高靈敏度、高穩(wěn)定度微波輻射計(jì)技術(shù)研究與實(shí)驗(yàn)驗(yàn)證
牛立杰 劉 浩 吳 季
?
高靈敏度、高穩(wěn)定度微波輻射計(jì)技術(shù)研究與實(shí)驗(yàn)驗(yàn)證
牛立杰①②劉 浩*①吳 季①
①(中國科學(xué)院國家空間科學(xué)中心微波遙感重點(diǎn)實(shí)驗(yàn)室 北京 100190)②(中國科學(xué)院大學(xué) 北京 100049)
使用星載綜合孔徑輻射計(jì)進(jìn)行海洋鹽度探測是微波遙感領(lǐng)域的一個(gè)研究熱點(diǎn)。為了達(dá)到海洋鹽度探測所需準(zhǔn)確度指標(biāo),綜合孔徑輻射計(jì)的輻射計(jì)單元需要同時(shí)具有非常高的靈敏度及定標(biāo)穩(wěn)定度。該文研究了一種兼顧高靈敏度和高穩(wěn)定度的輻射計(jì)技術(shù),通過實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)的方法保證穩(wěn)定度指標(biāo),通過定標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)平均的方法提高靈敏度指標(biāo)。首次通過頻域分析得到最優(yōu)定標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)平均時(shí)間。完成了長時(shí)間穩(wěn)定度實(shí)驗(yàn),實(shí)驗(yàn)結(jié)果表明:該輻射計(jì)穩(wěn)定度在3天(3 d)內(nèi)優(yōu)于0.12 K,靈敏度優(yōu)于0.1 K,達(dá)到了海洋鹽度探測綜合孔徑輻射計(jì)對輻射計(jì)單元的需求。
高穩(wěn)定度輻射計(jì);L波段微波輻射計(jì);噪聲注入式輻射計(jì);海洋鹽度
1 引言
星載微波輻射計(jì)技術(shù)使全球海洋鹽度測量成為可能[1]。海洋鹽度探測輻射計(jì)需要有很高的靈敏度、穩(wěn)定度、空間分辨率、刈幅指標(biāo)。2009年歐空局發(fā)射了SMOS衛(wèi)星,采用Y型陣2維綜合孔徑體制;2011年美國發(fā)射了Aquarius衛(wèi)星,采用“推帚式”真實(shí)孔徑體制。兩者發(fā)揮了重要作用,也發(fā)現(xiàn)了一些問題。文獻(xiàn)[2,3]介紹了SMOS載荷及最新的數(shù)據(jù)處理結(jié)果,文獻(xiàn)[4,5]介紹Aquarius載荷、狀態(tài)及測量結(jié)果。文獻(xiàn)[6]對比了兩顆衛(wèi)星數(shù)據(jù),總結(jié)問題:(1)2顆衛(wèi)星都未采用海溫同步測量手段;(2)都未解決RFI問題;(3) 2維綜合孔徑輻射計(jì)體制可實(shí)現(xiàn)大刈幅高分辨率,但系統(tǒng)復(fù)雜,誤差大;(4)實(shí)孔徑體制空間分辨率低,觀測刈幅小,不能滿足應(yīng)用需求。
中國科學(xué)院國家空間科學(xué)中心吸取經(jīng)驗(yàn),提出“主被動(dòng)聯(lián)合微波成像儀”(Microwave Imager Combined Active and Passive: MICAP)方案[7,8]。主載荷是一臺L波段1維綜合孔徑輻射計(jì),可實(shí)現(xiàn)高空間分辨率及觀測刈幅指標(biāo),同時(shí)避免復(fù)雜度過高的難題。1維綜合孔徑輻射計(jì)由15個(gè)輻射計(jì)單元組成,要求3天(3 d)內(nèi)穩(wěn)定度優(yōu)于0.12 K,靈敏度優(yōu)于0.1 K。
國內(nèi)研究方面,文獻(xiàn)[9]提出使用實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)提高輻射計(jì)穩(wěn)定度。文獻(xiàn)[10]采用一種數(shù)字增益波動(dòng)自動(dòng)補(bǔ)償微波輻射計(jì),航空實(shí)驗(yàn)證明能達(dá)到0.2 psu的鹽度分辨率。本文研究一種兼顧靈敏度和穩(wěn)定性的輻射計(jì),實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)實(shí)現(xiàn)高穩(wěn)定度,定標(biāo)平均方法提高靈敏度。頻域分析得到最優(yōu)定標(biāo)平均時(shí)間,并完成時(shí)序與注入噪聲的優(yōu)化及輻射計(jì)實(shí)驗(yàn),指標(biāo)達(dá)到了MICAP的輻射計(jì)單元要求。本文研究為MICAP計(jì)劃奠定基礎(chǔ),同時(shí)還將應(yīng)用于“全球水循環(huán)衛(wèi)星探測計(jì)劃”(Global Water Cycle Observation Mission: WCOM)的L/S/C三頻全極化綜合孔徑輻射計(jì)系統(tǒng)中[11]。
2 高靈敏度、高穩(wěn)定度輻射計(jì)理論基礎(chǔ)
2.1輻射計(jì)的靈敏度

