混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的優(yōu)化設(shè)計與試驗
趙 雄,崔海洋,代 麗※,徐亞丹,2,王 川,沈 錦
混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的優(yōu)化設(shè)計與試驗
趙 雄1,崔海洋1,代 麗1※,徐亞丹1,2,王 川1,沈 錦1
(1. 浙江理工大學(xué)機(jī)械與自動控制學(xué)院,杭州 310018; 2. 杭州職業(yè)技術(shù)學(xué)院青年汽車學(xué)院,杭州 310018)
為實現(xiàn)盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的輕簡化和運動設(shè)計的靈活性,該文以一種混合驅(qū)動五桿機(jī)構(gòu)來實現(xiàn)花卉穴盤苗盤栽運動。根據(jù)工作要求擬定機(jī)構(gòu)軌跡,以變速電機(jī)最小角速度波動為目標(biāo),基于遺傳算法優(yōu)化得到機(jī)構(gòu)中機(jī)架位置為(0,?150)和(?267.20,61.87),五桿機(jī)構(gòu)的桿長分別為152.80、324.55、336.56、100.40、302.60、341.00 mm。建立花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)三維模型,利用ADAMS進(jìn)行了機(jī)構(gòu)運動仿真,驗證了機(jī)構(gòu)優(yōu)化設(shè)計結(jié)果的正確性。對混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)控制系統(tǒng)進(jìn)行了設(shè)計,試制樣機(jī)并開展了花卉盤栽試驗。通過進(jìn)行花卉移栽試驗,測試得到花卉移栽軌跡高度為265 mm,取苗傾角為140°,取苗時入缽擺角為6.92°、出缽擺角為6.27°,取苗環(huán)扣寬度小于3 mm,植苗傾角為90°,植苗時入盤擺角為13.19°、出盤擺角為4.19°,植苗段垂直軌跡大于40 mm。花卉移栽的平均成功率為87.16%,表明混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)可以實現(xiàn)花卉盤栽工作。研究拓展了混合驅(qū)動的應(yīng)用領(lǐng)域,可為全自動花卉盤栽裝備的研發(fā)提供參考。
農(nóng)業(yè)機(jī)械;設(shè)計;優(yōu)化;混合驅(qū)動;并聯(lián)機(jī)構(gòu);逆向求解;花卉移栽
趙 雄,崔海洋,代 麗,徐亞丹,王 川,沈 錦. 混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的優(yōu)化設(shè)計與試驗[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2017,33(15):34-40. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.15.004 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhao Xiong, Cui Haiyang, Dai Li, Xu Yadan, Wang Chuan, Shen Jin. Optimal design and experiment of hybrid-driven five-bar flower potted-seedling transplanting mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(15): 34-40. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.15.004 http://www.tcsae.org
0 引 言
花卉盤栽是勞動密集型工作,美國和澳大利亞開發(fā)了全自動花卉移栽生產(chǎn)線,其花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)由機(jī)、電、氣共同構(gòu)成,具有獨立的機(jī)械部分與控制部分,采用四針氣缸驅(qū)動式[1-2],完成盤栽動作需要多套機(jī)構(gòu)協(xié)調(diào)配合,整套裝置造價高,中小花卉生產(chǎn)企業(yè)難以承受[3-5]。國內(nèi)目前的花卉移栽主要由人工完成,尚未開發(fā)出合適的機(jī)型適宜花卉移栽作業(yè)。旱地穴盤苗移栽通常由兩套機(jī)構(gòu)——取苗機(jī)構(gòu)和植苗機(jī)構(gòu)配合完成缽苗從穴盤取出到栽植入田塊功能[6-9]。花卉移栽裝備作為小型室內(nèi)裝備,取栽一體化作業(yè)是更適宜的方式,一套機(jī)構(gòu)實現(xiàn)移栽工作設(shè)計難度大,對機(jī)構(gòu)靈活性要求高。混合驅(qū)動機(jī)構(gòu)可以像傳統(tǒng)機(jī)構(gòu)那樣具有較強(qiáng)的剛性與較高的生產(chǎn)效率,也可以像全伺服機(jī)構(gòu)那樣實現(xiàn)較為復(fù)雜的輸出,具備一定的輸出柔性,很好地結(jié)合了傳統(tǒng)機(jī)構(gòu)和全伺服機(jī)構(gòu)的優(yōu)點,但目前其試驗及應(yīng)用研究大多局限于壓力機(jī)這類直線輸出機(jī)構(gòu)領(lǐng)域[10-14],尚未推廣應(yīng)用至農(nóng)業(yè)移栽領(lǐng)域。
論文研究以混合驅(qū)動五桿機(jī)構(gòu)實現(xiàn)花卉穴盤苗盤栽運動所需的工作軌跡與姿態(tài)。從花卉盤栽運動需求出發(fā),設(shè)定機(jī)構(gòu)預(yù)期軌跡,通過遺傳算法優(yōu)化五桿機(jī)構(gòu)的桿長、機(jī)架位置以及變速電機(jī)角位移規(guī)律,設(shè)計機(jī)構(gòu)的控制系統(tǒng),開展機(jī)構(gòu)的結(jié)構(gòu)設(shè)計并試制混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)樣機(jī),通過高速攝影測試移栽爪運動軌跡并進(jìn)行花卉移栽試驗驗證,證明該機(jī)構(gòu)在花卉盤栽工作中的適用性。
1 混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)逆向求解模型
1.1 機(jī)構(gòu)的傳動結(jié)構(gòu)
混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的結(jié)構(gòu)簡圖如圖1所示,機(jī)構(gòu)采用一個常速電機(jī)和一個變速電機(jī)同步驅(qū)動,其結(jié)構(gòu)和工作原理為:常速電機(jī)M1固定安裝在機(jī)座AE的E點上,曲柄DE的一端固定安裝在常速電機(jī)M1的輸出軸上,另一端鉸接在連桿CD的D點上,變速電機(jī)M2固定安裝在機(jī)座AE的A點上,搖桿AB的一端固定安裝在變速電機(jī)M2的輸出軸上,另一端鉸接在連桿BC的B點上,五桿機(jī)構(gòu)所有桿件之間都通過鉸鏈連接。連桿DF的末端F點表示移栽臂的秧針尖點位置。常速電機(jī)M1驅(qū)動曲柄DE,曲柄DE的角速度大小和方向不變,變速電機(jī)M2為伺服電機(jī),變速電機(jī)M2通過控制單片機(jī)發(fā)出的脈沖可以調(diào)節(jié)搖桿AB的角速度大小和方向。常速電機(jī)M1在中心軸E的帶動下做逆時針勻速轉(zhuǎn)動,變速電機(jī)M2在中心軸A的帶動下驅(qū)動搖桿AB做變速運動。混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)通過常速電機(jī)M1和變速電機(jī)M2的混合驅(qū)動,驅(qū)動曲柄DE和搖桿AB帶動連桿DF運動,使得連桿DF的末端F點形成特定的移栽軌跡,從而完成花卉苗的盤栽動作。

