解剖鎖定接骨板治療C型肱骨遠端骨折的療效分析
朱前拯 段亞景 楊雨潤 楊歡 陳星佐 王立強陳瀛 楊連發(fā) 林朋 劉成剛
?
·論著·
解剖鎖定接骨板治療C型肱骨遠端骨折的療效分析
朱前拯1段亞景2楊雨潤1楊歡1陳星佐1王立強1陳瀛1楊連發(fā)1林朋1劉成剛1
目的 觀察解剖鎖定接骨板治療C型肱骨遠端骨折以及術后規(guī)范化康復的療效。方法 2009年12月至2013年6月使用解剖鎖定接骨板治療17例C型肱骨遠端骨折患者,其中男性6例,女性11例;年齡24~84歲,平均51.2歲。損傷原因:低能量損傷9例(低能量組);高能量損傷8例(高能量組)。受傷至手術時間為1~30 d,平均8.4 d。術后患者開始規(guī)范化肘關節(jié)功能康復治療。末次隨訪時記錄患側肘關節(jié)活動范圍并采用Mayo肘關節(jié)功能評分。結果 所有患者術后獲9~48個月(平均18.59個月)隨訪,所有骨折均愈合,1例合并尺骨鷹嘴截骨處延遲愈合。末次隨訪時,肘關節(jié)伸直15.0°±10.2°,屈曲103.2°±16.3°,活動范圍88.2°±22.8°。MEPS評分(83.9±19.2)分,優(yōu)良率76.5%(13/17)。高能量組與低能量組MEPS評分分別為(71.9±22.5)分和(94.6±4.9)分,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P=0.025)。結論 AO解剖鎖定接骨板治療C型肱骨遠端骨折的療效肯定,高能量損傷患者的預后較差,初始損傷因素影響患者肘關節(jié)功能恢復,規(guī)范化的康復治療有助于肘關節(jié)功能恢復。
肱骨骨折,遠端;鎖定接骨板;治療
AO分型中C型肱骨遠端骨折是一類非常復雜的關節(jié)內骨折,其肱骨遠端干骺端及關節(jié)面常粉碎嚴重,治療難度大,易合并骨缺損、軟組織損傷、神經損傷及骨質疏松等,難以獲得穩(wěn)定固定,對預后產生不利影響[1-2]。AO肱骨遠端鎖定接骨板,使用雙鋼板垂直內固定,在設計上解剖預塑型,遠端使用2.7 mm鎖定螺釘,手術中使用時更為靈活、方便,可有效預防復位丟失,尤其適合于復雜類型骨折及骨質疏松的患者。通過對我院2009年12月至2013年6月使用AO肱骨遠端解剖鎖定接骨板治療的17例C型肱骨遠端骨折患者資料進行回顧性研究,旨在對肘關節(jié)功能及術后康復訓練的療效進行觀察和分析。
資 料 與 方 法
一、一般資料
本組17例,其中男性6例,女性11例;年齡24~84歲,平均51.2歲;左側8例,右側9例;閉合性骨折16例,開放性骨折1例。損傷原因:低能量損傷(摔倒)9例(低能量組);高能量損傷8例(高能量組),包括交通傷3例,高處墜落傷4例,皮帶絞傷1例。骨折AO分型:C1型2例,C2型5例,C3型10例。合并損傷:尺神經斷裂1例,同側尺骨鷹嘴骨折1例,同側肱三頭肌斷裂1例,同側肱骨近端骨折1例,顱腦損傷蛛網膜下腔出血1例,同時合并骨盆骨折、髖臼骨折、股骨頸骨折、瘧疾1例。受傷至手術時間為1~30 d,平均8.4 d,其中7 d內手術11例,7~14 d手術3例,>14 d手術3例,最長者因合并瘧疾延遲手術治療時間。高能量組與低能量組患者在年齡、性別、傷側、受傷至手術時間、屈肘角度、伸肘角度、活動范圍方面差異均無統(tǒng)計學意義(P>0.05,表1),具有可比性。
二、手術及康復方法
術前30 min預防應用抗生素,采用全身麻醉,患者側臥位,患肢上氣囊止血帶,取肘后正中切口,顯露并保護尺神經,經尺骨鷹嘴截骨入路,顯露肱骨遠端及關節(jié)面[3]。在截骨時需要注意在尺骨鷹嘴關節(jié)面的“裸區(qū)”內截骨,大約在尺骨鷹嘴尖下方約2 cm處。術中可以首先顯露鷹嘴內、外側面,選擇鷹嘴滑車的中點處的“裸區(qū)”進行截骨,截骨時首先用薄鋸片截斷背側皮質骨直到軟骨下骨,最后的關節(jié)面用薄骨刀截斷。肱骨遠端骨折的固定原則是首先恢復關節(jié)面的平整,可用1.0 mm克氏針經關節(jié)軟骨下方穿入臨時或永久固定[4],復位肱骨遠端內、外側柱,使用克氏針及復位鉗臨時固定。使用AO肱骨內、外側解剖鎖定接骨板(辛迪斯強生,美國)固定,橈側板放置于外側柱的橈背側,尺側板與內側柱的內側骨嵴貼附。所有患者均行尺神經前置術,對合并尺神經斷裂患者予手術縫合,需要注意尺神經不能與內固定金屬接觸。在關閉傷口前充分屈、伸肘關節(jié),觀察是否存在尺神經卡壓的情況并及時糾正。
