血管內皮細胞生長因子、基質金屬蛋白酶—2和基質金屬蛋白酶抑制因子—2在非小細胞肺癌中的表達及意義
余雪君+劉欣艷+李彩榮+王錦俊+趙純誠+盛霞+陶玙婧

[摘要] 目的 探討非小細胞肺癌(NSCLC)組織中血管內皮細胞生長因子(VEGF)、基質金屬蛋白酶-2(MMP-2)和基質金屬蛋白酶抑制因子-2(TIMP-2)的表達與肺癌侵襲和轉移的關系。 方法 收集上海市普陀區(qū)中心醫(yī)院2012年1月~2015年12月臨床和病理確診的56例NSCLC標本,其中25例肺鱗癌、31例肺腺癌;另取20例癌旁正常肺組織作為陰性對照,用免疫組化SP法檢測標本中VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2的表達。 結果 VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2在肺癌和正常肺組織中的表達差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P < 0.05);VEGF和MMP-2的表達與肺癌淋巴結轉移和臨床分期呈正相關(P < 0.05),TIMP-2的表達與肺癌淋巴結轉移和臨床分期呈負相關(P < 0.05),但都與病理類型無關(P > 0.05)。 結論 VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2的表達與非小細胞肺癌的侵襲和轉移相關,可作為評價肺癌組織侵襲和轉移能力的指標。
[關鍵詞] 非小細胞肺癌;血管內皮細胞生長因子;基質金屬蛋白酶-2;基質金屬蛋白酶抑制因子-2;免疫組織化學;腫瘤轉移
[中圖分類號] R734.2 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1673-7210(2017)03(b)-0107-04
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in non small cell lung carcinoma and its clinical significance
YU Xuejun1 LIU Xinyan1 LI Cairong1 WANG Jinjun1 ZHAO Chuncheng2 SHENG Xia3 TAO Yujing1
1.Department of Geriatrics, Central Hospital of Shanghai Putuo District, Shanghai 200062, China; 2.Department of Thoracic Surgery, Central Hospital of Shanghai Putuo District, Shanghai 200062, China; 3.Department of Pathology, Central Hospital of Shanghai Putuo District, Shanghai 200062, China
[Abstract] Objective To study the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 (TIMP-2) in non small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) and their relationship with invasion and metastasis of the lung cancerous tissues. Methods Fifty-six cases of human NSCLC tissues which had clinical and pathological diagnosis were collected from the Central Hospital of Shanghai Putuo District from January 2012 to December 2015. Among them, 25 cases had lung squamous cell carcinoma and 31 cases had lung adenocarcinoma. Another 20 cases of adjacent normal lung tissue were taken as a negative control. The expression of VEGF, MMP-2 and TIMP-2 were detected by SP immunohistochemical technique in all specimens. Results The expression of VEGF, MMP-2 and TIMP-2 in lung carcinoma and normal lung tissues were statistically significantly different (P < 0.05). There were positive correlations between the expression of VEGF and MMP-2 with lymph node metastasis and clinical stage (P < 0.05), but there was negative correlation between the expression of TIMP-2 with lymph node metastasis and clinical stage respectively (P < 0.05). The expression of VEGF, MMP-2 and TIMP-2 had no association with pathological type (P > 0.05). Conclusion The expression of VEGF, MMP-2 and TIMP-2 are associated with the invasion and metastasis in lung carcinoma, which may be potentially useful for indicating the metastasis and invasion of lung carcinoma.
