GLOBAL BOUNDEDNESS OF SOLUTIONS IN A BEDDINGTON-DEANGELIS PREDATOR-PREY DIFFUSION MODEL WITH PREY-TAXIS
MA Wen-jun,SUN Liang-liang
(1.Longqiao College,Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics,Lanzhou 730101,China)(2.School of Mathematics and Statistics,Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730030,China)
GLOBAL BOUNDEDNESS OF SOLUTIONS IN A BEDDINGTON-DEANGELIS PREDATOR-PREY DIFFUSION MODEL WITH PREY-TAXIS
MA Wen-jun1,SUN Liang-liang2
(1.Longqiao College,Lanzhou University of Finance and Economics,Lanzhou 730101,China)(2.School of Mathematics and Statistics,Lanzhou University,Lanzhou 730030,China)
In this paper,we study a Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey di ff usion model with prey taxis,where the prey-taxis describes a direct movement of the predator in response to a variation of the prey.We prove that the global classical solutions are globally bounded by theLp-Lqestimates for the Neumann heat semigroup andLpestimates with Moser’s iteration of parabolic equations.
predator-prey;di ff usion;prey-taxis;classical solution;global boundedness
1 Introduction
In recent years,more and more attention were given to the reaction-di ff usion system of a predator-prey model with prey-taxis.For example,for the existence and uniqueness of weak solutions[1,11],the global existence and uniqueness of classical solutions[2,17,18],pattern formation induced by the prey-taxis[12],global bifurcation for the predator-prey model with prey-taxis[13],boundedness or blow up in a chemotaxis system[14-16].
In this paper,we study the following reaction-di ff usion system of a predator-prey model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and prey-taxis

where Ω is a bounded domain in RNwith smooth boundary?Ω,initial datau0(x),v0(x)∈C2+α()compatible on?Ω,andνis the normal outer vector on?Ω,uandvrepresent the densities of the predator and prey,respectively,d1,d2,n,h,e,m,a,b,c,r,Kare positive constants that stand for di ff usion coefficients,death rate ofu,intra-speci fi c competition ofu,conversion rate,consumption rate,predator interference,prey saturation constant,another saturation constant,intrinsic growth and carrying capacity ofv,respectively.
The Beddington-DeAngelis model(1.1)is similar to the well known Holling type II model with an extra termauin the denominator which models the mutual interference among predators.In 2008,Ainseba et al.[1]proposed a Holling type II model with preytaxis and established the existence of weak solution by Schauder fi xed point theorem and the uniqueness via duality technique.In 2010,Tao[2]gave the global existence and uniqueness of classical solution to Ainseba’s model by contraction mapping principle together withLpestimates and Schauder estimates of parabolic equations.In 2015,He and Zheng[3]proved further more that the global classical solution is globally bounded.
There were also many works published for model(1.1).For the ODE system corresponding to(1.1),Cantrell and Cosner[4]presented some qualitative analysis of solutions from the view point of permanence and the existence of a global asymptotic stable positive equilibrium;Hwang[5]demonstrated that the local asymptotic stability of the positive equilibrium implies its global asymptotic stability.Chen and Wang[6]presented the qualitative analysis of system(1.1)from the view point of local asymptotic stability of the positive constant steady state and the existence and nonexistence of a nonconstant positive steady state.Haque[7]investigated the the in fl uence of intra-speci fi c competition among predators in the original Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey model and o ff ered a detailed mathematical analysis of the model.Yan and Zhang[8]studied model(1.1)without prey-taxis and obtained that the di ff usion can destabilize the positive constant steady state of the system.
However,the emergency of the prey-taxis makes it more difficult to deal with the original problems.It is known that the global existence and bounedeness of solutions in(1.1)without prey-taxis can be easily obtained by using energy estimates and bootstrap arguments.In this paper,however,we will prove that the global classical solutions of(1.1)are moreover globally bounded by using theLp-Lqestimates for the Neumann heat semigroup andLpestimates with Moser’s iteration of parabolic equations.
Throughout this paper,we assume thatχ(u)∈C1([0,+∞)),χ(u)≡ 0 foru>um,andχ′(u)is Lipschitz continuous,i.e.,|χ′(u1)-χ′(u2)|≤L|u1-u2| for anyu1,u2∈[0,+∞),whereumandLare two positive constants.The assumption ofχis a regularity requirement for our qualitative analysis,and the assumption thatχ(u) ≡ 0 foru>umhas a clear biological interpretation[1].Our main result is stated as follows.
Theorem 1Under the assumptions forχand initial data described above,the unique nonnegative classical solution of(1.1)is globally bounded.
The paper is organized as follows.We introduce some known results as preliminaries in Section 2.In Section 3,we give the proof of Theorem 1.
2 Preliminaries
First we introduce the well-known classicalLp-Lqestimates for the Neumann heat semigroup on bounded domains.
Lemma 1(see Lemma 1.3 in[9])Suppose(etΔ)t>0is the Neumann heat semigroup in Ω,and letλ1denote the fi rst nonzero eigenvalue of-Δ in Ω under Neumann boundary conditions.Then there existC1,C2>0 only depending on Ω such that the following estimates hold
(i)If 1≤q≤p≤+∞,then
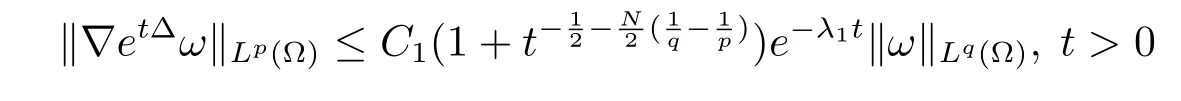
for allω∈Lq(Ω);
(ii)If 2≤q≤p≤+∞,then