圖1 機(jī)構(gòu)結(jié)構(gòu)分析圖Fig.1 Analysis chart of mechanism structure
1.2 機(jī)構(gòu)的逆向設(shè)計模型
第一步:設(shè)計機(jī)構(gòu)的預(yù)期軌跡。逆向設(shè)計的步驟是預(yù)先設(shè)計機(jī)構(gòu)的目標(biāo)軌跡,然后采用三次非均勻B樣條擬合方法來擬合得到機(jī)構(gòu)軌跡。由于擬合過程中需要給定預(yù)期目標(biāo)軌跡上的若干個點坐標(biāo)作為控制頂點坐標(biāo),再利用控制頂點及德布爾遞推公式可計算得到移栽軌跡曲線上的任意點,故需要給定坐標(biāo)系原點來建立直角坐標(biāo)系,并將控制頂點在坐標(biāo)系中用直角坐標(biāo)表示[4,9,15]。以O(shè)點為原點,以水平方向為x軸、垂直方向為y軸建立直角坐標(biāo)系,如圖1所示。在所建立的直角坐標(biāo)系中確定控制頂點坐標(biāo),并擬合得到機(jī)構(gòu)目標(biāo)軌跡。
第二步:反求混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的角位移規(guī)律[16-18]。根據(jù)第一步得到的整個運動過程中軌跡點坐標(biāo)為桿長計算提供參數(shù)。五桿機(jī)構(gòu)由2個二桿開鏈機(jī)構(gòu)組成,求解步驟分為2個部分。根據(jù)機(jī)構(gòu)末端的運動軌跡點F與機(jī)架點E間的最大距離和最小距離求得。

式中L4為曲柄DE的長度,L5為連桿DF的長度,mm;Ex為常速電機(jī)M1安裝點E點的橫坐標(biāo),Ey為E點的縱坐標(biāo),F(xiàn)x為連桿DF的端點F的橫坐標(biāo),F(xiàn)y為端點F的縱坐標(biāo)。
在求得L4和L5的基礎(chǔ)上,利用反正切、反余弦函數(shù)求得曲柄DE與x軸的夾角θ4。

根據(jù)機(jī)構(gòu)運動規(guī)律分析得出,連桿DF的端點F由軌跡最遠(yuǎn)點向最近點運動過程中,上式中第2項前取正號;連桿DF的端點F由軌跡最近點向最遠(yuǎn)點運動過程中,上式中第2項前取負(fù)號。
在求得θ4的基礎(chǔ)上,利用三角函數(shù)求得曲柄DE中的D點坐標(biāo)。
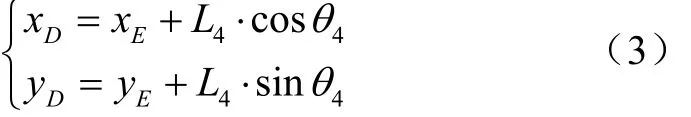
在求得xD及yD的基礎(chǔ)上,利用反正切函數(shù)直接求得連桿DF與x軸的夾角θ5。
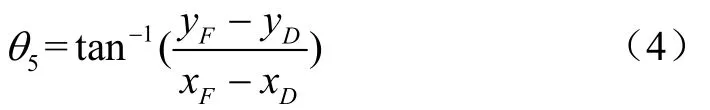
在求得θ5的基礎(chǔ)上,利用桿長關(guān)系可求得連桿CD中的C點坐標(biāo)。

