鎘/鉛超分子配合物的合成、晶體結構及理論計算
劉 宏 李傳碧 李國峰 李秀梅 潘亞茹
(1吉林師范大學信息技術學院,四平 136000)
(2吉林師范大學環境友好材料制備與應用教育部重點實驗室(省部共建),四平 136000)
(3通化師范學院化學學院,通化 134002)
鎘/鉛超分子配合物的合成、晶體結構及理論計算
劉 宏1李傳碧*,2李國峰2李秀梅3潘亞茹3
(1吉林師范大學信息技術學院,四平 136000)
(2吉林師范大學環境友好材料制備與應用教育部重點實驗室(省部共建),四平 136000)
(3通化師范學院化學學院,通化 134002)
通過水熱法合成了2個新的金屬-有機超分子配合物[CdCl2(L1)]n(1)和[Pb(BDC)0.5(HBDC)(L2)]·2H2O(2)(H2BDC=對苯二甲酸,L1=2-(4-氨基苯酚)-1H-咪唑并[4,5-f]菲咯啉,L2=2-(4-N,N′-二甲基苯)-1H-咪唑并[4,5-f]菲咯啉)。 并對其進行了元素分析、紅外光譜、熱重、熒光光譜和X射線單晶衍射測定。配合物1是一維鏈狀結構,配合物2為零維結構,它們均通過氫鍵和π-π堆積形成了三維超分子結構。此外,還用高斯09程序PBE0/LANL2DZ方法對配合物1和2進行了自然鍵軌道(NBO)分析,計算結果表明配位原子與Cdギ、Pbギ離子之間存在著共價作用。
水熱合成;晶體結構;鎘配合物;鉛配合物;自然鍵軌道
0 Introduction
Metallosupramolecular species assembled from transition metals and organic bridging ligands with new structures and properties have been rapidly developed due to their interesting structural diversity and potential applications as functional materials[1-5].However,the reasonable design of new materials for special applications is still attractive.During the past years,several types of forces,such as coordination bonding[6-8],hydrogen bonding[9-11],and π-π stacking[12-13]have been wellused in constructing extended supramolecularnetworks.Up to now,the most important driving forces in crystal engineering are coordination,hydrogen-bonding and π-π stacking interactions,and manynetworksassembled from mono-or polynuclear metal complexes via hydrogen bonding, π-π stacking interactions were reported recently[14-16].The unique strength,directionality and complementary of such non-covalent interactions play key roles in the construction of various architectures for molecular self-assembly and recognition[17-19].
Based on all the aspects stated above,herein we report the synthesis and crystal structure of two coordination supramolecule,[CdCl2(L1)]n(1)and[Pb(BDC)0.5(HBDC)(L2)]·2H2O(2).In the solid state,complexes 1 and 2 form a novel three-dimensional(3D)network resulted from intermolecular hydrogen-bonding and ππ stacking interactions.
1 Experimental
1.1 General procedures
All reagents were purchased commercially and used without further purification.Elemental analyses(C,H and N)were measured on a Vario ELⅢElemental Analyzer.IR spectrum was recorded in the range of 4 000~400 cm-1on a Nicolet 6700 spectrometer using a KBr pellet.TG studies were carried on a STA7300 analyzer under nitrogen at a heating rate of 10℃·min-1.The fluorescent spectrum was obtained on a computer-controlled JY Fluoro-Max-3 spectrometer at room temperature.The power X-ray diffraction(PXRD)studies were performed with a Bruker D8 Discover instrument(Cu Kα radiation,λ=0.154 184 nm,U=40 kV,I=40 mA)over the 2θ range of 5°~50°at room temperature.
1.2 Synthesis
[CdCl2(L1)]n(1).A mixture of L1(0.065 g,0.2 mmol),CdCl2·2.5H2O(0.091 g,0.4 mmol)and 18 mL H2O was adjust pH=6 with 40%NaOH,sealed in a Teflon-lined stainless steel vessel,heated to 140℃for 3 days,and followed by slow cooling(a descent rate of 5℃·h-1)to room temperature.Yellow block crystals were obtained.Yield:53%.Anal.Calcd.For C19H13Cd Cl2N5O(%):C,44.69;H,2.57;N,13.71.Found(%):C,44.05;H,2.14;N,13.02.IR (cm-1):3 043w,1 610w,1 584m,1 457m,1 346m,1 136s,839w,811w,732w,619w,514w.