for allω∈W1,q(Ω).
One can obtain the boundedness ofvbased on the comparison principle of ODEs.
Lemma 2Let(u,v)be a solution of(1.1).Thenu≥0 and 0≤v≤K1=max{K,maxv0(x)}.
3 Proof of Theorem 1
In this section,we give proof of Theorem 1,which is motivated by Tao and Winkler[10].
Proof of Theorem 1
Step 1Boundedness of‖u‖L1(Ω).
Integrating the sum of the fi rst equation andetimes of the second equation in(1.1)on Ω by parts,we have

Step 2Boundedness of‖u‖Lp(Ω)withp≥ 2.
Multiplying the fi rst equation of(1.1)byup-1and integrate on Ω by parts,combining Lemma 2.2,we have
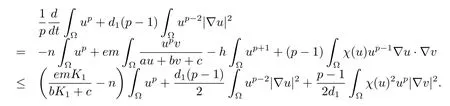
Together withχ(u)≤Mdue toχ∈C1andχ≡ 0 foru≥um.This yields
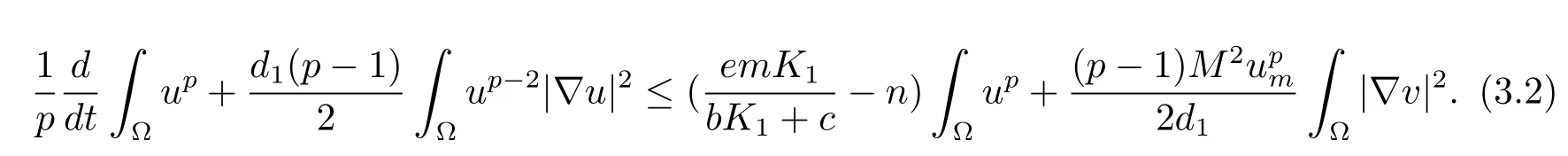
Multiply the second equation of(1.1)by-Δv,and integrate on Ω by parts to get
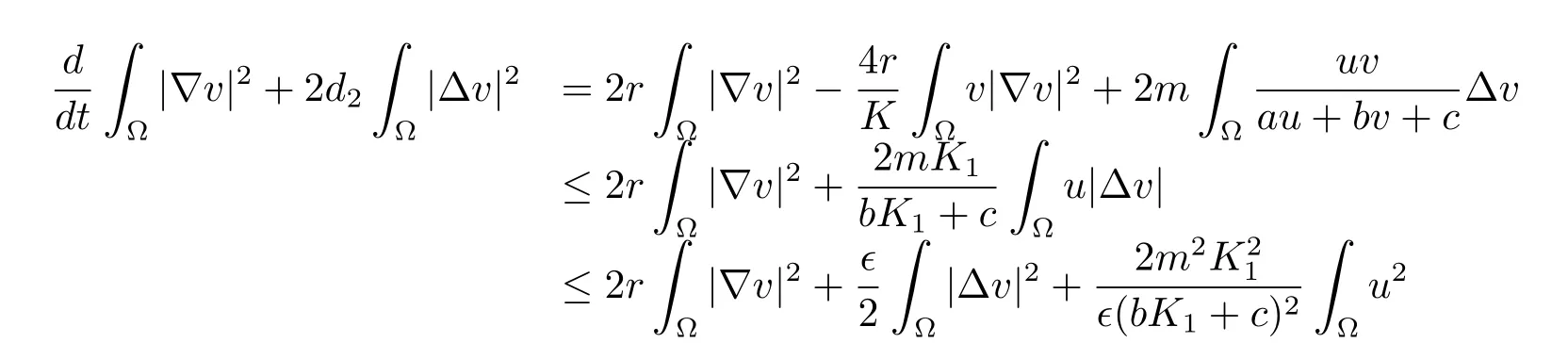
by the Young inequality.Choosing?=2d2,we have

