貝葉斯神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)在城市短期用水預(yù)測(cè)中的應(yīng)用
占敏+薛惠鋒+王海寧+萬(wàn)毅


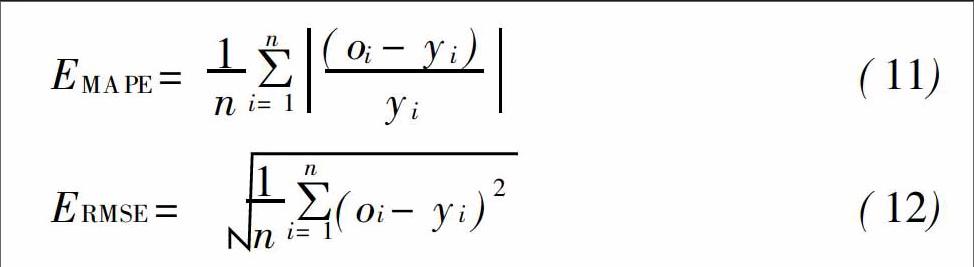
摘要:嚴(yán)格水資源管理制度實(shí)施的背景下,短期用水量預(yù)測(cè)對(duì)城市供水系統(tǒng)調(diào)度的作用日益顯著。在分析日用水量時(shí)序演化規(guī)律及隨機(jī)性影響因素的基礎(chǔ)上,以前7天每日用水量、日最高溫度、當(dāng)月用水量占全年比、日降水量、節(jié)假情況作為短期用水量預(yù)測(cè)指標(biāo),構(gòu)建了BP神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)城市短期用水量預(yù)測(cè)模型,并利用貝葉斯正則化對(duì)BP神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)進(jìn)行優(yōu)化。將兩種模型應(yīng)用于廣州市某自來(lái)水公司進(jìn)行對(duì)比驗(yàn)證,結(jié)果表明,貝葉斯神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)預(yù)測(cè)模型與BP神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)預(yù)測(cè)模型的平均絕對(duì)百分比誤差分別達(dá)0.87%與1.85%,經(jīng)貝葉斯正則化的BP神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò)模型泛化能力更強(qiáng),精度提高了約0.98%,更符合城市短期用水量預(yù)測(cè)的高精度要求。
關(guān)鍵詞:短期用水量;神經(jīng)網(wǎng)絡(luò);貝葉斯正則化;預(yù)測(cè)模型
中圖分類號(hào):TV213 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A 文章編號(hào):1672-1683(2017)03-0073-07
Abstract:Under the background of implementation of the most stringent management regulations on water resources,the prediction of short-term water consumption is playing an increasingly significant role in urban water supply system scheduling.Based on the analysis of the temporal evolution pattern and random factors of short-term water consumption,a Bayesian neural network prediction model for urban short-term water consumption was built with the daily maximum temperature,daily water consumption of the previous 7 days,ratio of water consumption of the current month to the annual amount,daily precipitation,and holidays as predictors of short-term water consumption.Meanwhile,Bayesian regularization was used to optimize BP neural network.Both BP network model and the optimized model were applied to a running-water company in Guangzhou City for tesing.The results indicated that the mean absolute percentage error of the Bayesian neural network prediction model was 0.87%,while that of the BP neural network prediction model was 1.85%.Compared to the BP neural network prediction model,the optimized model has stronger generalization ability,with accuracy improved by about 0.98%.Thus,it fits better with the high-precision requirement of urban short-term water prediction.
Key words:short-term water consumption;neural network;Bayesian regularization;prediction model
水資源是保障區(qū)域發(fā)展和人民生活基礎(chǔ)性資源與戰(zhàn)略性資源,然而我國(guó)近2/3的城市呈“缺水”或“嚴(yán)重缺水”狀態(tài),多地已逼近用水總量紅線。在最嚴(yán)格水資源管理制度[1]實(shí)施的背景下,日益突出的水資源供需平衡矛盾給城市供水調(diào)度帶來(lái)了空前的挑戰(zhàn)。長(zhǎng)期用水總量紅線目標(biāo)需要短期用水實(shí)時(shí)控制與調(diào)節(jié)來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn),且短期用水量預(yù)測(cè)作為城市供水系統(tǒng)運(yùn)行工況模擬與調(diào)度決策基礎(chǔ)和前提,是城市供水調(diào)度關(guān)鍵的一環(huán),本文試圖建立高精度的逐日用水量預(yù)測(cè)模型,以提高供水系統(tǒng)工況模擬的合理性及調(diào)度決策的可靠性,支撐城市供水系統(tǒng)的穩(wěn)定運(yùn)行,促進(jìn)區(qū)域水資源的高效利用與節(jié)約。……
