STABLE RECOVERY OF SIGNALS WITH THE HIGH ORDER D-RIP CONDITION?
Wengu CHEN(諶穩固)
Institute of Applied Physics and Computational MathematicsBeijing 100088,China
Yaling LI(李亞玲 )
Graduate School,China Academy of Engineering PhysicsBeijing 100088,China
STABLE RECOVERY OF SIGNALS WITH THE HIGH ORDER D-RIP CONDITION?
Wengu CHEN(諶穩固)
Institute of Applied Physics and Computational MathematicsBeijing 100088,China
E-mail:chenwg@iapcm.ac.cn
Yaling LI(李亞玲 )
Graduate School,China Academy of Engineering PhysicsBeijing 100088,China
E-mail:leeyaling@126.com
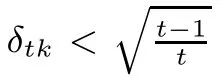
compressed sensing;D-restricted isometry property;tight frame
2010 MR Subject Classifcation94A12;90C59;94A15
1 Introduction
Compressed sensing(CS)is a new type of sampling theory drawing the attention of many researchers in various felds.The crucial problem in CS is to recover a high-dimensional sparse signal from a small number of linear measurements

where observed signal y∈Rm,sensing matrix A∈Rm×nwith m?n,f∈Rnis an unknown signal,and z∈Rmis a vector of measurement errors.In the standard CS framework,if f is sparse or approximately sparse,namely,the sparsity is expressed in an orthonormal basis,one can recover f under suitable conditions on the matrix A,such as a restricted isometry property (RIP)condition,see[1–17].
However,in practical examples,there were numerous signals of interest which are not sparse with respect to an orthonormal basis but sparse in an overcomplete dictionary or a frame[18–21]and references therein,which means that the unknown signal f has a sparse expansion in some coherent and redundant dictionaries or a matrix of frame vectors(as columns) D∈Rn×d(n≤d),i.e.,f=Dx where x∈Rdis a sparse coefcient vector.Considering a matrix D∈Rn×d,let its d columns D1,D2,···,Ddform a tight frame,i.e.,

Clearly,
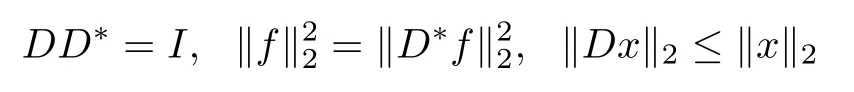
for any f∈Rnand x∈Rd(see[22],Chapter 3),where D?is the transpose of D.More details about frames can refer to[23–27].
One often obtains a reconstruction from model(1.1)by the method of l1-analysis
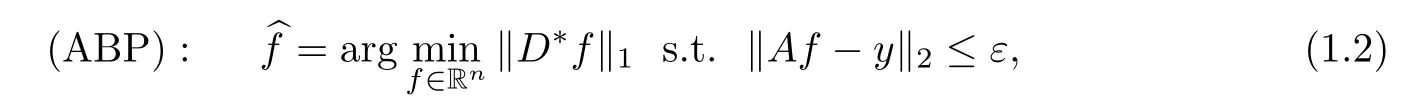
where D∈Rn×dis a tight frame and ε represents the noise level.
In this paper,we investigate the model as below
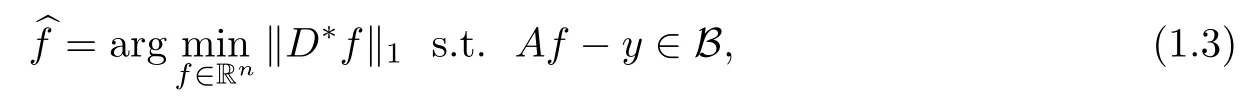
where D∈Rn×d(n≤d)is a tight frame and B is a set determined by the noise structure.And we only consider two types of bounded noise setting
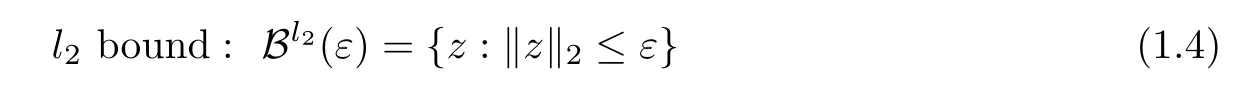
and

Analogous to the standard RIP condition,the concept of the D-RIP condition,which is a natural extension to the standard RIP was introduced by Cand′es et al.in[21].The defnition of D-RIP is as follows.
Defnition 1.1(D-RIP) Let D∈Rn×dbe a matrix.The restricted isometry property adapted to D(abbreviated D-RIP)of order k for a measurement matrix A with constant δkis defned as the smallest constant such that
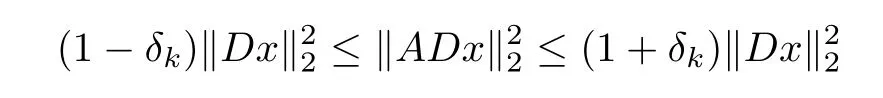
holds for all k-sparse vector x∈Rd.A vector x∈Rdis k-sparse if kxk0=|supp(x)|≤k,where supp(x)={i:xi6=0}is the support of x.When k is not an integer,we defne δkas δ?k?.
Diferent conditions on the D-RIP for unknown signal recoverywere studied in the literature. For instance,sufcient conditions for the stable or exact recovery via the l1-analysis(1.2)include δ2s<0.08 in[21],δ2s<0.472 and δs<0.307 in[28].Li and Lin[29]improved the bound to δ2s<0.4931 and to δ2s<0.656 in some special cases.Later,Zhang and Li[30]improved the bound to δ2s<√2/2 and δs<1/3.Moreover,there are sufcient conditions δ7s<0.6(see [21],Theorem 1.4),9δ2s+4δ4s<5(see[31],Remark 5)and δ7s<0.687[28].
Similarly,for model(1.3)with(1.5),Lin and Li provided δ3s<0.5(see[32],Theorem 2.3). Lin et al.[28]improved the bound to δ3s<0.558 and got δs<0.307.And,Zhang and Li improved the bound to δ2s<√2/2 and δs<1/3 in[30].