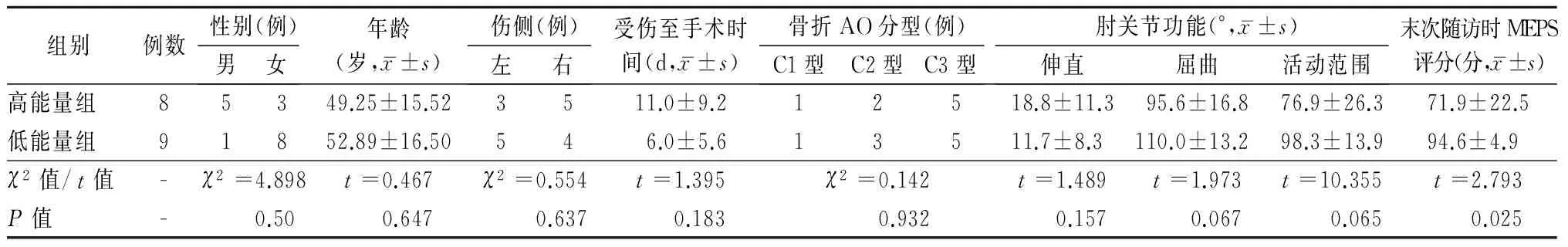
表1 高能量組與低能量組患者術前一般資料和末次隨訪時MEPS評分的比較
注:MEPS為Mayo肘關節(jié)功能評分
術畢放置引流管,術后24 h拔除引流管,并指導患者肘關節(jié)功能鍛煉,每天進行肘關節(jié)屈伸活動,以主動活動為主。患者口服吲哚美辛至術后6周。患者采用經尺骨縱軸垂直平面截骨5例,尖端在遠端的"V"形截骨12例。截骨固定方法:克氏針張力帶固定4例,張力帶鋼板固定2例,鋼纜捆綁系統(tǒng)固定11例。
術后開始規(guī)范化肘關節(jié)康復程序:患者術后根據(jù)具體骨折固定穩(wěn)定程度及軟組織損傷情況決定是否使用石膏或者支具外固定保護,保護時間為1~3周。對于損傷較輕,骨折固定堅強的患者,術后次日開始主動功能鍛煉。康復內容包括:(1)肘關節(jié)主動屈伸運動。(2)肩關節(jié)主動活動,要求患者傷后進行肩關節(jié)主動上舉、外展、外旋及內旋活動。(3)手的功能鍛煉,包括握拳、分指、并指、拇指及各指的對指運動。(4)前臂的旋轉運動,要求進行旋后及旋前運動。(5)以上運動每天3次,每次10~15次。根據(jù)肘關節(jié)腫脹情況逐漸增加次數(shù),若肘關節(jié)疼痛及腫脹加重。減少訓練次數(shù)及時間。術后6周根據(jù)X線片復查骨折愈合情況逐漸開始肘關節(jié)力量訓練。(6)物理治療:患者進行上肢主動訓練前對治療部位進行熱敷5~10 min,訓練后進行冷敷5~10 min。若患者存在明顯腫脹,進行該部位磁療,20 min,每天一次。
三、功能評價
末次隨訪時記錄患側肘關節(jié)活動范圍并采用Mayo肘關節(jié)功能(mayo elbow performance score,MEPS)評分從疼痛、活動度、穩(wěn)定性及生活能力4個方面進行功能評價,滿分為100分:90~100分為優(yōu),75~89分為良,60~74分為可,<60分為差。
四、統(tǒng)計學處理
采用SPSS 16.0統(tǒng)計學軟件,高能量損傷與低能量損傷兩組患者的年齡、受傷至手術間隔、伸肘角度、屈肘角度、活動范圍及MEPS評分采用獨立樣本t檢驗,兩組間性別及傷側對比采用Fisher檢驗。P<0.05為差異有統(tǒng)計學意義。
結 果
所有患者術后獲9~48個月(平均18.59個月)隨訪,所有骨折均愈合,無內固定失效表現(xiàn)。末次隨訪患側時,肘關節(jié)伸直15.0°±10.2°,屈曲103.2°±16.3°,活動范圍88.2°±22.8°;MEPS評分(83.9±19.2)分;優(yōu)11例,良2例,可2例,差2例,優(yōu)良率76.5%;高能量損傷組與低能量損傷組MEPS評分分別為(71.9±22.5)分和(94.6±4.9)分,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P=0.025,表1),典型病例見圖1。術后并發(fā)癥包括:尺骨鷹嘴截骨延遲愈合1例、尺神經麻痹2例,均得以自主康復。
討 論
肱骨遠端骨折大約占成人骨折的7%,占肘關節(jié)骨折的30%。除了合并嚴重骨質疏松、不能耐受手術、合并肢體神經功能障礙、軟組織缺損或感染的患者,切開復位堅強內固定是肱骨遠端骨折的首選治療方式[2]。
C型肱骨遠端骨折類型復雜,骨折粉碎程度嚴重,需要仔細的術前計劃了解骨折類型,以制定完善的手術方案[5]。我們建議術前行牽引位的肘關節(jié)正、側位X線檢查,可以更清晰地觀察骨折情況。隨著CT應用的日趨廣泛,如具備條件也可以行CT三維重建。術中要首先搞清楚各個骨折塊間的位置關系,特別是較小的骨折塊,在克氏針固定時盡量一次成功,避免重復操作。

