普通話版伯明翰認知評估量表的常模及在廣州人群中的信度檢驗
陳浩博 潘小平△ 鄭莉莉 胡鍵浠 吳 玉 陳浩揚 郭愛華 周 進 汪志遠
1)廣州醫科大學附屬廣州市第一人民醫院神經內科,廣東 廣州 510080 2)廣州市花都區人民醫院神經內科,廣東 廣州 510000 3)廣州市第十二人民醫院神經內科,廣東 廣州 510000
·論著科研之窗·
普通話版伯明翰認知評估量表的常模及在廣州人群中的信度檢驗
陳浩博1)潘小平1)△鄭莉莉2)胡鍵浠1)吳 玉3)陳浩揚1)郭愛華1)周 進1)汪志遠1)
1)廣州醫科大學附屬廣州市第一人民醫院神經內科,廣東 廣州 510080 2)廣州市花都區人民醫院神經內科,廣東 廣州 510000 3)廣州市第十二人民醫院神經內科,廣東 廣州 510000
目的國內目前缺乏針對腦卒中后認知障礙的測評量表,伯明翰認知評估量表(BCoS)以篩查卒中后認知障礙為目的,其粵語版的信度、效度已經得到檢驗,本研究擬建立普通話版伯明翰認知評估量表的常模及檢驗其在廣州人群中的信度。方法在廣州地區納入135例健康老年人,所有受試者均行普通話版伯明翰認知評估量表測評,在此基礎上建立普通話版伯明翰認知評估量表常模。本研究通過計算克朗巴赫系數評價該量表的內部一致性,同時對其中的11名受試者進行隨訪,通過Wilcoxon signed rank檢驗評價其重測信度。結果本研究建立了普通話版伯明翰認知評估量表的常模,內部一致性信度檢驗顯示該量表有較好的內部一致性(克朗巴赫系數為:0.785),重測信度檢驗顯示普通話版BCoS量表大多數亞項目有較好的重測信度。結論普通話版BCoS量表具有較好的信度,適于進一步推廣使用。
伯明翰認知評估量表;信度;認知測評;常模
缺血性卒中是高發病率、高致殘率的疾病,可以引起包括運動和認知等多方面的功能障礙,是血管性認知障礙的常見原因[1]。由于研究方法不同,國內外研究發現卒中后認知障礙的發病率在17%~92%[2- 5],而6%~32%的患者則會出現明顯的癡呆[6]。卒中可引起累及多個認知域的能力下降,包括語言[7]、記憶力[8]、視空間能力[8- 10]、注意力[11]、執行功能[8]和實踐能力[9]等,和其功能康復[8]、卒中后抑郁[12]等密切相關,嚴重影響卒中后患者的生活質量,降低其回歸社會比例。早期篩查并給予相應處理是改善卒中后認知障礙的有效手段[5,13]。因此,對卒中患者的早期篩查及干預顯得尤為重要。
國內目前常用的卒中后認知篩查工具包括了簡易智能精神狀態檢查量表(Mini Mental State Examination,MMSE)[14]和蒙特利爾認知評估量表(Montreal Cognitive Assessment Test,MOCA)[15]。這兩個量表簡單實用,耗時短,應用廣泛,但均存在不足之處。MMSE量表對輕度的認知障礙不夠敏感[16],同時缺少對執行功能、視空間功能障礙等血管性癡呆常見受損認知域的檢測[17],而MOCA盡管比MMSE敏感,但在評估卒中后患者時也存在局限性。對于卒中后中常見的一些認知障礙如視空間忽略、失用等缺乏足夠的探測能力[18- 20]。于此同時,上述兩個量表測評時均高度依賴于患者語言能力的完整,不適用于合并有失語癥的患者,從而使得他們在篩查卒中后認知障礙時受到限制。
伯明翰認知評估量表(Birmingham Cognitive Screen test,BCoS)[21]是一個新的全面評估卒中和其他腦損傷后患者認知功能的工具,測評內容涵蓋了注意力和執行功能、語言、記憶、數字、實踐和行動等五大模塊,涉及多個認知領域,包括了情景記憶、長期記憶和短期記憶,計劃能力、工作記憶,維持注意、選擇注意,視空間忽略、觸覺忽略,書寫能力、表達能力、理解能力,數字的計算、閱讀,邏輯運算等。BCoS量表測評時最大限度了保證了結果的客觀性,能減少測評結果受到共存的語言障礙或視空間忽略的干擾。如通過使用高頻、簡短的介紹語,圖像輔助閱讀及用手指示代替語言回答等形式,BCoS量表可以適用于部分失語的患者[22]。BCoS量表自引進我國后,先后翻譯制定了粵語版本和普通話版本,其中,粵語版本的常模已經建立,完成信度、效度檢驗后目前應用于部分粵語使用地區[22]。普通話版本在大多數條目上與粵語版本相同,但在幾個語言相關條目上做了修正,本研究擬對其進行常模建立和信度檢驗。
1 資料與方法
1.1研究對象本研究共納入135例>50歲的健康老年受試者,來源包括在廣州市第一人民醫院、廣州市第一人民醫院南沙醫院進行體檢的老年人群、廣州數個不同街區進行招募的志愿者和部分住院患者家屬。入選標準:(1)年齡≥50歲;(2)熟練掌握普通話;(3)能維持至少45 min的注意力;(4)已閱讀受試者知情同意并簽署書面知情同意書;(5)愿意且能遵守實驗方案及時復診。排除標準:(1)既往腦梗死、帕金森病、癲癇等中樞神經系統病變;(2)有慢性心功能不全、貧血或其他影響認知的病史;(3)既往診斷癡呆的患者或有認知障礙主訴的患者,本次篩查蒙特利爾認知評估量表北京版<22分[23];(4)注意力不能持續維持45 min;(5)受試者未知情或者拒絕簽署知情同意書。
