坡體滲流與氣溫變化相關(guān)性分析
劉剛+童富果+習(xí)念念+郝霜

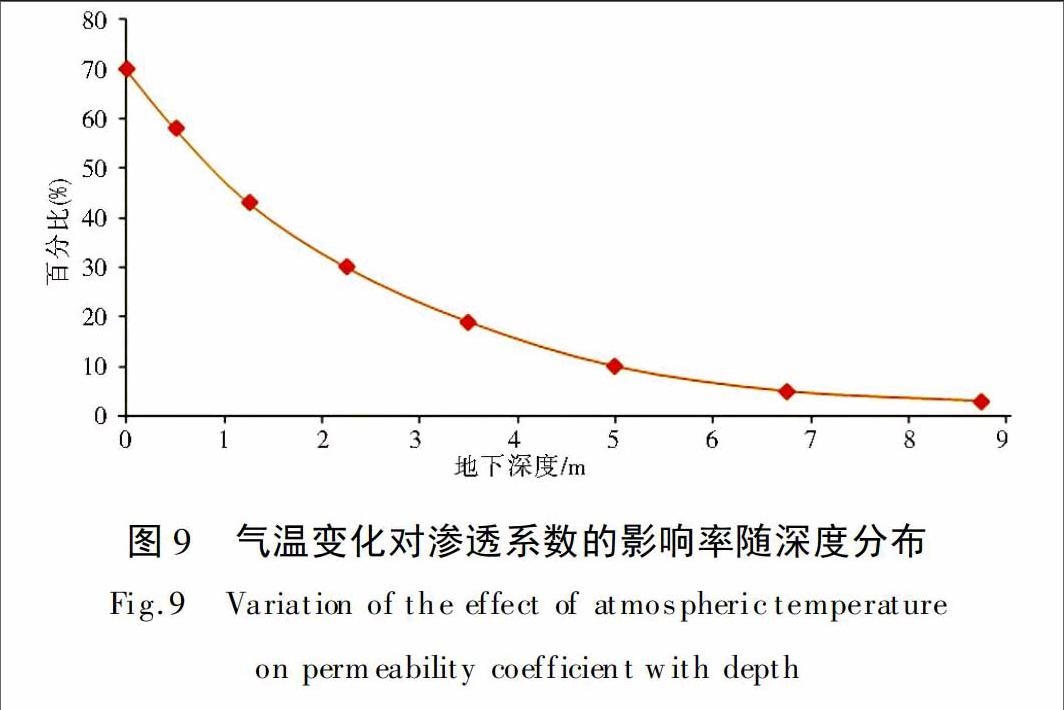

摘要:基于多相流及多場(chǎng)耦合理論,采用有限單元法計(jì)算了三峽庫(kù)區(qū)木魚(yú)包滑坡體溫度隨氣溫變化情況,進(jìn)而依據(jù)溫度與水體黏滯性的相關(guān)關(guān)系分析氣溫變化對(duì)坡體滲流的影響。計(jì)算表明,坡內(nèi)溫度受氣溫影響僅限于坡體淺層區(qū)域,距地表深度越深,影響程度越小,在時(shí)間上的滯后性越大。溫度變化可改變水的黏滯性,進(jìn)而引起土體滲透參數(shù)的改變,計(jì)算表明因氣溫變化引起的坡體滲透性改變較為顯著。坡體滲透系數(shù)受氣溫變化的影響隨深度呈非線性分布,距地表越深受氣溫變化的影響越弱,通常大于雨水最大入滲深度以后,坡體滲透系數(shù)不再發(fā)生顯著變化。另外,坡體滲透系數(shù)隨氣溫呈現(xiàn)季節(jié)性變化規(guī)律,夏季氣溫高于坡內(nèi)土體溫度,滲透系數(shù)隨深度的增加而減小;冬季坡體內(nèi)溫度高于氣溫,滲透系數(shù)隨深度的增加而增加。
關(guān)鍵詞:氣溫;滲透系數(shù);坡體滲流;多相流;季節(jié)性
中圖分類號(hào):TV223.4 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A 文章編號(hào):1672-1683(2017)03-0158-06
Abstract:Based on the multi-phase flow & multi-field coupling theory,this paper adopted the finite element method to calculate the temperature distribution of Muyubao landslide as the atmospheric temperature changes.Further,it analyzed the influence of atmospheric temperature changes on the slope seepage according to the correlation between temperature and viscosity of water.The results of calculation showed that the effect of atmospheric temperature on temperature of the slope body is limited to the shallow surface;as the depth increases,the influence decreases and the hysteresis increases concurrently.The mobility of the water is affected by the change of the slope body′s temperature and it can change the water permeability in the inner slope.The effect of atmospheric temperature on permeability coefficient of the slope has a nonlinear relationship with depth.The effect of atmospheric temperature on the permeability coefficient declines as the depth increases.Generally,the permeability coefficient of the slope no longer change significantly when the depth is deeper than the maximum depth of infiltration.The permeability coefficient of the slope shows seasonal variation with the atmospheric temperature.The permeability coefficient decreases with the increase of depth when the atmospheric temperature is higher than the soil in summer.In contrast,the permeability coefficient increases with the increase of depth in winter.
Key words:air temperature;permeability coefficient;slope seepage;multiphase flow;seasonal
坡體滲流通常屬于非飽和滲流的范疇,涉及到土(石)、水、氣組成的多相物質(zhì)的耦合作用[1]。坡體滲流通常與坡內(nèi)水體滲透性、坡體初始含水率、滲透邊界等諸多因素有關(guān)[2-3],其中水體滲透性是影響坡體滲流的關(guān)鍵因素之一。水在土體中的滲透性主要受水的黏滯性、相對(duì)飽和度以及土體本征滲透性的影響[4],而氣溫變化對(duì)土體本征滲透性以及相對(duì)飽和度的影響較小,因此氣溫變化主要通過(guò)改變水的黏滯性來(lái)影響坡內(nèi)水體滲透性。……