[Pb(BDC)0.5(HBDC)(L2)]·2H2O(2).A mixture of L2(0.068 g,0.2 mmol),Pb(NO3)2(0.066 g,0.2 mmol),H2BDC (0.033 g,0.2 mmol),and 18 mL H2O was adjust to pH=7 with 40%NaOH,sealed in a Teflonlined stainless steel vessel,heated to 150℃for 5 days,and followed by slow cooling (a descent rate of 5℃·h-1)to room temperature.Colorless block crystals were obtained.Yield:48%.Anal.Calcd.For C66H52N10O14Pb2(%):C,48.82;H,3.23;N,8.63.Found(%):C,48.05;H,2.93;N,8.01.IR (cm-1):3 419w,1 695m,1 625w,1 548s,1 585w,1 511m,1 377s,1 260m,1 148w,1 015m,945m,875w,750m,735w,643w,514w.
1.3 Structure determination
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction data for 1 and 2 wererecordedonaBrukerD8QUESTCMOS diffractometer with graphite-monochromated Mo Kα radiation (λ=0.071 073 nm)at 293 K.The structure was solved with the direct method of SHELXS-97 and refined with full-matrix least-squares techniques using the SHELXL-97 program[20-21].The non-hydrogen atoms ofthe complexes were refined with anisotropic temperature parameters.The hydrogen atoms attached to carbons were generated geometrically.Crystallographic parameters and the data collection statistics for complexes 1 and 2 are given in Table 1.Selected bond lengths and bond angles are listed in Table 2.
CCDC:1472404,1;1551304,2.

Table1 Crystal data and structure refinement for 1 and 2

Table2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)for 1 and 2
2 Results and discussion
2.1 IR spectrum
In the IR spectrum of complex 1,the C-H stretching mode for the phenyl ring is relatively weak and observed at about 3 043 cm-1.Peaks at 1 610,1 584 and 1 457 cm-1could belong to ν(C=C)vibration of aromatic ring.The peak at 1 346 cm-1is ascribed to the ν(C=N)vibration of L1.
In the IR spectra of the complex 2,νas(CO2)and νs(CO2)stretching vibrations at 1 548 and 1 377 cm-1show that the BDC2-ligand adopts bidentate and chelating coordination modes.A strong band at 1 695 cm-1is assigned to the protonated carboxylic group[22].The spectrum also exhibits one intense broad band with the frequency of 3 419 cm-1,which can be assigned to the stretching vibration of crystal water molecule[23].