[Key words] Non small cell lung carcinoma; Vascular endothelial growth factor; Matrix metalloproteinase-2; Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2; Immunohistochemistry; Tumor metastasis
非小細胞肺癌(NSCLC)是肺癌最常見的組織學類型,占肺癌總數的80%~85%,已成為致死率最高的腫瘤[1],而且,有80%以上的患者死于侵襲和轉移[2],因此研究NSCLC侵襲與轉移的可能機制,對制訂正確的治療方案及判斷預后具有重要的臨床意義。腫瘤的侵襲和轉移是多因素、多步驟的生物學過程,涉及到腫瘤血管生成、細胞外基質(ECM)降解等變化[3]。血管內皮細胞生長因子(VEGF)是目前發(fā)現的刺激腫瘤血管生成最重要的因子,可直接或間接地促進血管生成[4]。基質金屬蛋白酶(MMPs)水解ECM,基質金屬蛋白酶抑制因子-2(TIMP-2)是MMP-2的抑制劑,正常情況下二者處于平衡狀態(tài),當TIMP-2水平高時,會抑制MMP-2的激活,而當TIMP-2水平低時,則介導MMP-2的激活[5-6]。本研究采用免疫組化SP法檢測肺癌中VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2的表達,探討肺癌組織侵襲和轉移的可能機制,為其生物學行為的判斷和臨床預后提供依據。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
收集普陀區(qū)中心醫(yī)院2012年1月~2015年12月行手術治療且術前未經化療、放療及免疫治療的56例NSCLC標本(NSCLC組),均經臨床表現和手術病理確診為NSCLC,均在患者的知情同意下進行。另取20例癌旁正常肺組織作為陰性對照(對照組),所取組織距病灶邊緣5 cm以上。NSCLC組中,男41例,女15例,年齡43~73歲,平均(62.25±12.37)歲;對照組中,年齡44~72歲,平均(61.86±11.83)歲,兩組年齡比較,差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P > 0.05)。NSCLC中,鱗癌25例,腺癌31例;臨床分期采用國際抗癌聯盟分期標準,Ⅰ期12例,Ⅱ期26例,Ⅲ期14例,Ⅳ期4例;伴淋巴結轉移34例,無淋巴結轉移22例;腫瘤分化中、高度44例,低分化12例。
1.2 研究方法
所有組織標本均經10%甲醛固定,常規(guī)石蠟包埋和切片,HE染色和病理學診斷。石蠟切片厚4 μm,采用免疫組化常規(guī)SP法,按說明書操作進行。VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2單克隆抗體、SP免疫組化試劑盒均購自福州邁新生物技術公司。以PBS代替一抗作陰性對照,用已知陽性片作為陽性對照。采用圖像分析軟件Image-Pro Plus 6.0分析免疫組化片結果。
1.3 結果判斷
VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2陽性判定:均以細胞漿內出現明顯的棕黃色顆粒為陽性[7-8]。根據腫瘤細胞胞漿染色的程度及染色細胞百分率,以下列符號表示[9]:“-”表示無陽性細胞或陽性細胞率為0;“+”表示陽性細胞率為10%~<40%;“++”表示陽性細胞率為40%~ <70%;“+++”表示陽性細胞率≥70%。
1.4 統(tǒng)計學方法
采用SPSS 22.0統(tǒng)計軟件包進行統(tǒng)計分析,計量資料以均數±標準差(x±s)表示,采用t檢驗,計數資料采用χ2檢驗,以P < 0.05為差異有統(tǒng)計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2在肺癌組織和正常癌旁組織中的表達
PBS陰性對照組未著色。VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2在NSCLC組中的表達陽性率均明顯高于對照組,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P < 0.05)。見表1。
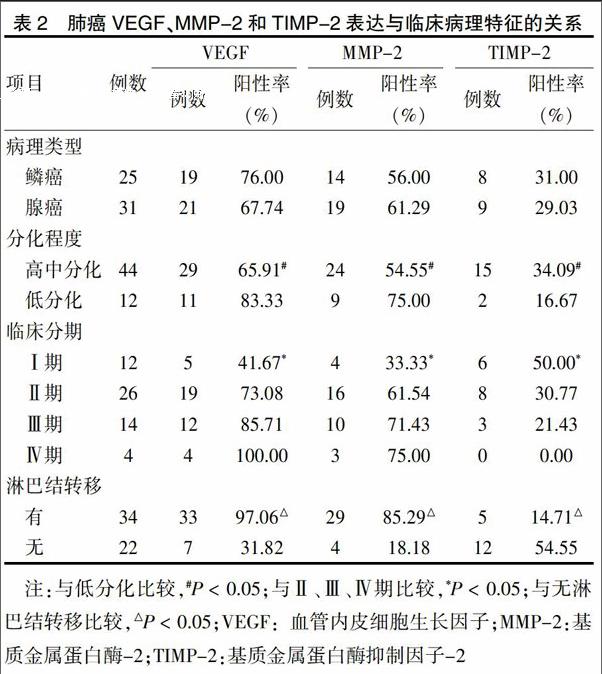
2.2 肺癌VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2表達與臨床病理特征的關系
NSCLC腺癌組織VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2的表達均略高于鱗癌,但差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P > 0.05),說明三者的表達均與肺癌的病理類型無關。VEGF和MMP-2的表達在高中分化肺癌組織中比低分化組織中低,但TIMP-2的表達卻比低分化組織的高(P < 0.05),說明三者的表達與肺癌的分化程度有關。VEGF和MMP-2的表達隨臨床分期的增加而增加,Ⅰ期患者的陽性率均高于Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ期,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P < 0.05),但TIMP-2的表達隨臨床分期的增加而減少(P < 0.05)。有淋巴結轉移者VEGF和MMP-2的表達高于無淋巴結轉移者(P < 0.05),但TIMP-2的表達低于無淋巴結轉移者(P < 0.05)。見表2。
