腦源性神經生長因子對mir124表達及興奮性電流的影響
王鳳軍, 王洪朋, 單晶麗, 邵正凱, 姜楊薇, 陳元元, 宋婷婷, 邱麗婷
腦源性神經生長因子對mir124表達及興奮性電流的影響
王鳳軍1, 王洪朋2, 單晶麗3, 邵正凱1, 姜楊薇1, 陳元元1, 宋婷婷1, 邱麗婷1
目的 探討BDNF對海馬miRNA-124表達及齒狀回顆粒細胞興奮性突觸后電流(sEPSCs)的影響,以明確BDNF對顳葉內側癲癇(MTLE)發病機制的影響。方法 選取哈爾濱醫科大學附屬第一臨床醫院神經外科2008年4月-2010年10月手術治療的MTLE患者12例。RT-pcr技術檢測BDNF孵育后MTLE患者海馬組織mir-124表達、膜片鉗技術檢測BDNF對海馬顆粒細胞sEPSCs的影響。結果 (1)BDNF降低了顳葉癲癇海馬miRNA-124的表達(P<0.01);(2)BDNF增加了顆粒細胞sEPSCs的頻率和幅度(P<0.01)。結論 BDNF降低了顳葉癲癇海馬mir-124的表達,提高顆粒細胞sEPSCs的頻率和幅度,從而可能對人類MTLE的發病起到促進作用。
腦源性神經生長因子; 顳葉內側癲癇; miRNA-124; 自發性興奮性突觸后電流
癲癇是中樞神經系統常見疾病,以反復癇樣發作為特征,全世界大約有5000萬患者,癲癇的發作類型超過40種,MTLE為最常見的一種難治性癲癇。近年來, 腦源性神經生長因子(BDNF)成為癲癇的研究熱點。BDNF于1982年由德國科學家Brade從豬腦里提取的一類神經生長因子[1],其對維持神經細胞的生理功能有重要的作用,分布廣泛,海馬和皮質分布最多,其它腦區也有表達[2]。BDNF能夠增強大鼠海馬齒狀回的突觸信號傳導[3,4]及通過調節NMDA受體的活性來增強突觸傳遞功能[5]和影響TrkB信號而促進了癲癇發病[6]。然而也有報道BDNF對癲癇的發生起到明顯抑制作用[7]。BDNF在多種癲癇模型鼠腦內表達明顯上調[8~10]。Hideo等報道癲癇動物模型驚厥發作4 h后海馬區BDNF miRNA表達明顯增高[11]。BDNF的多態性與不同種族之間的聯系可能不同[12]及通過改變氯離子協同轉運蛋白對顳葉癲癇的發生起到調節作用[13]。眾多研究表明BDNF與癲癇二者關系密切,但BDNF對癲癇的發病究竟是促進還是抑制作用不得而知。miRNA對細胞基本生理過程有著重要的調控作用,miRNA的表達異常必然會導致細胞功能紊亂,引起疾病的發生。現今已發現的miRNA中,約70%在哺乳類動物的腦組織中有表達,如腦組織所特有的miRNA(miRNA-124a、miRNA-128、miRNA-101等),腦組織富含的miRNA(如miRNA-125b),在神經系統的不同生理過程、不同信號傳導通路的基因表達調控,如神經系統發生和發育、神經干細胞分化、細胞凋亡等過程中發揮重要作用[14]。多項研究表明miRNA與癲癇發病密切相關如miRNA-124、miRNA-203能夠抑制癲癇的發作[15~17]。部分miRNA在人類和癲癇的模型鼠都會不同程度表達上調[18]。BDNF與miRNA在癲癇的發病機制中可能有交互作用[19]。以上研究表明BDNF與miRNA對顳葉癲癇的發生可能存在一定的作用,探索此種機制或許會成為治療顳葉內側癲癇的一個新手段。
1 資料與方法
1.1 試劑與材料 腦源性神經生長因子(BDNF),甲碘荷包牡丹堿(BMI),生物胞素(Biocytin)異去甲檳榔次堿(Isoguvacine hydrochloride),木防己苦毒素(picrotoxin,PTX)多聚甲醛(paraformaldehyde), NaCl,NaH2PO4,KCl,CaCl2,MgSO4·7H2O,NaHCO3, KOH,EGTA,MgCl2,HEPES, dextrose,K2-ATP,Sucrose以上試劑均購自Sigma公司(St Louis,MO,USA)。超純水、蒸餾水、組織膠水、PCR 引物(上海生物工程技術有限公司)。
選取哈爾濱醫科大學附屬第一臨床醫院神經外科2008年4月-2010年10月手術治療的MTLE患者12例手術時切下的海馬組織為標本,男性7例,女性5例,年齡15~35歲,平均年齡(25.91±5.51)歲。應用BDNF灌流前后對照。
1.2 方法 RT-PCR術中海馬組織切下后迅速用冰冷的(4 ℃)S-ACSF保存,使用震動切片機將海馬組織切成350-400 μm腦片在培養槽中孵育1 h,槽內裝有A-CSF并持續的供給95%O2和5%CO2,溫度控制在32 ℃。部分腦片在A-CSF含有BDNF(100 ng/ml)組孵育1 h后與A-CSF組對比檢測海馬組織mir-124的表達。實驗方法按照試劑盒說明書,循環閾值的形式表達結果,均值加減SD,各組間的差異以△△CT=△CT(目的基因)-△CT(actin),通過2-△△CT方法來檢測各組相對miRNA的表達[20]。
