ON A CLASS OF DOUGLAS FINSLER METRICS?
Hongmei ZHU(朱紅梅)
College of Mathematics and Information Science,Henan Normal University,Xinxiang 453007,China
E-mail:zhm403@163.com
1 Introduction
In Finsler geometry,Douglas curvature is an important projectively invariant,which is introduced by J.Douglas in 1927.It it also a non-Riemannian quantity,because all the Riemannian metrics have vanishing Douglas curvature inherently.Finsler metrics with vanishing Douglas curvature are called Douglas metrics.Roughly speaking,a Douglas metric is a Finsler metric which is locally projectively equivalent to a Riemannian metric[5].
Douglas metrics form a rich class of Finsler metrics including locally projectively flat Finsler metrics[4]and Berwald metrics;The later are those metrics which Berwald curvatures vanish[1].It is known that a Finsler metric is locally projectively flat,namely,its geodesics are all straight line segments in some suitable locally coordinate system,if and only if its both Douglas curvature and Weyl curvature vanish.
A Randers metric,introduced by a physicist G.Randers in 1941,is of the form F=α+β,whereis a Riemannian metric and β=bi(x)yiis a 1-form.However,it can also be expressed in the following navigation form
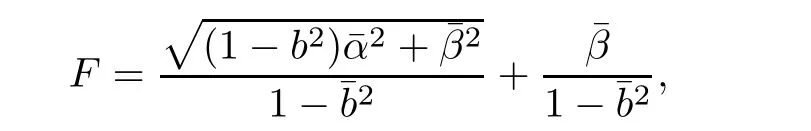
(α,β)-metrics are a rich and important class of Finsler metrics,partly because they are“computable”.The researches on(α,β)-metrics enrich Finsler geometry and the approaches offer references for further study.In 2009,B.Li,Y.Shen,and Z.Shen gave a characterization of Douglas(α,β)-metrics with dimension n ≥ 3[5].
A more general class named general(α,β)-metric was first introduced in[11]in the following form
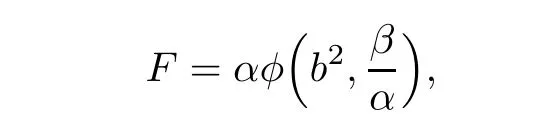
where α is a Riemannian metric,β is a 1-form,b:= ‖βx‖α,and φ(b2,s)is a smooth function.If φ = φ(s)is independent of b2,then F=is an(α,β)-metric.If α =|y|, β = 〈x,y〉,thenis the so-called spherically symmetric Finsler metrics[9,13,15].Moreover,general(α,β)-metrics include part of Bryant’s metrics[2,11]and part of fourth root metrics[7].In[9],X.Mo,N.M.Solórzano,and K.Tenenblat determined all of spherically symmetric Douglas Finsler metrics.Under the condition that β is closed and conformal,the author determined all of Douglas general(α,β)-metric[14].
In this article,we only need the condition that β is not parallel with respect to α determines all of Douglas general(α,β)-metric on a manifold of dimension n > 2.The main result is given below.
Theorem 1.1Let F= αφ(b2,s),s=,be a regular general(α,β)-metric on an open subset U ? Rn(n ≥ 3).Suppose that β is not parallel with respect to α and F is not of Randers type.Then,F is a Douglas metric if and only if F lies in one of the following cases:
(1)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies
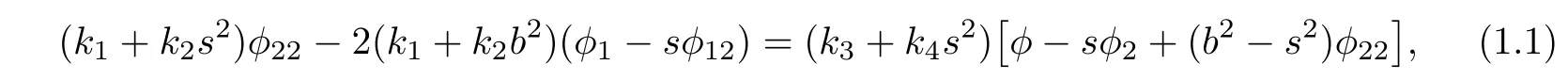
where ki:=ki(b2),i=1,2,3,4 and β satisfies

where τ= τ(x)is a scalar function on U.
(2)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies(1.1)and
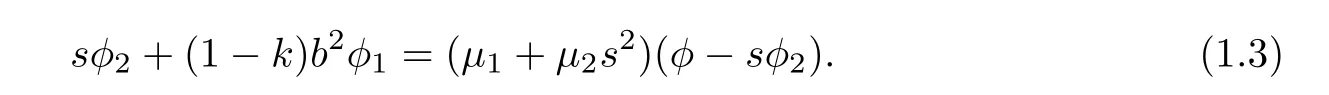
Moreover,β satisfies
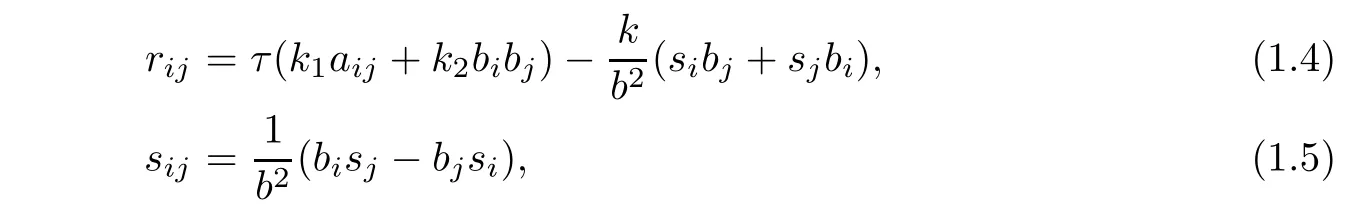
where k:=k(b2)/=1,μi:=μi(b2),i=1,2 andμ1+μ2b2=(k+1).In this case,dβ /=0.
(3)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies(1.1)and

Moreover,β satisfies

Let us take a look at a special case;When φ1=0,takingthe case 1 of Theorem 1.1 is reduced to a result which characterizes Douglas(α,β)-metrics with dimension n ≥ 3(Theorem 1.1 in[5]).Notice that Theorem 1.1 contains some important singular,Finsler metrics,for example Finsler metrics of Kropina type.
X.Wang and B.Li studied Douglas general(α,β)-metrics in[10].Their result is just case 1 of Theorem 1.1.However,we find that case 2 and case 3 also exist recently.For example,for case 2,takeand k=3,then in this case,(1.1)and(1.3)are reduced to the followings:

By a direct computation,it is easy to verify that the following function

satisfies(1.8)and(1.9),where f(t)is an arbitrary function satisfying the following inequalities:

In this case,the corresponding general(α,β)-metric is a regular Finsler metric.
In the following,according to(1.10),for case 2,let us take a look at an example.
Example 1.1Let M be a manifold of dimension n > 2.TakeandIt is easy to verify that α and β satisfy

Moreover,dβ/=0.Choose f=(t+2)2in(1.10),then

where b:= ‖β‖α=Hence,the corresponding Finsler metrics
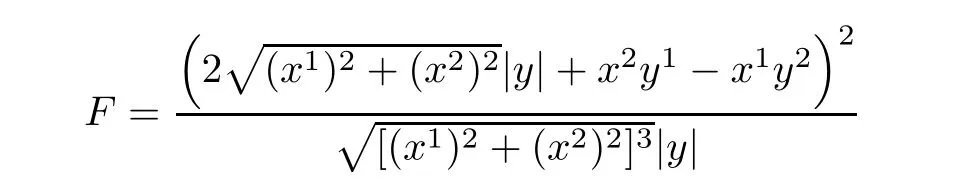
are Douglas metrics.
Similarly,we can find regular Finsler metrics in case 3.Mostly important,β is closed in the case of(α,β)-metrics;However,it is seen from Theorem 1.1 that β permits not closed in the case of general(α,β)-metrics.That is to say,our results express that Douglas general(α,β)-metrics are much more and richer than Douglas(α,β)-metrics.
For three cases of Theorem 1.1,it is easier to solve case 1 because it is close to the result of Douglas(α,β)-metrics.However,case 2 and case 3 do not occur in the case of Douglas(α,β)-metrics,especially β is not closed.It is a pleasure and surprised to us.The two cases are complicated.
2 Preliminaries
In local coordinates,the geodesics of a Finsler metric F=F(x,y)are characterized by

where
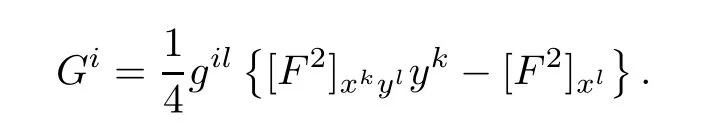
The local function Gi=Gi(x,y)define a global vector fieldon TM{0},which is called the spray.For a Riemannian metric,the spray coefficients are determined by its Christoffel symbols as
Douglas metrics can be characterized by
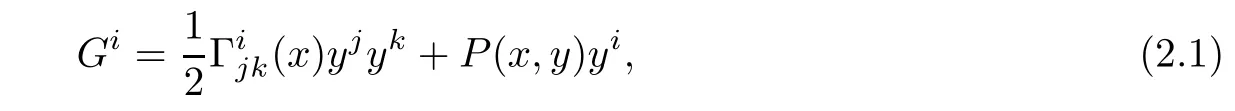
It is known that Douglas metrics can be also characterized by the following equations[1]

By definition,a general(α,β)-metric is a Finsler metric expressed in the following form,

where φ(b2,s)is a positive smooth function defined on the domain|s|≤ b < bofor some positive number(maybe in finity)bo.Then,the function F= αφ(b2,s)is a Finsler metric for any Riemannian metric α and any 1-form β if and only if φ(b2,s)satisfies
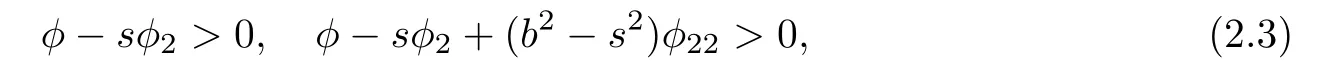
when n≥3 or

when n=2[11].
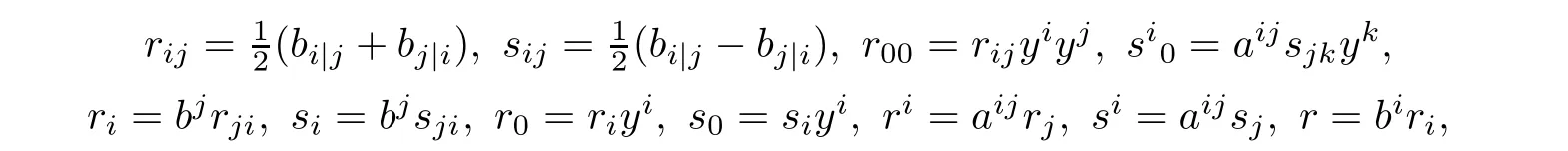
where(aij):=(aij)?1and bi:=aijbj.It is easy to see that β is closed if and only if sij=0.
According to[11],the spray coefficients Giof a general(α,β)-metricare related to the spray coefficientsαGiof α and given by

where


3 Necessary Conditions
In this section,we are going to show the necessary conditions for a general(α,β)-metric to be a Douglas metric.
Lemma 3.1Let F= αφ(b2,s),s=be a regular general(α,β)-metric on an open subset U ? Rn(n ≥ 3).Suppose that β is not parallel with respect to α and F is not of Randers type.If F is a Douglas metric,then F lies in one of the following cases:
(1)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies

where ki:=ki(b2),i=1,2,3,4 and β satisfies

where τ= τ(x)is a scalar function on U.
(2)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies(3.1)and
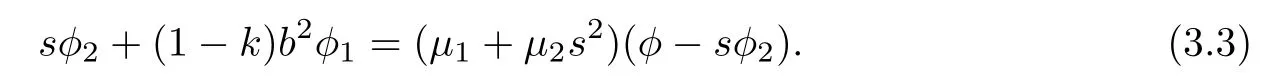
Moreover,β satisfies


Moreover,β satisfies

where θ:= θiyiis a 1-form which is perpendicular to β. ξi:= ξi(b2),i=1,2 and
ProofBy(2.2)and(2.5),we can show that a general(α,β)-metric is a Douglas metric if and only if