式中β為叉形連桿CDF之間的夾角。
在求得二桿開鏈機(jī)構(gòu)DEF的基礎(chǔ)上,同理也可求解得到二桿開鏈機(jī)構(gòu)ABC中搖桿AB與x軸的夾角θ1。

式中L1為搖桿AB的長度,L2為連桿BC的長度,mm;xA為變速電機(jī)M2安裝點A點的橫坐標(biāo),yA為A點的縱坐標(biāo)。其中根據(jù)機(jī)構(gòu)運動規(guī)律分析得出,連桿BC的端點C由軌跡最遠(yuǎn)點向最近點運動過程中, 上式中第2項前取正號;連桿BC的端點C由軌跡最近點向最遠(yuǎn)點運動過程中,上式中第2項前取負(fù)號。
在求得θ1的基礎(chǔ)上,利用三角函數(shù)求得搖桿AB中的B點坐標(biāo)。

在求得θ4的基礎(chǔ)上,利用反正切函數(shù)直接求得連桿BC與x軸的夾角θ2。

由式(1)-(8)可求得每個軌跡點所對應(yīng)連桿的運動規(guī)律。
第三步:求得對應(yīng)于軌跡每一點的θ1值與θ4值,進(jìn)而確定θ1與θ4的函數(shù)關(guān)系,得到混合驅(qū)動五桿機(jī)構(gòu)中搖桿和曲柄的運動規(guī)律,即得到驅(qū)動電機(jī)的控制參數(shù)。
由于二桿開鏈機(jī)構(gòu)為輸入兩自由度機(jī)構(gòu),逆向設(shè)計求解方法有多種,但此種求解方法易于得到滿足單調(diào)性轉(zhuǎn)角的角位移曲線,故選用此種算法。
2 優(yōu)化設(shè)計
2.1 參數(shù)優(yōu)化
采用混合驅(qū)動五桿機(jī)構(gòu)實現(xiàn)花卉盤栽動作,機(jī)構(gòu)的設(shè)計難度主要體現(xiàn)在:一是由于傳統(tǒng)取苗機(jī)構(gòu)作業(yè)是將苗從植苗機(jī)構(gòu)上方投入植苗嘴,對苗移送距離要求低,若要通過一套裝置直接將苗由送苗機(jī)構(gòu)移送至花盤,結(jié)合送苗機(jī)構(gòu)尺寸、輸送機(jī)構(gòu)尺寸及花卉苗的高度,需要將盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)軌跡的取苗點至植苗點間距離設(shè)為260 mm;二是需要滿足取苗和植苗2個工作段姿態(tài)要求;三是需要滿足曲柄轉(zhuǎn)角的單調(diào)性要求;四是需要滿足五桿機(jī)構(gòu)形成雙曲柄的條件,避免出現(xiàn)奇異位置;五是需要盡量使得變速電機(jī)的角速度波動小。在優(yōu)化中將第5點作為優(yōu)化目標(biāo),把軌跡、姿態(tài)目標(biāo)等其他條件轉(zhuǎn)化為約束。
通過以上轉(zhuǎn)化,在設(shè)計機(jī)構(gòu)的預(yù)期軌跡時,混合驅(qū)動當(dāng)中必須要有一個常速電機(jī)驅(qū)動,即需要滿足角位移單調(diào)性;同時變速電機(jī)的轉(zhuǎn)速在不停地波動,需要將角速度波動量盡可能降低。這兩點要求可通過規(guī)劃五桿機(jī)構(gòu)的桿長、機(jī)構(gòu)機(jī)架點的位置和調(diào)整叉形連桿CDF的夾角β來實現(xiàn),使得變速電機(jī)易于實現(xiàn)盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)傳動的控制要求,從而避免過大的角速度波動。擬合軌跡點原本有5 000多個,為了減少遺傳算法優(yōu)化時間,采取等間隔的方法,設(shè)置間隔為10,使算法循環(huán)的次數(shù)減少,以減少遺傳算法優(yōu)化時間[19-22]。采用遺傳算法的種類為輪轉(zhuǎn)算法,設(shè)置遺傳算法控制參數(shù)如下:種群個體數(shù)目為80個,最大遺傳代數(shù)為100代,變異概率為0.01,交叉概率為0.8。針對花卉移栽工作要求,具體優(yōu)化設(shè)計為:
目標(biāo):min[θ1(i+1)?θ1(i )];
變量:X=[xE,yE,xA,yA,L1,L2,β];

約束:1)L4+L5≤max(s1);

花卉盤栽運動除軌跡目標(biāo)外還涉及移栽爪姿態(tài),為實現(xiàn)移栽爪合理姿態(tài),論文將姿態(tài)要求轉(zhuǎn)化為約束條件(4)和(5),其設(shè)置依據(jù)為:由取苗點確定移栽爪在取苗時的角位移,根據(jù)秧盤的傾角為α和取苗角為γ推算出移栽爪所需的角位移為α+(π/2)+γ;同樣由植苗點確定移栽爪在植苗時的角位移,根據(jù)取苗角為γ也可推算出此時移栽爪所需的角位移為(π/2)+γ,只要約束(4)、(5)兩個條件,使其與移栽爪在移栽過程中所需的角位移保持一致,就可確保花卉移栽時移栽爪的姿態(tài)。
遺傳算法優(yōu)化結(jié)果為