2.2輻射計(jì)的穩(wěn)定度
輻射計(jì)的不穩(wěn)定性主要由系統(tǒng)參數(shù)變化帶來:增益和接收機(jī)噪聲溫度漂移;定標(biāo)平面前天線、無源器件及電纜物理溫度波動(dòng)導(dǎo)致的自身噪聲波動(dòng);定標(biāo)源(負(fù)載、噪聲源)噪聲溫度波動(dòng)。精密溫控、高穩(wěn)定噪聲源、實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)等可以減小這些不穩(wěn)定性。
文獻(xiàn)[13]中提出了漂移方差的概念,表示輻射計(jì)積分時(shí)間為時(shí),周期為的漂移的大小:

其中,
2.3高靈敏度、高穩(wěn)定度輻射計(jì)類型的選擇
輻射計(jì)實(shí)現(xiàn)高穩(wěn)定度需要實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo),但實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)會(huì)增加噪聲,降低靈敏度。噪聲注入輻射計(jì)實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)修正增益和接收機(jī)噪聲溫度的漂移,穩(wěn)定度高,但定標(biāo)噪聲導(dǎo)致靈敏度比全功率輻射計(jì)差。本文選用噪聲注入式輻射計(jì),在獲得高穩(wěn)定度的同時(shí)通過特定的定標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)平均方法(詳細(xì)見3.4節(jié))減小定標(biāo)噪聲,可以兼顧高靈敏度和高穩(wěn)定性的指標(biāo)需求。
3 高靈敏度、高穩(wěn)定度噪聲注入式輻射計(jì)理論分析
3.1 噪聲注入式輻射計(jì)原理
傳統(tǒng)噪聲注入輻射計(jì)使用硬件技術(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)檢波電壓抵消,通過脈寬反推天線溫度。現(xiàn)在可以使用數(shù)字技術(shù)對電壓采樣后直接數(shù)字處理,簡化系統(tǒng)[14]。原理框圖如圖1所示。工作時(shí)序如圖2所示。
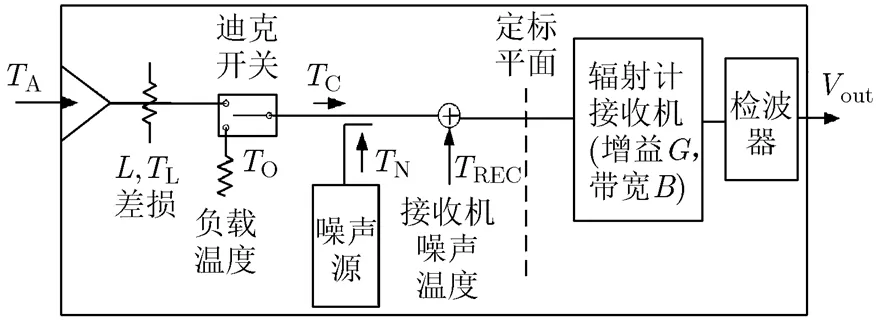
圖1 噪聲注入式輻射計(jì)原理框圖