Whole-cell記錄 術中海馬組織切下后迅速用冰冷的(4 ℃)S-ACSF保存,使用震動切片機將海馬組織切成350~400 μm腦片,顯微鏡下齒狀回顆粒細胞形成全細胞記錄將膜電位鉗制在-65 mV,灌流液為ACSF中加入PTX(100 μmol)或BMI(10 μmol),電壓鉗下記錄sEPSCs,觀測應用BDNF后sEPSCs頻率、幅度的變化。

2 結 果
2.1 BDNF降低了MTLE腦組織mir-124的表達(P<0.01) 術中海馬組織制備350~400 μm腦片,腦片在A-CSF含有BDNF(100 ng/ml)組孵育1 h后與腦片在僅有A-CSF組比較mir-124的表達明顯降低(P<0.01)(見圖1)。
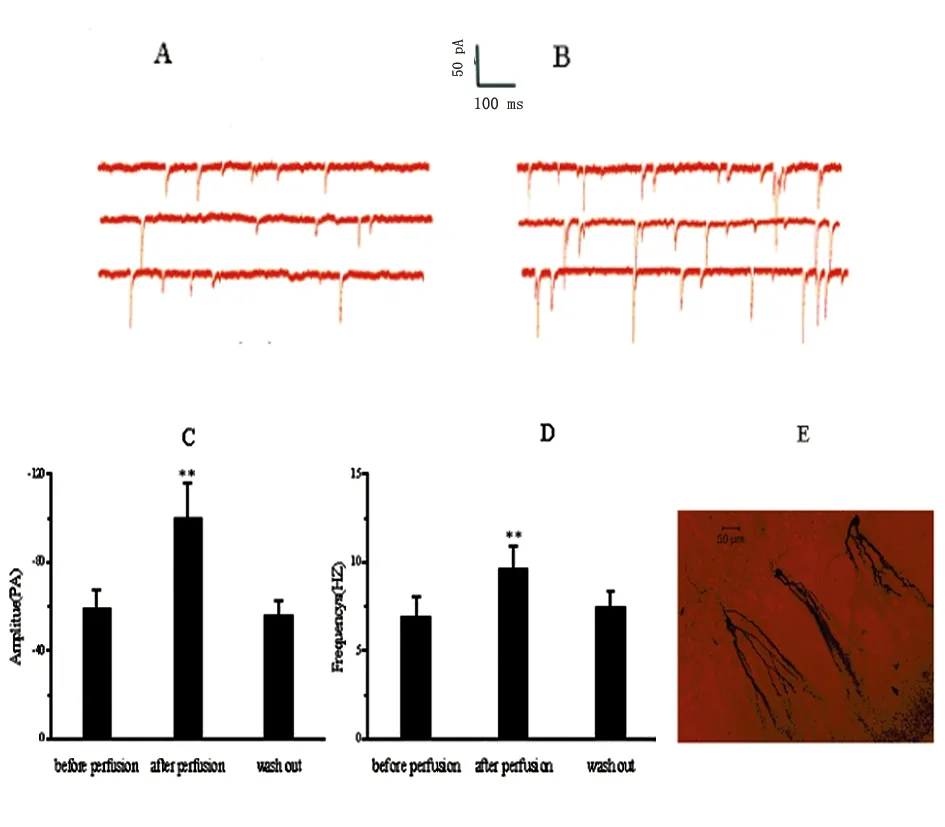
2.2 BDNF升高了顆粒細胞sEPSCs的頻率和幅度 術中海馬組織制備350-400 μm腦片,顯微鏡下識別齒狀回顆粒細胞,膜電位鉗制-65 mV, 成功記錄sEPSCs,灌流液內PTX(100 μmol)或BMI(10 μmol)消除GABA影響。灌流液內加入BDNF(100 ng/ml)。記錄6個顆粒細胞測量sEPSC的動力學特性。常規監測輸入阻抗(10-25 MΩ),以輸入阻抗變化不超過15%為標準。統計結果表明BDNF應用前后比較sEPSC幅度明顯升高,差異顯著(P<0.01);BDNF灌流前后比較sEPSC頻率明顯升高,差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。洗脫組與灌流前比較,無統計學意義(P>0.05)(見圖2)。

圖1 BDNF應用前后mir-124的表達
與灌流前比較**P<0.01;與Washout比較**P<0.01
圖2 BDNF上調了顆粒細胞sEPSCs的頻率和幅度
3 討 論
癲癇是最為常見的慢性腦疾病,病因復雜,患病率高為其特點,對癲癇的發病機制研究,在神經科學的研究中占有重要的意義。BDNF為癲癇研究的熱點之一,對癲癇的發病作用結果不一甚至有些相對立。多數學者認為BDNF對癲癇的發生有促進作用,BDNF對神經遞質有調節作用,可以促進神經元NPY的表達[21]和提高了興奮性谷氨酸的濃度[22],及胞膜NMDA受體[23]。BDNF可調節突觸的形成,增加樹突棘突的密度及TRPC3通道[24,25]。研究表明部分miRNA與癲癇發病密切相關[26],在人類TLE或動物模型中mir-146a都有較高的表達[27]。有研究表明mir-134有明顯的致癲癇作用[28,29],MiR-155的拮抗劑通過激活BDNF對癲癇持續狀態發作起到了保護作用。大多數研究都是以動物癲癇模型為基礎,探討其在癲癇發生發展中的作用,本實驗研究以顳葉內側癲癇患者術中切下的海馬為標本。結果表明BDNF對mir-124的表達及sEPSCs的影響表明其對癲癇的發生可能有其促進作用,但二者是否具有相關性,我們將繼續進行下一步研究。
[1]Wang M,Li D,Yun D,et al.Translation of BDNF-gene transcripts with short 3’ UTR in hippocampal CA1neurons improves memory formation and enhances synaptic plasticity-relevant signaling pathways[J].Neurobiol Learn Mem,2016,16:30104-30106.
[2]Von Bartheld CS,Johnson JE.Target-derived BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) is essential for the survival of developing neurons in the isthmo-optic nucleus[J].Journal of Comparative Neurology,2001,433:550-564.
[3]Messaoudi E,Bardsen K,Srebro B,et al .Acute intrahippocampal infusion of BDNF induces lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the rat dentate gyrus[J].Neurophysiol,1998, 799:496-499.
