STAT4基因多態性與乙型肝炎病毒感染相關性肝細胞癌易感性的關系
潘明潔 劉 懿 周乙華
210008 南京大學醫學院附屬鼓樓醫院
?
STAT4基因多態性與乙型肝炎病毒感染相關性肝細胞癌易感性的關系
潘明潔劉懿周乙華
210008 南京大學醫學院附屬鼓樓醫院
【摘要】目的分析信號傳導與轉錄激活因子4(STAT4)基因多態性與中國人群肝細胞癌(HCC)易感性的關系。方法154例乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)感染相關HCC為肝癌組,135例性別及年齡匹配的HBsAg陽性患者為非肝癌組。采用聚合酶鏈反應-限制性片段長度多態性法(PCR-RFLP),檢測STAT4 rs7574865位點的基因型,并經測序分析驗證。Logistic回歸分析比較不同基因型與HCC易感風險的關系。結果STAT4 rs7574865 位點3種基因型TT、GT、和GG型在肝癌組的分布頻率分別是5.8%(9/154)、37.0%(57/154)和57.1%(88/154),在非肝癌組分別是8.9%(12/135)、43.7%(59/135)和47.4%(64/135)。各基因型在兩組間差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);以TT基因型作參照,攜帶rs7574865 GG型的個體HCC患病風險差異無統計學意義(OR=1.833,95%CI=0.729~4.611,P=0.221)。結論STAT4 rs7574865多態性位點可能與中國人群HBV感染相關HCC易感性無明顯相關性。
【關鍵詞】肝細胞癌;乙型肝炎病毒;信號傳導與轉錄激活因子4;單核苷酸多態性
(ThePracticalJournalofCancer,2016,31:704~706)
肝細胞癌(hepatocellular carcinoma,HCC)是我國常見惡性腫瘤[1]。文獻報道信號傳導與轉錄激活因子4(signal transducer and activators of transcription 4,STAT4)單核苷酸多態性與多種自身免疫性疾病相關如類風濕性關節炎、系統性紅斑狼瘡和原發性膽汁性肝硬化等[2]。Jiang等[3]全基因組關聯分析,發現STAT4 rs7574865與HCC易感性有關,rs7574865位點G等位基因使HBV并發的HCC發病風險增加。本文探討STAT4 rs7574865多態位點與慢性HBV感染并發HCC易感性的關系。
1材料與方法
1.1標本來源
研究對象包括154例乙型肝炎表面抗原(hepatitis B surface antigen,HBsAg)陽性肝癌患者和135例HBsAg陽性非肝癌患者。肝癌組來自2008年11月至2013年4月南京鼓樓醫院肝膽外科住院治療的經臨床和影像學和(或)病理診斷確診為HCC的患者。非肝癌對照組為年齡及性別匹配的無腫瘤病史的HBsAg陽性者。所有研究對象均為漢族。
1.2方法
1.2.1基因組DNA 提取研究對象外周血分離白細胞,白細胞經蛋白酶K在55℃消化3 h。用酚/氯仿2次抽提DNA,無水乙醇沉淀獲得基因組DNA,提取的DNA用TE溶解。紫外分光光度計檢測DNA含量,放置-20℃冰箱保存。
1.2.2STAT4基因rs7574865 G>T 位點多態性分析
應用聚合酶鏈反應-限制性片段長度多態性(PCR-RFLP)技術對STAT4 rs7574865位點進行基因分型。根據參考文獻[4-7]合成引物,引物序列為:上游引物5′-AAA GAA GTG GGA TAA AAA GAA GTTTG-3′,下游引物5′-CCA CTG AAA TAA GAT AAC CAC TGT-3′,PCR擴增片段為147 bp。
