桂林毛村地下河水質評價
蔣 然,朱小平,梁志宏,雷列輝, 劉藝斯
(珠江水利委員會珠江水利科學研究院,廣東 廣州 510000)
?
桂林毛村地下河水質評價
蔣然,朱小平,梁志宏,雷列輝, 劉藝斯
(珠江水利委員會珠江水利科學研究院,廣東 廣州510000)

地下河;氨氮;總磷;水質評價;桂林毛村
巖溶系統作為一種脆弱的陸地生態系統,其資源環境問題越來越受到人們的廣泛關注。地下河是南方巖溶地下水賦存、運動的重要場所,也是當地群眾生產、生活的主要水源,中國南方巖溶水天然資源量為1 874億m3/a[1]。廣西壯族自治區地下河發育規模大,全區地下河有604條,巖溶地下水資源占全區地下水資源的66%[2]。在巖溶農業區,化肥、農家肥的密集使用以及化糞池污水、工廠廢水等的任意排放,致使巖溶區地下水受到氮磷等營養鹽污染的可能性增大。巖溶含水層一旦受到污染,其修復比非巖溶區更加困難,不僅經濟投入巨大,技術上也有難度,時間周期也很長,給人類安全利用地下水帶來嚴重隱患。因此,對地下河水體的氮磷變化及其污染源進行分析對于供水安全和下游河流保護有重要重義。

1 研究區概況
毛村地下河流域位于桂林市東南的靈川縣潮田鄉,距桂林市區30 km。地下河出口在毛村,經緯坐標為N25°11′38″,E110°31′35″,高程為178 m。地下河所在地屬中亞熱帶季風氣候,氣候溫和,降水充沛,年平均氣溫18.6℃,年均降雨量1 980 mm。受季風活動影響,降雨量的年內分配不均。一般雨季從3月開始到8月結束,最大的降雨量連續出現在4—7月,9月到次年2月一般為枯季。
毛村地下河流域土地利用類型主要有水稻田、林地、果園、灌叢、居民用地等。