[4]Lee S,Yang M,Kim J,et al .Involvement of BDNF/ERK signaling in spontaneous recovery from trimethyltin-induced hippocampal neurotoxicity in mice[J].Brain Res Bull,2016,121:48-58.
[5]Palomer E,Martin-Segura A,Baliyan S,et al.Aging triggers a repressive chromatin state at Bdnf promoters in Hippocampal neurons[J].Cell Rep,2016,16(11):2889-2900.
[6]Heinrich C,Lahteinen S,Suzuki F,et al.Increase in BDNF-mediated TrkB signaling promotes epileptogenesis in a mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy[J].Neurobiol Dis,2011,42:35-47.
[7]Prince DA,Gu F,Parada I.Antiepileptogenic repair of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic connectivity after neocortical trauma[J] .Prog Brain Res,2016,226:209-227.
[8]Binder DK,Croll SD,Gall CM,et al.BDNF and epilepsy:too much of a good thing[J].Trends Neurosci,2001,24:47-53.
[9]Zhu WJ,Roper SN.Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances fast excitatory synaptic transmission in human epileptic dentate gyrus[J].Ann Neurol,2001,50:188-194.
[10]Fumagalli F,Moro F,Caffino L,et al.Region-specific effects on BDNF expression after contingent or non-contingent cocaine i.v.self-administration in rats[J].Int J Neuropsychopharmacol,2013,16(4):913-918.
[11]Hagihara H,Hara M,Tsunekawa K,et al.Tonic-clonic seizures induce division of neuronal progenitor cells with concomitant changes in expression of neurotrophic factors in the brain of pilocarpine-treated mice[J].Brain Res Mol Brain Res,2005,139:258-266.
[12]Sha’ari HM,Haerian BS,Baum L,et al.Association of BDNF polymorphisms with the risk of epilepsy:a multicenter study[J].Mol Neurobiol,2016,53(5):2869-2877.
[13]Eftekhari S,Mehrabi S,Soleimani M,et al.BDNF modifies hippocampal KCC2 and NKCC1 expression in a temporal lobe epilepsy model[J].Acta Neurobiologiae Experimentalis,2014,74:276-287.
[14]Gao FB.Posttranscriptional control of neuronal development by microRNA networks[J].Trends Neurosci,2008,31:20-26.
[15]Wang W,WangX,Chen L,et al.The microrna Mir-124 suppresses seizure activity and regulates Creb1 activity[J].Expert Rev Mol Med,2016,18:e4.