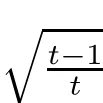
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.In Section 2,we will introduce some notations and establish some basic lemmas that will be used.The main result and its proof are given in Section 3.
2 Preliminaries
Let D ∈Rn×d(n≤d)be a tight frame.Then its row vectors are orthonormal.Let ˉD∈R(d?n)×dbe its orthonormal complement,which is also a tight frame.Hence
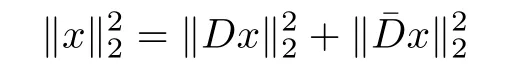
for all x∈Rd.Obviously,for all matrices A satisfying D-RIP with δk,
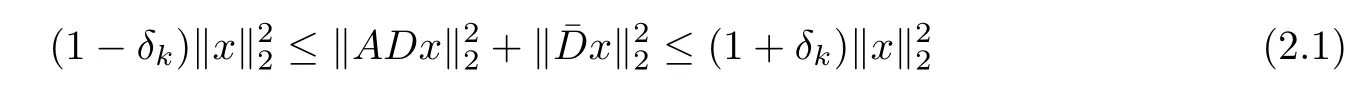
holds for all k-sparse vector x∈Rd.
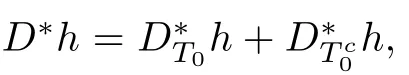
Cai and Zhang developed a new elementary technique which represents any point in a polytope as a convex combination of sparse vectors(see[10],Lemma 1.1).It provides a key technical tool for the proof of our main result.The specifc content is presented in Lemma 2.1.
Lemma 2.1For a positive number α and a positive integer k,defne the polytope T(α,k)?Rdby

For any v∈Rd,defne the set of sparse vectors U(α,k,v)?Rdby
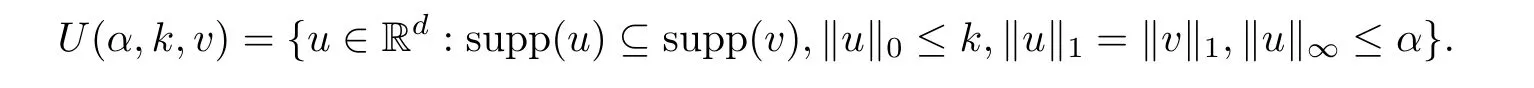
Then any v∈T(α,k)can be expressed as
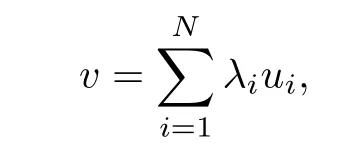
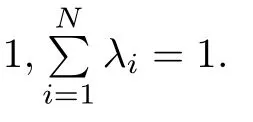

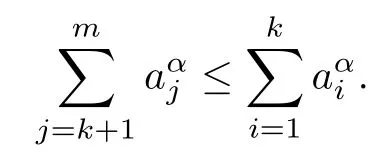

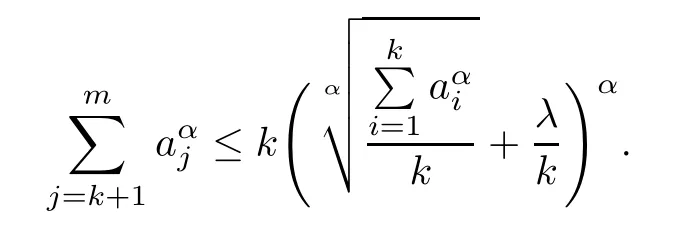
Lemma 2.3For any T?{1,2,···,d},we have
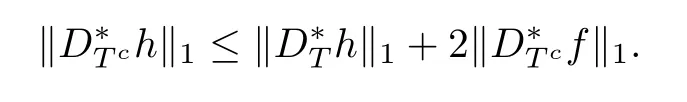
ProofFrom the assumptions,we have
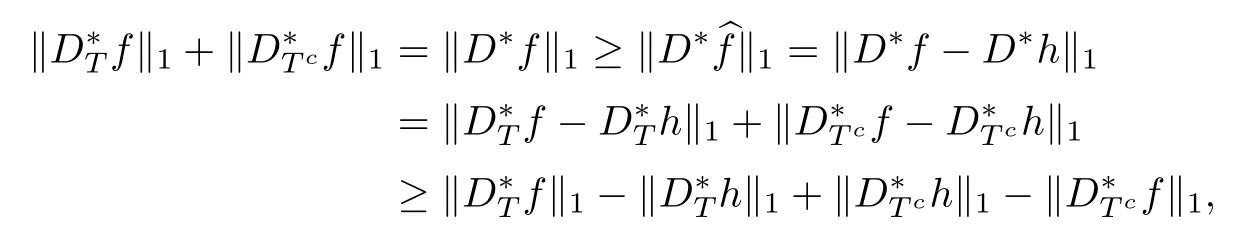
where the frst inequality follows from the factbf is a minimizer of problem(1.3),the second inequality from the reverse triangle inequalities and the second equality from the defnitions of f and h.Hence
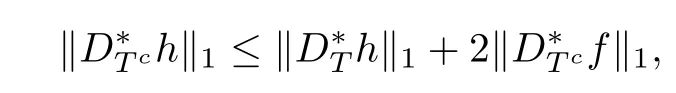
which completes the proof of the lemma.