其他幾根桿長為

由優(yōu)化結(jié)果得知,優(yōu)化后的五桿機(jī)構(gòu)機(jī)架位置為(0,?150)和(?267.20, 61.87),五桿機(jī)構(gòu)的桿長分別為152.80、324.55、336.56、100.40、302.60、341.00 mm。
2.2 結(jié)果與分析
算法迭代80次,優(yōu)化終止。具體的目標(biāo)參數(shù)迭代優(yōu)化過程如圖2所示,由圖可知迭代次數(shù)從第10代開始緩慢下降,直到第65代開始趨于穩(wěn)定。遺傳算法本身就是一種智能尋優(yōu)的隨機(jī)算法,搜索過程中存在隨機(jī)性,遺傳算法初始給的群體是隨機(jī)產(chǎn)生的,它的結(jié)果不是絕對的,只能是更優(yōu)或者次優(yōu)[23]。

圖2 遺傳算法結(jié)果Fig.2 Genetic algorithm result
圖3 中紅色的軌跡為鷹嘴形移栽軌跡[5],綠色的軌跡為水稻毯狀苗移栽軌跡[24-26],藍(lán)色的軌跡為混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽軌跡。

圖3 軌跡對比分析圖Fig.3 Comparison analysis chart of trajectories
為了便于比較,3種軌跡的取苗點被設(shè)置在同一位置,各軌跡的最低點為植苗點,對取苗點至植苗點間的軌跡高度進(jìn)行比較,混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽軌跡的高度較鷹嘴形移栽軌跡增加了50至100 mm,較水稻毯狀苗移栽軌跡增加了150~200 mm。同時,取苗段軌跡的形狀也有了較大改善,混合驅(qū)動五桿花卉盤栽軌跡的取苗段軌跡尖端環(huán)扣相對較小,植苗段軌跡的垂直距離約40 mm,有利于提高取苗成功率和植苗直立度,也可以減少移栽時對花卉苗木的損傷。如圖3所示,取苗段為取苗點上下兩側(cè)的軌跡段,尖端環(huán)扣為取苗段所形成的環(huán)形軌跡,植苗段為植苗點左側(cè)的近似直線段的軌跡段。
3 控制系統(tǒng)設(shè)計
系統(tǒng)選用的伺服電機(jī)驅(qū)動器在最高轉(zhuǎn)速為3 000 r/min時,對應(yīng)的頻率值為500 kHz,電機(jī)所需轉(zhuǎn)速值范圍為0~600 r/min,因而伺服驅(qū)動器對應(yīng)所需的頻率值范圍為0~100 kHz。樣機(jī)選用STC15F2K60S2高晶振類型的單片機(jī),利用其高速脈沖輸出模塊方便實現(xiàn)可變頻率輸出。特定轉(zhuǎn)速下,伺服電機(jī)所對應(yīng)單片機(jī)所需頻率的計算式為