To simplify the computations,we take the following coordinate transformation:(s,ua)→(yi)by
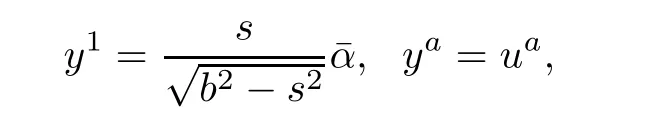
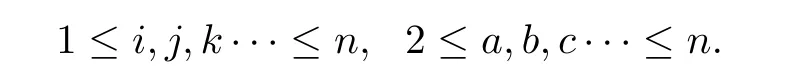
Then,
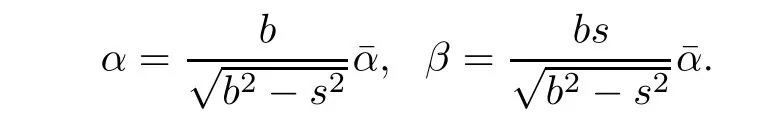
Let
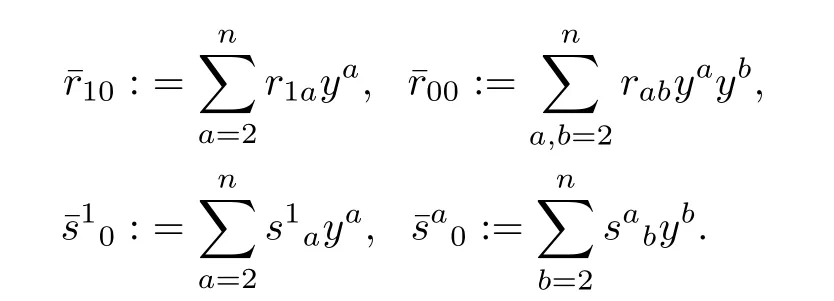
Because expression(3.8)involves rij,sijetc,one needs the following expression:
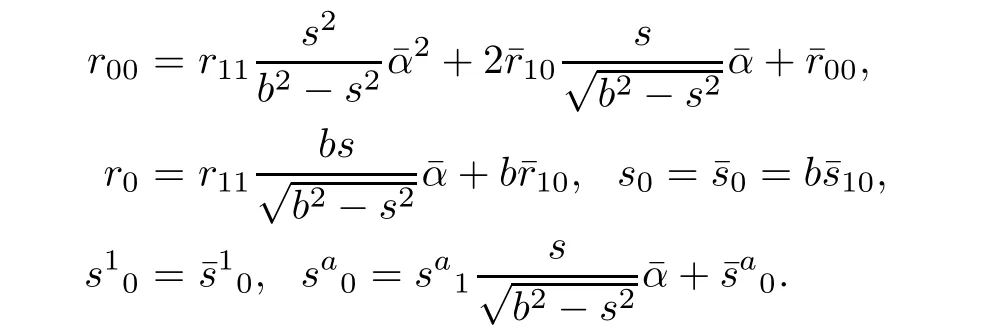
Note that s1=bs11=0.Plugging the above identities into(3.8),we get a system of equations in the following form

where Aijand Bijare polynomials in ya.We must have

Let
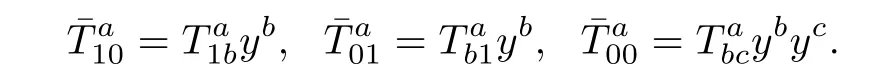
For i=1,j=a,by(3.8),we get
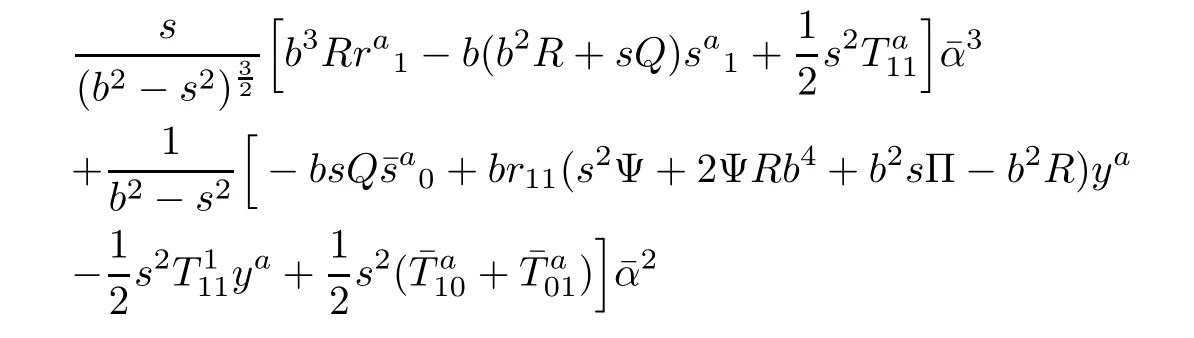
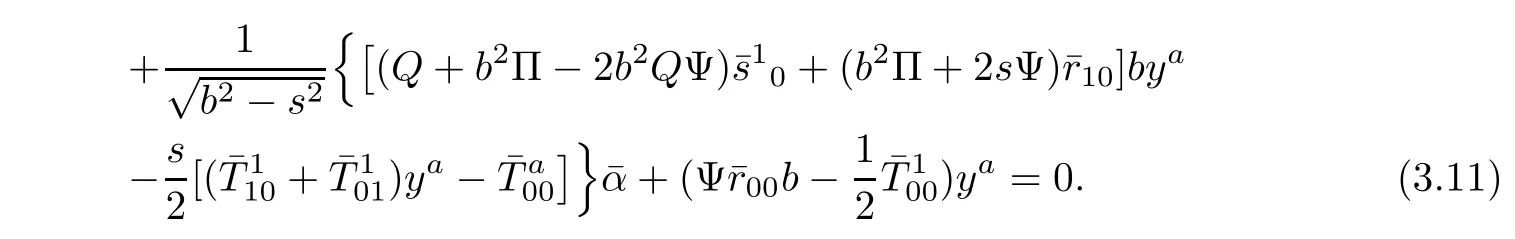
From(3.9)and(3.10),then(3.11)is equivalent to
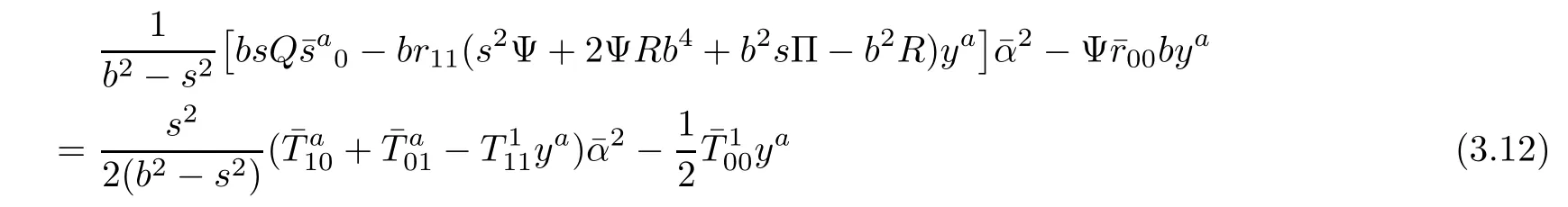
and
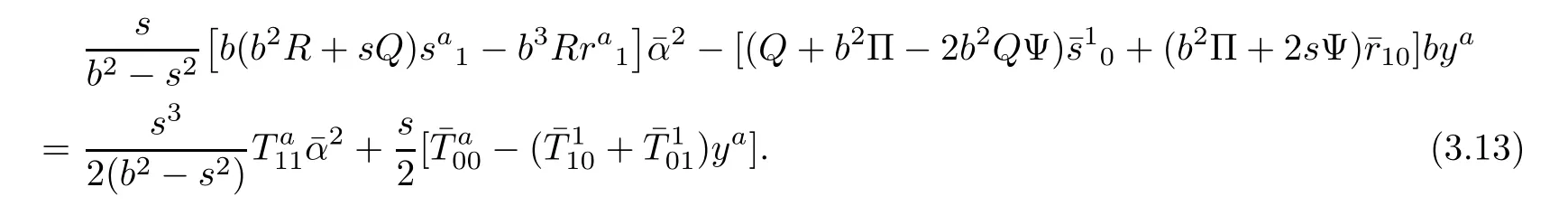
For i=a,j=b,by(3.8)we get
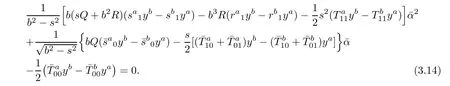
It follows from(3.9)and(3.10)that(3.14)is equivalent to