1.2資料收集及評估(1)設計專門的資料收集表,進行一般資料(包括姓名、性別、出生年月、受教育年限、住址、電話、居住情況等)及既往疾病史、家族史、個人史等信息的收集。(2)評估:對每位入選樣本人群給予BCoS普通話版量表、北京版MOCA評估,所有的量表評估均在1 d內完成,評估人員均由研究組內的工作人員完成,共9位人員參加了一致性培訓,負責測評工作,并對其中11例受試者進行了再次隨訪。
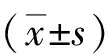
2 結果
2.1 BCoS常模的建立本研究共納入135例健康老年對照組,年齡(64.24±8.93)歲,受教育年限(12.34±3.10)a,男70例,女65例,右利手130例,左利手5例。按照年齡將其分為2組:(1)50~69歲組共93例,年齡(59.25±5.29)歲,受教育年限(11.76±2.84)a,男53例,女40例,右利手88例,左利手5例。(2)≥70歲組共42例,年齡(75.31±4.00)歲,受教育年限(13.61±3.29)a,男17例,女25例,均為右利手。按照2組BCoS數據結合年齡分組(高齡組常模劃界值不高于低齡組)制定常模,具體劃界值數值。見表1。
2.2內部一致性信度檢驗本文通過計算克朗巴赫系數(Cronbach’s alpha)評價普通話版BCoS量表的內部一致性,其結果為0.785,提示該量表在正常老年人群中均擁有較好的內部一致性。
2.3重測信度檢驗本研究共邀請11例受試者先后接受了2次普通話版BCoS量表測評,包括8名男性和3例女性,年齡(57±4.63)歲,受教育年限(11.73±2.41)a,第一次測試與第二次測試間隔14~315(78.27±112.51)d。其中,2例受試者重測時間間隔較長,分別為294 d和315 d,其余9例受試者間隔2~8周。對2次測驗得分進行了Wilcoxon符號秩和檢驗評價其重測信度。統計結果顯示,大部分BCoS亞項目具有很好的重測信度,僅在圖片命名和做手勢、故事回想等個別小項上兩次結果有差別。見表2。

表1 普通話版BCoS各亞項目常模
注:*高齡組表現優于低齡組,常模取值按照低齡組分數

表2 Wilcoxon秩和檢驗測試重測信度
*重測結果有不同
3 討論
卒中后患者可出現多種多樣的認知障礙,嚴重影響患者的生活質量。英國國家衛生醫療質量標準署(National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence,NICE)關于卒中后長程康復的指南指出,對于急性腦卒中患者,應該盡可能快的對其完成包括認知評估在內的全面評估,而認知評估應包含注意力、記憶力、空間能力、失用癥、感知力等多個方面[24]。中國血管性認知障礙診治指南和中國卒中后認知障礙管理專家共識都推薦對血管性認知障礙患者采用適合國人的測驗,進行包括記憶力、注意執行功能、視空間結構功能等在內的多個認知域的測評[25- 26]。美國2016 AHA/ASA 成人卒中康復指南同樣強調了對卒中患者認知評估的重要性[27]。
伯明翰認知評估量表作為一個新的先進的評估工具,其粵語版已被證明為有效全面的認知評估工具[22]。普通話版依據普通話語言及文化的特點,對量表中若干與語言相關的亞項進行了修訂。修改的過程中考慮到了語言的使用頻率、漢字的發音、結構特點等,具體內容可參考粵語版量表的譯制步驟[22]。
本文通過收集健康對照組數據建立了普通話版伯明翰認知評估量表的常模,可以看到其常模絕大部分與粵語版量表相近,具有一定代表性。但普通話版取劃界值時有若干小項出現高齡組分數較低齡組高的情況。我們考慮這是由于高齡組學歷較低齡組高的緣故。廣州絕大多數老年人群母語為粵語,不符合我們的入組要求,而許多高齡被試均為當年南下干部,學歷構成較高。因此我們在設置常模數值的時候,對高齡組的劃界值進行了校正,使其不高于低齡組分數。進一步的常模確定,需要我們擴大數據庫,同時在更多普通話使用地區進行健康被試招募,不斷地進行完善。在檢測普通話版的BCoS量表內部一致性信度時,克朗巴赫系數值為0.785,高于0.7,表明該量表在廣州人群中的內部一致性信度較滿意。對于重測信度,我們納入了11例健康被試進行了2次測評。因為本研究納入重測的樣本例數數量較小,數據不符合正態分布,我們采用了非參數檢驗的方法對數據進行分析。Wilcoxon符號檢驗結果也提示除了圖片命名、故事回想、做手勢三個亞項目外,其他所有亞項目(接近90%)2次測評得分均沒有不同,顯示出良好的重測信度。
BCoS量表目的在于快速全面的描述患者認知概況,以助于卒中后病人的管理和康復。目前,我們在國內首先引進改量表并協助進行了粵語版和普通話版的翻譯修訂工作,在本研究中,我們提供了普通話版的常模值的制定及其信度檢驗,結果提示普通話版的BCoS量表適用于廣州地區人群。盡管如此,本研究仍存在一些局限性,缺乏母語為普通話的老年人群的學歷、性別、年齡統計資料,收集的數據不一定能反映廣州地區的人口構成,且高齡組入選被試學歷偏高,需要在下一步的研究中加以改進。
[1] 彭丹濤.血管性認知障礙的診治進展[J].中國卒中雜志,2014,9(6):463- 465.