3 討論
VEGF是一種高度特異性的血管內皮細胞有絲分裂因子,通過與其特異性受體結合,釋放多種細胞因子與生長因子,刺激血管內皮細胞增殖和遷移,促進新生血管生成,在腫瘤的侵襲和轉移中起重要作用[10-11]。本研究表明,VEGF的表達隨臨床分期的增加而增加,而且與肺癌分化程度相關,分化程度越低,表達越高,在臨床上,惡性程度越高的腫瘤,越容易發(fā)生遠處轉移[12],這就提示VEGF可能在肺癌的發(fā)生發(fā)展過程中起到了重要的作用。而且,實驗結果還顯示,VEGF的表達在正常肺組織和肺癌中有顯著性差異,有淋巴結轉移者的VEGF表達明顯高于無淋巴結轉移者,說明VEGF的表達促進腫瘤血管的生成,進而促進腫瘤的生長和轉移,在肺癌的侵襲和轉移過程中發(fā)揮作用。梁乃超等[13]檢測NSCLC組織的VEGF水平,發(fā)現肺癌組織中的VEGF水平遠遠高于正常肺組織,本研究結果與其一致。常超等[14]發(fā)現VEGF-C、VEGF-D及其受體VEGFR-3蛋白在NSCLC中表達顯著增高,并可促進淋巴結轉移和腫瘤生長,可見VEGF表達率有可能作為診斷肺癌的一項生物學標志,同時具有能夠判斷肺癌是否轉移的潛能。
MMPs是一類在腫瘤侵襲與轉移過程中發(fā)揮降解基底膜和細胞外基質作用的鋅離子依賴的內源性蛋白水解酶[15],基質金屬蛋白酶抑制因子是MMPs的天然抑制劑,TIMP-2可與活化的或無活性的MMP-2結合,抑制MMP-2的活性,從而抑制腫瘤細胞侵襲[16-19]。MMP-2與TIMP-2之間的平衡在腫瘤進展中具有重要意義,正常或早期的腫瘤MMP-2/TIMP-2的比值接近1.0,而重度和晚期的腫瘤卻高得多[20-23],體外腫瘤侵襲實驗也證明,MMP-2/TIMP-2的比值與其侵襲能力相關[24-25]。在本研究中,正常肺組織MMP-2和TIMP-2陽性表達率遠遠低于肺癌,表達量的差異具有顯著性,說明在正常生理情況下,MMP-2和TIMP-2的表達處于一種動態(tài)的平衡狀態(tài)。MMP-2的表達與臨床分期、肺癌分化程度和淋巴結轉移呈正相關,但TIMP-2的表達與臨床分期、分化程度和淋巴結轉移呈負相關,說明在惡性程度越高的腫瘤中,TIMP-2由于其表達量降低,因而不能抑制表達越來越多的MMP-2的活性,導致MMP-2/TIMP-2的比值不斷增高,MMP-2發(fā)揮其水解細胞外基質的作用,最終腫瘤發(fā)生侵襲和轉移。
總之,本研究結果提示,VEGF、MMP-2和TIMP-2的表達與NSCLC的發(fā)生、侵襲和轉移有著密切的聯系,也可能是肺癌發(fā)生遠處轉移的可能機制之一,可作為臨床判斷肺癌轉移能力的指標,為深入研究肺癌的侵襲和轉移提供了新的方向。
[參考文獻]
[1] O'Kane GM,Leighl NB. Are immune checkpoint blockade monoclonal antibodies active against CNS metastases from NSCLC?-current evidence and future perspectives [J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res,2016,5(6):628-636.
[2] Che TF,Lin CW,Wu YY,et al. Mitochondrial translocation of EGFR regulates mitochondria dynamics and promotes metastasis in NSCLC [J]. Oncotarget,2015,6(35):37349-63766.
[3] 陳曉鋒,顧振綸,梁中琴,等.基質金屬蛋白酶與腫瘤侵襲和轉移研究進展[J].中國藥理學通報,2001,17(3):253-256.
[4] Saharinen P,Eklund L,Pulkki K,et al. VEGF and angiopoietin signaling in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis [J]. Trends Mol Med,2011,17(7):347-362.
[5] Zhang S,Zhong B,Chen M,et al. Epigenetic reprogramming reverses the malignant epigenotype of the MMP/TIMP axis genes intumor cells [J]. Int J Cancer,2014,134(7):1583-1594.
[6] Ara T,Kusafuka T,Inoue M,et al. Determination of imbalance between MMP-2 and TIMP-2 in human neuroblastoma by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and its correlation with tumor progression [J]. J Pediatr Surg,2000, 35(3):432-437.