and
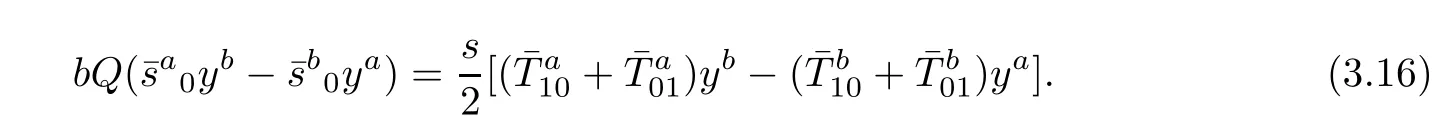
Let

Then,(3.16)can be rewritten as

By(3.17),it is easy to show that

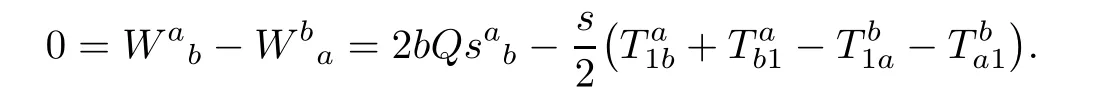

We also get


where
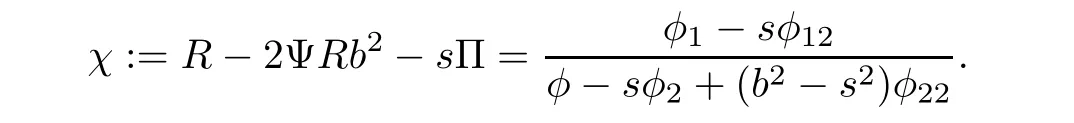
Taking s=b in(3.20),we find that the ratio of r11and?B is a function of b2.Hence,suppose thatplugging them into(3.20)yields

Let s=0,then(3.21)is reduced to
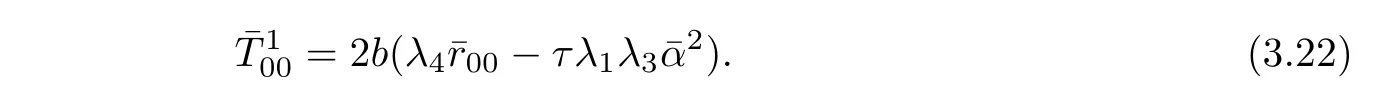
where λ3(b2)= χ(b2,0)and λ4(b2)= Ψ(b2,0).Plugging(3.22)into(3.21)yields

By(3.23),there exists a scalar function λ5(b2)such thatIn this case,(3.23)is reformed as

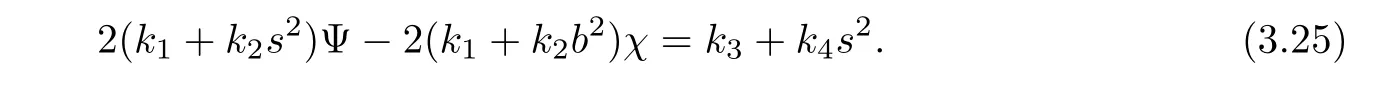
Inserting Ψ and χ into(3.25)yields
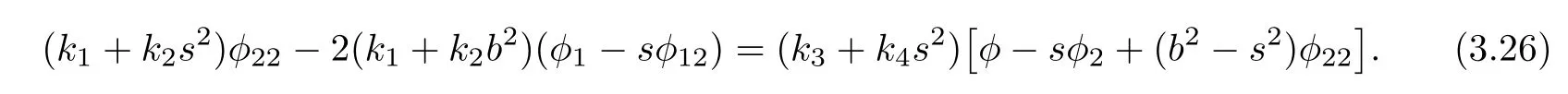
By now,we have obtained

