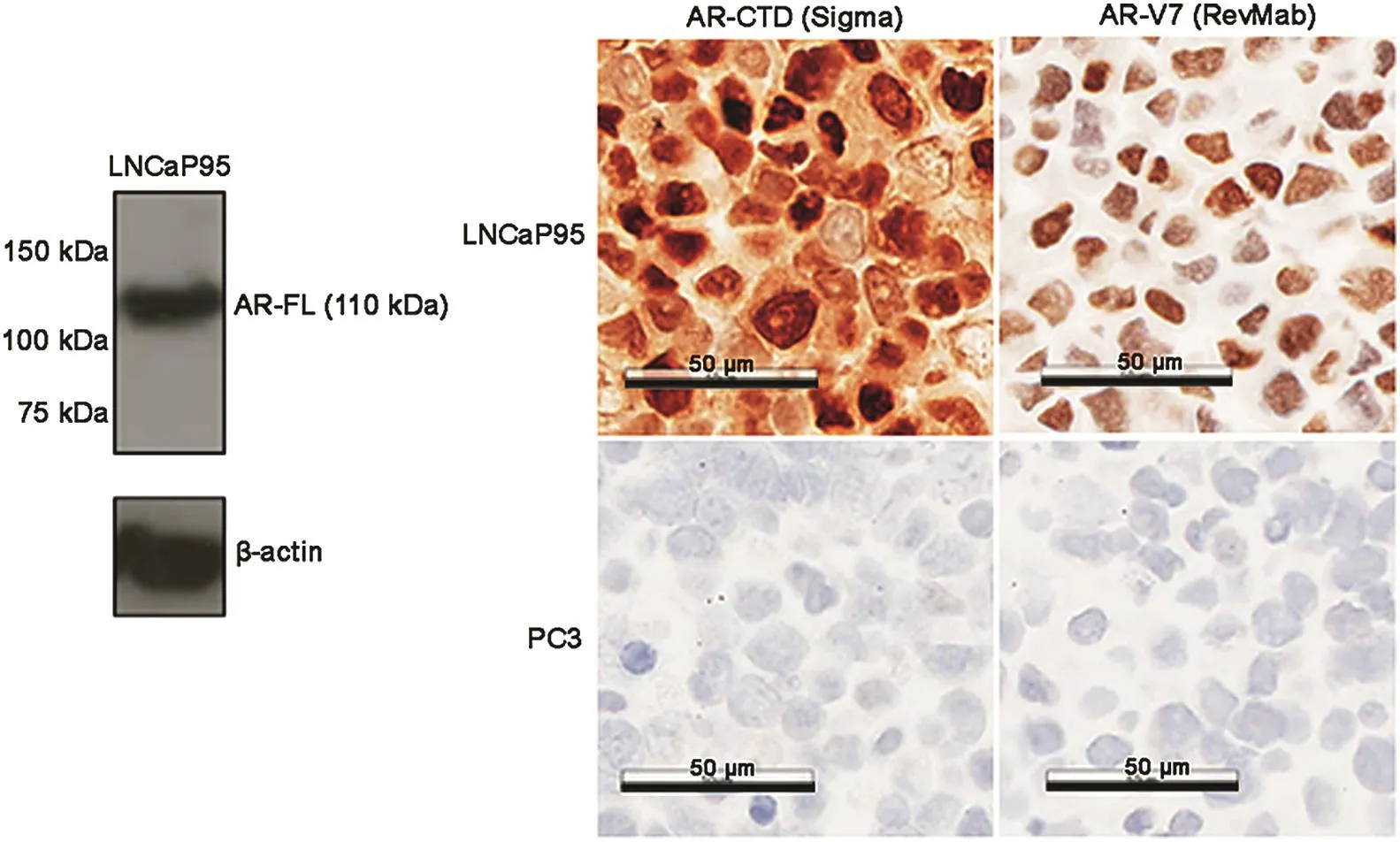
Figure 1 Western blot of the full length androgen receptor(AR-FL)with androgen receptor C-terminal domain(AR-CTD)antibody and immunohistochemistry(IHC)staining of different AR isoforms in LNCaP95 and PC3 cell lines.