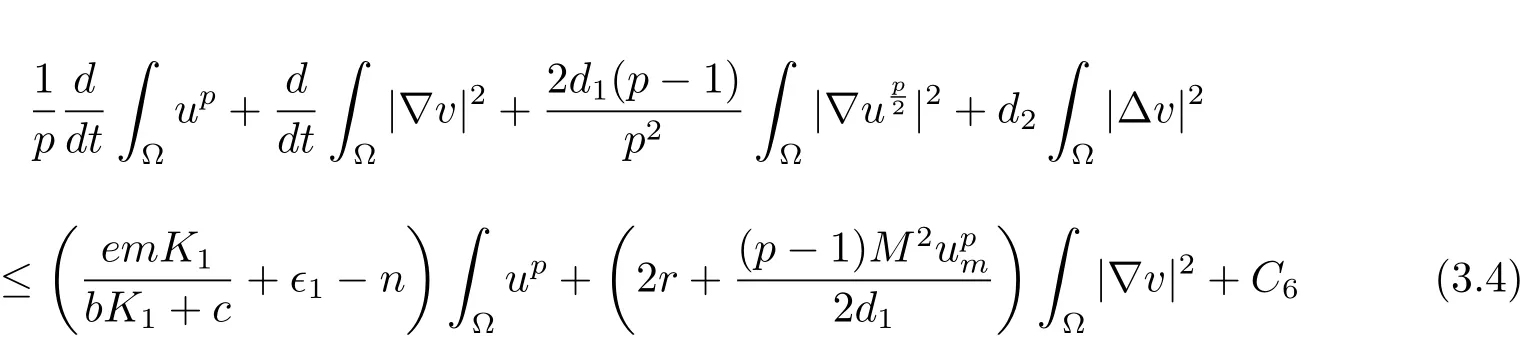
withC6>0 depending on?1.By the Sobolev interpolation inequality and Lemma 2.2,we have for any?2>0 that
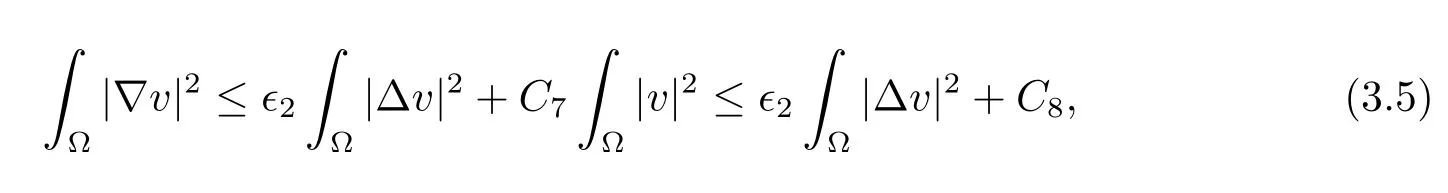
whereC7,C8>0 depending on?2.Applying the Gagliardo-Nirenberg inequality yields


for any?3>0,withC10>0 depending on?3.By Step 1,we know‖u‖1≤C5.So

withC11>0.Now fix?2,?3such thatFrom(3.4)-(3.6),we have

withC12>0.De finefor allt>0 with.By the Gronwall inequality,we havefor allt>0.
Step 3Boundedness of‖?v‖Lp(Ω)withp≥ 2.