Next,we are going to obtain ra1and sa1from(3.13)and(3.15).Let s=0 in(3.15),we obtain

where ε1= ε1(b2).Plugging(3.28)into(3.15)yields

Taking s=b in(3.29),we have
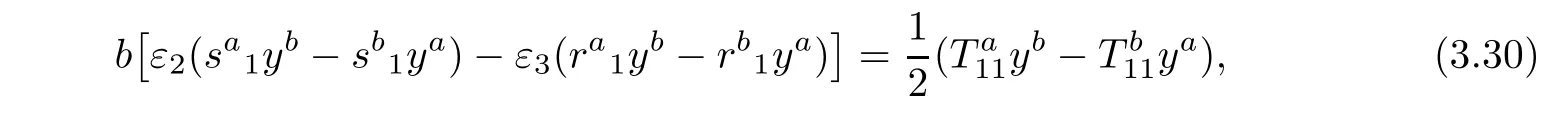
where ε2:= ε2(b2)and ε3:= ε3(b2).Inserting(3.30)into(3.29)yields

By(3.31),we divide the problem into three cases:
(1)ra1=0,sa1=0;
(2)ra1=k(b2)sa1,sa1/=0;
(3)sa1=0,ra1/=0.
Case 1ra1=0,sa1=0.
In this case,by(3.13)and(3.15),it is obtained thatBy sa1=0 and(3.18),then β is closed.From ra1=0 and(3.27),it follows that
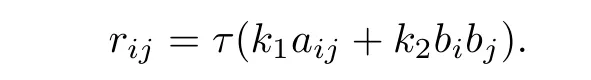
By the above equality and β being closed,we obtain(3.2).By(3.26),we obtain(3.1).
Case 2ra1=k(b2)sa1,sa1/=0.
Because sa1/=0,β is not closed.Moreover,we have obtained
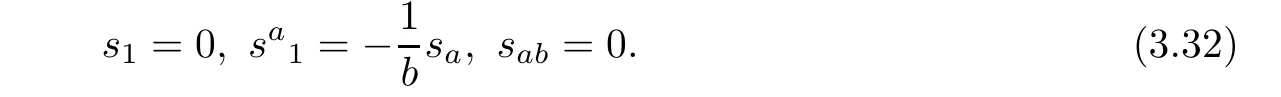
Noting that sijis skew symmetric,by(3.32),we obtain(3.5).In this case,ra1=?;Let us summarize what we have proved so far

By(3.33),we have(3.4).
By(3.31)and sa1/=0,we have
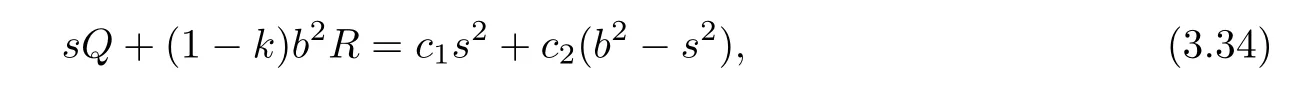
where c1= ε2?kε3and c2:=(1?k)ε1.From(3.34),we claim that k/=1.If k=1,then(3.34)is reduced to bQ=c1s.In this case,φ=1+c1bs2.Hence,F is Riemannian.Plugging Q and R into(3.34),we rewrite it as
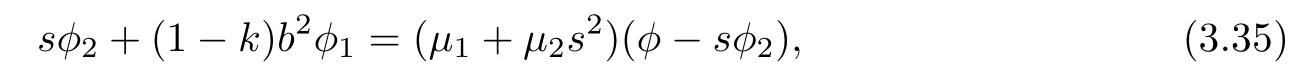
whereμ1:=c2b2,μ2:=c1?c2.
Differentiating(3.35)with respect to s yields
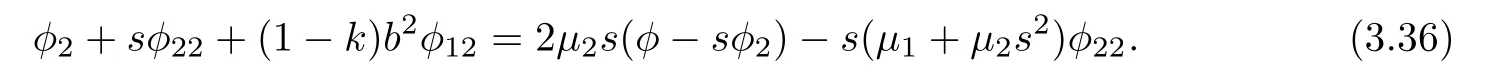
Contracting(3.13)with yayields
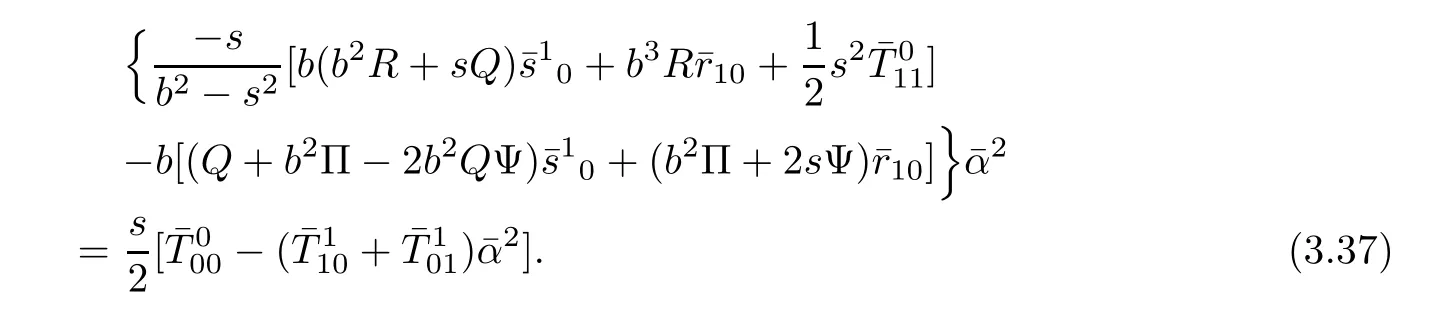
Plugging ra1=ksa1into(3.30)yields
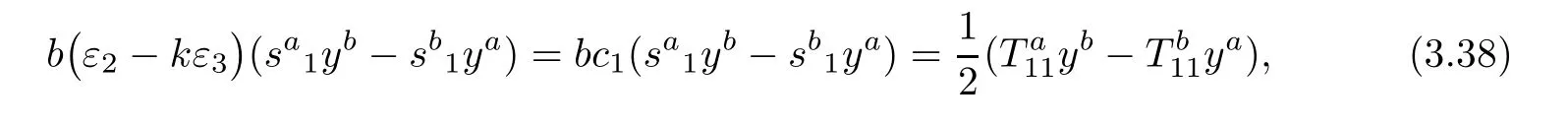
By(3.38),we get