Twelve surgical(RP or TURP)SCPC specimens were collected from patients after neoadjuvant hormonal therapy at Indiana University School of Medicine.The diagnosis of SCPC was based on 2016 WHO classification system[10].Seventy- five percent(9/12)of the specimens showed positive AR-FL nuclear staining with varying intensities.Thirty-three percent(4/12)of the specimens showed positive nuclear staining for AR-V7.The summary of the staining results is shown in Table 1.The quanti fication of the staining was achieved by using Aperio ImageScope(Leica Biosystems Imaging,Vista,CA,USA)and the algorithm was developed by Johns Hopkins University.
Among the four specimens with positive AR-V7 staining,two samples(SC-03 and SC-04)displayed very weak staining,one sample(SC-02)showed weak-to-moderate staining,and one sample(SC-01)showed strong staining.All positive specimens displayed a heterogeneous pattern ofAR/AR-V7 staining.All specimens positive for AR-V7 were also positive for the AR-FL.Sample staining results of AR-V7 and AR-CTD are shown in Fig.2.
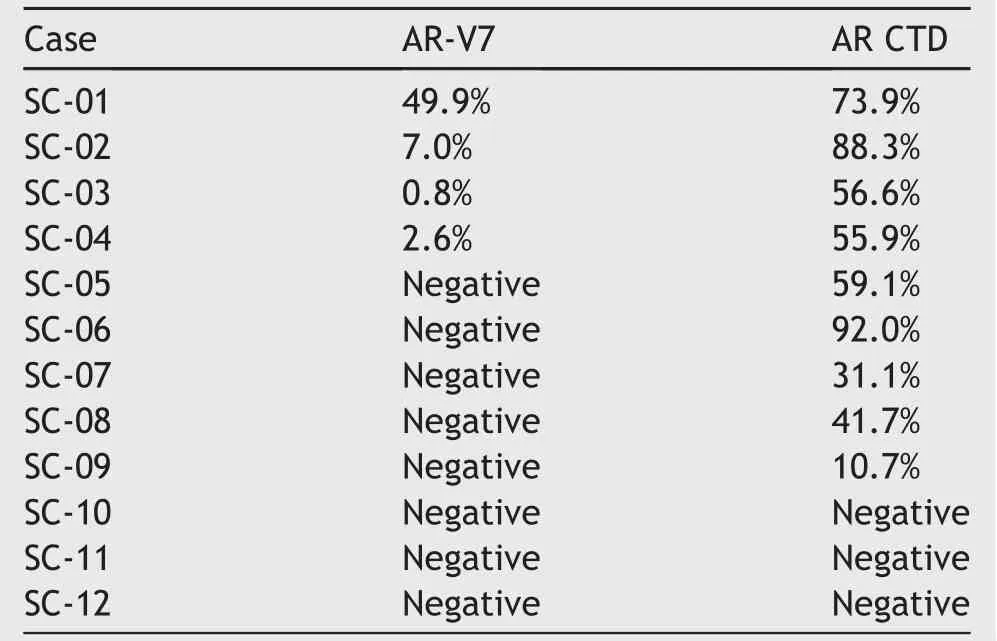
Table 1 Positive staining percentage of AR-V7 and AR-CTD IHC for 12 SCPC tissue specimens.
4.Discussion
SCPC is one of the most lethal forms of prostate cancer.It has usually metastasized at initial diagnosis,and would not respond to hormonal therapy.Cisplatin or doxorubicinbased chemotherapies are the main treatment,and the median overall survival of SCPC is significantly shorter compared to usual adenocarcinoma.In general,SCPC does not express prostate cancer specific markers such as AR and PSA.However,recent studies suggested SCPC may also express detectable level of AR and AR targeted genes[11].In a recent xenograft study,a fraction of AR-positive enzalutamide-resistanttumors carried neuroendocrine features,indicating an AR-indifferent status[12].This finding indicate that SCPC,especially those that arise after treatments,may continue to express AR-FL and AR-V7.ARFL is detected in a substantial proportion of SCPC specimens.It is currently unknown why detection of AR-FL do not confer response to AR-targeting therapies(e.g.,enzalutamide or abiraterone)in SCPC patients.It is possible that although some SCPC cells remains AR-FL positive,they may become “AR-indifferent” [13].