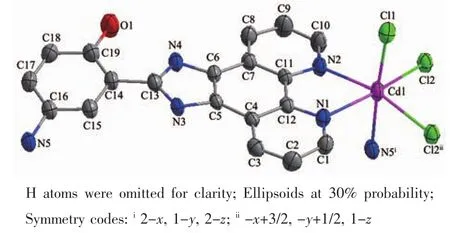
Fig.1 ORTEP view of complex 1 with atom labeling
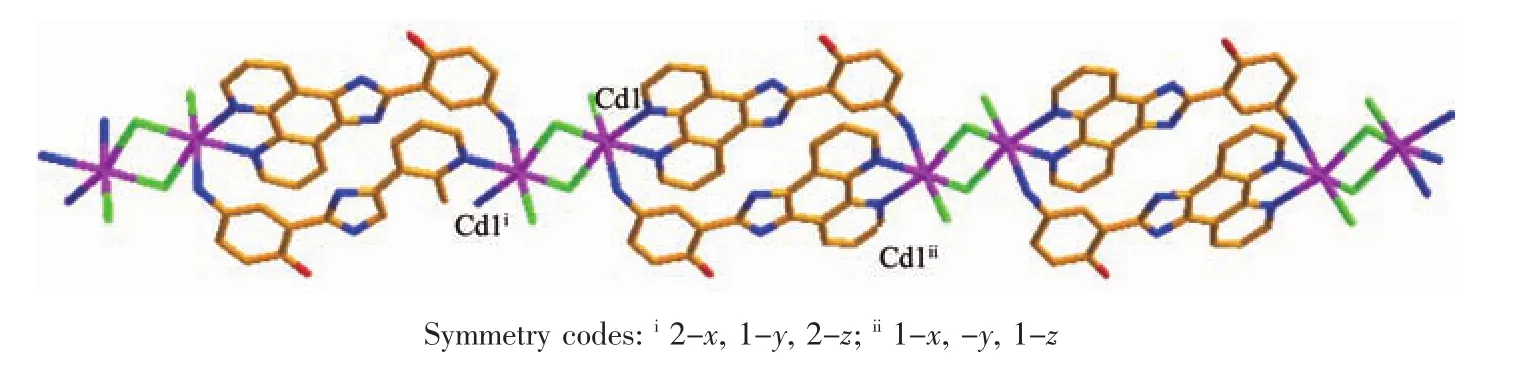
Fig.2 View of the one-dimensional double-chain structure in 1
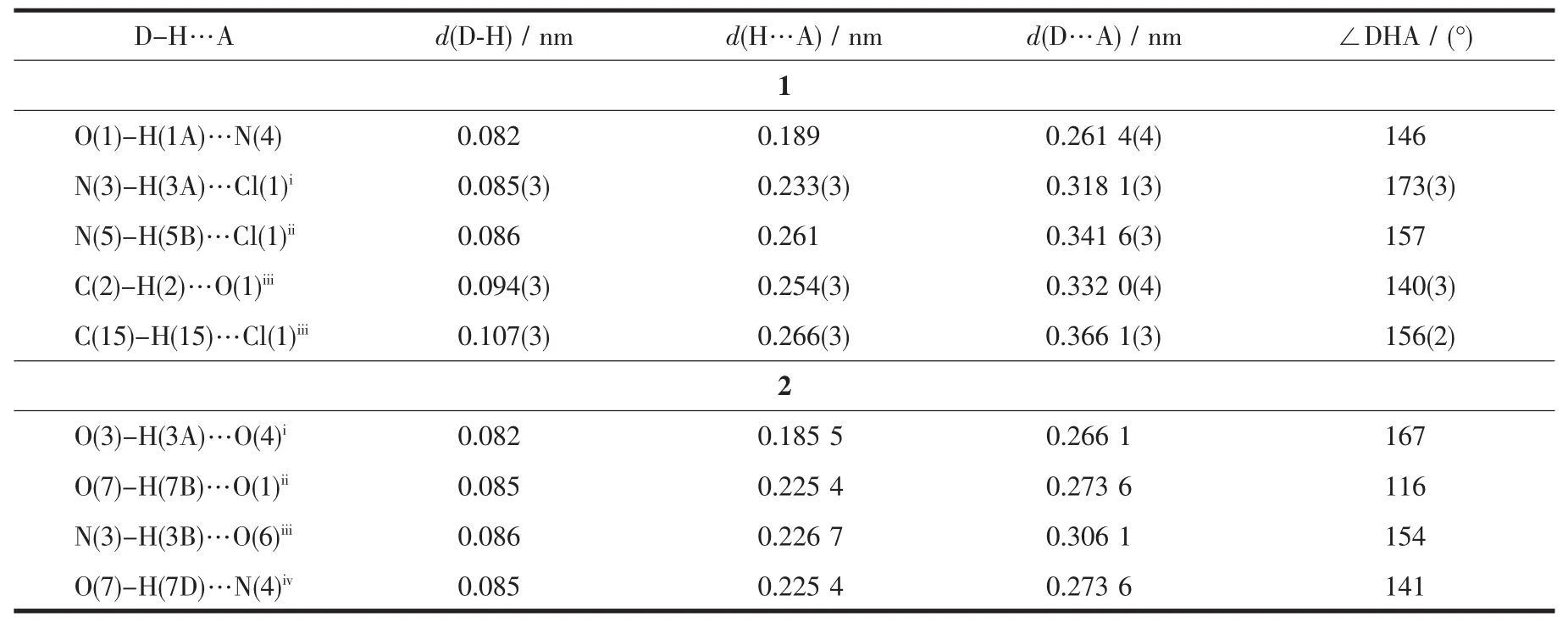
Table3 Hydrogen bonds for complex 1 and 2
2.2 Description of the structure
X-ray crystallography reveals that complex 1 consists of one Cdギion,one L1ligand and two chloride ions in each independent crystallographic unit.The ORTEP view of complex 1 with atom labeling is shown in Fig.1.The coordination geometry around the Cdギcenter could be described as a distorted octahedral environment generated by Cl(2)-Cl(2B)-N(1)-N(2)consisting of the basal plane,and one chloride ion(Cl(1)),one nitrogen atom(N(5A))occupying the axialpositionsfrom the opposite direction.The bond distances of Cd-N in complex 1 fall in the range of 0.232 1(2)~0.255 4(3)nm,and those of Cd-Cl in 0.258 65(8)~0.258 96(9)nm.The coordination angles around the Cd atom vary from 71.44(8)°to 176.81(6)°.
In 1,two chloride ions take μ2bridging mode and each L1ligand adopts μ3coordination fashion to bridge Cdギions into an infinite one-dimensional doublechain,which contains 4-membered rings and 28-membered rings in turn with Cd…Cd distances of 0.355 1 and 1.251 5 nm,respectively(Fig.2).Further investigation of the crystal packing of complex 1 shows that there are O-H…N,C-H…O,C-H…Cl and N-H…Cl hydrogen bonding interactions between hydroxyl oxygen atom,nitrogen atom,carbon atoms of L1ligands and chloride ions (Table 3),as shown in Fig.3.In addition,there are π-π interactions in complex 1 between 5-membered rings and 6-membered rings of L1ligands.The most shortest distance between ring centroids is 0.348 91(18)nm and dihedral angle is 2°(Table 4).As a result,the one-dimensional double-chains are further extended into a threedimensional supramolecular architecture through hydrogen bonds and π-π interactions.