Plugging ra1=ksa1and(3.39)into(3.37)yields

Because the coefficients of the right side in(3.40)is independent of s,if(3.40)holds,then by(3.34),we obtain
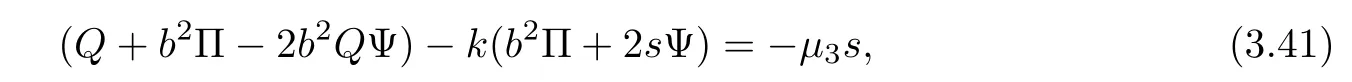
where μ3:=and λ3:= λ3(b2).
By making using of(3.35)and(3.36),we have

Plugging(3.42)into(3.41)yields

We claim that k+1+2μ1?μ3b2=0 and 2μ2+μ3=0.If k+1+2μ1?μ3b2/=0,by solving(3.43),we obtain
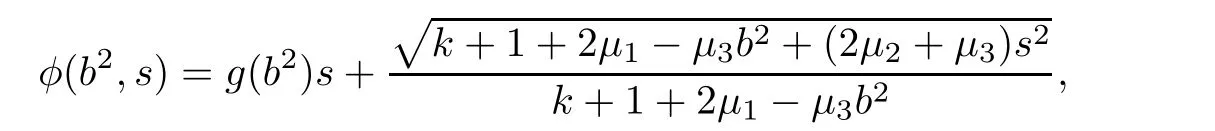
where g(b2)is an arbitrary smooth function.Hence,the corresponding general(α,β)-metric is of Randers type.This case is excluded in the assumption of Theorem 1.1.If k+1+2μ1?μ3b2=0 and 2μ2+μ3/=0,then we obtain

At this time,the corresponding general(α,β)-metric is of Kropina type.This case is excluded because this class of metrics are singular.Hence,
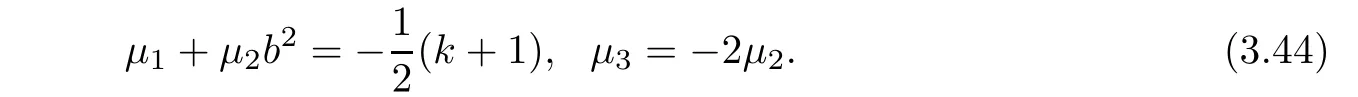
Case 3sa1=0,ra1/=0.
In this case,for rij,we have obtained

Therefore,by(3.45),we have
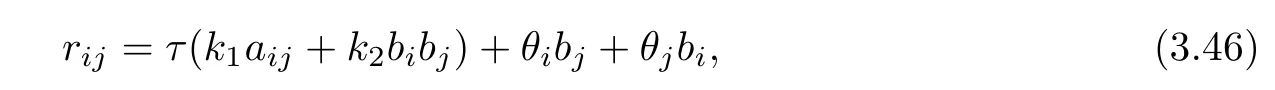
where θ := θiyiis a 1-form,which is perpendicular to β.By sa1=0 and(3.18),then β is closed.Hence,it follows from(3.46)that we obtain(3.7).
Because sa1=0 and ra1/=0,by(3.31),we obtain

Plugging R into(3.47)yields
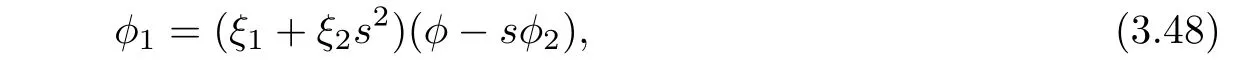
where ξ1:= ε1and.Differentiating(3.48)with respect to s yields
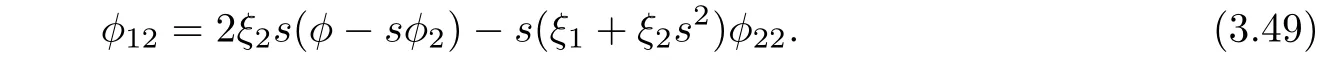
Plugging sa1=0 into(3.13)yields
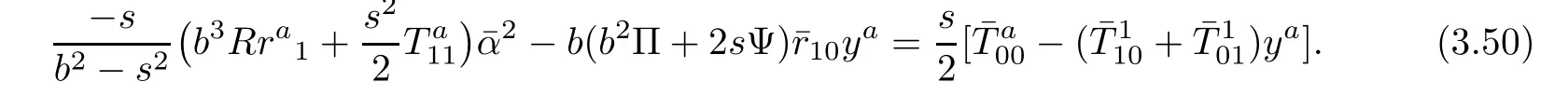
Contracting(3.50)with respect to yayields

Plugging sa1=0 into(3.30)yields

By(3.52),we conclude that

Plugging(3.53)into(3.51)yields

By(3.47),the above equality is reduced to the following
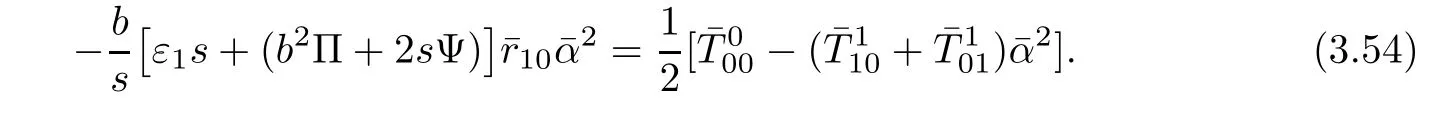
Because the right side in(3.54)is independent of s,there exists a function η(b2)such that