By Lemma 2.1,we conclude that

Step 4Global boundedness.
On the basis of Steps 2 and 3,using Lemma A.1 in[10],we can obtain the global boundedness of solutions to(1.1)by the standard Moser iterative technique.
Remarkwe used the assumption thatχ′(u)is Lipschitz continuous,which is a necessary condition for existence of the global solutions(see[2]).
On the other hand,the intra-speci fi c competition termhu2makes our estimates easier,which is a “good” term.This also coincides with Haque’s[7]result that competition among the predator population is bene fi cial for both populations co-existence.
[1]Ainseba B E,Bendahmane M,Noussair A.A reaction-di ff usion system modeling predator-prey with prey-taxis[J].Nonl.Anal.:RWA,2008,9:2086-2105.
[2]Tao Y S.Global existence of classical solutions to a predator-prey model with nonlinear prey-taxis[J].Nonl.Anal.:RWA,2010,11:2056-2064.
[3]He X,Zheng S N.Global boundedeness of solutions in a reaction-di ff usion system of predator-prey model with prey-taxis[J].Appl.Math.Lett.,2015,49:73-77.
[4]Cantrell R S,Cosner C.On the dynamics of predator-prey models with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response[J].J.Math.Anal.Appl.,2001,257:206-222.
[5]Hwang T W.Global analysis of the predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response[J].J.Math.Anal.Appl.,2003,281:395-401.
[8]Chen W,Wang M.Qualitative analysis of predator-prey models with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and di ff usion[J].Math.Comput.Model.,2005,42:31-44.
[10]Haque M.A detailed study of the Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey model[J].Math.Biosci.,2011,234(1):1-16.
[8]Yan X P,Zhang C H.Stability and turing instability in a di ff usive predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response[J].Nonl.Anal.:RWA,2014,20:1-13.
[10]Winkler M.Aggregation vs.global di ff usive behavior in the higher-dimensional Keller-Segel model[J].J.Di ff.Eqs.,2010,248:2889-2905.
[10]Tao Y S,Winkler M.Boundedness in a quasilinear parabolic-parabolic Keller-Segel system with subcritical sensitivity[J].J.Di ff.Eqs.,2012,252:692-715.
[11]Bendahmane M.Analysis of a reaction-di ff usion system modeling predator-prey with prey-taxis[J].Netw.Heterog.Media,2008,3(4):863-879.
[12]Lee J M,Hillen T,Lewis M A.Pattern formation in prey-taxis systems[J].J.Biol.Dyn.,2009,3(6):551-573.
[13]Wang X L,Wang W D,Zhang G H.Global bifurcation of solutions for a predator-prey model with prey-taxis[J].Math.Meth.Appl.Sci.,2015,38:431-443.
[14]Xiang T.Boundedness and global existence in the higher-dimensional parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis system with/without growth source[J].J.Di ff.Eqs.,2015,258(12):4275-4323.
[15]Winkler M.Boundedness in the higher-dimensional parabolic-parabolic chemotaxis system with growth source[J].Comm.Partial Di ff.Eqs.,2010,35(8):1516-1537.
[16]Horstmann D,Winkler M.Boundedness vs.blow up in a chemotaxis system[J].J.Di ff.Eqs.,2005,215(1):52-107.
[17]Wu S N,Shi J P,Wu B Y.Global existence of solutions and uniform persistence of a di ff usive predator-prey model with prey-taxis[J].J.Di ff.Eqs.,2016,260:5847-5874.
[18]Li X J.Global solutions for the ratio-dependent food-chain model with cross-di ff usion[J].J.Math.,2015,35(2):267-280.
一類帶食餌趨向的Beddington-DeAngelis捕食者-食餌擴散模型整體解的有界性
馬文君1,孫亮亮2
(1.蘭州財經大學隴橋學院,甘肅蘭州730101)(2.蘭州大學數學與統計學院,甘肅蘭州730030)
本文研究一類帶食餌趨向的Beddington-DeAngelis捕食者-食餌擴散模型,其中食餌趨向性描述的是捕食者對食餌數量變化而產生的一種正向遷移.利用Neumann熱半群的Lp-Lq估計和帶拋物型方程Moser迭代的Lp估計,獲得了該模型經典解的整體有界性.
捕食者-食餌;擴散;食餌趨向;經典解;整體有界性
??35B35;35K57;92D25
O175.26
on:35B35;35K57;92D25
A Article ID: 0255-7797(2017)04-0731-06
date:2016-03-15Accepted date:2016-04-22
Biography:Ma Wenjun(1987-),female,born at Gangu,Gansu,lecturer,major in partial di ff erential equations.
- 數學雜志的其它文章
- THE GROWTH ON ENTIRE SOLUTIONS OF FERMAT TYPE Q-DIFFERENCE DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
- A MODIFIED BIC TUNING PARAMETER SELECTOR FOR SICA-PENALIZED COX REGRESSION MODELS WITH DIVERGING DIMENSIONALITY
- FINITE GROUPS WHOSE ALL MAXIMAL SUBGROUPS ARE SMSN-GROUPS
- ON PROJECTIVE RICCI FLAT KROPINA METRICS
- 態R0代數
- Hom-弱Hopf代數上的Hom-smash積