圖1 女性患者,47歲,術前左側肘關節(jié)正、側位X線片示肱骨遠端骨折骨折(AO分型為C2型)(A,B);術后即刻肘關節(jié)正、側位X線片(C,D),術后1年肘關節(jié)正、側位X線片示肱骨遠端及尺骨鷹嘴截骨均愈合(E,F),術后1年伸肘、屈肘功能相(G,H),MEPS評分95分
影響肱骨遠端骨折預后的因素有很多,包括創(chuàng)傷的嚴重程度、創(chuàng)傷至手術的間隔時間、合并損傷、骨質量、關節(jié)面重建的程度、手術技術、使用的內固定物、固定的穩(wěn)定性、制動時間、感染和患者的合作程度等[6]。本研究結果顯示高能量組與低能量組在術后功能MEPS評分上的差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P=0.025),分析原因如下:首先,本組高能量損傷患者多合并其他部位損傷,如臂叢神經損傷、顱腦損傷蛛網膜下腔出血、骨盆骨折、髖臼骨折、右側股骨頸骨折;其次,高能量損傷組的患者受傷至手術的時間間隔較長,雖然差異無統(tǒng)計學意義,但間隔時間超過1周的患者以高能量損傷為主;另外,高能量損傷患者的局部軟組織損傷較重,部分合并有開放性骨折,影響肘關節(jié)功能康復;本研究中高能量損傷的患者,術后進行短期石膏外固定保護,開始功能鍛煉的時間較晚,對晚期屈伸肘產生了影響。
術后肘關節(jié)規(guī)范化康復訓練是影響關節(jié)功能的重要因素之一[7],通過臨床實踐總結以下幾點:(1)盡可能早期進行肘關節(jié)活動,需要結合骨折及手術固定情況,對于C3型骨折病例,術后早期可以輔助石膏固定,但時間不能超過3周。(2)以肘關節(jié)的屈伸功能恢復為優(yōu)先,屈肘功能對患者日常生活動作影響較大,而伸肘滯缺主要影響美觀、提物的力量和穿衣等功能,相對而言,屈肘更為重要。(3)主動訓練為主,避免暴力牽拉損傷肌肉及軟組織,過度力量的被動活動往往造成肌肉的拉傷、增加軟組織水腫,力量較大的被動活動容易促進異位骨化的形成,造成僵硬。主動活動時的肌肉收縮,產生泵性作用,利于體液的回流,可以避免腫脹。(4)活動的次數(shù)和強度根據(jù)骨折穩(wěn)定性和愈合情況逐漸增加。(5)重視物理治療在肘關節(jié)康復中的作用,包括冷療和磁療,通過冷療可以減輕肘關節(jié)訓練后滲出,減輕腫脹。磁療可以促進肢體血液循環(huán),改善血管通透性,從而減輕腫脹。
本組患者有1例采用垂直尺骨長軸的橫行截骨,術后出現(xiàn)截骨面分離,截骨處延遲愈合。在此之后手術改進為“V”字形截骨,尖端指向遠端[8],使用鋼纜捆綁系統(tǒng)[9]或張力帶鋼板固定,均未出現(xiàn)截骨面分離移位的情況。文獻[10-11]報道常規(guī)行尺神經前置會引起神經損傷,本組患者術中均顯露尺神經,術中尺神經走形位置被內固定物占據(jù),均行尺神經前置術,有2例患者術后出現(xiàn)尺神經麻痹,末次隨訪時神經麻痹恢復。
本組患者均采用雙鋼板垂直固定法[12],目前對于雙鋼板放置在90°還是180°位置仍存在爭議[13],平行鋼板技術是借助建筑學“拱門”原理來重建肱骨遠端解剖結構,通過鋼板螺釘與骨質的整體咬合來維持穩(wěn)定性[14-15]。AO肱骨遠端解剖鎖定接骨板在垂直方向固定,其設計不僅具有鎖定功能,并且遠端螺釘更小(2.7 mm),應對骨質疏松及關節(jié)面粉碎的骨折更為方便。
C型肱骨遠端骨折是一類復雜的肘關節(jié)骨折,我們經過隨訪發(fā)現(xiàn),使用AO解剖鎖定接骨板治療C型肱骨遠端骨折的療效肯定,高能量損傷患者的預后較差,初始損傷因素影響患者肘關節(jié)功能恢復,規(guī)范化的肘關節(jié)康復訓練有利于關節(jié)功能的恢復。本研究的不足在于入組的病例較少,隨訪時間較短,今后需繼續(xù)觀察,為臨床工作提供更有效的研究證據(jù)。