式中n為電機(jī)轉(zhuǎn)速,r/min,變速電機(jī)轉(zhuǎn)速由機(jī)構(gòu)運動學(xué)求解得到;f為脈沖頻率,Hz。
控制系統(tǒng)包含2個按鈕,按鈕1實現(xiàn)盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)開機(jī)后回到機(jī)構(gòu)初始設(shè)定位置的功能,按鈕2啟動花卉盤栽功能。常速電機(jī)的轉(zhuǎn)速被設(shè)置為60 r/min,由于單片機(jī)采用離散的時間間隔產(chǎn)生脈沖波形,變速電機(jī)整周運行的時間與常速電機(jī)整周運行的時間存在微小差異,導(dǎo)致兩電機(jī)軸周期中角度不能完全匹配,從而使移栽軌跡與理論軌跡產(chǎn)生誤差。若該誤差累積,則會造成無法實現(xiàn)花卉移栽動作,因而控制系統(tǒng)選用定時器T0來輔助兩臺電機(jī)轉(zhuǎn)速匹配,確保每一個周期內(nèi)電機(jī)軸角度誤差控制在微小范圍內(nèi),其控制流程框圖如圖4所示。
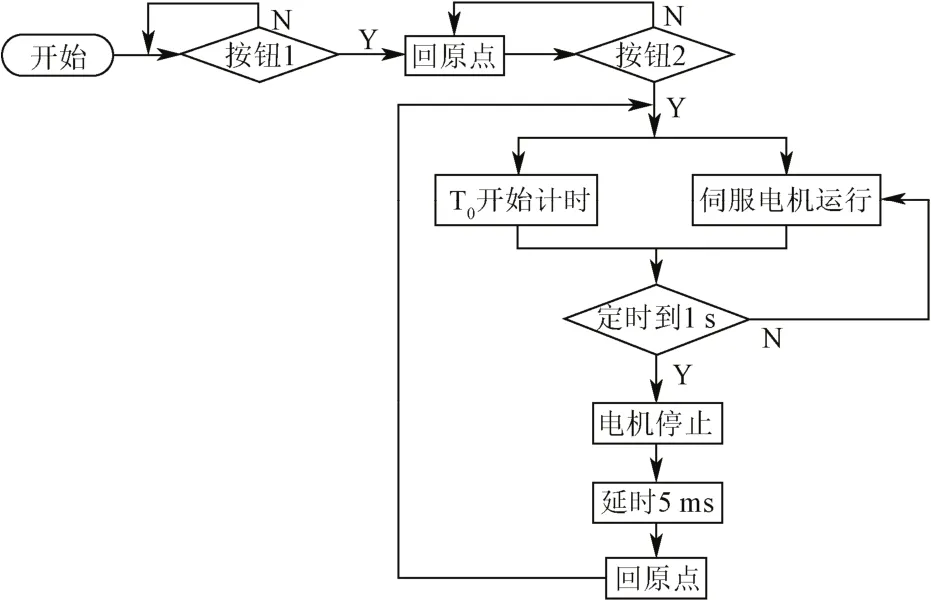
圖4 控制流程圖Fig.4 Chart of control flow
4 機(jī)構(gòu)設(shè)計及試驗驗證
4.1 機(jī)構(gòu)設(shè)計
根據(jù)優(yōu)化得到的機(jī)構(gòu)參數(shù),完成五桿機(jī)構(gòu)和移栽臂的結(jié)構(gòu)設(shè)計。其中,五桿機(jī)構(gòu)包含曲柄、連桿、搖桿等零件,移栽臂包含殼體、連接軸、凸輪、撥叉、撥叉軸、彈簧、彈簧座、推苗桿、定位板、轉(zhuǎn)動片、秧針等零件。在SOLIDWORKS中完成五桿花卉盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的三維建模,導(dǎo)入三維模型到ADAMS完成虛擬裝配并仿真驗證[27-29],驗證了計算方法的正確性。
4.2 盤栽試驗驗證
盤栽試驗在浙江理工大學(xué)農(nóng)業(yè)機(jī)械裝備實驗室試驗基地進(jìn)行,搭建了花卉移栽試驗臺。試驗臺由送苗機(jī)構(gòu)、盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)、輸送機(jī)構(gòu)3部分組成,具體結(jié)構(gòu)如圖5所示。試驗時間為2016年11月下旬,試驗條件為選用金魚草作為盤栽花卉苗[30-31],生理苗齡40 d,穴盤苗出苗率為85%~95%,苗缽含水率約55%,育苗基質(zhì)即泥炭與珍珠巖成分體積比為2:1。花卉盤栽的規(guī)格見表1,送苗機(jī)構(gòu)上花卉苗的傾角為50°。試驗時考察移栽臂動作能否滿足移栽設(shè)計的要求,以及盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)、送苗機(jī)構(gòu)和傳送帶運動是否匹配。同時通過在試驗過程中對機(jī)器安全性和轉(zhuǎn)速提高情況下帶傳動穩(wěn)定性的考察,驗證盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)設(shè)計的安全性及可靠性要求,送苗機(jī)構(gòu)、盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)與輸送機(jī)構(gòu)共同作業(yè),考察自動取苗、植苗過程中各機(jī)構(gòu)協(xié)同作業(yè)效果。利用高速攝影技術(shù),對盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)的高速運轉(zhuǎn)情況進(jìn)行拍攝,對盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)運動過程中的各位置進(jìn)行分析,包括花卉盤栽軌跡,機(jī)構(gòu)整體運轉(zhuǎn)情況,機(jī)構(gòu)取苗植苗時的關(guān)鍵姿態(tài)等,如圖5所示。

圖5 花卉移栽試驗臺結(jié)構(gòu)及移栽關(guān)鍵姿態(tài)圖Fig.5 Structure of transplanting test bench and key attitudes of flower transplanting experiment

表1 花卉盤栽規(guī)格Table 1 Size of flower pot tray
試驗臺輸送機(jī)構(gòu)中傳送帶的速度為0.48 m/s,傳送帶為間歇性運動,其周期與盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)保持一致,在常速電機(jī)轉(zhuǎn)速為60 r/min的條件下對花卉苗進(jìn)行盤栽試驗。通過進(jìn)行花卉移栽試驗,測試得到花卉移栽軌跡高度為265 mm,取苗傾角為140°,取苗時入缽擺角為6.92°、出缽擺角為6.27°,取苗環(huán)扣寬度小于3 mm,植苗傾角為90°,植苗時入盤擺角為13.19°、出盤擺角為4.19°,植苗段垂直軌跡大于40 mm。移栽試驗過程中,定義移栽臂的秧針將花卉苗從缽盤中取出并放入花盤即為試驗成功。試驗時秧針難免會對花卉苗有一定損傷,欲分析移栽時對花卉苗的損傷影響情況需觀察花卉苗移栽后的生長狀況,該過程需持續(xù)較長時間,故移栽試驗中定義移栽成功時未考慮對花卉苗的損傷影響。盤栽試驗總共進(jìn)行5次,每盤花卉苗的移栽成功率分別為85.2%、88.4%、87.6%、84.2%、90.4%,5次移栽的平均成功率為87.16%;取苗平均深度為30 mm、植苗平均深度為36 mm,盤栽機(jī)構(gòu)運動規(guī)律與送苗機(jī)構(gòu)及輸送機(jī)構(gòu)布局相適應(yīng),實現(xiàn)了花卉自動盤栽作業(yè)。采用高速攝影設(shè)備得出了移栽臂的真實運動軌跡,如圖6所示。移栽臂的實際運動軌跡與仿真軌跡基本一致,考慮到移栽試驗臺在加工及裝配過程中存在的尺寸偏差對實際試驗過程的影響,移栽臂的實際運動軌跡與仿真軌跡間存在適量微小偏差是正常的,從而驗證了機(jī)構(gòu)設(shè)計與仿真分析結(jié)果的一致性。