其中,水稻田主要分布在地下河上游匯水區的山灣、打谷坪、掌山底一帶,洼地內耕地面積約0.45 km2;果園一般分布在取水條件較好的洼地或洼地邊緣,種植白果、柑橘、沙田柚等果樹;林地主要分布在補給區位置較高的砂頁巖分布區;在地下河出口處為峰叢洼地與峰林平原交界,主要分布有水稻田及菜地。研究區內除零星分布開采方解石礦外,沒有其他工礦企業分布[7]。毛村地下河流域土地利用現狀[4]見圖1。
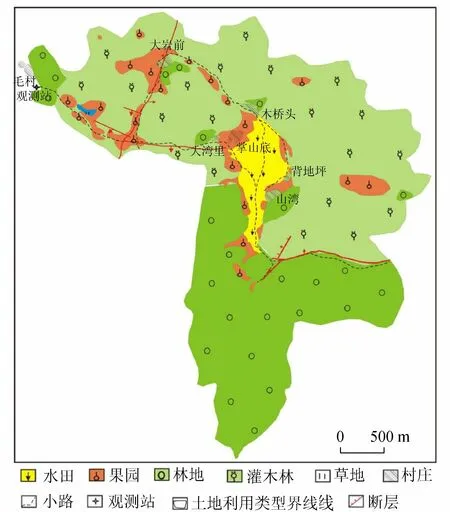
圖1 毛村地下河流域土地利用現狀
毛村地下河系統的補給來源包括內源補給與外源補給,內源補給主要是來自巖溶區的降水,外源補給有兩個來源:①小龍背地表河水經過一段距離的地表明流進入巖溶區地下管道由扁巖匯入;②磨刀江水流經巖溶區地下管道在社更巖匯入。這兩股水與來源于白云巖地區的背地坪巖溶水在掌山底匯合后進入地下管道,流經穿巖、小巖,明流與暗河相間,流經大巖前,最終在毛村地下河出口排出(圖1)。