We rewrite(3.55)as

where ξ3:= η ? ε1.By(3.48)and(3.49),we obtain

Plugging(3.57)into(3.56)yields

We claim that 1?2b2ξ1?b2ξ3=0 and ξ3?2b2ξ2=0.If 1?2b2ξ1?b2ξ3/=0,then by solving(3.58),we obtain
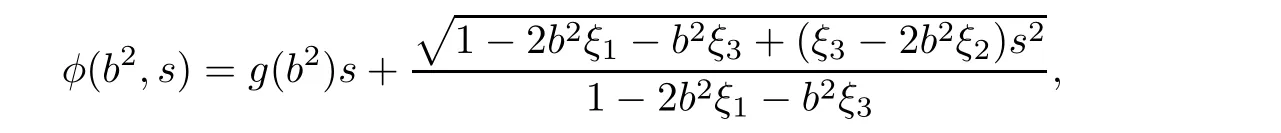
where g(b2)is an arbitrary smooth function.Hence,the corresponding general(α,β)-metric is of Randers type.This case is excluded in the assumption of Theorem 1.1.If 1?2b2ξ1?b2ξ3=0 and ξ3? 2b2ξ2/=0,then we obtain At this time,the corresponding general(α,β)-metric is of Kropina type.This case is excluded because this class of metrics are singular.Therefore,we obtain
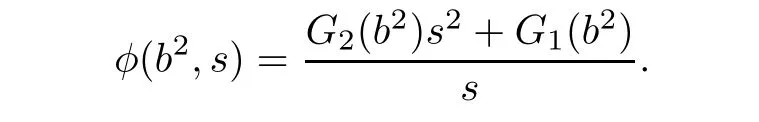

By(3.18),we have the following result.
Remark 3.1If a general(α,β)-metric is a Douglas metric,then the Rank of skew symmetric matrix(sij)is not greater than 2.
4 Sufficient Conditions
In this section,we show the sufficient conditions for a general(α,β)-metric to be a Douglas metric.
Lemma 4.1Let F= αφ(b2,s),s=,be a regular general(α,β)-metric on an open subset U ? Rn(n ≥ 3).Suppose that β is not parallel with respect to α and F is not of Randers type.Then,F is a Douglas metric if one of the following cases holds:
(1)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies
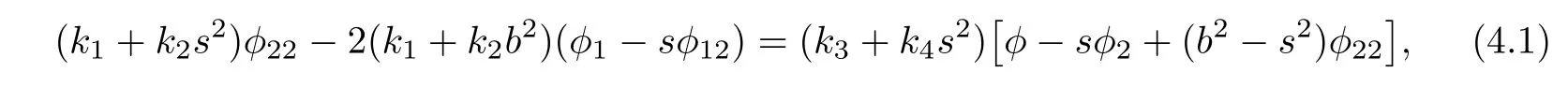
where ki:=ki(b2),i=1,2,3,4 and β satisfies
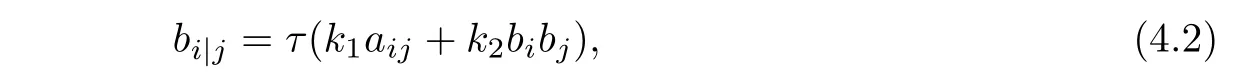
where τ= τ(x)is a scalar function on U.
(2)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies(4.1)and
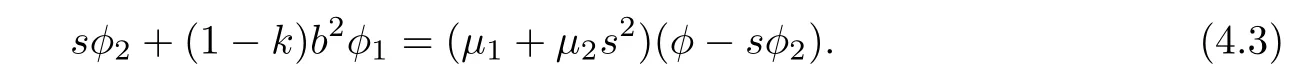
where k:=k(b2)/=1,μi:= μi(b2),i=1,2 and μ1+μ2b2= ?(k+1).Moreover,α and β satisfies

whereμ1+μ2b2=(k+1)and k=k(b2).In this case,dβ/=0.
(3)φ=φ(b2,s)satisfies(4.1)and

and β satisfies
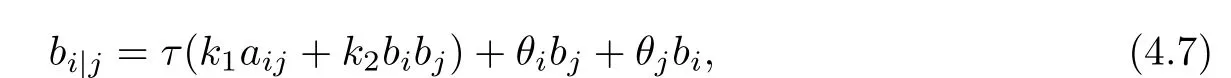
where θ := θiyiis a 1-form which is perpendicular to β. ξi:= ξi(b2),i=1,2 and ξ1+ξ2b2=
ProofAssume that case 1 holds.By(4.2),we have
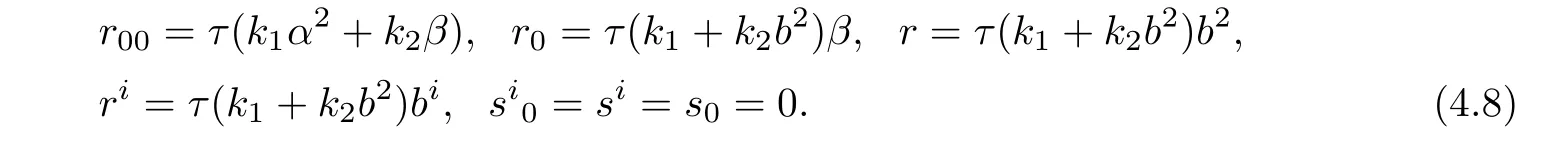
Plugging(4.8)into(2.5)yields
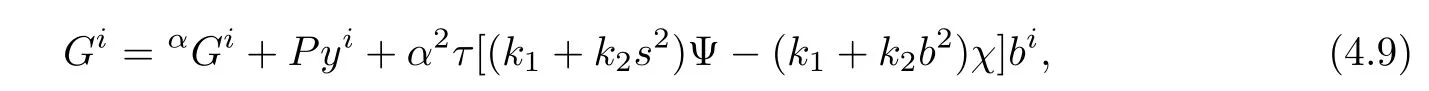
where χ :=R? 2RΨb2? sΠ and P:= ατ[(k1+k2s2)Θ+(2ΘRb2+s?)(k1+k2b2)].
Inserting(4.1)into(4.9)yields