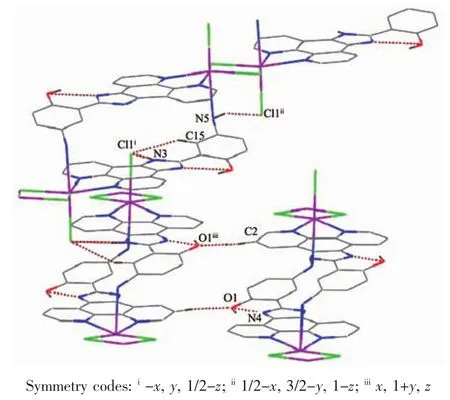
Fig.3 View of hydrogen-bonding interactions of 1
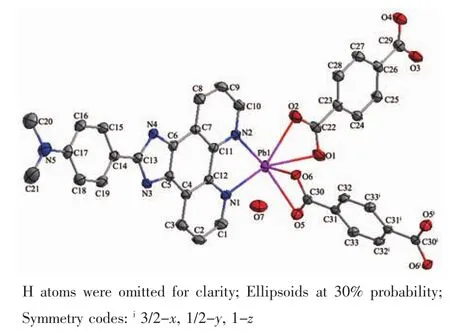
Fig.4 ORTEP view of complex 2 with atom labeling
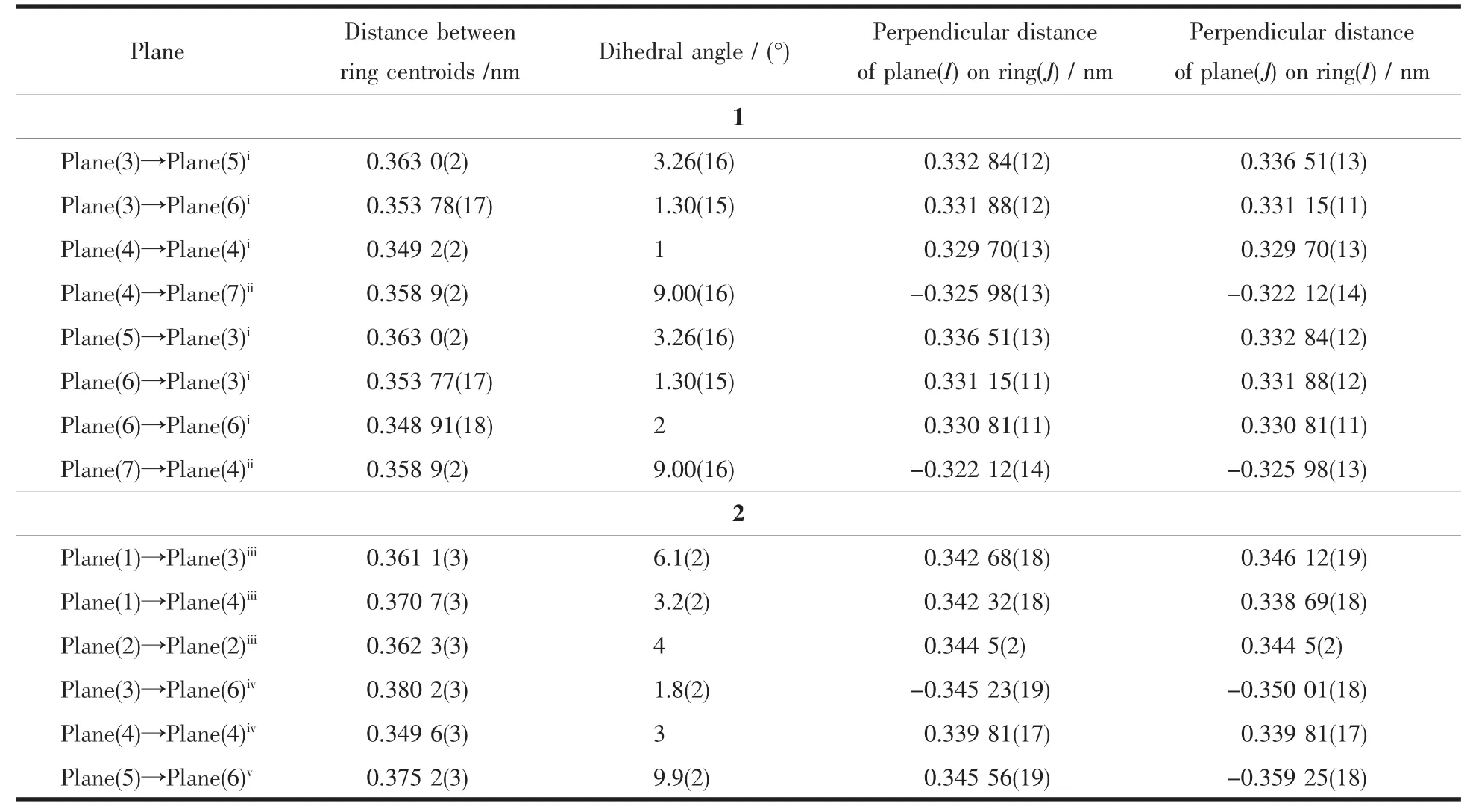
Table4 Parameters between the planes in 1 and 2
The structure of complex 2 consists of one Pbギion,half BDC2-ligand,one HBDC-ligand,one L2molecule and two lattice water molecule.The ORTEP view of complex 2 with atom labeling is shown in Fig.4.In this complex,half ligand BDC2-takes the unusual bi-deprotonated BDC2-form,and adopts bidentate coordination mode using two oxygen atoms of two carboxylate groups,one ligand takes di-protonated HBDC-form,and adopts bidentate coordination mode using two oxygen atoms of one carboxylate group.The ligand L2chelates with the Pbギcenter to result in pentangular pyramid environment.The Pb-N and Pb-O bond distances lie in the range of 0.256 5(3)~0.262 3(4) nm and 0.236 3(3)~0.266 8(4)nm,respectively,all being normal for such coordination bonds.