[2] O′driscoll SW.Optimizing stability in distal humeral fracture fixation[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2005,14(1 Suppl S):186S-194S.
[3] Wilkinson JM,Stanley D.Posterior surgical approaches to the elbow:a comparative anatomic study[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2001,10(4):380-382.
[4] Molloy S,Jasper LE,Burkhart BG,et al.Interference kirschner wires augment distal humeral fracture fixation in the elderly[J].J Orthop Trauma,2005,19(6):377-379.
[5] O′driscoll SW,Jupiter JB,Cohen MS,et al.Difficult elbow fractures:pearls and pitfalls[J].Instr Course Lect,2003,52:113-134.
[6] Frattini M,Soncini G,Corradi M,et al.Mid-term results of complex distal humeral fractures[J].Musculoskelet Surg,2011,95(3):205-213.
[7] Helfet DL,Schmeling GJ.Bicondylar intraarticular fractures of the distal humerus in adults[J].Clin Orthop Relat Res,1993(292):26-36.
[8] 劉林濤,馬寶通.尺骨鷹嘴截骨入路切開復位內固定治療肱骨髁間骨折的中長期療效觀察[J].中華骨科雜志,2009,29(11):1015-1018.
[9] 林朋,朱前拯,陳瀛,等.Cable-pin系統(tǒng)與克氏針張力帶治療MayoⅡa型尺骨鷹嘴骨折的近期療效比較[J].中日友好醫(yī)院學報,2011,5(4):201-203.
[10] Chen RC,Harris DJ,Leduc S,et al.Is ulnar nerve transposition beneficial during open reduction internal fixation of distal humerus fractures?[J].J Orthop Trauma,2010,24(7):391-394.
[11] Ruan HJ,Liu JJ,Fan CY,et al.Incidence,management,and prognosis of early ulnar nerve dysfunction in type C fractures of distal humerus[J].J Trauma,2009,67(6):1397-1401.
[12] 蔣協(xié)遠,公茂琪,查曄軍,等.肱骨髁間骨折術后不愈合的原因分析及治療[J].中華創(chuàng)傷骨科雜志,2010,12(6):534-537.
[13] Zalavras CG,Vercillo MT,Jun BJ,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of parallel versus orthogonal plate fixation of intra-articular distal humerus fractures[J].J Shoulder Elbow Surg,2011,20(1):12-20.
