X線平片和CT檢查診斷肋骨骨折的臨床效果和對比分析
方東光
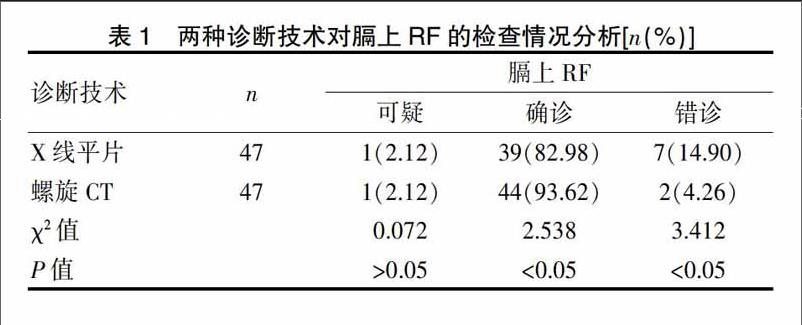
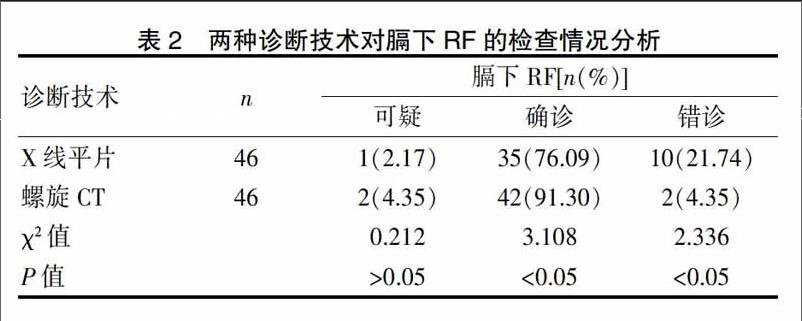
[摘要] 目的 分析肋骨骨折(rib fracture,RF)診斷時采用CT掃描和X線平片診斷的結(jié)果。 方法 選取我院2014年6月~2015年6月收治的62例確診為RF患者進(jìn)行實驗,分別采用X光和CT掃描方式予以診斷,判斷2種方式的確診率和錯診率。 結(jié)果 螺旋CT對膈上RF的檢查確診率顯著比X線平片高,而錯診率相比X線平片則有顯著下降,差異具有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05);螺旋CT對膈下RF的檢查確診率顯著比X線平片高,而錯診率相比X線平片則有顯著下降,差異具有統(tǒng)計學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。 結(jié)論 與X線平片相比,采取CT影像技術(shù)對RF患者進(jìn)行診斷,可獲得更高的骨折檢出率,同時盡量避免誤診的情況,值得加強(qiáng)推廣。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 肋骨骨折;X線平片;CT檢查;檢出率;誤診率
[中圖分類號] R320.1 [文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識碼] B [文章編號] 1673-9701(2017)13-0111-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the results of CT scan and X-ray plain film in diagnosis of rib fracture (RF). Methods 62 patients who were diagnosed with RF in our hospital from June 2014 to June 2015 were enrolled in this study. X-ray and CT scans were used to diagnose. The diagnosis rate and misdiagnosis rate of the two methods were judged. Results The diagnostic rate of RF on the diaphragm by spiral CT was significantly higher than that by X-ray, and the misdiagnosis rate by spiral CT was significantly lower than that by X-ray film. The data were satisfied with,and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The diagnostic rate of subphrenic RF by spiral CT was significantly higher than that by the X-ray, and the misdiagnosis rate by spiral CT was significantly lower than that by the X-ray film. The data were satisfied,and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion Compared with X-ray, CT imaging technique used in diagnosing RF patients can obtain higher detection rate of fracture and avoid misdiagnosis as much as possible,which is worthy of promotion.
[Key words] Rib fracture; X-ray film; CT examination; Detection rate; Misdiagnosis rate
肋骨骨折(rib fracture,RF)有兩種致病原因,即病理性致因與外力性致因。前者主要是由于各種骨科疾病(如骨質(zhì)疏松等)使骨質(zhì)受損繼發(fā)骨折引起[1],而后者多由間接或直接性外力撞擊造成。直接性外力撞擊容易折斷肋骨,導(dǎo)致胸腔被刺穿,因此患者多合并有內(nèi)臟損害;而間接性外力撞擊多累及胸壁軟組織。X線平片、CT影像技術(shù)等均是現(xiàn)階段臨床診斷不同病因所致RF的有效手段,但在實際操作中,所選檢查方法不同,其優(yōu)缺點也有很大差異。本文通過觀察62例接受X線平片及CT影像技術(shù)診斷的RF病例資料,以進(jìn)一步了解何種檢查技術(shù)對RF更具有應(yīng)用價值,現(xiàn)報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
本組62例實驗對象資料均有完整記錄,搜集資料時間為2014年6月~2015年6月。納入標(biāo)準(zhǔn):病歷資料完整,均簽署知情同意書。排除標(biāo)準(zhǔn):凝血功能障礙患者、精神疾病患者、肝腎功能障礙患者等。其中男36例,女26例,年齡分布:最高者77歲,最低者23歲,平均(41.8±8.3)歲。根據(jù)骨折病因劃分,其中有20例由交通車禍傷造成,18例由重物擊打造成,14例由擠壓過度造成,另有高處墜落與其他原因致傷者各7例和3例。……

