時間約束下帆板撓性振動抑制的預測與反演控制


摘要: 針對航天器撓性帆板的振動抑制問題開展研究,基于模態空間中狀態方程形式的動力學模型,在離散時間系統中求解太陽帆板振動受控下模態坐標隨時間變化的規律;對振動模態坐標的狀態轉移進行預測,利用模型預測方法外推預測撓性各振動模態坐標狀態的預計偏差;采用廣義逆方法,反演得到抑制撓性振動所需的控制序列; 通過逐步逼近的方法,設計了在給定的振動抑制時間約束下,太陽帆板撓性振動抑制的模型預測與反演控制律;分析了該方法在應用中的一些特點;仿真結果表明,所提出的方法能夠實現指定時間約束下航天器太陽帆板的快速振動抑制。
關鍵詞: 太陽帆板; 振動抑制; 模型預測與反演控制; 撓性; 時間約束
中圖分類號: V414.3+3; TB535 文獻標志碼:A 文章編號1004-4523(2018)05-0744-08
DOI:10.16385/j.cnki.issn.1004-4523.2018.05.003
引 言
撓性結構在空間飛行器上普遍存在, 如太陽帆板、空間機械臂或天線等。這些結構通常尺寸大,質量輕,剛度相對較小,結構振動模態頻率低且密集、模態阻尼小,在伸展、轉動過程中容易受到各種內、外部激振,且振動常會持續較長時間,直接影響航天器本體姿態的高精度控制。為抑制撓性結構的振動,國內外先后有學者提出了輸入成形法[1-2]、線性二次型最優控制[3-4]、分力合成法[5]、正位置/速度反饋[6-8]、魯棒控制[9]、自適應控制[10-11]、滑模變結構控制[12-13]、最優控制[14-15]、模糊/神經網絡控制[16-17]、預測控制[18-21]等控制方法。其中預測控制采用模型預測、反饋校正和滾動優化,通過二次規劃方法求解關于控制偏差及控制量的加權目標函數以得到控制輸出,對于振動抑制過程通常沒有時間約束。系統控制周期的選擇對控制過程和結果有較大影響。上述方法中,在控制姿態的同時考慮抑制撓性振動的集中控制方法需要較快的采樣測控速度和較寬的控制系統帶寬,控制系統階數高,系統設計難以兼顧,常規的姿態敏感器、控制器、執行機構等難以滿足要求,工程實現困難。
隨著頻帶寬、響應速度快、體積小、質量輕、埋入粘貼方便的壓電材料的出現,在連接結構上減小航天器剛體部分與撓性附件的耦合影響,對航天器姿態控制和振動抑制分別進行設計,采用不同的測量敏感器、控制器和執行機構,形成相對獨立的控制回路,進行分散控制是目前航天器撓性附件振動抑制的一種有效途徑。
在模態空間[22-24]中進行控制器設計是撓性振動主動控制的一種常用方法。模態空間法采用模型降階將無限自由度的振動控制轉化為模態空間內有限個振動模態的控制,雖然可能存在不受控模態所引起的“溢出”問題,但在考慮足夠多的、能量較為集中的幾個主要模態,通過模態截斷準則對振幅小、能量少的高階模態進行截斷后,可以降低控制系統設計復雜程度,減小控制器階數,較好地抑制撓性結構振動所導致的姿態干擾,因此基于模態空間的控制方法在工程上得到了較為廣泛的應用。
本文在狀態方程形式的航天器帆板撓性振動動力學模型基礎上,對模態坐標的狀態轉移過程進行求解,獲得模態坐標狀態的演變規律,外推預測撓性振動各個模態坐標狀態的預計偏差,反演抑制撓性振動所需的控制序列;根據振動抑制的時間約束,控制模態坐標逐步逼近期望狀態,設計了在時間約束條件下,帆板撓性振動抑制的模型預測與反演控制律,討論了該方法在應用中的一些特點,通過仿真驗證了控制方法的有效性。
1 太陽帆板模態空間模型
航天器上的太陽帆板通常由鋁蜂窩兩側覆蓋碳纖維/環氧復合材料薄板組成,四周安裝有鋁框。太陽帆板及安裝于其上的應變片、壓電陶瓷片共同構成太陽帆板智能結構和主動振動控制回路。應變片測量帆板的彎曲位移,壓電片激勵和控制彎曲振動。
模態坐標狀態的振幅表征了振動的能量。比較圖1和2,易知隨著時間由0→3 s,需要阻尼和抵消的能量是逐漸增加的,故撓性抑制過程中壓電作動器輸入電壓隨時間逐漸增大。
對于有更多模態需要進行振動抑制的動力學系統,以及敏感器、控制器與執行機構能夠滿足控制要求的航天器姿態、帆板一體化集中控制系統,MPIC-TC方法同樣是適用的。此外,在不同的系統控制周期下,帆板撓性振動模態均能在3 s內較為精確地達到零位移狀態。
5 結 論
本文所提出的方法遵循撓性振動模態坐標狀態受控轉移的規律,可以較為精確地實現指定時間下帆板撓性的振動抑制。在每個采樣控制周期中,根據剩余的模態坐標狀態轉移時間控制器參數是時變自適應的,與初始狀態和期望狀態無關。后續可以在多輸入、控制輸出受限和能量最小等約束及目標下,基于預測模型反演控制的一般解,對控制方法和參數進行進一步優化。
參考文獻:
[1] 姚雨晗, 周 軍, 劉瑩瑩. 基于輸入成型法的空間站變構型過程撓性振動抑制策略[J]. 宇航學報, 2013, 34(5):665—670.
Yao Yuhan, Zhou Jun, Liu Yingying. Research on flexible vibration suppression strategy for variable configuration space station based on input shaping technique[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2013, 34(5):665—670.