[14] Penzkofer R,Hungerer S,Wipf F,et al.Anatomical plate configuration affects mechanical performance in distal humerus fractures[J].Clin Biomech (Bristol,Avon),2010,25(10):972-978.
[15] Kollias CM,Darcy SP,Reed JG,et al.Distal humerus internal fixation:a biomechanical comparison of 90° and parallel constructs[J].Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ),2010,39(9):440-444.
(本文編輯:李靜)
朱前拯,段亞景,楊雨潤,等.解剖鎖定接骨板治療C型肱骨遠端骨折的療效分析[J/CD].中華肩肘外科電子雜志,2015,3(2):89-94.
Analysis of the Outcomes of Anatomical Lock Plate for C Type Distal Humerus Fracture
ZhuQianzheng,DuanYajing,YangYurun,YangHuan,ChenXingzuo,WangLiqiang,ChenYing,YangLianfa,LinPeng,LiuChenggang.
1DepartmentofTraumaandOrthopedics,2DepartmentofRehabilitationMedicine,China-JapanFriendshipHospital,Beijing100029,China
LiuChenggang,Email:zqzpku@sina.com
Background Among AO types, C type distal humerus fracture is a very complicated intra-articular fracture. The distal humerus metaphysis and the articular surface are easy to get severe smash, which add more difficulties to the treatment. C type distal humerus fracture is complicated with bone defects, soft tissue injury, nerve injury, osteoporosis and other symptoms, which add to the unsteady fixation and can lead to adverse impacts to prognosis. AO distal humerus lock plates are paralleled plates that vertically fix the internal fracture. It designs to be anatomical plastotype and the distal point is fixed with the 2.7mm screws. It is more flexible and convenient to use in the operation, and can effectively prevent the restoration from loosing. It′s especially suitable for those patients with complicated fractures and osteoporosis. Through a retrospective study on the 17 cases of C type distal humerus fracture treated by AO distal humerus lock plate in our hospital from December 2009 to June 2013, we observed and analyzed the curative effects on the elbow joints functions and the prognosis rehabilitation training.Methods General data: 17 patients, 6 males and 11 females aging from 24-84 years old with the average age 51.2 years old were selected to be the study subjects. 8 of them injured the left side and 9 of them injured the right side. 16 cases were closed fracture and 1 case was open fracture. Injury reasons: 9 cases were due to low energy injury (low energy group) who fell over, and 8 cases were due to high energy injury (high energy group) including 3 cases of traffic accident injuries, 4 cases of high falling accident injuries and 1 case of belts wrapping injuries. AO types of the fracture: 2 cases were of C1 type, 5 cases were of C2 type, 10 cases were of C3 type. Complicated injuries: 1 case had ulnar nerve rupture, 1 case had ipsilateral olecranal fracture, 1 case had ipsilateral triceps brachii rupture, 1 case had ipsilateral proximal humerus fracture, 1 case had craniocerebral injury subarachnoid hemorrhage, 1 case had complications of perlvic fracture, acetabular fracture, femoral neck fracture and malaria. The injury time was 1-30 days before the operation time, with an average time of 8.4 days. There were 11 cases with operation done within 7 days, 3 cases with operation done from the 7th to the 14th day, 3 cases with operation done after the 14th day. The operation time of the patient who was complicated with malaria was delayed.Operation time and the rehabilitation methods: 30 minutes before the operation, the patients were given antibiotics as prophylaxis. The patients had general anesthesia and lay down in lateral position. The fracture limb was wrapped with pneumatic tourniquet and the incision was from the postmiddle side of the elbow. The ulnar nerve was revealed and protected, and the operation was started from the olecroanon resected surface, the distal humerus and the joint surface were revealed. The operators should be cautious of the osteotomy inside the olecroanon joint surface apterium, and the osteotomy location was 2cm below the olecroanon point. In the operation, firstly both the inner side and lateral side of olecranon should be exposed and then performed osteotomy to the midpoint apterium between elecranon and trochlear. When performing the osteotomy, the operators firstly used the thin saw blade to cut off from the dorsal cortical bone to the subchondral bone, and then cut off the final joint surface by osteotome. The principles of fixing the distal humerus fracture were firstly recovering the evenness of the joint surface, and then using 10mm kirschner pins temporally or permanently to fix beneath the articular cartilage. the distal humerus inner side and lateral side column were restored, and then they were temporally fixed with kirschner pins. The fixation couldbe achieved by using the AO humerus inner side and lateral side anatomical lock plates. The radial side plate was placed to the radial dorsal side of lateral column, the ulnar plate was placed next to the inner side of bone crest. Anterior transposition of ulnar nerve was performed in all patients, and