3 Main Result

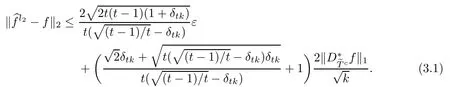
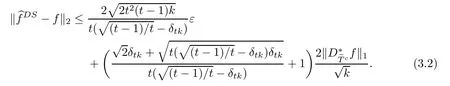
ProofFirst,we present the proof of(3.1).We suppose that tk is an integer.From Lemma 2.3 and the defnitions of T0andit is clear that
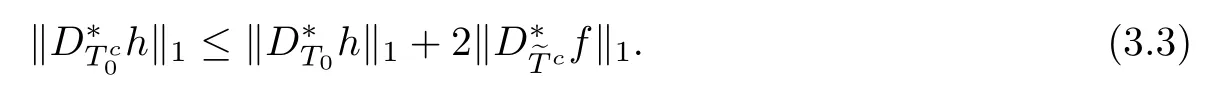
Let
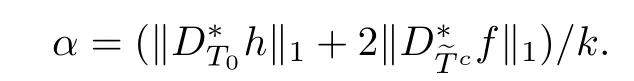
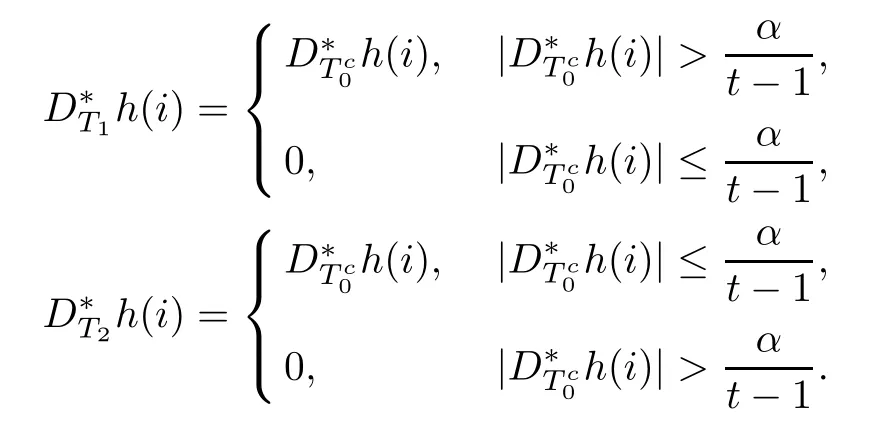
Combining above defnitions and(3.3),we have
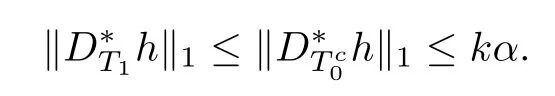
Denote
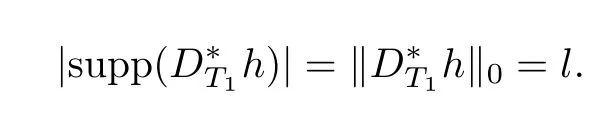
In view of the defnition of D?T1h,we get
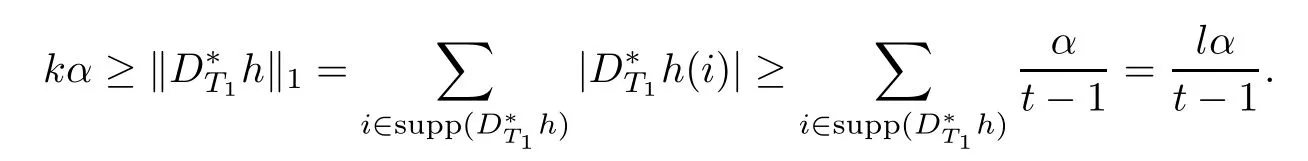
Namely,l≤k(t?1).Thus,it is clear that
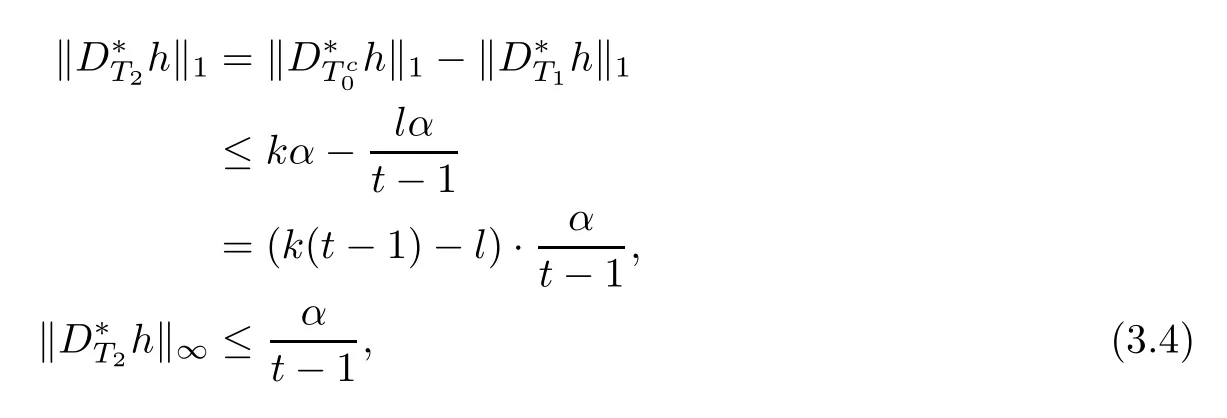
and
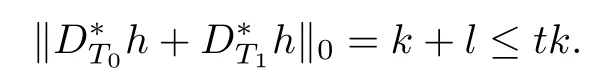
By the defnition of δkand the fact that
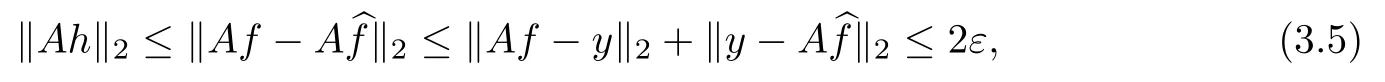
we obtain
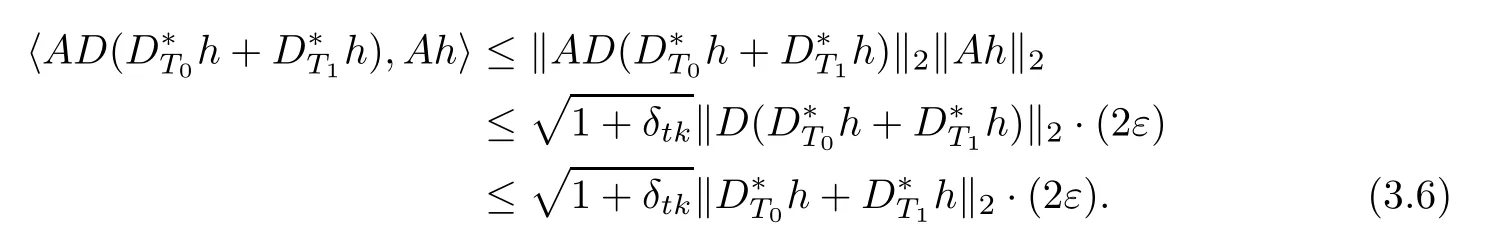
And using(3.4)and Lemma 2.1,we have
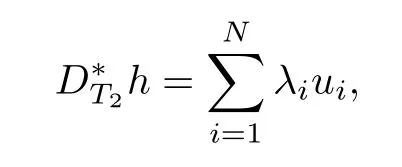
where uiis(k(t?1)?l)-sparse,namely,|supp(ui)|=kuik0≤k(t?1)?l and
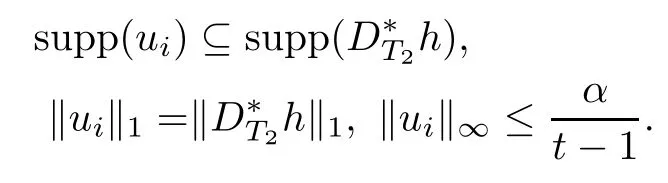
Thus
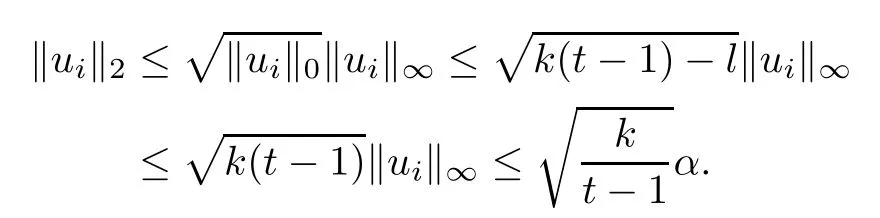
Taking
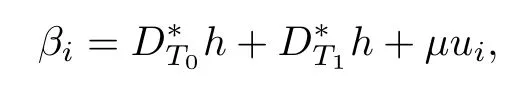
where 0≤μ≤1.We observe that
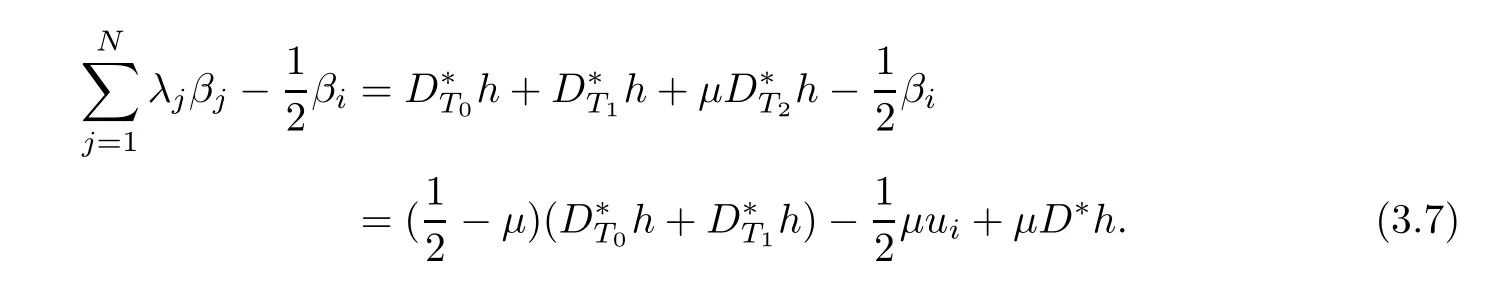
With
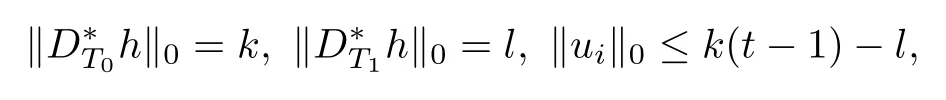