PCR反應體系總體積50 μL,內含基因組DNA 100 ng,dNTP 2.5 mmol/ L,10×PCR 緩沖液(包含Mgcl2)5 μL,Taq酶2 U,上、下游引物各10 pmol。PCR 擴增反應條件:94 ℃預變性3 min,94 ℃變性30 s,56 ℃復性30 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,35個循環,最后72 ℃延伸5 min。擴增產物的限制性酶切體系總體積10 μL,PCR產物5 μL,加入Hpa I內切酶2U(NEB,北京)37 ℃水浴2 h后,用2.5%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳分離后在紫外燈下判斷結果。酶切分型之后每種基因型各取3例PCR產物,DNA純化試劑盒(北京天根生化科技有限公司)純化后測序(ABI 3130,Applied Biosystems),驗證酶切方法的準確性。
1.3統計學處理
應用SPSS 18.0軟件進行數據錄入與統計分析。基因型和等位基因分布頻率、研究對象是否符合Hardy-Weinberg 平衡采用四格表χ2檢驗,Logistic單因素回歸分析計算比值比(odds rations,OR),95%可信區間(CI)比較不同基因型與HCC風險的相關性。均為雙側概率檢驗,P<0.05為差異有顯著性意義。
2結果
2.1肝癌組和非肝癌組一般情況比較
肝癌組154例,其中男性 131例(85.1%),女性23例(14.9%);平均年齡(51.62±10.94)歲。非肝癌組135例,其中男性109例(80.7%),女性26例(19.3%);平均年齡(51.94±12.90)歲。兩組的性別構成比、年齡差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
2.2STAT4 rs7574865多態性位點等位基因及基因型分布頻率與HCC的關系
PCR擴增產物大小符合,酶切圖譜清晰。基因型G/G純合子酶切片段為147 bp; T/T純合子為122 bp和25 bp兩條帶;G/T雜合子酶切片段應為147 bp、122 bp和25 bp三條帶,但25 bp片段已經跑出膠外,因此電泳圖可見兩條帶(圖1)。每種基因型各取3例PCR產物測序,序列分析與酶切結果一致,證實酶切方法準確,結果可靠。經χ2檢驗,STAT4 基因rs7574865在非肝癌對照組的基因型頻率分布符合Hardy-Weinberg 平衡(P>0.05),選取的標本具有人群代表性。
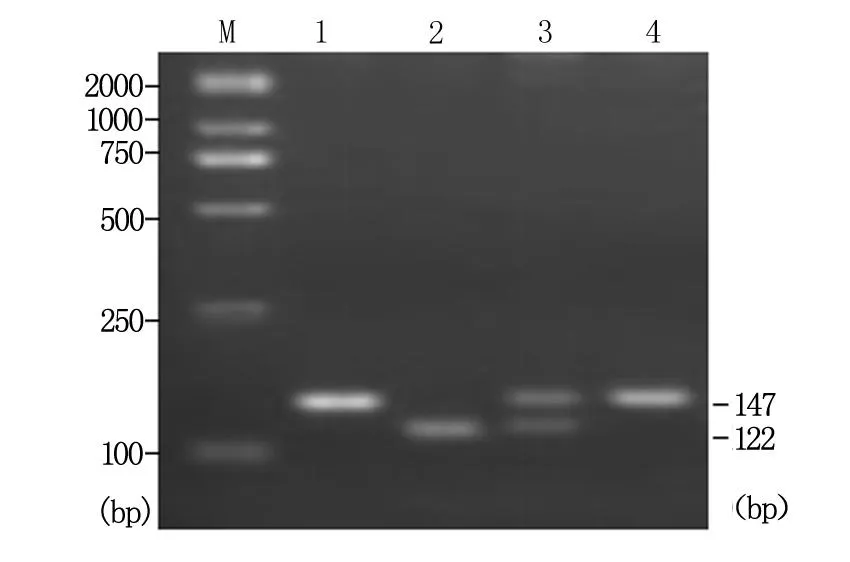
M為Marker;1為PCR擴增產物;2為T/T基因型;3為G/T
STAT4 rs7574865位點的3種基因型檢測結果見表1。T/T、G/T、和G/G基因型在肝癌組的分布頻率分別為5.8%(9/154)、37.0%(57/154)和57.1%(88/154),在非肝癌組分別為8.9%(12/135)、43.7%(59/135)和47.4%(64/135)。各種基因型兩組間差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。等位基因T和G在肝癌組中的頻率分別為24.4%(75/308)和75.6% (233/308),對照組中頻率分別為30.7%(83/270)和69.3%(187/270),等位基因分布頻率兩組間比較差異無統計學意義(χ2=3.016,P=0.221)。
單因素Logistic回歸分析顯示,STAT4 rs7574865位點各基因型與HCC患病風險的關聯性比較差異無統計學意義(P=0.223)。進一步調整年齡及性別影響因素后其差異仍無統計學意義(P=0.218)。STAT4 rs7574865位點多態性可能與HCC易感無關。

表1 兩組STAT4 rs7574865基因型及等位基因分布(例,%)
3討論
單核苷酸多態性(single nucleotide polymorphisms,SNP)是指基因組水平上由單個核苷酸變異引起的DNA序列多態性,人群中的發生頻率大于1%,是人類可遺傳的變異中最常見的一種。相關基因的單核甘酸多態性可影響基因的轉錄或表達,導致疾病易感性的差異[8]。本研究分析STAT4基因單核苷酸多態性多態性與中國人群HCC易感性的關系。