those patients who were complicated with ulnar nerve rapture were given suture. It should be noted that the ulnar nerve should be out of touch of the internal fixation metals. Before closing the wound, the patients should stretch their elbow joints and observed whether they ulnar nerve entrapment so as to rectify in time. Drainage tubes were placed after operation, and the drainage tubes should be taken away 24 hours after operation. Meanwhile, the patients should be guided to have elbow joint functional exercise, and keep doing the elbow joint flexion and extension movements, mainly active movements. The patients should take indometacin from the beginning of operation to 6 weeks after the operation. Among all the study subjects, 5 cases adopted the tran-ulnar osteotomy vertically, 12 cases adopted osteotomy from the V-shape distal point. Osteotomy fixation methods: 4 cases fixed with kirschner tension bands, 2 cases fixed with tension bands with plated, 11 cases fixed with wirerope bounding system. The normalized elbow rehabilitation process began after the operation: the patients will decide whether to use gypsum or external fixation for protection depending on their fracture fixation stability condition and the soft tissue injury conditions. And the protection period was 1-3 weeks. For those patients who had mild injury and strong fixation, they could start the active movements the next day after operation. The rehabilitation contents included:(1) elbow joint active flexion and extension movements.(2) shoulder joint active movements which include active lifting, outstretch, edxtorsion and internal rotation.(3) the hands functional exercise including clenching fists, separating fingers, closing fingers, fingers movements.(4) Rotation movement of the forearms. Rear rotation and forward rotation were requested.(5) the above-mentioned movements should be done for 3 times per day, and 10-15 rounds each time. When the swelling condition of the elbow joints was improved, the times of movements could be added accordingly. But if the joint pain and the swelling became more severe, the times and the time of movements should be reduced. 6 weeks after operation, the patients should start the joint strength training gradually when the fracture union condition indicated in the X-ray film became better. 6) Physiotherapy: the patients should have hot compress on the fraction for 5-10 minutes before doing the upper limb active movements training, and then cold compress on the same part for 5-10 minutes after training. If the fracture of the patient were swollen, this part should be performed magnet therapy for 20 minutes each day.Functional evaluation: At the last follow-up visit, the visitors recorded the lateral elbow joint movement ranges and adopted the Mayo elbow joint functions evaluation systems, namely, mayo elbow performance score and MEPS. The functions were evaluated from 4 aspects: the pain degree, movements degree, stability and living ability. The full scores are 100 points: 90-100 points is excellent, 75-89 points is good, 60-74 is ok, less than 60 points is poor.Statistical treatment: SPSS 16.0 statistical software was utilized. The ages of high energy injury and low energy injury, the period from being injured and performed operation, the elbow stretch angles, the elbow bending angles, the movement range and the MEPS evaluation were all adopted independent-samples t test. TFisher test was adopted for the genders of both groups and the injury inner side and lateral side comparison. AndP<0.05 is set as t statistically significance.Results All patients were followed up for 9-48 months and the average was 18.59 months. All the fractures became union and no failure of internal fixation was found. In the last follow-up visit, the results were: the elbow joints extension 15.0°±10.2°, flexion 103.2°±16.3°, movement range 88.2°±22.8°, MEPS evaluation (83.9±19.2) points. 11 cases were excellent, 2 cases were good, 2 cases were ok, and 2 cases were poor, the excellent and good rate was 76.5%. The MEPS evaluation of high energy injury was (71.9±22.5) points and the low energy injury was (94.6±4.9) points, the differences had statistically significance (P=0.025).The prognosis complications include: 1 case had delayed union in olecroanon osteotomy, 2 cases had ulnar nerve paralysis, but all of them were recovered in the end.Conclusion The curative effects of C type distal humerus fracture treated with AO anatomical lock plate deserves to be approved. The prognosis of high energy injury patients is poor. The initial injury factors can affect the patients′ elbow joints functional recovery. Normalized rehabilitation treatment helps the elbow joints functional recovery.
Humerus fracture,distal;Anatomical lock plate;Treatment
10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-5790.2015.02.005
骨科常見疾病術后康復模式和臨床路徑研究(D131100004913005)
100029 北京,中日友好醫(yī)院創(chuàng)傷骨科1,康復醫(yī)學科2
劉成剛,Email:zqzpku@sina.com
2014-09-26)