it is clear that
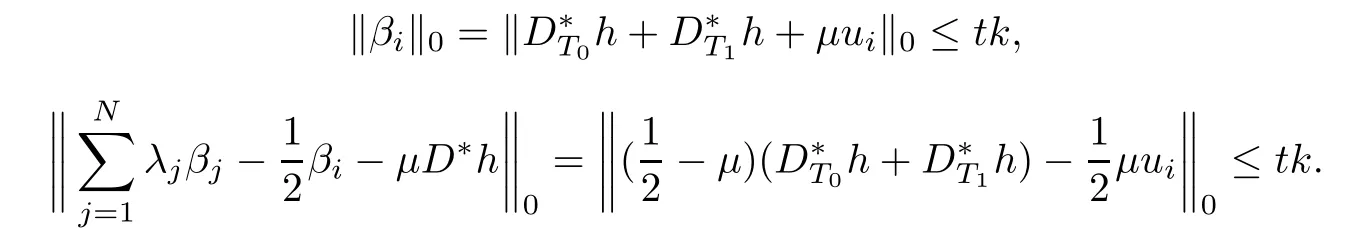
Let

Clearly,
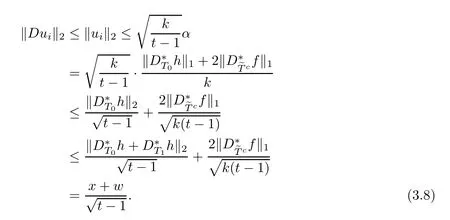
With the fact that for any B∈Rp×d,
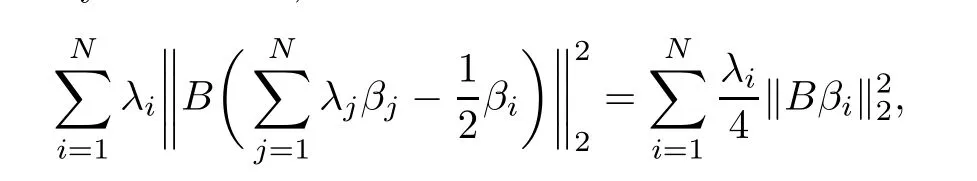
where p is an arbitrary integer(see[10,30]),we have
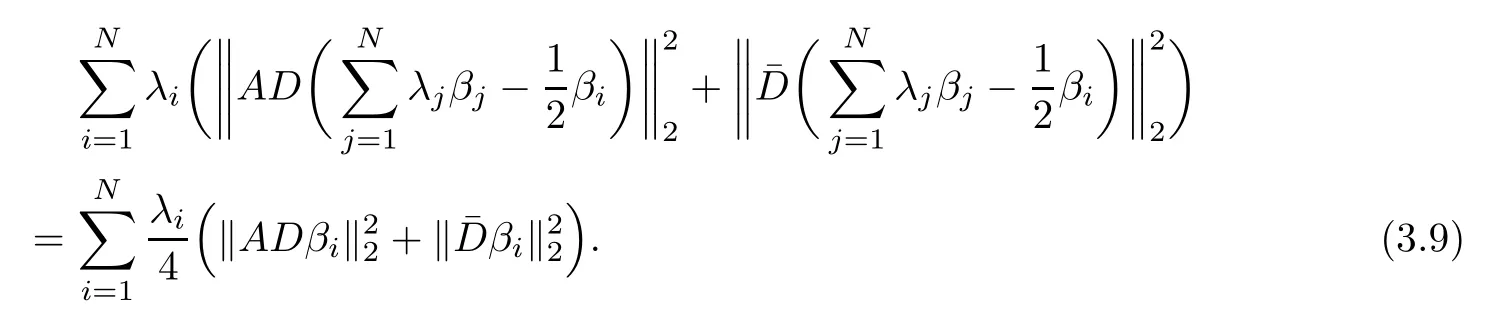
Combining(3.7),(2.1)and(3.6),we can estimate the left-hand side of the above equality
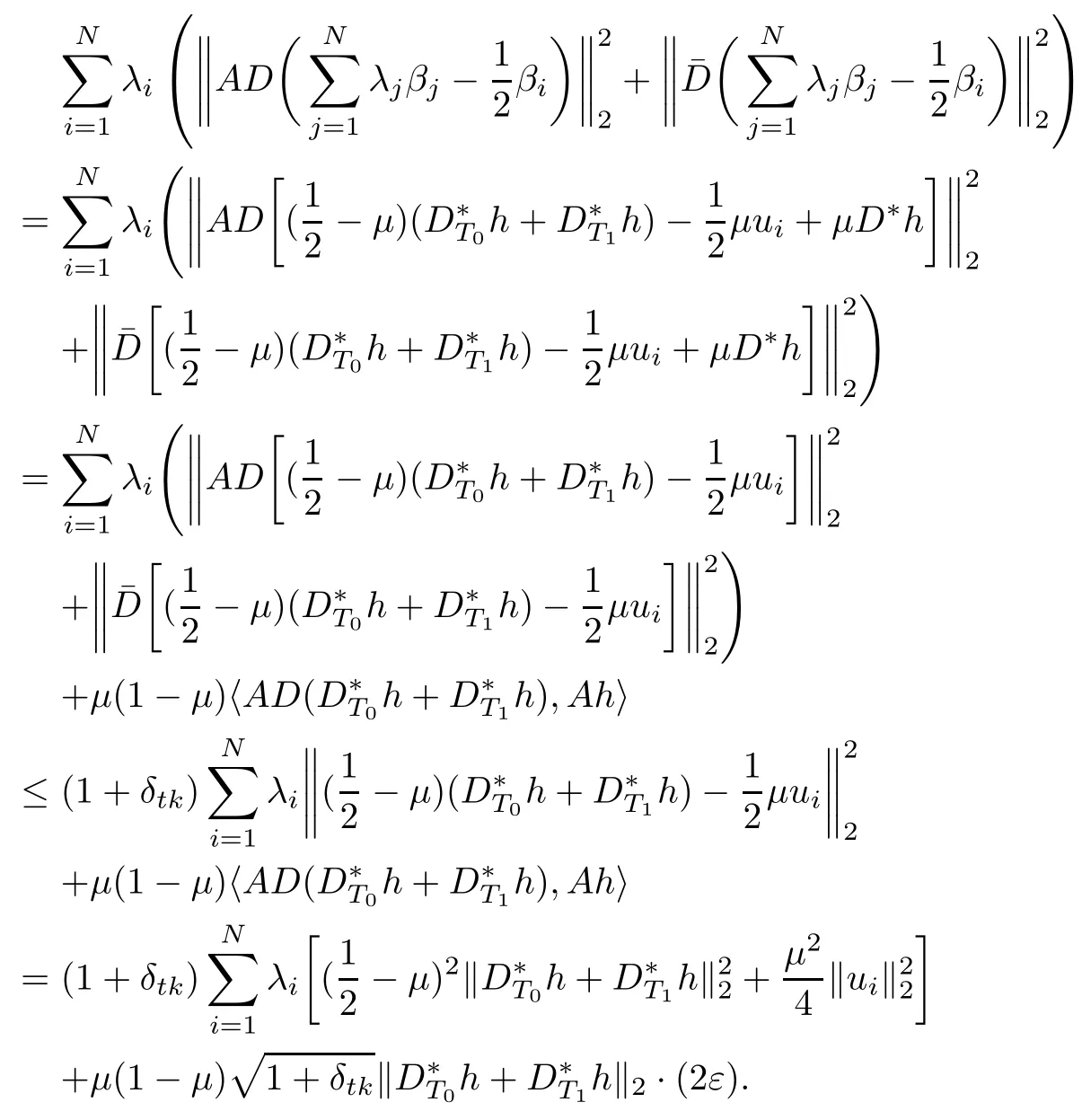
On the other side,it follows from(2.1)and the expression of βithat
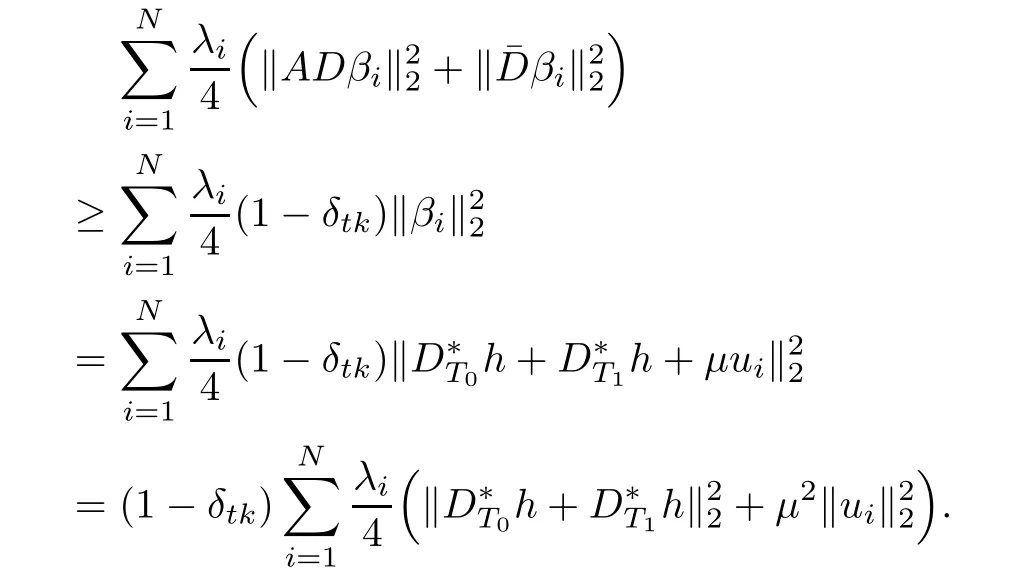
Combining the above two inequalities,we have
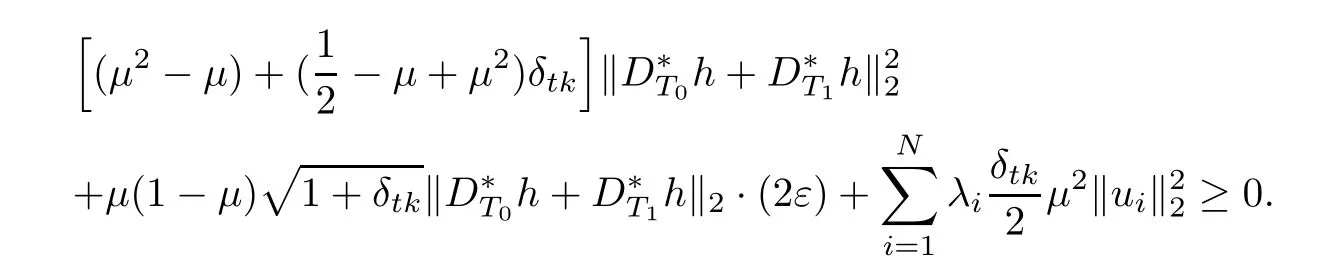
Namely,

By(3.8),we obtain
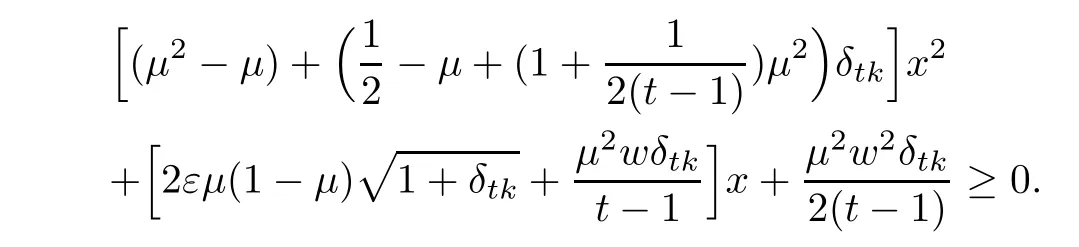
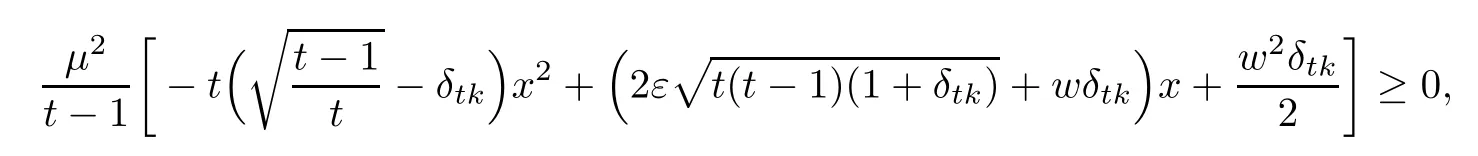
which is a second-order inequality for x.Thus,we obtain
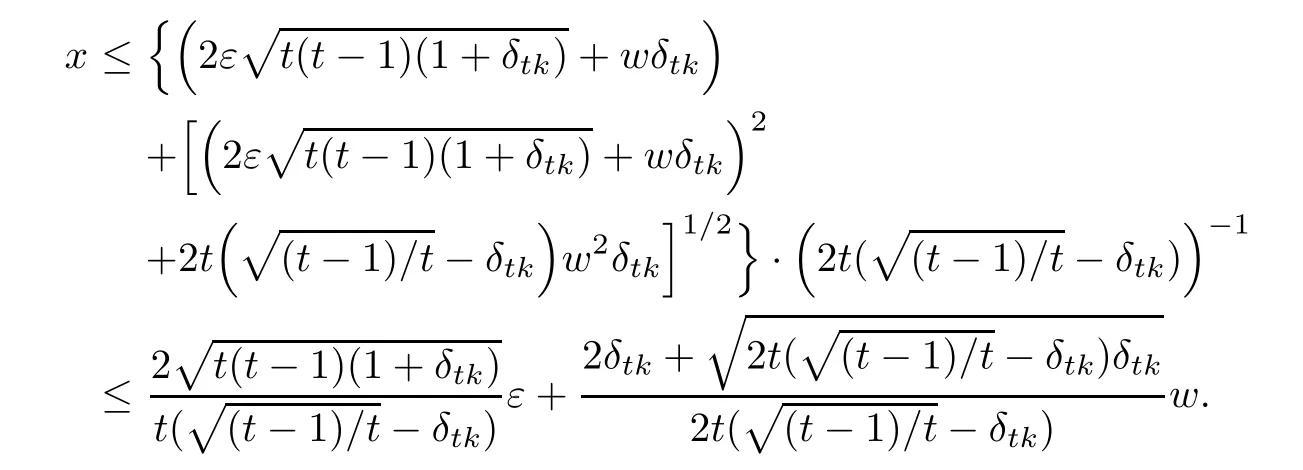
With(3.3)and the representation of w,it is clear that
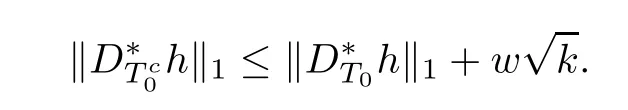
It follows from Lemma 2.2 that
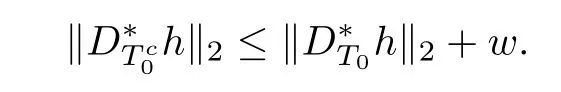
Thus,we have the estimate of khk2by the above inequality
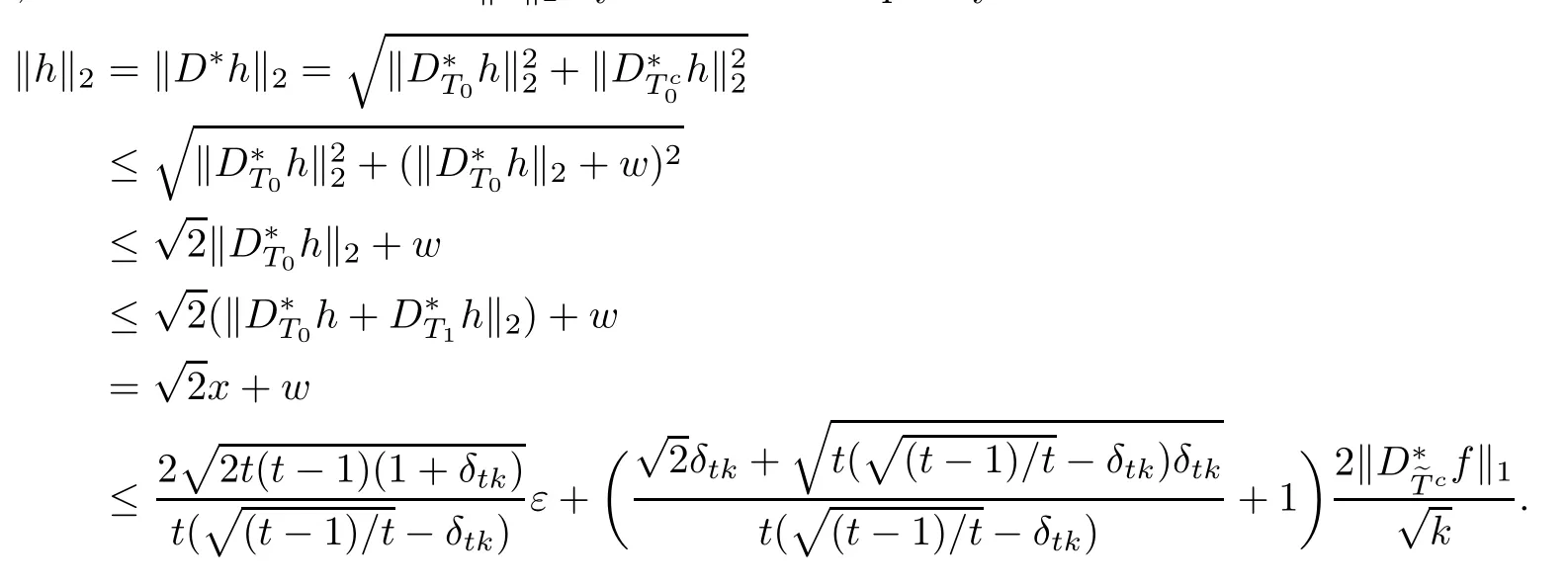