3.2 噪聲注入式輻射計(jì)靈敏度計(jì)算

3.3噪聲注入式輻射計(jì)穩(wěn)定度計(jì)算

3.4定標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)平均技術(shù)

圖2 應(yīng)用定標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)平均技術(shù)的輻射計(jì)時(shí)序

圖3 應(yīng)用定標(biāo)數(shù)據(jù)平均技術(shù)的輻射計(jì)時(shí)序與噪聲源溫度優(yōu)化

圖4 VO與VON的功率譜密度
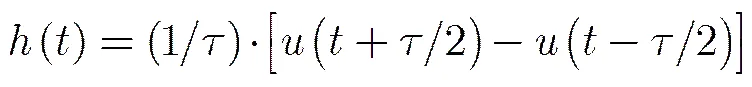
(7)

(9)

(11)

3.5 靈敏度仿真與時(shí)序、注入噪聲優(yōu)化

表1 L波段輻射計(jì)主要參數(shù)
4 輻射計(jì)實(shí)驗(yàn)驗(yàn)證
4.1輻射計(jì)實(shí)驗(yàn)過程
實(shí)驗(yàn)輻射計(jì)參數(shù)如表1所示。頻率1400~1427 MHz,為50%。完成了8天(8 d)穩(wěn)定性實(shí)驗(yàn)。精密溫控系統(tǒng)將輻射計(jì)工作溫度穩(wěn)定在范圍內(nèi)。觀測目標(biāo)為一個(gè)溫控在343 K的恒溫匹配負(fù)載,溫控精度,精密測溫實(shí)現(xiàn)天線溫度補(bǔ)償。
4.2 實(shí)驗(yàn)數(shù)據(jù)分析