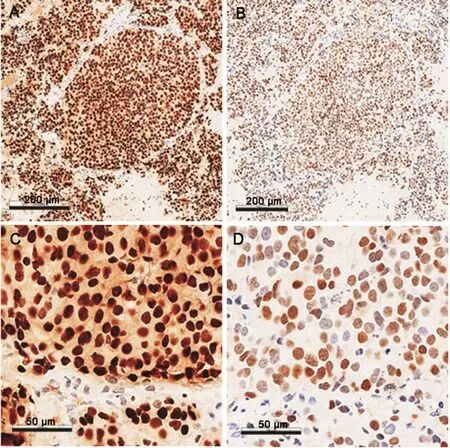
Figure 2 Representative images of the immunohistochemistry staining(IHC)for androgen receptor C-terminal domain(AR-CTD)and androgen receptor splice variant-7(AR-V7).(A)AR-CTD IHC for SC-01(100×magnification);(B)AR-V7 IHC for SC-01(100×magnification);(C)AR-CTD IHC for SC-01;(D)ARV7 IHC for SC-01.
Our study is limited by the small sample size(n=12).However,the purpose of the study was to evaluate AR-FL/AR-V7 protein expression in SCPC specimens.We used an AR-V7 antibody that had been extensively validated in a recent study using CRPC specimens[9].The current study generated a few notable observations.First,this is the first study establishing AR-V7 protein can be detected in SCPC specimens using a validated antibody.Second,the heterogeneous pattern of AR-FL/AR-V7 expression indicates that AR-FL/AR-V7 positive cells may coexist with AR negative cells in SCPC,possibly re flecting a transition state from an AR-driven disease to AR-indifferent or AR-independent disease.Third,consistent with results from non-SCPC CRPC specimens,we did not observe cells that were AR-V7 positive but AR-FL negative,further supporting the conclusion that AR-V7 always coexists with AR-FL[14].The results are informative and have important implications.Blood-based AR-V7 tests have been implemented for clinical use[15-17].Testing platform included the PCR-based test developed at our institution,and IHC-based test developed by EPIC Biosciences.AR-V7 positive cells presenting heterogeneous expression pattern may be detected by both test platforms.As such,positive results may be found in some patients with SCPC,even though such patients may present low serum PSA values.Therefore,some patients with low PSA but positive AR-V7 may be evaluated for the presence of SCPC,a diagnostic entity that may mandate metastatic biopsies.
5.Conclusion
The study demonstrated AR-FL/AR-V7 expression in a substantial fraction of treatment related SCPC specimens.The functional and clinical relevance of AR/AR-V7 detection in this setting remains unknown.This finding,however,may help to interpret liquid biopsy-based detection of AR-V7 in patients with low PSA.Future investigation will focus on clinical correlation in an expanded patient cohort.
Author contributions
Study design:Jun Luo,Liang Cheng,Pei Zhao.
Data acquisition:Pei Zhao,Yezi Zhu.
Data analysis:Pei Zhao,Yezi Zhu,Jun Luo,Liang Cheng.
Drafting of manuscript:Pei Zhao,Yezi Zhu,Jun Luo,Liang Cheng.
Critical revision of the manuscript:Pei Zhao,Yezi Zhu,Jun Luo,Liang Cheng.
Conflicts of interest
Jun Luo is a co-inventor of a relevant technology that has been licensed to A&G,Tokai,and Qiagen.Pei Zhao,Yezi Zhu and Liang Cheng declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The work at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants(R01 CA185297 and P30 CA006973),Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Research Program Grants(W81XWH-15-2-0050),Johns Hopkins Prostate SPORE Grant(P50 CA058236),and the Prostate Cancer Foundation.
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Donald S.Coffey.
 Asian Journal of Urology2019年1期
Asian Journal of Urology2019年1期
- Asian Journal of Urology的其它文章
- Application of fluorescence in situ hybridization in the detection of bladder transitional-cell carcinoma:A multi-center clinical study based on Chinese population☆
- Albumin-linked prostate-specific antigen-activated thapsigargin-and niclosamide-based molecular grenades targeting the microenvironment in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
- Prostate tumor neuroendocrine differentiation via EMT:The road less traveled
- Regulatory signaling network in the tumor microenvironment of prostate cancer bone and visceral organ metastases and the development of novel therapeutics
- Combination therapy with androgen deprivation for hormone sensitive prostate cancer:A new frontier
- Potential impact of combined inhibition of 3α-oxidoreductases and 5α-reductases on prostate cancer