地下河長約5.1 km,流域面積約11.2 km2,其中碳酸鹽面積與非碳酸鹽巖面積分別為7.6 km2和3.6 km2。
2 研究方法
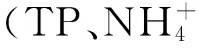
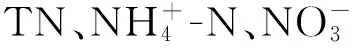
3 結果與討論
3.1氮磷濃度隨季節變化趨勢

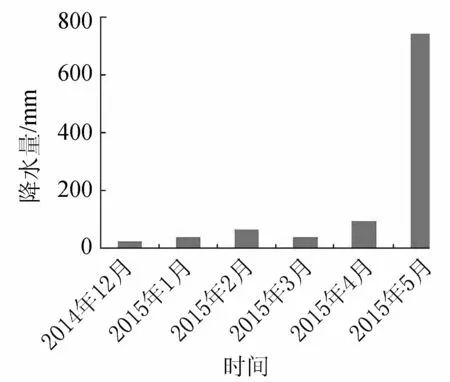
圖2 毛村地下河出口處的降雨量(2014年12月—2015年5月)

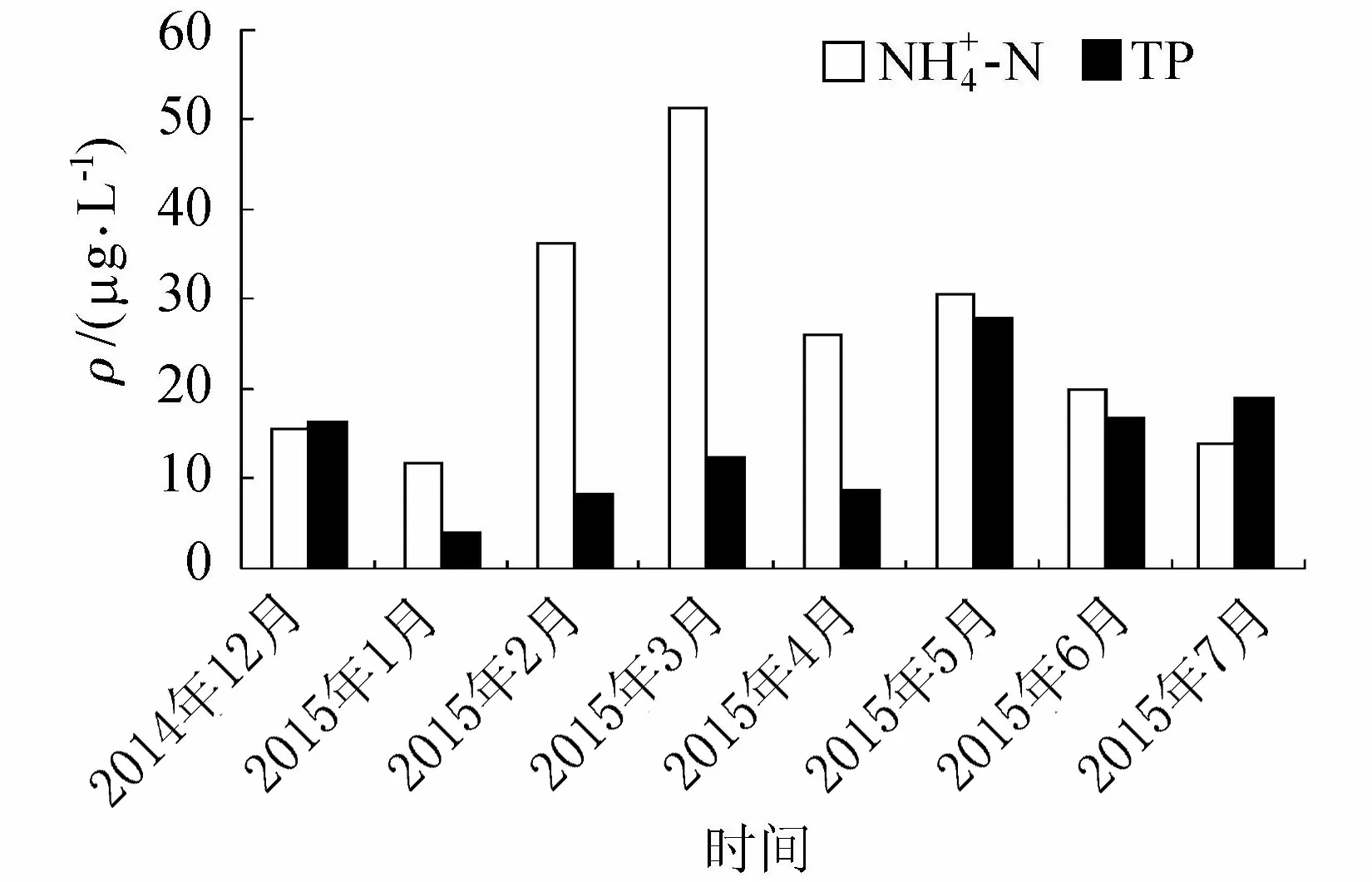
圖3 毛村地下河出口處的-N和TP變化(2014年12月—2015年7月)
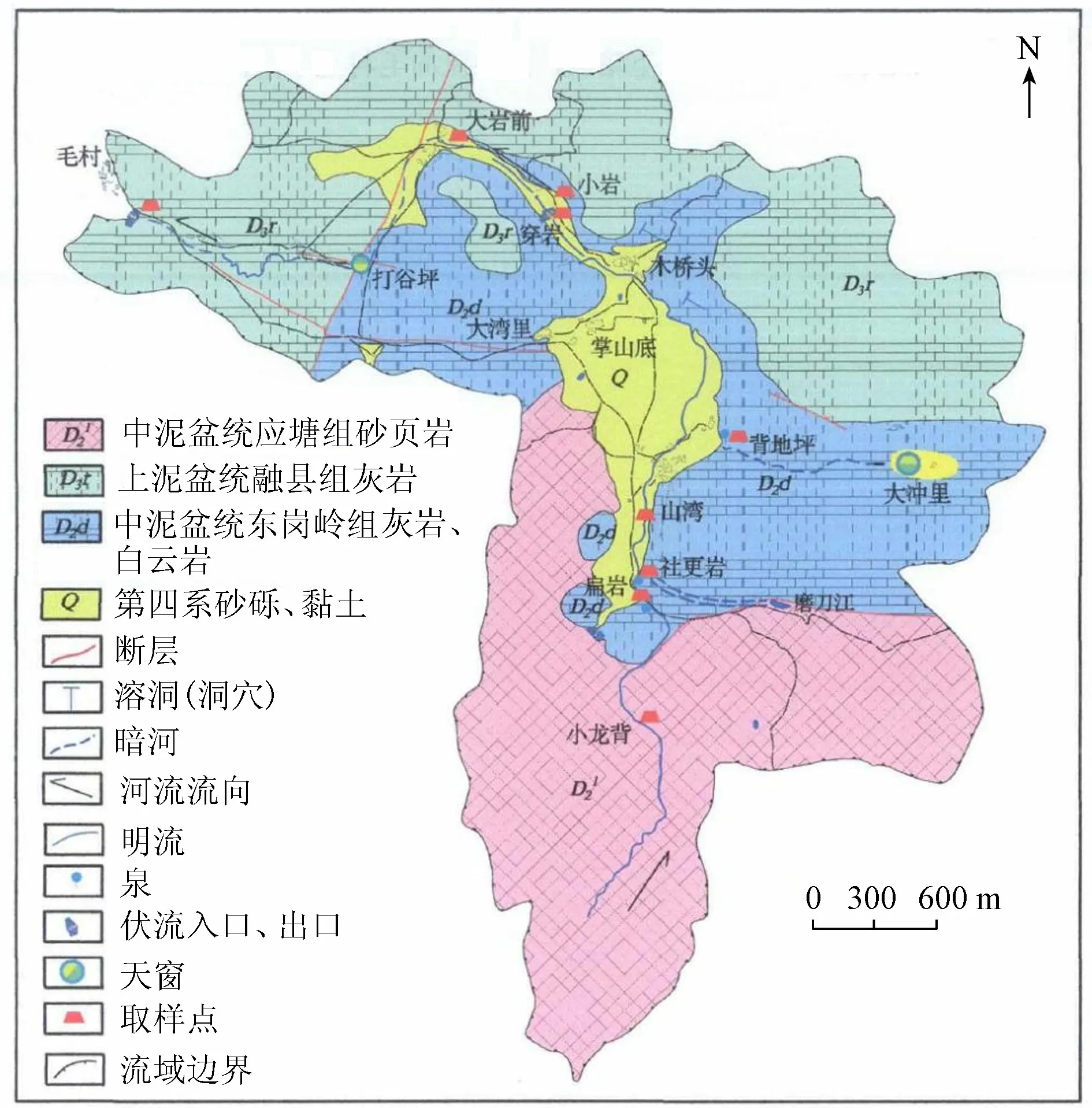