圖6 花卉移栽高速攝影軌跡圖Fig.6 High-speed photography trajectory of flower transplanting experiment
5 結(jié) 論
1)本文提出了一種輕簡化盤栽機(jī)構(gòu),利用混合驅(qū)動五桿機(jī)構(gòu)實現(xiàn)花卉苗盤栽取栽一體化工作,機(jī)構(gòu)結(jié)構(gòu)簡潔、設(shè)計靈活、柔度高。
2)針對花卉盤栽運動要求,進(jìn)行了機(jī)構(gòu)的參數(shù)優(yōu)化,優(yōu)化后的五桿機(jī)構(gòu)機(jī)架位置為(0,?150)和(?267.20, 61.87),五桿機(jī)構(gòu)的桿長分別為152.80、324.55、336.56、100.40、302.60、341.00 mm。通過進(jìn)行花卉移栽試驗,測試得到花卉移栽軌跡高度為265 mm,取苗傾角為140°,取苗時入缽擺角為6.92°、出缽擺角為6.27°,取苗環(huán)扣寬度小于3 mm,植苗傾角為90°,植苗時入盤擺角為13.19°、出盤擺角為4.19°,植苗段垂直軌跡大于40 mm,實現(xiàn)了花卉自動盤栽作業(yè),驗證了該機(jī)構(gòu)的實用性。
[1] Kutz L J, Miles G E, Hammer P A, et al. Robotic transplanting of bedding plants[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 1987, 30(3): 586-590.
[2] Choi W C, Kim D C, Ryu I H, et al. Development of a seedling pick-up device for vegetable transplanters[J]. Transactions of the ASAE, 2002, 45(1): 13.
[3] 王蒙蒙,宋建農(nóng),劉彩玲,等. 蔬菜移栽機(jī)曲柄擺桿式夾苗機(jī)構(gòu)的設(shè)計與試驗[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2015,31(14):49-57.
Wang Mengmeng, Song Jiannong, Liu Cailing, et al. Design and experiment of crank rocker type clamp seedlings mechanism of vegetable transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(14): 49-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 趙雄,王川,楊茂祥,等. 非圓齒輪行星輪系自動取苗機(jī)構(gòu)逆向設(shè)計分析[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2015,31(16):30-36.
Zhao Xiong, Wang Chuan, Yang Maoxiang, et al. Reverse design and analysis of automatic seedling pick-up mechanism with non-circular gear planetary train[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(16): 30-36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 趙雄,沈明,陳建能,等. 棉花移栽機(jī)旋轉(zhuǎn)式取苗機(jī)構(gòu)的運動學(xué)分析及虛擬試驗[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2014,30(8):13-20.
Zhao Xiong, Shen Ming, Chen Jianneng. Kinematic analysis and virtual experiment of rotary pick-up mechanism on cotton transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(8): 13-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 徐麗明,張鐵中,史志清. 玉米自動移栽機(jī)取苗機(jī)構(gòu)的設(shè)計[J]. 中國農(nóng)業(yè)大學(xué)學(xué)報,2000,5(4):58-60.
Xu Liming, Zhang Tiezhong. Shi Zhiqing. Design on the picking seedling machinery in the maize auto-transplanter[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2000, 5(4): 58-60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 石鐵. 全自動玉米秧苗移栽機(jī)的研制與試驗[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2015,31(3):23-30.
Shi Tie. Development and test of automatic corn seedling transplanter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(3): 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 陳建能,王伯鴻,張翔,等. 多桿式零速度缽苗移栽機(jī)植苗機(jī)構(gòu)運動學(xué)模型與參數(shù)分析[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2011,27(9):7-12.
Chen Jianneng, Wang Bohong, Zhang Xiang, et al. Kinematics modeling and characteristic analysis of multi-linkage transplanting mechanism of pot seeding transplanter with zero speed[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(9): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 趙勻,朱慧軒,辛亮,等. 擬合齒輪五桿水稻缽苗移栽機(jī)構(gòu)的機(jī)理分析與試驗[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2016,32(1):12-21.
Zhao Yun, Zhu Huixuan, Xin Liang, et al. Mechanism analysis and experiment of transplanting mechanism with fitting gear five-bar for rice pot seedling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(1): 12-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 孔建益,F(xiàn)unk W,吳干城. 具有一個受控原動件的五桿機(jī)構(gòu)精確實現(xiàn)給定傳動比的研究[J]. 武漢冶金科技大學(xué)學(xué)報,1997,20(2):189-193.
Kong Jianyi, Funk W, Wu Gancheng. Research on transmission ratio about five-bar mechanism with a programmable driver[J]. Journal of Wuhan Univ. of Metallurgical Science and Technology, 1997, 20(2): 189-193. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 賀利樂,劉宏昭. 一種六自由度混合驅(qū)動并聯(lián)機(jī)構(gòu)的位置正解分析研究[J]. 中國機(jī)械工程,2007,8:920-923,970.
He Lile, Liu Hongzhao. Research on forward solution of position of 6-DOF hybrid driven parallel mechanism[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 8: 920-923, 970. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李輝,張策,孟彩芳. 基于正運動學(xué)分析的混合驅(qū)動壓力機(jī)優(yōu)化設(shè)計[J]. 中國機(jī)械工程,2004,9:19-22.
Li Hui, Zhang Ce, Meng Caifang. Optimum design of hybrid-driven mechanical press based on forward kinematics analysis[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 9: 19-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 傅蔡安,陳文. 混合輸入沖壓機(jī)構(gòu)的運動學(xué)分析及參數(shù)優(yōu)化[J]. 中國機(jī)械工程,2011,6:666-670.