[7] Kyzas PA,Stefanou D,Batistatou A,et al. Prognostic sig?鄄nificance of VEGF immunohistochemical expression and tumor angiogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carc?鄄inoma [J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2005,131(9):624-630.
[8] Mashhadiabbas F,Mahjour F,Mahjour SB,et al. The imm?鄄unohistochemical characterization of MMP-2,MMP-10,TIMP-1,TIMP-2,and podoplanin in oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol,2012,114(2):240-250.
[9] Kukreja I,Kapoor P,Deshmukh R,et al. VEGF and CD 34:A correlation between tumor angiogenesis and micr?鄄ovessel density-an immunohistochemical study [J]. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol,2013,17(3):367-373.
[10] Qi X,Du L,Chen X,et al. VEGF-D-enhanced lymph node metastasis of ovarian cancer is reversed by vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein [J]. Int J Oncol,2016,49(1):123-132.
[11] Eswarappa SM,Fox PL. Antiangiogenic VEGF-Ax:A New Participant in Tumor Angiogenesis [J]. Cancer Res,2015, 75(14):2765-2769.
[12] Nakajima K,Kho DH,Yanagawa T,et al. Galectin-3 in bone tumor microenvironment:a beacon for individual skeletal metastasis management [J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev,2016,35(2):333-346.
[13] 梁乃超,萬曉年.基質金屬蛋白酶MMP-9、TIMP-1及VEGF的表達情況與非小細胞肺癌組織侵襲的相關性[J].昆明醫(yī)科大學學報,2016,37(10):67-70.
[14] 常超,王平,程宏忠,等.非小細胞肺癌VEGF-C VEGF-D VEGFR-3表達與淋巴轉移關系的研究[J].中國腫瘤臨床,2009,36(16):937-942.
[15] Song J,Peng P,Chang J,et al. Selective non-zinc binding MMP-2 inhibitors:Novel benzamide Ilomastat analogs with anti-tumor metastasis [J]. Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2016, 26(9):2174-2178.
[16] Lee MS,Jung JI,Kwon SH,et al. TIMP-2 fusion protein with human serum albumin potentiates anti-angiog?鄄enesis-mediated inhibition of tumor growth by suppre?鄄ssing MMP-2 expression [J]. PLoS One,2012,7(4):e35710.
[17] 梁秋萍,殷俊.EGFR TKI+TP方案及TP方案對晚期非小細胞肺癌治療臨床效果及腫瘤標志物水平的影響[J].成都醫(yī)學院學報,2016,11(1):40-44.
[18] 陳建英,胡先全,黃三雄,等.華蟾素膠囊聯合GP方案對晚期非小細胞肺癌患者免疫功能的影響[J].中國現代醫(yī)生,2016,54(14):12-15.
[19] Shrestha B,Bajracharya D,Byatnal AA,et al. May High MMP-2 and TIMP-2 Expressions Increase or Decrease the Aggressivity of Oral Cancer? [J]. Pathol Oncol Res,2017, 23(1):197-206.
[20] 崔英,王淑世,成健,等.125I放射性粒子植入聯合GP加重組人血管內皮抑素治療老年晚期非小細胞肺癌臨床研究[J].中外醫(yī)學研究,2015,13(33):3-5.
[21] 徐玉娥,肖正國,宋薇,等.扶正升白口服液聯合NP方案治療晚期非小細胞肺癌的臨床研究[J].西部中醫(yī)藥,2016,29(2):1-4.
[22] Hoikkala S,P?覿?覿kk?觟 P,Soini Y,et al. Tissue MMP-2 and MMP-9 [corrected] are better prognostic factors than serum MMP-2/TIMP-2--complex or TIMP-1 [corrected] in stage [corrected] Ⅰ-Ⅲ lung carcinoma [J]. Cancer Lett,2006,236(1):125-132.
[23] Kolude B,Adisa AO,Lawal AO,et al. Stoichiometric exp?鄄ression of MMP-2/TIMP-2 in benign and malignant tumours of the salivary gland [J]. Tumour Biol,2015,36(4):2351-2357.
[24] 張賢蘭,黎少琴,蘇寧,等.晚期非小細胞肺癌組織中BRCA1、RAP80的表達與化療療效的關系[J].現代醫(yī)院,2015,15(6):11-13.
[25] 陳濱海,龐德湘,張雅麗,等.肺金生方通過調控MMP-2/TIMP-2平衡抗肺癌侵襲轉移研究[J].中華中醫(yī)藥學刊,2015,33(12):2828-2830.