Further investigation of the crystal packing of complex 2 suggests that there are persistent O-H…O,N-H…O and O-H…N hydrogen bonding interactions(Fig.5)between carboxylate oxygen atoms,nitrogen atom of L2ligands and crystal water molecules(Table 3)and are usually important in the synthesis of supramolecular architecture.Moreover,there are π-π interactions in complex 2 between imidazole rings,pyridine rings,benzene rings of L2ligands and between benzene rings of HBDC-ligands.The most shortest distance between ring centroids is 0.349 6(3)nm and dihedral angle is 3°(Table 4).Therefore,through hydrogen bonds and π-π interactions,complex 2 is further extended into a two-dimensional supramolecular network framework.
To confirm the phase purity of complex 1 and 2,powderX-ray diffraction (PXRD)patternswere recorded for 1 and 2,and they were comparable to the corresponding simulated patterns calculated from the single-crystal diffraction data(Fig.6),indicating a pure phase of bulky sample.
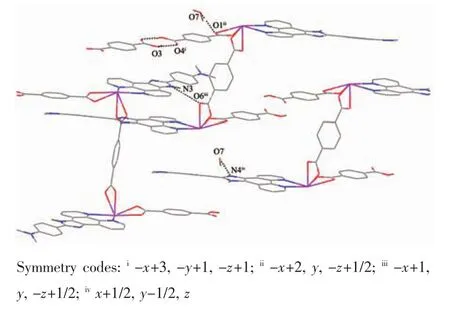
Fig.5 View of hydrogen-bonding interactions of 2
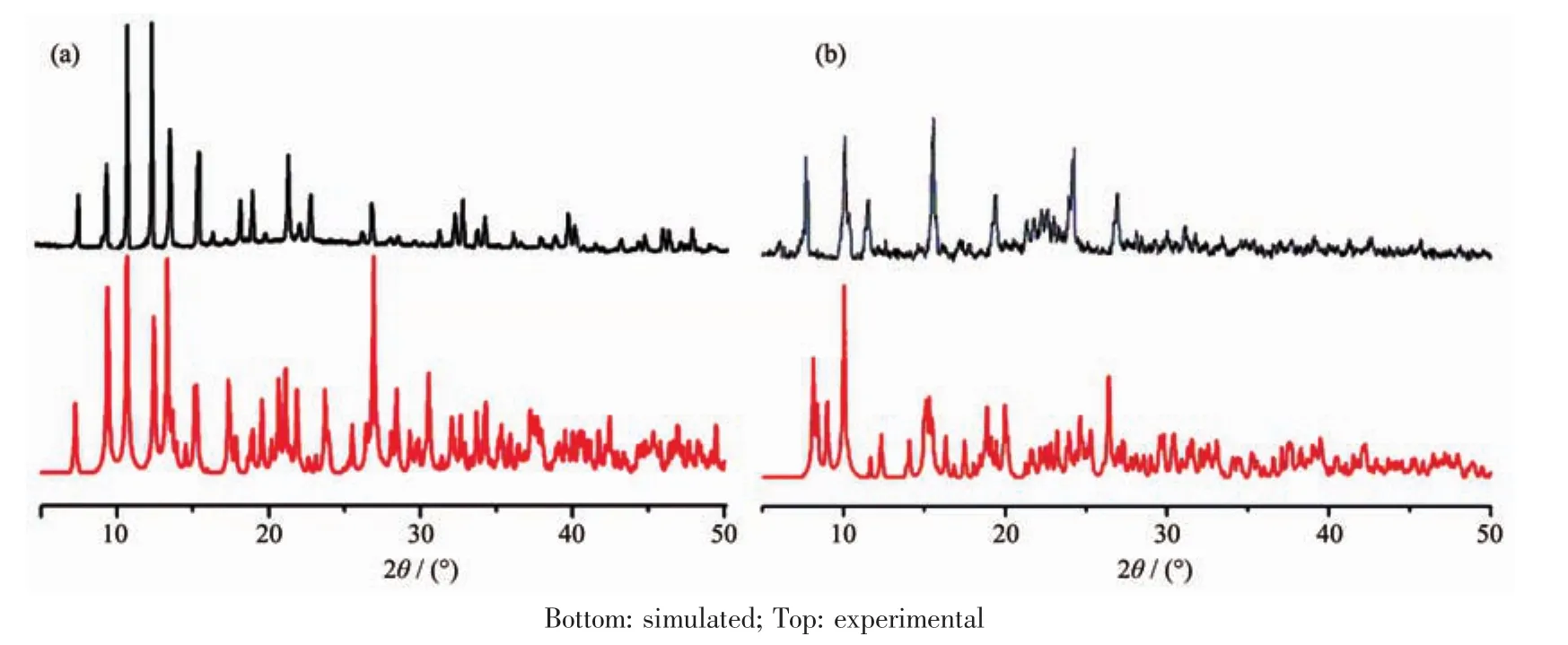
Fig.6 PXRD analysis of the title complex 1(a)and 2(b)
2.3 Photoluminescent properties
Luminescence property is very significant in photochemistry and photophysics[24-25].So in this study,we measured the solid-state photoluminescence spectra of 1 and 2 (Fig.7)at room temperature.Excited by 325 nm,complex 1 exhibits blue emission with the maximum peak at 435 nm.Complex 2 gives green photoluminescence with an emission maximum at 546 nm upon excitation at 325 nm.In order to study the nature of these emission bands,we first analyzed the photoluminescence properties of free L1,L2,H2BDC ligands,and confirmed that they do not emit any luminescence