[2] Deng H, Sun J D, Huang S D. Vibration suppression of the flexible manipulator using optimal input shaper and linear quadratic regulator [C]. 12th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence, Goyangcity, Korea, 2015:255—260.
[13] 肖 巖,葉 東, 孫兆偉. 面向剛柔耦合衛星的有限時間輸出反饋姿態控制[J]. 宇航學報, 2017, 38(5):516—525.
Xiao Yan, Ye Dong, Sun Zhaowei. Finite-time output feedback attitude control for rigid-flexible coupling satellites [J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(5): 516—525.
[14] 王曉明, 周文雅, 尋廣彬, 等. 帶有振動抑制的壓電結構動態形狀主動控制[J]. 宇航學報, 2017, 38(2):185—191.
Wang Xiaoming, Zhou Wenya, Xun Guangbin, et al. Dynamic shape control of piezoelectric structures with vibration suppression [J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(2):185—191.
[15] Yu Y, Han F, Leng X Z, et al. Design and implementation of a wireless optimal controlscheme for active structural vibration control [C].Fifth International Conference on Instrumentation and Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, Qinhuangdao, China, 2015:901—906.
[16] Chen Y, Dong C Y. A fuzzy-neural network sliding mode control for flexible spacecraft[C]. 2nd International Conference on Information Engineering and Computer Science, Wuhan, China, 2010, 5677732.
[17] Qiu Z C, Zhang X T, Ye C D. Vibration suppression of a flexible piezoelectric beam using bp neural network controller [J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2012, 25(4):417—428.
[18] Lin C Y, Huang Y H. Enhancing vibration suppression in a periodically excited flexible beam by using a repetitive model predictive control strategy[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2016, 22(16) 3518—3531.
[19] Takács G, Batista G, Gulan M, et al.Embedded explicit model predictive vibration control [J]. Mechatronics, 2016, 36 :54—62.
[20] Yuan Y, Zhang H T,Wu Y, et al. Bayesian learning-based model predictive vibration control for thin-walled workpiece machining processes [J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(1):509—520.
[21] 胡俊峰, 張憲民, 徐貴陽. 基于模型預測控制的高速柔性并聯機構振動控制[J]. 振動與沖擊, 2014, 33(1):24—32.
Hu Junfeng, Zhang Xianmin, Xu Guiyang. Vibration control of a high-speed flexible parallel mechanism based on model predictive control [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(1):24—32.
