空腹血糖調節受損人群維生素D與胰島素抵抗的相關性
闞正華 馬靜靜 石 敏 高鵬霞 張 紅
(南京醫科大學附屬淮安第一醫院康復醫學科,江蘇 淮安 223300)
?
空腹血糖調節受損人群維生素D與胰島素抵抗的相關性
闞正華馬靜靜1石敏1高鵬霞1張紅1
(南京醫科大學附屬淮安第一醫院康復醫學科,江蘇淮安223300)
〔摘要〕目的探討血清25-羥維生素D〔25(OH)D〕與空腹血糖調節受損(IFG)人群胰島素抵抗(IR)的相關性。方法選擇116例IFG患者(設為IFG組)和128例正常人群(設為NC組),所有受試者測身高、體重、血壓(SBP、DBP),檢測空腹血糖(FPG)、空腹胰島素(FINS)、血脂(TG、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C)、血清25(OH)D。用穩態模式估計法公式評估胰島素抵抗水平分析各因素與胰島素抵抗指數(HOMA-IR)的相關性。結果經Pearson相關分析,BMI、SBP、DBP與IR呈正相關,HDL-C、血清25(OH)D與HOMA-IR呈負相關(r=-0.502,P<0.01)。多元逐步線性回歸分析顯示FPG、BMI、HOMA-IR與〔25(OH)D〕密切相關。結論在排除飲食等其他影響因素后,血清25(OH)D可作為IR的獨立預測指標,血清〔25(OH)D〕有可能成為IFG發生發展危險因素的預測指標。
〔關鍵詞〕空腹血糖調節受損;25-羥基維生素D;胰島素抵抗
胰島素抵抗(IR)在2型糖尿病的發病中起重要作用〔1~3〕。隨著維生素D受體(VDR)在各種器官的發現,人們對維生素D的認識已經超出傳統范圍,涉及內分泌、心血管疾病、自身免疫等多方面〔4~7〕。有研究表明,維生素D與糖尿病密切相關〔8,9〕,糖尿病人群短期補充維生素D與鈣劑,胰島β細胞功能、胰島素敏感性、血糖代謝均得到一定程度的改善〔10〕。目前,對于空腹血糖調節受損(IFG)人群維生素D與IR的研究尚少。本試驗擬探討25-羥維生素D〔25(OH)D〕與IR的關系。
1對象和方法
1.1對象選取2014年1~12月到南京醫科大學附屬淮安第一醫院體檢的人群〔空腹血糖(FPG)6.1~6.9 mmol/L-1〕,行OGTT試驗,糖負荷后2 h血糖<7.8 mmol/L診斷為IFG(按照國際上通用的1999年WHO糖尿病專家委員會報告提出的分類標準,并參照了2014年ADA糖尿病診斷新指南)。選取符合條件的116例FPG患者設為IFG組〔男69例,女47例,年齡(51.01±6.49)歲〕同時期健康查體性別及年齡相匹配的128例健康人設為正常對照組〔NC組,男69例,女59例,年齡(47.45±7.16)歲〕,兩組年齡、性別比例無差異(P>0.05)。
排除標準:肝腎功能障礙、現有的消化系統疾病影響吸收、糖尿病史、骨質疏松及其他骨代謝異常疾病史。所有受試者均無維生素D類藥物及鈣劑服用史。
1.2方法所有受試者清晨空腹10 h以上,采集空腹靜脈血,及時分離血清。均免冠脫鞋穿貼身衣服測量身高、體重,計算體重指數(BMI)。安靜狀態下受試者取坐位,專人用水銀柱血壓計測量右上臂血壓。所有受試者測定靜脈FPG、空腹胰島素(FINS)、總膽固醇(TC)、低密度脂蛋白膽固醇(LDL-C)、高密度脂蛋白膽固醇(HDL-C)、甘油三酯(TG)、25(OH)D。羅氏化學發光儀器E170測定FINs水平,日立7600型全自動生化儀測定血糖及血脂,酶聯免疫法測定25(OH)D,試劑盒由北京博暉創新光電技術股份有限公司提供。胰島素抵抗指數(HOMA-IR)依據穩態模式(HOMA)計算:HOMA-IR,評估IR水平。
1.3統計學處理應用SPSS22.0軟件。計量資料組間比較采用t檢驗、單因素方差分析,各變量間相關性采用Pearson相關分析。IFG人群各因素與IR之間采用多元線性回歸分析。
2結果
2.1各組與生化指標比較IFG組FPG、FINS、TG高于NC組,而25-(OH)D低于NC組(P<0.05)。BMI、SBP、DBP、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C值兩組之間無差異(P>0.05)。見表1。
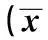
表1 各組生化指標比較±s)
與NC組比較:1)P<0.05
2.2各因素與HOMA-IR的相關性所有受試者各因素與HOMA-IR的Pearson相關分析顯示,年齡、性別、TG、TC、LDL-C與HOMA-IR不相關;FPG、FINS、25(OH)D、HDL-C、BMI、SBP、DBP與HOMA-IR相關(r=0.564、r=0.985、r=-0.502、r=-0.144、r=0.219、r=0.197、r=0.144,均P<0.05)。
2.3多元逐步線性回歸分析對所有受試者進行多元逐步線性回歸分析,以25(OHD)D為因變量,進入回歸方程的為BMI、IR、FPG(表2),表明BMI、IR、FPG與25(OH)D獨立相關。對所有受試者,以HOMA-IR為因變量,進行多元逐步線性回歸分析,進入回歸方程的為FPG、FINS、TG(偏回歸系數β分別為1.886,0.281,0.062)。以IFG組為研究對象,進行多元逐步線性回歸分析,以25(OH)D為因變量,進入回歸方程的為FINs(偏回歸系數β為-0.430),表明25(OH)D與FINs水平獨立相關。以IFG組為研究對象,以HOMA-IR為因變量,進行多元逐步線性回歸分析,進入回歸方程的為FPG、FINS、BMI(偏回歸系數β分別為3.002,0.289,0.041)。

表2 多元逐步線性回歸進入方程的因素
3討論
IFG代表了正常葡萄糖穩態和糖尿病高血糖之間的中間代謝狀態,最后進展至糖尿病,是發展為糖尿病的必經階段和預警信號。研究表明,IFG與糖尿病可能存在共同的危險因子,在IFG狀態就已經存在IR〔6〕。因此,如何降低此類人群中糖尿病的發病率、改善異常的糖代謝狀態成為目前亟待解決的問題。
從本研究結果可以看出,25(OH)D與IR密切相關,在IR機制形成過程中起到重要作用。但二者是否存在因果關系及相關機制不清。有研究顯示,25(OH)D水平降低是IFG發展的一個敏感和早期生物學標志〔7〕。血清25(OHD)水平降低可能是反映IFG人群IR的有用指標〔8~10〕。
由于本研究觀察例數較少,關于25(OH)D能否作為IFG患者的危險因素及預測標志還有待進一步研究證實。
4參考文獻
1Tangvarasittichai S.Oxidative stress,insulin resistance,dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus〔J〕.World J Diabetes,2015;6(3):456.