圖4 桂林毛村地下河水文地質簡圖及采樣布點[7]
3.2氮磷空間分布
在2015年4月對毛村河流域布點和匯入的潮田河進行采樣分析,采樣點分布見圖4。選點布設方案如下:在毛村河的兩個外源之一的小龍背河選兩個點:老龍水和扁巖(匯入地下管道前);在外源之一的磨刀江經由地下管道匯入的明流選兩點:社更巖和山灣;在內源補給的背地坪巖溶水出露處背地坪選點;在三股水匯合后進入地下管道,流經大巖前及最終的毛村地下河出口選點。
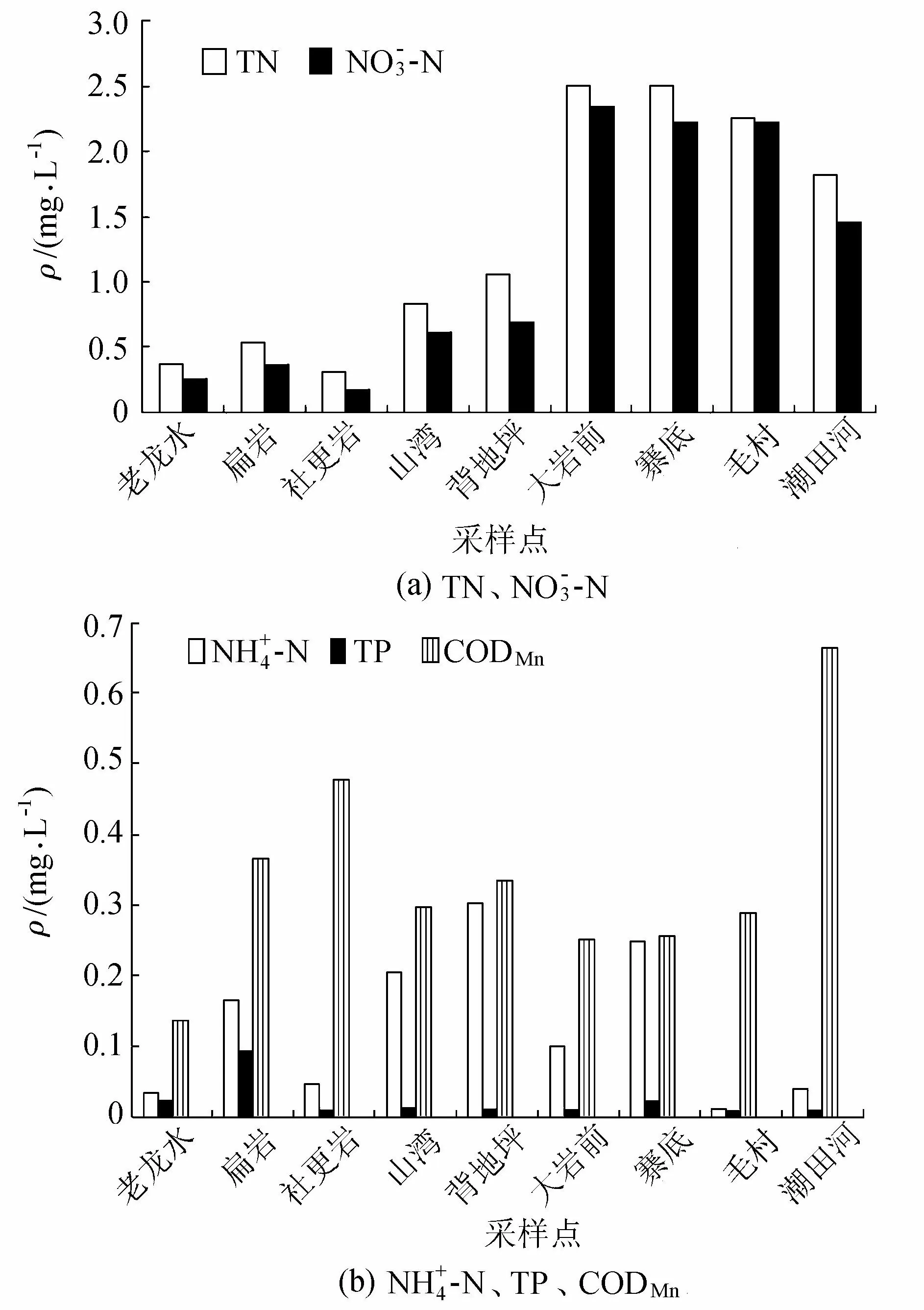
圖5 毛村地下河流域水質指標空間分布
3.3降雨效應與氮磷濃度變化分析

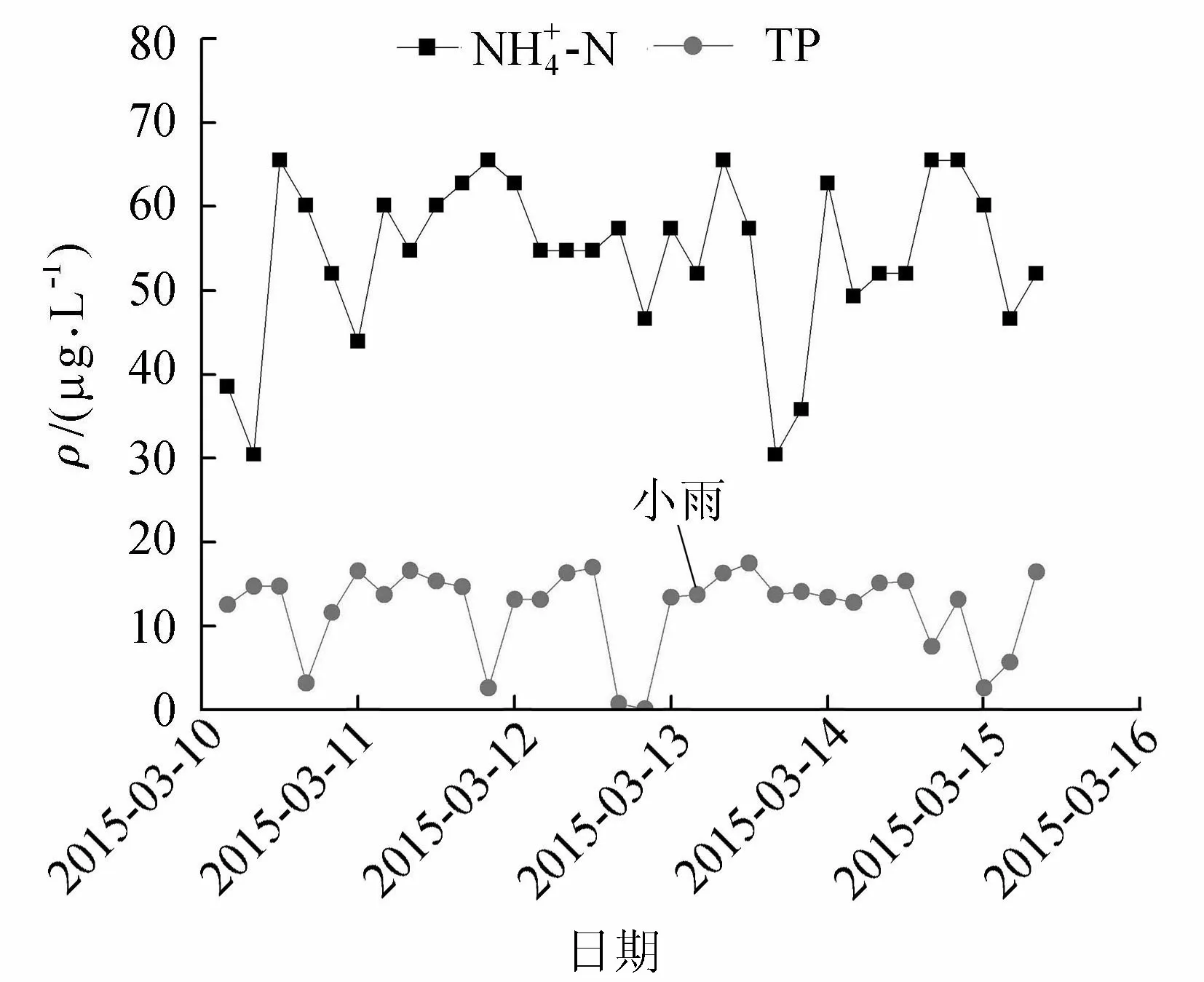
圖6 小雨期間-N和TP質量濃度變化趨勢


圖7 中雨期間-N和TP質量濃度變化趨勢