圖5 輻射計(jì)8天(8 d)穩(wěn)定性實(shí)驗(yàn)得到的天線溫度

圖6 輻射計(jì)漂移標(biāo)準(zhǔn)差
5 結(jié)束語
本文研究了一種兼有高靈敏度及高穩(wěn)定度指標(biāo)的噪聲注入輻射計(jì)技術(shù),通過實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)保證高穩(wěn)定度指標(biāo),通過定標(biāo)平均進(jìn)一步提高靈敏度指標(biāo)。通過實(shí)驗(yàn)驗(yàn)證了采用精密溫度控制,定標(biāo)平均技術(shù)的L波段輻射計(jì)靈敏度優(yōu)于0.1 K(4 s積分時(shí)間),3天(3 d)內(nèi)穩(wěn)定度優(yōu)于0.12 K,達(dá)到了海洋鹽度探測綜合孔徑輻射計(jì)對輻射計(jì)單元的需求。
[1] 李青俠, 張靖, 郭偉, 等. 微波輻射計(jì)遙感海洋鹽度的研究進(jìn)展[J]. 海洋技術(shù)學(xué)報(bào), 2007, 26(3): 8-12.
LI Qingxia, ZHANG Jing, GUO Wei,. Research progress of remote sensing of ocean salinity by microwave radiometer [J]., 2007, 26(3): 8-12.
[2] Mcmullan K D, Brown M A, Martin-Neira M,. SMOS: The payload[J]., 2008, 46(3): 594-605.doi: 10.1109/ TGRS.2007.914809.
[3] MartIn-Neira M, Oliva R, Corbella I,. SMOS instrument performance and calibration after 6 years in orbit[J]., 2016, 180(8): 19-39. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.02.036.
[4] Le Vine D M, Lagerloef G S E, Colomb F R,. Aquarius: An instrument to monitor sea surface salinity from space[J]., 2007, 45(7): 2040-2050. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007. 898092.
[5] Vine D M L, Dinnat E P, Meissner T,Status of Aquarius/SAC-D and Aquarius salinity retrievals[J]., 2015, 8(12): 5401-5415. doi: 10.1109/ JSTARS.2015.2427159.
[6] 殷小軍, 張慶君, 王睿, 等. 海洋鹽度探測衛(wèi)星的現(xiàn)狀分析和未來趨勢[J]. 航天器工程, 2016, 25(1): 119-123. doi: 10.3969/ J.ISSN.1673-8748.2016.01.016.
YIN Xiaojun, ZHANG Qingjun, WANG Rui,Development status and trends of sea surface salt satellite[J]., 2016, 25(1): 119-123. doi: 10.3969/ J.ISSN.1673-8748.2016.01.016.
[7] LIU Hao, ZHU Di, NIU Lijie,MICAP (Microwave Imager Combined Active and Passive): A new instrument for Chinese ocean salinity satellite[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Milan, Italy, 2015: 184-187.
[8] NIU Lijie, LIU Hao, WU Lin,. Experimental study of an L-band synthetic aperture radiometer for ocean salinity measurement[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 418-421.
[9] 李靖, 張俊榮, 趙凱. 實(shí)時(shí)定標(biāo)微波輻射計(jì)[J]. 電子科學(xué)學(xué)刊, 1998, 20(2): 285-288.
LI Jing, ZHANG Junrong, and ZHAO Kai. Real-time calibrated microwave radiometer[J].,1998, 20(2): 285-288.
[10] 趙凱, 史久新, 張漢德. 高靈敏度機(jī)載L波段微波輻射計(jì)探測海表鹽度[J]. 遙感學(xué)報(bào), 2008, 12(2): 277–283.
ZHAO Kai, SHI Jiuxin, and ZHANG Hande. High sensitivity airborne L-band microwave radiometer measurements of sea surface salinity[J].,2008, 12(2): 277-283.
[11] LIU Hao, NIU Lijie, WU Lin,IMI(Interferometric Microwave Imager): A L/S/C tri-frequency radiometer for Water Cycle Observation Mission(WCOM)[C]. Proceedings of IEEE International on Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 3445-3447.
[12] WU Lin. Contribution to spatial bias mitigation in interferometric radiometers devoted to earth observation: Application to the SMOS mission[D]. [Ph.D. dissertation], Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya (UPC), 2014.
[13] Goodberlet M A and Mead J B. Measuring precision and accuracy drift of radiometer-reported brightness temperature[J]., 2008, 46(11): 3827-3831. doi: 10.1109/ TGRS.2008.2001034.
[14] Goodberlet M A and Mead J B. Two-load radiometer precision and accuracy[J]., 2006, 44(1): 58-67. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2005.860206.
[15] Wilson W J, Tanner A, and Pellerano F. Ultrastable microwave radiometers for future sea surface salinitymissions[C]. Earth Science Technology Conference, Pasadena, USA,2002: 11-13.
Research and Experimental Verification on High Sensitivity and High Stability Microwave Radiometer
NIU Lijie①②LIU Hao①WU Ji①
①(,,,100190,)②(,100049,)
Global measurement of ocean salinity using satellite borne synthetic aperture radiometer is one of the research focuses in the field of microwave remote sensing. In order to achieve the accuracy of the ocean salinity detection, the radiometer units of the synthetic aperture radiometer need to have very high sensitivity and very high calibration stability. In this paper, the technique of the radiometer with high sensitivity and high stability is researched. High stability is realized by the real-time calibration method, and the sensitivity is effectively improved by the calibration data average technology. The optimal average time is obtained by the frequency domain analysis for the first time. Long time stability experiments are completed to demonstrate its performance. Experimental results show that the stability of this L-band radiometer reaches 0.12 K (in 3 days), and the sensitivity reaches 0.1 K, which can reach the requirement of the synthetic aperture radiometer for ocean salinity detection.
High stability radiometer; L-band microwave radiometer; Noise injection radiometer; Ocean salinity
TP732.1
A
1009-5896(2017)08-2028-05
10.11999/JEIT161112
2016-10-20;
改回日期:2017-02-21;
2017-04-14
劉浩 liuhao@mirslab.cn
牛立杰: 男,1974年生,博士生,副研究員,研究方向?yàn)檩椛溆?jì)系統(tǒng)及定標(biāo)技術(shù).
劉 浩: 男,1978年生,研究員,研究方向?yàn)楦缮媸骄C合孔徑輻射計(jì)的系統(tǒng)和信號處理.
吳 季: 男,1958年生,研究員,主要從事微波遙感及空間探測方面研究.