2Mizokami-Stout K,Cree-Green M,Nadeau KJ.Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic youth〔J〕.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes,2012;19(4):255.
3Chapagain A,Caton PW,Kieswich J,etal.Elevated hepatic 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 induces insulin resistance in uremia〔J〕.Proc Nat Acad Sci,2014;111(10):3817-22.
4Holick MF.Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases,cancers,and cardiovascular disease〔J〕.Am J Clin Nutr,2004;80(6):1678S-88S.
5Ruwanpathirana T,Reid CM,Owen AJ,etal.Assessment of vitamin D and its association with cardiovascular disease risk factors in an adult migrant population:an audit of patient records at a Community Health Centre in Kensington,Melbourne,Australia〔J〕.BMC Cardiovasc Dis,2014;14(1):157.
6Manson JE,Bassuk SS,Lee IM,etal.The Vitamin D and OmegA-3 Trial(VITAL):rationale and design of a large randomized controlled trial of vitamin D and marine omega-3 fatty acid supplements for the primary prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease〔J〕.Contemp Clin Trials,2012;33(1):159-71.
7Iruretagoyena M,Hirigoyen D,Naves R,etal.Immune response modulation by vitamin D:role in systemic lupus erythematosus〔J〕.Frontiers Immunol,2015;6.
8Mitri J,Pittas AG.Vitamin D and diabetes〔J〕.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am,2014;43(1):205-32.
9Nwosu BU,Maranda L.The effects of vitamin D supplementation on hepatic dysfunction,vitamin D status,and glycemic control in children and adolescents with vitamin D deficiency and either type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus〔J〕.PLoS One,2014;9(6):e99646.
10Mitri J,Dawson-Hughes B,Hu FB,etal.Effects of vitamin D and calcium supplementation on pancreatic β cell function,insulin sensitivity,and glycemia in adults at high risk of diabetes:the Calcium and Vitamin D for Diabetes Mellitus(CaDDM)randomized controlled trial〔J〕.Am J Clin Nutr,2011;94(2):486-94.
〔2015-11-19修回〕
(編輯徐杰)
The correlation analysis of serum vitamin D and insulin resistance in impaired fasting glucose cases
KAN Zheng-Hua,MA Jing-Jing,SHI Min,etal.
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,Huai'an First People's Hospital,Nanjing Medical University,Huai'an 223300,Jiangsu,China
【Abstract】Objectiveinvestigate the correlation of insulin resistance and serum vitamin D in impaired fasting glucose(IFG)cases.Methods116 IFG group and 128 nondiabetic individuals were chosen.Height,weight,systolic and diastolic blood pressure(SBP/DBP)were measured.Fasting plasma glucose(FPG),fasting insulin(FINS),blood lipid indexes and serum 25(OH)D concentrations were determined.Insulin resistance was estimated from fasting plasma measurements using the HOMA-IR(Insulin〔pmol/L〕×Glucose 〔mmol/L〕/22.5).The cohort was divided according to FPG.ResultsBMI,SBP,DBP and insulin resistance index were positively correlated,HDL-C,serum 25(OH)vitamin D and insulin resistance index were negatively correlated.The correlation coefficient between the insulin resistance index and 25(OH)vitamin D was -0.502,P<0.05.Multivariate stepwise linear regression analysis showed,FPG,BMI,insulin resistance index were independently associated with 25(OH)vitamin D.ConclusionsAfter the exclusion of other factors such as diet,the serum level of 25(OH)vitamin D is associated with insulin resistance in impaired fasting blood glucose regulation.While,25(OH)vitamin D may be a predictor of the risk factors of IFG regulation.
【Key words】Impaired fasting glucose;25(OH)D;Insulin resistance
〔中圖分類號〕R589
〔文獻標識碼〕A
〔文章編號〕1005-9202(2016)06-1316-03;
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.06.016
通訊作者:馬靜靜(1983-),女,主治醫師,碩士,主要從事糖尿病發病機制以及并發癥影響因素的研究。
基金項目:國家自然科學基金資助項目(81200595,81400807);江蘇省衛計委科研項目(H201253)
1南京醫科大學附屬淮安第一醫院內分泌科
第一作者:闞正華(1977-),男,主治醫師,主要從事2型糖尿病患者胰島素抵抗相關影響因子的研究。