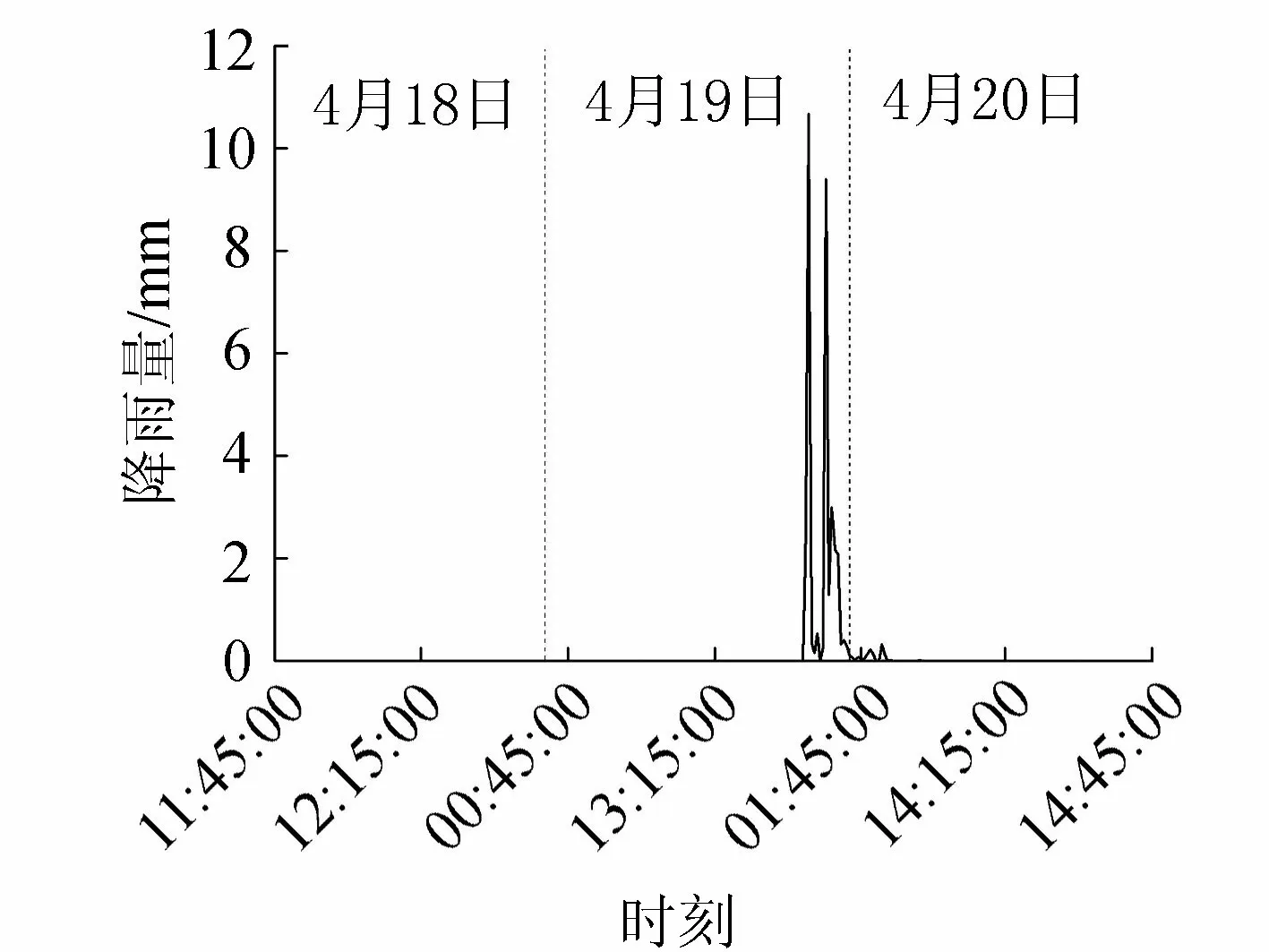
圖8 大雨期間的降雨量變化(2015年4月18日—20日)
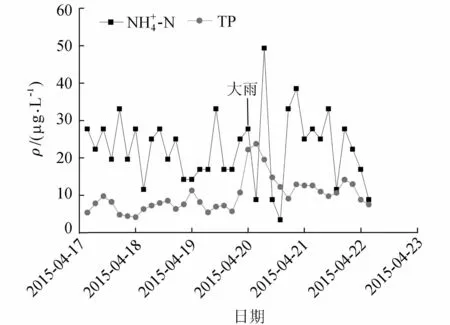
圖9 大雨期間的-N與TP質量濃度變化

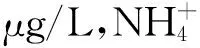

4 結 論
b. 毛村地下河流域TN的濃度呈現出從上游至下游逐漸升高,流經巖溶洼地的采樣點TN和NO3-N有明顯的上升趨勢,經過洼地的大巖前采樣點和毛村出口的TN超過地表水水質Ⅴ類標準,TP達到地表水質Ⅱ類標準,CODMn達地下水Ⅱ類標準。
c. 在小雨和中雨期間,與無雨條件相比氮磷濃度波動規律無明顯變化,說明農業施肥和生活污水對地下河水質影響途徑除了集中降雨之外,存在著巖溶地下管道直接流入。

e. 毛村河地下水整體水質較好,土地利用方式及生活污水排放導致水體受氮素污染的風險較大,須做好農業面源污染防治及農村生活污水處理,避免下游的重要河流漓江遭受污染風險。
[1] 袁道先.對南方巖溶石山地區地下水資源及生態環境地質調查的一些意見[J].中國巖溶,2000,19(2):103-108.(YUAN Daoxian.Aspects on the new round land and resources survey in karst rock desertification areas of south China[J].Carsologica Sinica,2000,19(2):103-108.(in Chinese))
[2] 廣西地方志編纂委員會,廣西通志(巖溶志)[M].南寧:廣西人民出版社,2000.