Thus,it follows from(2.1)and(4.10)that F is a Douglas metric.
Assume that case 2 holds.By(4.4)and(4.5),we obtain
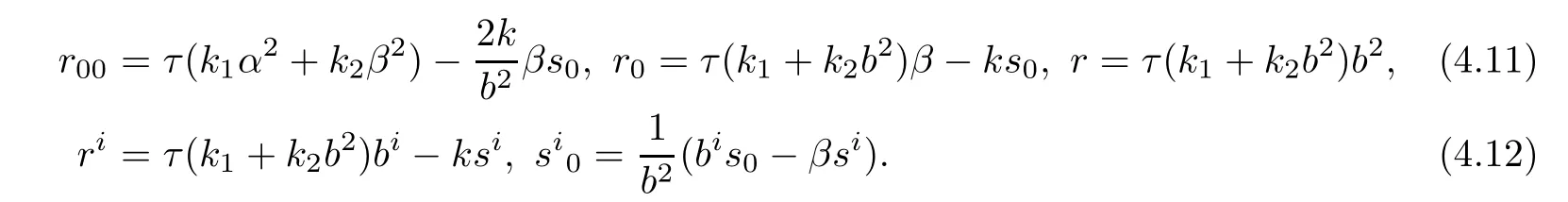
Inserting(4.1),(4.3),(4.11),(4.12)and(3.42)into(2.5)yields
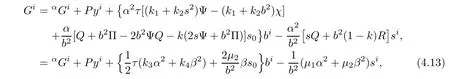
where we have used the first formula of(3.44)and P:= ατ[(k1+k2s2)Θ+(2ΘRb2+s?)(k1+Hence,from(2.1)and(4.13),then F is a Douglas metric.
Assume that case 3 holds.From(4.7),we obtain
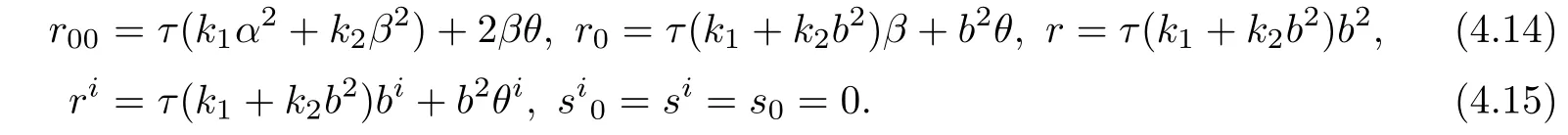
Plugging(4.14)and(4.15)into(2.5)yields

where P:= ατ[(k1+k2s2)Θ +(2ΘRb2+s?)(k1+k2b2)]+(2sΘ +b2?)θ.
Plugging(4.1),(4.6),and(3.57)into(4.16)yields

where we have used the first formula of(3.59).Hence,by(2.1)and(4.17),then F is a Douglas metric.
AcknowledgementsThe author would like to thank Professor Changtao Yu for his helpful discussion and the valuable comments.
[1]Bácsó S,Matsumoto M.On Finsler spaces of Douglas type.A generalization of the notion of Berwald space.Publ Math Debrecen,1997,51:385–406.MR 98j:53024
[2]Bryant R.Some remarks on Finsler manifolds with constant flag curvature.Houston J Math,2002,28:221–262
[3]Bácsó S,Matsumoto M.On Finsler spaces of Douglas type-a generalization of the notion of Berwald space.Publ Math Debrecen,1997,51:385–406
[4]Cheng X Y,Shen Z M.Projectively flat Finsler metrics with almost isotruplc-S-curvature.Acta Mathematica Scientia,2006,26B(2):307–313
[5]Li B L,Shen Y B,Shen Z M.On a class of Douglas metrics.Studia Sci Math Hung,2009,46:355–365
[7]Li B L,Shen Z M.On a class of projectively flat Finsler metrics with constant flag curvature.Int J Math,2007,18:749–760
[7]Li B L,Shen Z M.Projectively flat fourth root Finsler metrics.Can Math Bull,2012,55:138–145
[8]Matsumoto M.Finsler spaces with(α,β)-metric of Douglas type.Tensor(N S),1998,60:123–134
[9]Mo X H,Solórzano N M,Tenenblat K.On spherically symmetric Finsler metrics with vanishing Douglas curvature.DiffGeom Appl,2013,31:746–758
[10]Wang X M,Li B L.On Douglas general(α,β)-metrics,arXiv:1606.08043v1.
[11]Yu C T,Zhu H M.On a new class of Finsler metrics.DiffGeom Appl,2011,29:244–254
[12]Yu C T,Zhu H M.Projectively flat general(α,β)-metrics with constant flag curvature.J Math Anal Appl,2015,429:1222–239
[13]Zhou L F.Spherically symmetric Finsler metrics in Rn.Publ Math Debrecen,2012,80:67–77
[14]Zhu H M.On general(α,β)-metrics with vanishing Douglas curvature.Int J Math,2015,26(9):Article ID:1550076,16pp
[15]Zhu H M.A class of Finsler metrics of scalar flag curvature.DiffGeom Appl,2015,40:321–331
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2018年2期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2018年2期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- EXISTENCE AND BLOW-UP BEHAVIOR OF CONSTRAINED MINIMIZERS FOR SCHR?DINGER-POISSON-SLATER SYSTEM?
- STABILITY AND BIFURCATION ANALYSIS OF ADELAYED INNOVATION DIFFUSION MODEL?
- SOLUTIONS TO BSDES DRIVEN BY BOTH FRACTIONAL BROWNIAN MOTIONS AND THE UNDERLYING STANDARD BROWNIAN MOTIONS?
- LIOUVILLE THEOREM FOR CHOQUARD EQUATION WITH FINITE MORSE INDICES?
- THE GLOBAL ATTRACTOR FOR A VISCOUS WEAKLY DISSIPATIVE GENERALIZED TWO-COMPONENT μ-HUNTER-SAXTON SYSTEM?
- A NOTE IN APPROXIMATIVE COMPACTNESS AND MIDPOINT LOCALLY K-UNIFORM ROTUNDITY IN BANACH SPACES?