If tk is not an integer,we denote t′=?tk?/k,then t′k is an integer and t Then we can prove the result the same as the proof above by working on δt′k. Hence,we obtain(3.1). Next,we prove(3.2).The proof of(3.2)is similar to the proof of(3.1).We only need to replace(3.5)and(3.6)with(3.10)and(3.11),respectively, We also can get(3.2). This completes the proof of Theorem 3.1. Remark 3.2In Theorem 3.1,we observed that every signal f∈Rnwith D?f is k-sparse can be stably recovered.And if B={0}and D?f is a k-sparse vector,then the recovery of the signal f is exact. [1]Amit Y,Fink M,Srebro N,et al.Uncovering shared structures in multiclass classifcation.Proc 24th Int Conf Mach Learn,2007:17–24 [2]Chartrand R.Exact reconstruction of sparse signals via nonconvex minimization.IEEE Signal Process Lett, 2007,14:707–710 [3]Cand`es E J.The restricted isometry property and its implications for compressed sensing.Compte Rendus Math,2008,346(9/10):589–592 [4]Chartrand R,Staneva V.Restricted isometry properties and nonconvex compressive sensing.Inverse Problems,2008,24:1–14 [5]Cand`es E J,Tao T.Decoding by linear programming.IEEE Trans Inform Theory,2005,51:4203–4215 [6]Cai T T,Wang L,Xu G W.Shifting inequality and recovery of sparse signals.IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2010,58(3):1300–1308 [7]Cai T T,Wang L,Xu G W.New bounds for restricted isometry constants.IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 2010,56(9):4388–4394 [8]Cai T T,Zhang A.Sharp RIP bound for sparse signal and low-rank matrix recovery.Appl Comput Harmon Anal,2013,35:74–93 [9]Cai T T,Zhang A.Compressed sensing and afne rank minimization under restricted isometry.IEEE Trans Signal Process,2013,61(13):3279–3290 [10]Cai T T,Zhang A.Sparse representation of a polytope and recovery of sparse signals and low-rank matrices. IEEE Trans Inform Theory,2014,60(1):122–132 [11]Foucart S.A note on guaranteed sparse recovery via l1-minimization.Appl Comput Harmon Anal,2010, 29:97–103 [12]Foucart S.Sparse recovery algorithms:sufcient conditions in terms of restricted isometry constants. Springer Proceeding in Mathemetics,2010,13:65–77 [13]Foucart S,Lai M J.Sparsest solutions of underdetermined linear systems via lq-minimization for 0 [14]Mo Q,Li S.New bounds on the restricted isometry constant δ2k.Appl Comput Harmon Anal,2011,31(3): 460–468 [15]Sun Q Y.Recovery of sparsest signals via lq-minimization.Appl Comput Harmon Anal,2012,32(3): 329–341 [16]Wen J M,Li D F,Zhu F M.Stable recovery of sparse signals