[3] 唐偉,裴建國,殷建軍,等.桂林毛村巖溶地下河二十多年來的水質演化趨勢研究[J].中國巖溶,2010,29(3):331-335.(TANG Wei,PEI Jianguo,YIN Jianjun,et al.Water quality evolution tendency in Maocun karst underground river in Guilin for the past more than 20 years[J].Carsologica Sinica,2010,29(3):331-335.(in Chinese))

[5]王開然,郭芳,姜光輝,等.桂林峰林平原區巖溶含水層氮污染空間分布特征[J].環境科學研究,2013,26(3):281-283.(WANG Kairan,GUO Fang,JIANG Guanghui,et al.Spatial distribution of nitrogen contamination in karst aquifer in Guilin peak forest plain[J].Research of Environmental Sciences,2013,26(3): 281-286.(in Chinese))
[6] 蔡文靜,常春平,宋帥,等.德州地區地下水中磷的空間分布特征及來源分析[J].中國生態農業學報,2013,21(4):456-462.(CAI Wenjing,CHANG Chunping,SONG Shuai,et al.Spatial distribution and sources of groundwater phosphorus in Dezhou Region[J].Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture,2013,21(4):456-462.(in Chinese))
[7] 黃芬,唐偉,汪進良,等.外源水對巖溶碳匯的影響:以桂林毛村地下河為例[J].中國巖溶,2011,30(4):417-420.(HUANG Fen,TANG Wei,WANG Jinliang,et al.The influence of allo-genic water on karst carbon sink:a case study in the Maocun Subterranean River in Guilin[J].Carsologica Sinica,2011,30(4):417-420.(in Chinese))
[8] JUSSY J H,COLIN-BELGRAND M,DAMBRINE E,et al.N deposition,N transformation and N leaching in acid forest soils[J].Biogeochemistry,2004,69:241-262.
Water quality evaluation in subterranean river at Maocun Village in Guilin
JIANG Ran, ZHU Xiaoping, LIANG Zhihong, LEI Liehui, LIU Yisi
(PearlRiverHydraulicResearchInstitute,PearlRiverWaterResourcesCommission,Guangzhou510000,China)
In order to determine the nitrogen and phosphorus levels and sources in the subterranean river at Maocun Village in Guilin, an automatic water quality monitor was located at the outlet of the river, and sampling sites were set up simultaneously in the river basin according to the river distribution. The results show that ammonia nitrogen in 63.4% of the samples exceeded the grade II level prescribed by theQualityStandardforGroundwater(GB/T14848—93), and total phosphorus reached the grade II level prescribed by theQualityStandardforSurfaceWater(GB3838—2002). There was no significant relationship between the concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus and dry (or wet) seasons. The concentrations of total nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen gradually increased from upstream to downstream in the Maocun subterranean river basin. The total nitrogen in the Dayanqian sampling site and the subterranean river’s outlet exceeded the grade V level from theQualityStandardforSurfaceWater, while other indices reached the grade II level. Through comparison of real-time dynamic changes of ammonia nitrogen and total phosphorus in different rainfall conditions, it can be found that there was no visible change of the concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus during the periods with light and moderate rain, indicating that agricultural fertilizers and domestic sewage can affect the water quality of subterranean rivers not only by means of concentrated rainfall, but also by flowing into the rivers through Karst underground pipelines. The concentration of total phosphorus reached 23.5 μg/L, which was the instantaneeusly highest concentration during heavy rain, and ammonia nitrogen carried and diluted by rainfall was not stable due to soil erosion caused by concentrated rainfall.
subterranean river; ammonia nitrogen; total phosphorus; water quality evaluation; Maocun Village in Guilin
10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2016.05.017
水利部引進國際先進農業科學技術計劃(948項目)(201413)
蔣然(1974—),女,博士,主要從事水生態評價研究。E-mail:458750084@qq.com
X523
A
1004-6933(2016)05-0085-06
2015-10-10編輯:徐娟)