[2] Hachinski V,Iadecola C,Petersen RC,et al.National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke- Canadian Stroke Network vascular cognitive impairment harmonization standards[J].Stroke,2006,37(9):2 220- 2 241.
[3] Tu QY,Ding BR,Yang X,et al.The current situation on vascular cognitive impairment after ischemic stroke in Changsha[J].Arch Gerontol Geriatr,2014,58(2):236- 247.
[4] Blackburn DJ,Krishnan K,Fox L,et al.Prevention of Decline in Cognition after Stroke Trial (PODCAST):a study protocol for a factorial randomised controlled trial of intensive versus guideline lowering of blood pressure and lipids[J].Trials,2013,14(1):401.
[5] Sun JH,Tan L,Yu JT.Post- stroke cognitive impair- ment:epidemiology,mechanisms and management[J].Ann Transl Med,2014,2(8):80.
[6] Pasi M,Poggesi A,Salvadori E,et al.Post- stroke dementia and cognitive impairment[J].Front Neurol Neurosci,2012,30(30):65- 69.
[7] Lau JKL,Humphreys GW,Douis H,et al.The relation of object naming and other visual speech production tasks:A large scale voxel- based morphometric study[J].Neuroimage Clinical,2015,(7):463- 475.
[8] Jokinen- Salmela H,Melkas S,Ylikoski R,et al.Post- stroke cognitive impairment is common even after successful clinical recovery[J].Eur J Neurol,2015,22(9):1 288- 1 294.
[9] Chen H,Pan X,Lau JK,et al.Lesion- symptom mapping of a complex figure copy task:A large- scale PCA study of the BCoS trial[J].Neuroimage Clinical,2016,11:622- 634.
[10] Chechlacz M,Novick A,Rotshtein P,et al.The neural substrates of drawing:A voxel- based morphometry analysis of constructional,hierarchical,and spatial representation deficits[J].J Cogn Neurosci,2014,26(12):2 701- 2 715.
[11] Bickerton WL,Samson D,Williamson J,et al.Separa- ting forms of neglect using the Apples Test:Validation and functional prediction in chronic and acute stroke[J].Neuropsychology,2011,25(5):567- 580.
[12] Ayerbe L,Ayis S,Wolfe CD,et al.Natural history,predictors and outcomes of depression after stroke:systematic review and meta- analysis[J].Br J Psychiatry,2013,202(1):14- 21.
[13] Gillespie DC,Bowen A,Chung CS,et al.Rehabilitation for post- stroke cognitive impairment:an overview of recommendations arising from systematic reviews of current evidence[J].Clin Rehabil,2015,29(2):120- 128.