Fu Cai’an, Chen Wen. Kinematics analysis and parameter optimization of a hybrid input mechanical press[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 6: 666-670. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] Li Hui, Zhang Ce, Meng Caifang. A hybrid-driven nine-bar press for precision drawing[C]//Proceeding of the 11th World Congress in Mechanism and Machine Science, Tianjing, China, 2004: 1141-1145.
[15] 左閆軍,曹鵬,趙勻,等. B樣條非圓齒輪行星輪系水稻缽苗移栽機(jī)構(gòu)的設(shè)計與優(yōu)化[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2014,30(15):10-17. Zuo Yanjun, Cao Peng, Zhao Yun, et al. Design and optimization of transplanting mechanism with B-spline non-circular planet gear train for rice pot seedling[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(15): 10-17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 陳建能,夏旭東,王英,等. 缽苗在鴨嘴式栽植機(jī)構(gòu)中的運動微分方程及應(yīng)用試驗[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2015,31(3):31-39.
Chen Jianneng, Xia Xudong, Wang Ying, et al. Motion differential equations of seedling in duckbilled planting nozzle and its application experiment[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(3): 31-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 雷昌毅,陳建能,李鵬鵬,等. 非圓齒輪—曲柄滑塊壓捆機(jī)構(gòu)反求設(shè)計[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2012,28(13):22-27.
Lei Changyi, Chen Jianneng, Li Pengpeng, et al. Reverse design of non-circular gear-crank slider hay baler mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(13): 22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 楊茂祥. 非圓齒輪行星輪系取苗機(jī)構(gòu)的反求設(shè)計與優(yōu)化[D].杭州:浙江理工大學(xué),2015.
Yang Maoxiang. Reverse Design and Optimization of Non-Circular Planetary Gears Train Seedling Pick-Up Mechanism[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 代麗,孫良,趙雄,等. 基于運動學(xué)目標(biāo)函數(shù)的插秧機(jī)分插機(jī)構(gòu)參數(shù)優(yōu)化[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2014,30(3):35-42.
Dai Li, Sun Liang, Zhao Xiong, et al. Parameters optimization of separating-planting mechanism in transplanter based on kinematics objective function[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(3): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王金武,葛宜元,王金峰. 基于遺傳算法的水稻整株秸稈還田埋草彎刀的設(shè)計與試驗[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2010,26(1):166-170.
Wang Jinwu, Ge Yiyuan, Wang Jinfeng. Design and test on straw-mulching cutlass of whole rice straw returning machine based on genetic algorithm[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2010, 26(1): 166-170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 楊啟文,蔣靜坪,張國宏. 遺傳算法優(yōu)化速度的改進(jìn)[J].軟件學(xué)報,2001,12(2):270-275.
Yang Qiwen, Jiang Jingping, Zhang Guohong. Improving optimization speed for genetic algorithms[J]. Journal of Software, 2001, 12(2): 270-275. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 馮立艷,劉騰,李學(xué)剛,等. 基于遺傳算法的混合驅(qū)動鉸鏈五桿機(jī)構(gòu)的優(yōu)化綜合[J]. 機(jī)械設(shè)計與制造,2011(10):173-175.
Feng Liyan, Liu Teng, Li Xuegang, et al. Optimum synthesis of harbid-driven hinge five-bar mechanism based on genetic algorithm[J]. Mechinery Design & Manufacture, 2011(10): 173-175. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王戰(zhàn)權(quán),云慶夏,毋建宏. 關(guān)于遺傳算法收斂的隨機(jī)性研究[J]. 電腦開發(fā)與應(yīng)用,1999(7):2-4.
[24] 李澤華,馬旭,齊龍,等. 華南雙季稻區(qū)水稻不同機(jī)械化栽植方式對比試驗與評價[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2015,31(3):40-47.
Li Zehua, Ma Xu, Qi Long, et al. Comparison and evaluation of different rice mechanized transplanting methods in double cropping area of South China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(3): 40-47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 俞高紅,黃小艷,葉秉良,等. 旋轉(zhuǎn)式水稻缽苗移栽機(jī)構(gòu)的機(jī)理分析與參數(shù)優(yōu)化[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2013,29(3):16-22.
Yu Gaohong, Huang Xiaoyan, Ye Bingliang, et al. Principle analysis and parameters optimization of rotary rice pot seedling transplanting mechanism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions ofthe CSAE), 2013, 29(3): 16-22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 徐洪廣,趙勻,張允慧,等. 水稻缽苗移栽機(jī)變性卵形齒輪分秧機(jī)構(gòu)的運動機(jī)理分析[J]. 農(nóng)業(yè)工程學(xué)報,2012,28(11):9-15.
Xu Hongguang, Zhao Yun, Zhang Yunhui, et al. Analysis on kinematic principle for seedling-picking machinery of rice transplanter with deformed oval gears[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(11): 9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 李增剛. ADAMS入門詳解與實例[M]. 北京:國防工業(yè)出版社,2006.
[28] 范成建,熊光明,周明飛. MSC.ADAMS應(yīng)用與提高[M].北京:機(jī)械工業(yè)出版社,2006.
[29] 陳立平,張云清,任衛(wèi)群. 機(jī)械系統(tǒng)動力學(xué)分析及ADAMS應(yīng)用教程[M]. 北京:清華大學(xué)出版社,2005.
[30] 李樹和,張磊,王震,等. 不同基質(zhì)對幾種花卉組培苗移栽影響的試驗研究[J]. 北方園藝,2004(4):66-68.