[22] Canfield R A, Meirovitch L. Integrated structural design and vibration suppression using independent modal-space control[J]. AIAA Journal, 1994, 32(10): 3404—3413.
[23] 陳學前, 汪小華, 阮劍華,等. 兩種獨立模態空間控制法在柔性結構振動主動控制中的應用研究[J]. 中國科學技術大學學報, 2001, 31(6):700—706.
Chen Xueqian, Wang Xiaohua, RUAN Jianhua, et al. Study on two independent modal space control methods in the vibration active control of flexible structure[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology of China, 2001, 31(6):700—706.
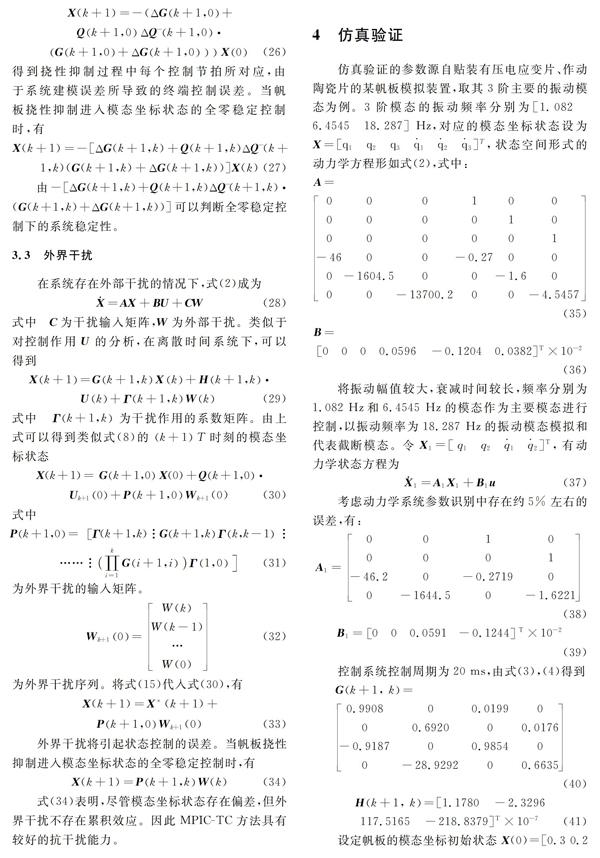
[24] 司洪偉, 李東旭. 大型撓性結構基于獨立模態空間的模糊PID控制[J]. 中國空間科學技術, 2005, 25(3):59—65.
Si Hongwei, Li Dongxu. Fuzzy PID vibration control of large flexible structures based on IMSC[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2005, 25(3):59—65.
[25] 靳永強, 劉向東, 王 偉, 等. 基于模態觀測器的撓性航天器姿態控制[J]. 宇航學報, 2008, 29(3):844—848.
Jin Yongqiang, Liu Xiangdong, Wang Wei, et al. Sliding mode attitude control for flexible spacecraft based on modal observer[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2008, 29(3):844—848.
[26] 王松桂, 楊振海. 廣義逆矩陣及其應用[M]. 北京:北京工業大學出版社, 1996:1—3.
[27] 席裕庚. 預測控制[M].第2版.北京: 國防工業出版社, 2013:24—28.
[28] 通雁輝. 撓性航天器的姿態控制及振動抑制研究[D]. 沈陽: 東北大學, 2009.
Abstract: To study vibration suppression of spacecraft flexible solar arrays, based on state transition model of dynamical system in modal space, the evolution law of mode coordinates of solar arrays is solved in discrete time systems. Deviation of mode coordinates is predicted by model prediction method. Generalized inverse method is used to obtain the control sequence needed for vibration suppression. A model predictive and inversive control law for flexible vibration suppression of solar arrays under given time is designed by the method of gradual approximation. Some characteristics of the method in application are discussed. Simulation results show that the proposed method can achieve fast vibration suppression of spacecraft solar panels under specified time constraints.
Key words: solar arrays; vibration suppression; model predictive and inversive control; flexible; timing constraint
作者簡介: 譚天樂(1973-),男,博士,研究員。電話:(021)24183453, 18616017107;E-mail:18616017107@163.com