in the range of 400~800 nm.Therefore,on the basis of the previous literature[26],the emission band could be vested to the emission of ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT). For possessing strong fluorescent intensity,it seems to be good candidates for novel hybrid inorganic-organic photoactive materials.
2.4 Theoretical calculation
All calculations in this work were carried out with the Gaussian09 program[27].The parameters of the molecular structure for calculation were all from the experimental data ofthecomplex.Naturalbond orbital (NBO)analysis was performed by density functional theory(DFT)[28]with the PBE0[29]hybrid functional and the LANL2DZ basis set[30].
The selected natural atomic charges,natural electron configuration,Wiberg bond indices and NBO bond orders for the compound 1 are displayed in Table 5.The electronic configurations of Cd(1)ion,N and Cl atoms are 5s0.404d9.995p0.44,2s1.22~1.342p4.17~4.55and 3s1.83~1.933p5.42~5.79,respectively.In view of the above effects,one can infer that the Cd(1)ion coordination with N and Cl atoms is mainly on 4d,5s,and 5p orbitals.Nitrogen atoms form coordination bonds with Cd(1)ion using 2s and 2p orbitals.All Cl atoms provide electrons of 3s and 3p to Cd(1)ion and form the coordination bonds.Therefore,the Cd(1)ion gained some electrons from three nitrogen atoms of L1ligand,three Cl atoms[30-31].So,on the basis of valence-bond theory,the atomic net charge distribution and the NBO bond orders of the complex 1 (Table 5)exhibits the obvious covalent interaction between the coordinated atoms and Cd(1)ion.The differences of the NBO bond orders for Cd-Cl and Cd-N bonds make their bond lengths be different[31],which are in good agreement with the X-ray crystal structural data of complex 1.