[16]Brennan GP,Dey D,Chen Y,et al.Dual and opposing roles of MicroRNA-124 in epilepsy are mediated through inflammatory and NRSF-dependent gene networks[J].Cell Reports,2016,14:2402-2412.
[17]Isgor C,Pare C,McDole B,et al.Expansion of the dentate mossy fiber-CA3projection in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-enriched mouse hippocampus[J].Neuroscience,2014,288:10-23.
[18]Roncon P,Soukupova M,Binaschi A,et al.Microrna profiles in hippocampal granule cells and plasma of rats with pilocarpine-induced epilepsy-comparison with human epileptic samples[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5:141-143.
[19]Cai Z,Li S.Antagonist targeting micro RNA-155 protects againstLithium-ilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in C57BL/6 mice by activating brain-derived neurotrophic factor[J] .Frontiers in Pharmacology,2016,7:129.
[20]Lanfranco MF,Seitz PK,Morabito MV,et al.An innovative real-time pcr method to measure changes in rna editing of the serotonin 2c receptor [5-ht(2c) r] in brain[J].Neurosci Methods,2009,179:247-257.
[21]Reibel S,Vivien-Roels B,Le BT,et al.Overexpression of neuropeptide Y induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the rat hippocampus is long lasting[J].Eur J Neurosci,2000,12:595-605.
[22]Matsumoto T,Numakawa T,Adachi N,et al.Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances depolarization-evoked glutamate release in cultured cortical neurons[J].Neurochem,2001,79:522- 530.
[23]Caldeira MV,Melo CV,Pereira DB,et al.BDNF regulates the expression and traffic of NMDA receptors in cultured hippocampal neurons[J].Mol Cell Neurosci,2007,35:208- 219.
[24]Alonso M,Medina JH,Pozzo-Miller L,et al.ERK1/2 activation is necessary for BDNF to increase dendritic spine density in hippocampal CA1pyramidal neurons[J].Learn Mem,2004,11:172-178.
[25]Amaral MD,Pozzo-Miller L.TRPC3 channels are necessary for brain-derived neurotrophic factor to activate a nonselective cationic current and to induce dendritic spine formation[J].Neurosci,2007,27:5179-5189.
[26]Li MM,Li XM,Zheng XP,et al.MicroRNAs dysregulation in epilepsy[J].Brain Research,2014,1584:94-104.
[27]Aronica E,Fluiter K,Iyer A,et al.Expression pattern of miR-146a,an inflammation-associated microRNA,in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy[J].Eur J Neurosci,2010,31:1100-1107.
[28]Jimenez-Mateos EM,Engel T,Merino-Serrais P,et al.Silencing microRNA-134 produces neuroprotective and prolonged seizure-suppressive effects[J].Nat Med,2012,18:1087-1 094.
[29]Wang XM,Jia RH,Wei D,et al.MiR-134 blockade prevents status epilepticus like-activity and is neuroprotective in cultured hippocampal neurons[J].Neurosci Lett,2014,572:20-25.
The effect of BDNF on levels of miRNA-124 and sEPSCs
WANG Fengjun,WANG Hongpeng,SHAN Jingli,et al.
(Department of Neurology,The Fourth Hospital of Harbin Medical University,Harbin 150001,China)
Objective To study the effect of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the pathogenesis from patients with MTLE.Methods The study was performed between April 2008 and October 2010.Surgically removed specimens were collected from the patients with MTLE.All patients gave written informed consent for research use of the biopsy materials.Surgically resected hippocampal were collected and immediately immersed in oxygenated ice-cold SACSF.The expression of Mir-124 was detected by RT-PCR and sEPSCs by patch-clamp.Results Expression of mir-124 was significantly decreased in Dentate Gyrus of MTLE compared with that of controls (P<0.01).BDNF increases frequency and amplitude of sEPSC (P<0.01).Conclusions The results indicate that BDNF significantly decreased the expression of mir-124 as in Dentate Gyrus from patients with MTLE.Our electrophysiological findings indicate that BDNF increase excitability on dentate granule cells.In conclusion,our work supports a role of BDNF in pathophisyology of MTLE and raises the possibility that interference with BDNF action may be a therapeutic method for patients of MTLE.
BDNF; mir-124; MTLE; sEPSCs
2017-04-23;
2017-05-30
黑龍江省教育廳面上項目(No.12541509)
(1.哈爾濱醫科大學附屬第四醫院神經內科,黑龍江 哈爾濱 150001;2.牡丹江市婦女兒童醫院,黑龍江 牡丹江 157000;3.哈爾濱市第二醫院,黑龍江 哈爾濱 150056) 通迅作者: 王鳳軍,E-mail:fengjun19791209@163.com
1003-2754(2017)08-0718-03
R742.1
A