信號傳導與轉錄激活因子(signal transducer and activator of transciption,STAT)是一組能與DNA結合的蛋白質,有40多種細胞多肽物質可與細胞表面的特異性受體結合,從而引發胞漿中的STATs的激活。STAT4編碼的轉錄因子參與了多種重要細胞因子如IL-12、IFN-α/β和IL-23的信號傳導過程。 IL-12、IFN-α/β通過STAT4的信號傳導刺激幼稚CD4+ T細胞向Th1分化,刺激Th1產生IFN-γ[9]。IFN-γ是多效性細胞因子,在宿主免疫防御中發揮重要作用[10]。STAT4基因多態性消弱IFN-γ的活性,從而可能降低機體抗病毒和抗腫瘤活性[11],過表達IFN-γ可能導致自身免疫性疾病的發生[12]。
Jiang等[3]三階段包括七組病例對照(HBV感染并發肝癌+慢性HBV攜帶者)人群全基因組關聯分析發現STAT4 rs7574865位點G等位基因與HBV并發的HCC發病風險增加(OR=1.22,95%CI=1.15 ~1.29,P=1.66×10-11)。而且SNP rs7574865 GG基因型STAT4 mRNA在HCC腫瘤組織和非腫瘤組織的表達水平低于TG基因型和TT基因型,這與文獻報道STAT4 rs7574865 G等位基因降低各種自身免疫性疾病風險相一致,如類風濕性關節炎、系統性紅斑狼瘡和原發性膽汁性肝硬化等[2]。本研究發現rs7574865 GG基因型與HCC易感性無關,雖然GG基因型在肝癌組的頻率高于非肝癌組,增加HCC風險的趨勢與全基因組關聯分析[3]一致,但差異無統計學意義(OR=1.572,95%CI=0.641~3.855,P=0.218),與韓國對287例HBV感染并發肝癌和671例慢性HBV感染對照的研究結果類似[13],同樣Chen等[14]比較506例HBV感染并發肝癌,和772例慢性HBV感染者,rs7574865位點基因型在兩組人群無顯著區別。Clark等[15]445例越南患者包括206例慢性HBV感染和239例肝癌研究中在HCC和慢性HBV感染組以G等位基因做參比,T等位基因風險降低(OR=0.84,95%CI =0.7~0.99,P=0.048)也就是G是危險等位基因,結果與Jiang一致,但是2篇文獻OR值(比值比)即相對危險度都接近1,說明rs7574865位點基因多態性對HBV肝癌易感性的影響并不明顯。
本研究發現STAT4 rs7574865位點與肝癌易感性無明顯相關性。肝癌的發生是1個多基因、多途徑、由遺傳和環境因素等綜合影響的過程,有必要納入更多的位點進行聯合分析,遺傳因素與環境因素的協同作用也值得更深入的研究。
參考文獻
[1]Ferlay J,Shin HR,Bray F,et al.Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008:GLOBOCAN 2008〔J〕.Int J Cancer,2010,127(12):2893-2917.
[2]Mells GF,Floyd JA,Morley KI,et al.Genome-wide association study identifies 12 new susceptibility loci for primary biliary cirrhosis〔J〕.Nat Genet,2011,43(4):329-332.
[3]Jiang DK,Sun J,Cao G,et al.Genetic variants in STAT4 and HLA-DQ genes confer risk of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma〔J〕.Nat Genet,2013,45(1):72-75.
[4]Zervou MI,Sidiropoulos P,Petraki E,et al.Association of a TRAF1 and a STAT4 gene polymorphism with increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis in a genetically homogeneous population〔J〕.Hum Immunol,2008,69(9):567-571.