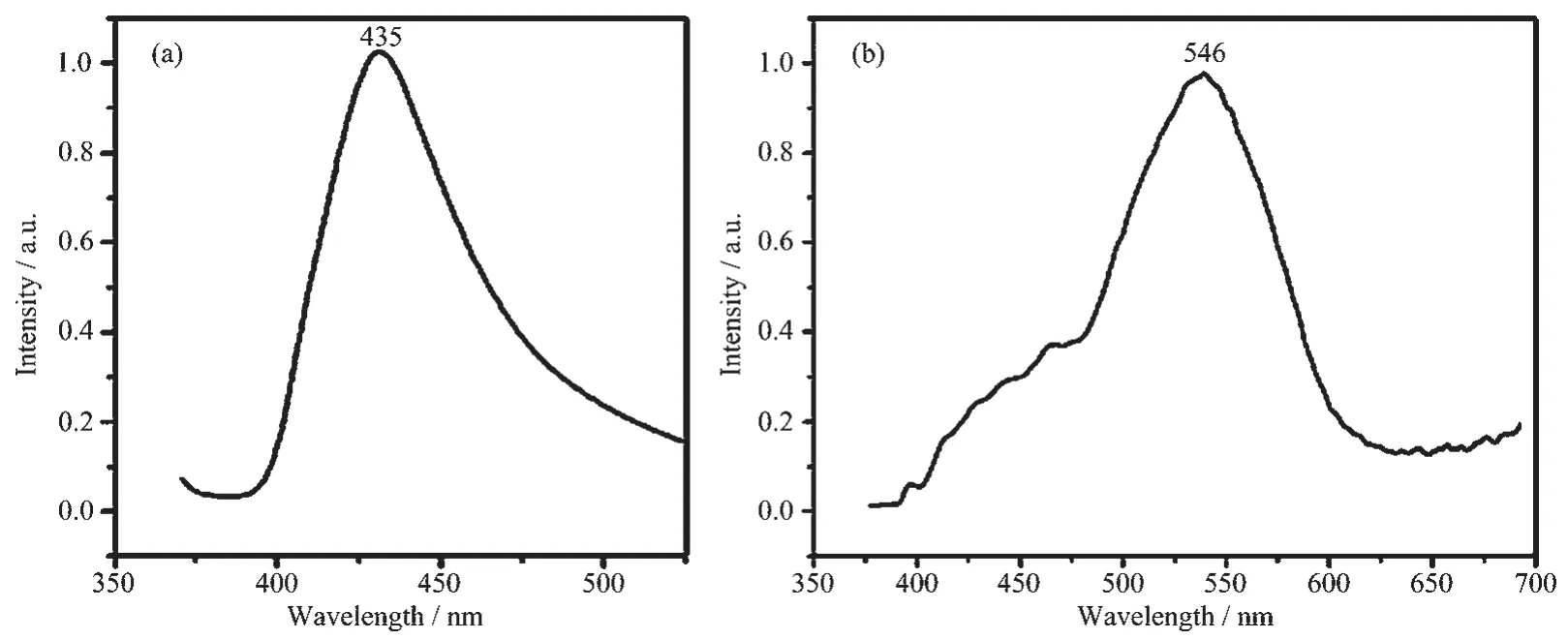
Fig.7 Solid-state emission spectra of 1(a)and 2(b)at room temperature
As can be seen from the Fig.8, lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO)is mainly consistsofL1ligand,whereashighestoccupied molecular orbital (HOMO)mainly composed of L1ligand too.So,the charge transfer from ligand to ligand and ligand to metal may be deduced from some contours of molecular orbital of complex 1.
The selected natural atomic charges,natural electron configuration,Wiberg bonds and NBO bond orders for the complex 2 are shown in Table 5.It is indicated that the electronic configurations of Pb(1)ion,N and O atoms are 6s1.936p0.66,2s1.352p4.13~4.16and 2s1.70~1.722p5.00~5.16,respectively.Based on the above results,one can conclude that the Pb(1)ion coordination with N and O atoms is mainly on 6s and 6p orbitals.N atoms form coordination bonds with Pb(1)ion using 2s and 2p orbitals.All O atoms supply electrons of 2s and 2p to Pb(1)ion and form the coordination bonds.Therefore,the Pb(1)ion obtained some electrons from N atoms and O atoms of ligands[30-31].Thus,according to valence-bond theory,the atomic net charge distribution of the complex 2 shows the obvious covalent interaction between the coordinated atoms and Pb(1)ion.
As can be seen from the Fig.9,LUMO is mainly composed ofL2ligand,whereasHOMO mainly consists of L2 ligand too.So,ILMT may be inferred from some contours of molecular orbital of complex 2.