[14] Cummings JL,Cummings JL.“Mini- mental state”.A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician.J Psychiatr Res[J].J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry,1975,47(5):496- 499.
[15] Nasreddine ZS,Phillips NA,Bédirian V,et al.The Montreal Cognitive Assessment,MoCA:A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment[J].J Am Geriatr Soc,2005,53(4):695- 699.
[16] Dong Y,Sharma VK,Chan BPL,et al.The Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) is superior to the Mini- Mental State Examination (MMSE) for the detection of vascular cognitive impairment after acute stroke[J].J Neurol Sci,2010,299(1):15- 18.
[17] Bour A,Rasquin S,Boreas A,et al.How predictive is the MMSE for cognitive performance after stroke ?[J].J Neurol,2010,257(4):630- 637.
[18] Bickerton WL,Riddoch MJ,Samson D,et al.System- atic assessment of apraxia and functional predictions from the Birmingham Cognitive Screen[J].J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry,2012,83(5):513- 521.
[19] Chechlacz M,Rotshtein P,Roberts KL,et al.The Prognosis of Allocentric and Egocentric Neglect:Evidence from Clinical Scans[J].PLoS One,2012,7(11):e47 821.
[20] Nys GMS,van Zandvoort MJE,de Kort PLM,et al.The prognostic value of domain- specific cognitive abilities in acute first- ever stroke[J].Neurology,2005,64(5):821- 827.
[21] Bisiker J,Bickerton WL.Using a comprehensive and standardised cognitive screen to guide cognitive rehabilitation in stroke[J].Br J Occup Ther,2013,76(3):151- 156.
[22] Pan X,Chen H,Bickerton WL,et al.Preliminary fin- dings on the reliability and validity of the cantonese birmingham cognitive screen in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J].Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat,2015,11(11):2 377- 2 390.
[23] Li J,Yu J.A Chinese Version of Montreal Cognitive Assessment as a Brief Screening Tool for Mild Cognitive Impairment:a Population- Based Study[J].Eur Psychiatry,2012,12(1):156.
[24] Intercollegiate Stroke Working Party RC of PL.National clinical guideline for stroke[M].4th edition.London:Royal College of Physicians,2012:21.
[25] 中華醫學會神經病學分會癡呆與認知障礙學組寫作組.血管性認知障礙診治指南[J].中華神經科雜志,2011,44(2):142- 147.
[26] 董強.《中國卒中后認知障礙管理專家共識》解讀[J].中華醫學信息導報,2016,31(12):21.
[27] Winstein CJ,Stein J,Arena R,et al.Guidelines for Adult Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery:A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J].Stroke,2016,47(6):e98- e169.
ThenormandreliabilityoftheMandarinversionofBirminghamCognitiveScreen
CHENHaobo*,PANXiaoping,ZHENGLili,HUJianxi,WUYu,CHENHaoyang,GUOAihua,ZHOUJin,WANGZhiyuan
*DepartmentofNeurology,GuangzhouFirstPeople’sHospital,GuangzhouMedicalUniversity,Guangzhou510080,China
ObjectiveThere are no currently effective cognitive assessment tools for patients who have suffered stroke in China.The Birmingham Cognitive Screen (BCoS) has been shown to be a promising tool for revealing patients’ post- stroke cognitive deficits in specific domains.The Cantonese version of BCoS has been proved to be an effective tool for the detection of cognitive problems in Cantonese speakers.Here we aim to set up normative data for the mandarin version of BCoS and examine its reliability in Guangzhou.MethodsWe recruited a total of 135 healthy individuals in our study.All the subjects were assessed with the mandarin version of the BCoS.Based on the results,a norm for the Mandarin version of BCoS was set up.We calculated the Cronbach’s alpha to test the internal consistency reliability,and the test- retest reliability was examined by calculating the Wilcoxon signed rank tests.ResultsWe set up a norm for the Mandarin version of BCoS.The Cronbach’s alpha was 0.785,which indicated decent internal consistency reliability.Most of the subtests of the BCoS- Canonese version had good test- retest reliability based on the Wilcoxon signed rank tests results.ConclusionThis study suggests good reliability of the BCoS- Mandarin version,which is worthy of clinical promotion.
Birmingham Cognitive Screen;Reliability;Cognitive assessment;Norm
10.3969/j.issn.1673- 5110.2017.20.003
廣州市科技計劃項目(2012J5100039)
△通信作者:潘小平(1959-),女,主任醫師,教授。研究方向:神經退行性疾病和神經心理疾病。Email:qpanxp@163.com
R749.1+3
A
1673- 5110(2017)20- 0010- 06
(收稿2017- 02- 17)
張喜民