[5]Hu K,Yang P,Jiang Z,et al.STAT4 polymorphism in a Chinese Han population with Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome and Beh?et's disease〔J〕.Hum Immunol,2010,71(7):723-726.
[6]Ge M,Zheng Y,Li X,et al.The polymorphisms of T cell-specific TBX21 and STAT4 genes may contribute to the susceptibility of Chinese individuals to aplastic anemia〔J〕.Hum Immunol,2012,73(1):118-121.
[7]Yang H,Zhou Q,Chen ZM,et al.Polymorphisms in STAT4 increase the risk of acute renal allograft rejection in the Chinese population〔J〕.Transpl Immunol,2011,24(4):216-229.
[8]宋霞,程世紅,劉純,等.環氧化酶-2765G/C基因多態性對原發性肝癌易感性的研究〔J〕.實用癌癥雜志,2011,26(3):255-258.
[9]Nguyen KB,Watford WT,Salomon R,et al.Critical role for STAT4 activation by type 1 interferons in the interferon-gamma response to viral infection〔J〕.Science,2002,297(5589):2063-2066.
[10]Dunn GP,Koebel CM,Schreiber RD.Interferons,immunity and cancer immunoediting〔J〕.Nat Rev Immunol,2006,6(11):836-848.
[11]Saha B,Jyothi Prasanna S,Chandrasekar B,et al.Gene modulation and immunoregulatory roles of interferon gamma〔J〕.Cytokine,2010,50(1):1-14.
[12]Schwarting A,Tesch G,Kinoshita K,et al.IL-12 drives IFN-gamma-dependent autoimmune kidney disease in MRL-Fas(lpr)mice〔J〕.J Immunol,1999,163(12):6884-6891.
[13]Kim LH,Cheong HS,Namgoong S,et al.Replication of genome wide association studies on hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility loci of STAT4 and HLA-DQ in a Korean population〔J〕.Infect Genet Evol,2015,33:72-76.
[14]Chen K,Shi W,Xin Z,et al.Replication of Genome Wide Association Studies on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Susceptibility Loci in a Chinese Population〔J〕.PLoS One,2013,8(10):e77315.
[15]Clark A,Gerlach F,Tong Hv,et al.A trivial role of STAT4 variant in chronic hepatitis B induced hepatocellular carcinoma〔J〕.Infect Genet Evol,2013,18:257-261.
(編輯:吳小紅)
Relationship between Polymorphisms of STAT4 and the Susceptibility to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Hepatitis B Virus
PANMingjie,LIUYi,ZHOUYihua.
NanjingDrumTowerHospitalAffiliatedtoNanjingUniversityMedicalSchool,Nanjing,210008
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo investigate the relationship between single nucleotide polymorphism(SNP)of STAT4 and hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC)susceptibility in chinese population.Methods154 patients with hepatitis B virus(HBV)-related HCC and 135 age-and gender-matched non-HCC controls infected with HBV were enrolled.The genotypes of STAT4 rs7574865 were detected by polymerase chain reaction based restriction fragment length polymorphism(PCR-RFLP)and verified by sequencing analysis.Logistic regression model was used to analyze the relationship between different genotypes and their susceptibility to HCC.ResultsThe frequencies of genotypes TT,GT and GG on STAT4 rs7574865 were 5.8%(9/154),37.0%(57/154),57.1%(88/154)in the HCC group,and 8.9%(12/135),43.7%(59/135),47.4%(64/135)in non-HCC group,respectively,showing no statistical significance(P>0.05).Compared with TT genotype,there was no significant association at rs7574865 GG in the susceptibility to HCC(OR=1.833,95%CI=0.729~4.611,P=0.221).ConclusionThe polymorphism of STAT4 rs7574865 is not associated with susceptibility to HCC in chinese population.
【Key words】Hepatocellular carcinoma;Hepatitis B virus;Signal transducer and activators of transcription 4;Single nucleotide polymorphism
通訊作者:周乙華
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5930.2016.05.003
中圖分類號:R735.7
文獻標識碼:A
文章編號:1001-5930(2016)05-0704-03
(收稿日期2015-08-07修回日期 2016-01-25)