via lp-minimization.Appl Comput Harmon Anal,2015,38:161–176 [17]Wu R,Chen D R.The improved bounds of restricted isometry constant for recovery via lp-minimization. IEEE Trans Inform Theory,2013,59(9):6142–6147 [18]Bruckstein A M,Donoho D L,Elad M.From sparse solutions of systems of equations to sparse modeling of signals and images.SIAM Rev,2009,51:34–81 [19]Chen S S,Donoho D L,Saunders M A.Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit.SIAM Rev,2001,43: 129–159 [20]Mallat S,Zhang Z.Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries.IEEE Trans Signal Process,1993, 41(12):3397–3415 [21]Cand`es E J,Eldar Y C,Needell D,et al.Compressed sensing with coherent and redundant dictionaries. Appl Comput Harmon Anal,2011,31:59–73 [22]Daubechies L.Ten lectures on wavelets//CBMS-NSF Regional Conf Ser Appl Math,Philadelphia:SIAM, 1992 [23]Christensen Q.An introduction to frames and Riesz bases.Boston,MA:Birkh¨auser,2003:87–121 [24]Christensen Q.Frames,Riesz bases,and discrete Gabor/wavelet expansions.Bulletin(New Series)of the American Mathematical Society,2001,38(3):273–291 [25]Khosravi A,Azandaryani M M.Approximate duality of g-frames in Hilbert spaces.Acta Math Sci,2014, 