[31] 裘文達(dá),李曙軒,姚毓璆. 幾種花卉試管苗移栽試驗[J]. 浙江農(nóng)業(yè)大學(xué)學(xué)報,1986,12(2):129-135.
Optimal design and experiment of hybrid-driven five-bar flower potted-seedling transplanting mechanism
Zhao Xiong1, Cui Haiyang1, Dai Li1※, Xu Yadan1,2, Wang Chuan1, Shen Jin1
(1. College of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou 310018, China; 2. College of Qingnian Automotive, Hangzhou Vocational and Technical College, Hangzhou 310018, China)
Flower potted-seedling transplanter is usually a complex system of cylinder, hydraulic rod and electromagnetic valve, and its high price brings impediment for its promotion. Utilizing a single mechanism to achieve the kinematics requirement of seedling transplanting can be very difficult. Hybrid-driven mechanism can not only have the high transmission efficiency and carrying capacity as the single degree-of-freedom mechanism, but can also have the high flexible degree as the multi degree-of-freedom mechanism. Aiming at simplifying the potted-seedling transplanting mechanism and adding the flexibility of kinematic design, a hybrid-driven five-bar mechanism was proposed to realize the flower potted-seedling transplanting. The trajectory of the mechanism was proposed according to the work requirements and a mathematical model of hybrid-driven five-bar flower potted-seedling transplanting mechanism was built. Aiming at the minimum angular velocity fluctuation of the variable speed motor, the parameters of the mechanism were optimized through genetic algorithm toolbox of MATLAB. The rack location of mechanism was set as (0, -150) and (-267.20, 61.87) based on the optimization results of genetic algorithm. The bar lengths of five-bar mechanism were 152.80, 324.55, 336.56, 100.40, 302.60 and 341.00 mm. A three-dimensional model of flower potted-seedling transplanting mechanism was built, the kinematic simulation of mechanism was carried out by ADAMS software, and the correctness of the mechanism’s optimization results was verified through kinematic simulation. A control system of the hybrid-driven five-bar flower potted-seedling transplanting mechanism was designed and the position mode of servo motor was adopted in order to achieve the precise position control required by the mechanism. Meanwhile, the design of the control system realized the requirements of synchronous control and real-time match control in flower potted-seedling transplanting mechanism. The structures of the five-bar mechanism and transplanting arm mechanism were designed and the parts of these mechanisms were machined, and then a prototype was assembled to carry out the experiment research of flower potted-seedling transplanting. Through the experiment, the height of flower transplanting trajectory was measured as 265 mm. When the transplanting claw was picking up the potted-seedling, the azimuth angle was 140°, the swinging angle was 6.92° in the process of claw entering the potted-seedling, the swinging angle was 6.27° in the process of claw leaving the potted-seedling, and the width of buckle was less than 3 mm. When the transplanting claw was planting the potted-seedling, the azimuth angle was 90°, the swinging angle was 13.19° in the process of claw entering the potted-seedling, the swinging angle was 4.19° in the process of claw leaving the potted-seedling, and the vertical trajectory height was longer than 40 mm. The average successful rate of 5 transplanting experiments was 87.16% which indicated that hybrid-driven five-bar flower potted-seedling transplanting mechanism can realize the flower potted-seedling transplanting work. Meanwhile, the upright degree and success rate of picking up and planting the flower potted-seedling were ensured in the process of transplanting work. The application field of hybrid drive is extended in this article and a new choice for the design of automatic flower potted-seedling transplanting equipment is provided as well.
agricultural machinery; design; optimization; hybrid drive; parallel mechanism; reverse solution; flower potted-seedling transplanting
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.15.004
S223.92
A
1002-6819(2017)-15-0034-07
2017-04-14
2017-06-15
國家自然科學(xué)基金(51575496);浙江省自然科學(xué)基金(LY15E050025&LZ16E050003);浙江省重大科技專項重點農(nóng)業(yè)項目(2015C02004);浙江省科技廳公益項目(2017C32100)。
趙 雄,男,湖北黃梅人,副教授,主要從事機(jī)構(gòu)優(yōu)化設(shè)計方面的研究。杭州 浙江理工大學(xué)機(jī)械與自動控制學(xué)院,310018。
Email:zhaoxiong@zstu.edu.cn
※通信作者:代 麗,女,黑龍江哈爾濱人,副教授,主要從事機(jī)構(gòu)創(chuàng)新優(yōu)化、農(nóng)業(yè)機(jī)械等方面的研究。杭州 浙江理工大學(xué)機(jī)械與自動控制學(xué)院,310018。Email:daili@zstu.edu.cn