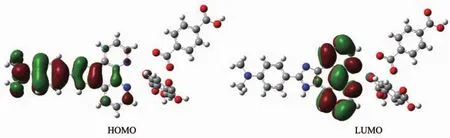
Fig.8 Frontier molecular orbitals of the complex 1

Fig.9 Frontier molecular orbitals of the complex 2
[1]Wu J F,Zhao L,Zhang L,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2016,55:5514-5519
[2]Du M,Bu X H,Guo Y M,et al.Chem.Commun.,2002:1478-1479
[3]Ye B H,Tong M L,Chen X M.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2005,249:545-565
[4]WANG Qing-Wei(王慶偉),SUI Wei(隋薇),WANG Ya-Nan(王亞楠),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(無機化學學報),2016,32:1120-1126
[5]Evans O R,Lin W B.Acc.Chem.Res.,2002,35:511-522
[6]Yaghi O M,Li G,Li H.Nature,1995,378:703-706
[7]Fujita M,Oka H,Yamaguchi K,et al.Nature,1995,378:469-471
[8]Power K N,Hennigar T L,Zaworotko M J.Chem.Commun.,1998:595-596
[9]Sadakiyo M,Yamada T,Kitagawa H.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2011,133:11050-11063
[10]Rigane I,Walha S,Salah A B.J.Chem.Sci.,2016,128:1395-1404
[11]Juan C M R,Lee B.Coord.Chem.Rev.,1999,183:43-80
[12]Melnic E,Tocana E,Siminel A V,et al.Polyhedron,2015,102:410-416
[13]Tse M C,Cheung K K,Chan M C W,et al.Chem.Commun.,1998:2295-2296
[14]Li X M,Wang Q W,Zhan P Y,et al.J.Chem.Crystallogr.,2016,43:163-169
[15]Jiang D Y,Sui W,Li X M,et al.Chin.J.Struct.Chem.,2016,35:505-513
[16]Sun Y X,Wang L,Dong X Y,et al.Synth.React.Inorg.Met.-Org.Nano-Metal Chem.,2013,43:599-603
[17]Lehn J M.Supramolecular Chemistry.Weinheim:VCH,1995.
[18]Whitesides G M,Mathias J P,Seto C T.Science,1991,254:1312-1319
[19]Rebek J.Angew.Chem.,Int.Ed.,1990,29:245-255
[20]Sheldrick G M.SHELXS-97,Program for the Solution of Crystal Structure,University of G?ttingen,Germany 1997.
[21]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structure,University of G?ttingen,Germany 1997.
[22]Fu Z Y,Wu X T,Dai J C,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2002:2730-2735
[23]Nakomoto K.Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds.New York:Wiley,1986.
[24]Mizukami S,Houjou H,Sugaya K,et al.Chem.Mater.,2005,17:50-56
[25]Tang C W,Vanslyke S A.Appl.Phys.Lett.,1987,51:913-915
[26]Zheng S L,Chen X M.Aust.J.Chem.,2004,57:703-712
[27]Frisch M J,Trucks G W,Schlegel H B,et al.Gaussian09,Revision B.09,Gaussian,Inc.,Pittsburgh,2009.
[28]Parr R G,Yang W.Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules.Oxford:Oxford University Press,1989.
[29](a)Ernzerhof M,Scuseria G E.J.Chem.Phys.,1999,110:5029-5036(b)Adamo C,Barone V.J.Chem.Phys.,1999,110:6158-6170
[30]Wang L,Zhao J,Ni L,et al.Z.Anorg.Allg.Chem.,2012,638:224-230
[31]LI Zhang-Peng(李章朋),XING Yong-Heng(邢永恒),ZHANG Yuan-Hong(張元紅),et al.Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin.(物理化學學報),2009,25:741-746
Syntheses,Crystal Structures and Theoretical Calculation of Cadmium/Lead Supramolecular Coordination Compounds
LIU Hong1LI Chuan-Bi*,2LI Guo-Feng2LI Xiu-Mei3PAN Ya-Ru3
(1College of Information&Technology,Jilin Normal University,Siping,Jilin 136000,China)(2Key Laboratory of Preparation and Applications of Environmental Friendly Materials,Ministry of Education,Jilin Normal University,Siping,Jilin 136000,China)(3Faculty of Chemistry,Tonghua Normal University,Tonghua,Jilin 134002,China)
Two new metal-organic supramolecular coordination compounds[CdCl2(L1)]n(1)and[Pb(BDC)0.5(HBDC)(L2)]·2H2O(2)(H2BDC=terephthalic acid,L1=2-(4-aminophenol)-1H-imidazo[4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline,L2=2-(4-N,N′-dimethylbenzene)-1H-imidazo[4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline)have been hydrothermally synthesized and structurally characterized by elemental analysis,IR spectrum,TG,fluorescence spectrum and single-crystal X-ray diffraction.Complex 1 is one-dimensional chain-like structure,and complex 2 exhibits zero-dimensional framework.They all display three-dimensional supramolecular network via hydrogen bonding and π-π stacking interactions.In addition,we analyzed natural bond orbital(NBO)of 1 and 2 in using the PBE0/LANL2DZ method built in Gaussian09 program.The calculation results showed the obvious covalent interaction between the coordinated atoms and Cdギ,Pbギ ion.CCDC:1472404,1;1551304,2.
hydrothermal synthesis;crystal structure;cadmium complex;lead complex;natural bond orbital
O614.24+2;O614.43+3
A
1001-4861(2018)01-0161-09
10.11862/CJIC.2018.003
2017-05-21。收修改稿日期:2017-11-07。
吉林省科技發展計劃(No.201205080)資助項目。
*通信聯系人。 E-mail:lcblh2017@163.com