34B(3):639–652 [26]Li Y F,Yang S Z.A class of multiwavelets and projected frames from two-direction wavelets.Acta Math Sci,2014,34B(2):285–300 [27]Gavruta L,Gavrut P.Some properties of operator-valued frames.Acta Math Sci,2016,36B(2):469–476 [28]Lin J H,Li S,Shen Y.New bounds for resticted isometry constants with coherent tight frames.IEEE Trans Signal Process,2013,61(3):611–621 [29]Li S,Lin J H.Compressed sensing with coherent tight frame via lq-minimination for 0 [30]Zhang R,Li S.Optimal D-RIP bounds in compressed sensing.Acta Math Sin(Engl Ser),2015,31(5): 755–766 [31]Liu Y L,Mi T B,Li S D.Compressed sensing with general frames via optimal-dul-based l1-analysis.IEEE Trans Infor Theory,2012,58(7):4201–4214 [32]Lin J H,Li S.Sparse recovery with coherent tight frames via analysis Dantzig selector and analysis LASSO. Appl Comput Harmon Anal,2014,37(1):126–139 ?Received June 3,2015;revised December 25,2015.This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China(11271050 and 11371183).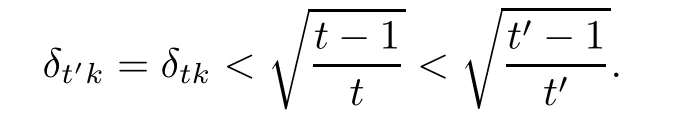
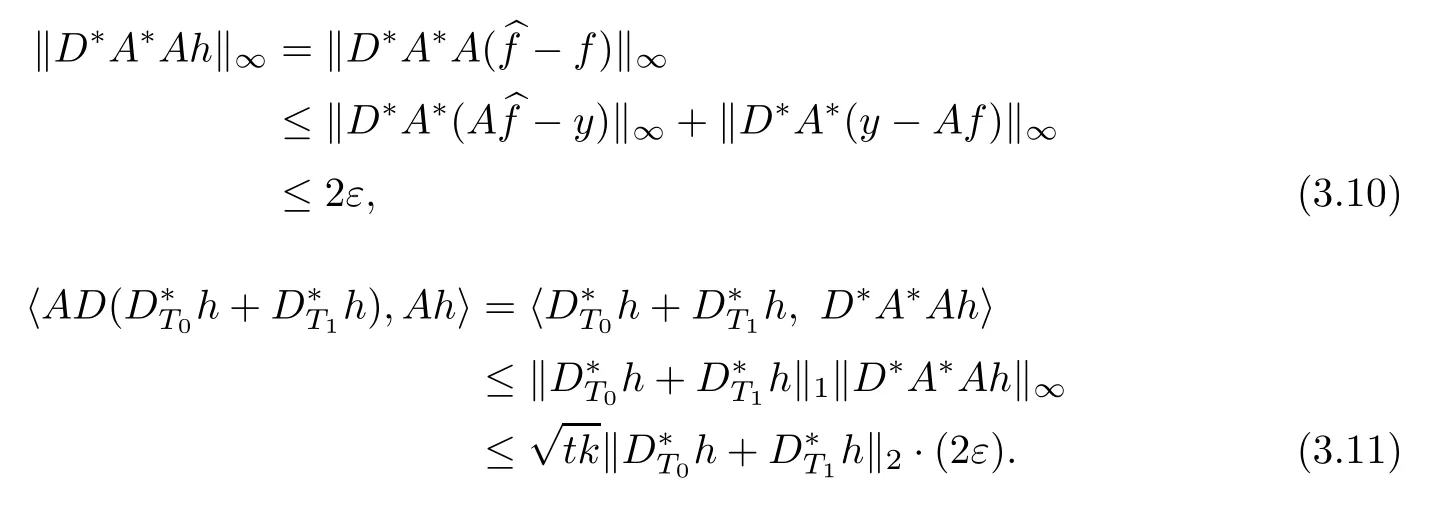
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2016年6期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2016年6期
