Matrilin-1基因rs1149048單核苷酸多態性與青少年特發性脊柱側凸易感性的Meta分析
劉曉敏,陳銀河,申才良
(1.安徽醫科大學附屬省立醫院神經內科,安徽 合肥 230001;2.安徽醫科大學附屬阜陽醫院骨科,
安徽 阜陽 236000;3.安徽醫科大學第一附屬醫院骨科,安徽 合肥 230022)
?
Matrilin-1基因rs1149048單核苷酸多態性與青少年特發性脊柱側凸易感性的Meta分析
劉曉敏1,陳銀河2,申才良3
(1.安徽醫科大學附屬省立醫院神經內科,安徽 合肥230001;2.安徽醫科大學附屬阜陽醫院骨科,
安徽 阜陽236000;3.安徽醫科大學第一附屬醫院骨科,安徽 合肥230022)
摘要:目的綜合分析Matrilin-1基因rs1149048單核苷酸多態性(SNP)與青少年特發性脊柱側凸(AIS)易感性的關系。方法計算機檢查Medline、Cochrane圖書館、Ovid、Wiley Online圖書館、EBSCO、 Elsevier Science Direct、Springer、CBM、CNKI、萬方、維普等數據庫,查詢關于Matrilin-1 rs1149048 SNP與AIS易感性的病例對照文獻,利用Revman 5.3和Stata12.0軟件分析相關數據。結果最終共有4篇文獻納入。結果顯示GG基因型[OR=1.21,95%CI(0.93,1.56),P=0.15]、AA基因型[OR=0.92,95%CI(0.75,1.13),P=0.44]與AIS易感性無關聯性,G等位基因[OR=1.12,95%CI(1.01,1.24),P=0.03]、A等位基因[OR=0.89,95%CI(0.80,0.99),P=0.03]與AIS易感性有關聯性。僅GG基因型有明顯異質性(P=0.10,I2=52%),剔除來自日本的研究后,異質性降低(P=0.19,I2=41%),結果發生明顯變化[OR=1.39,95%CI(1.10,1.75),P=0.005],提示該研究為異質性來源之一。納入文獻僅4篇,發表偏倚未評估。結論Matrilin-1 rs1149048 G和A等位基因與AIS的易感性有關聯性,G等位基因攜帶者對AIS的易感性增高。
關鍵詞:脊柱側凸;青少年;Matrilin-1基因;單核苷酸多態性;Meta分析
1資料與方法
1.1檢索策略計算機檢索國外的Medline、Cochrane圖書館、Ovid、Wiley Online圖書館、EBSCO、Elsevier Science Direct、Springer數據庫,國內的CBM、CNKI、萬方、維普數據庫,均為以上數據庫的建庫時間至2015年2月。國內數據庫以“脊柱側凸”或“脊柱側彎”、“matrilin”或“MATN”、“多態性”檢索,國外數據庫以“scoliosis”、“matrilin”或“MATN”、“polymorphism”檢索;自由詞檢索與主題詞檢索結合,語種不限。
1.2納入標準病例對照研究;病例組符合AIS的診斷標準;兩組的樣本量、基因型或等位基因例數數據明確。
1.3排除標準病例對照研究形式以外的文獻;同一單位同一作者或不同作者以雷同或類似內容相對早期發表于不同期刊雜志的文獻。
1.4文獻篩選和資料提取由前2名研究者分別獨立進行文獻篩選、閱讀納入的文獻全文,提取AIS組和對照組的樣本量、基因型或等位基因的例數,意見不同時商討決定。
1.5方法學質量評價網絡在線(http://www.genes.org.uk/software/hardy-weinberg.html)評估對照組次要等位基因頻率(minor allele frequency,MAF)。若P≤0.05,提示該原始研究統計效能較低;若P>0.05,提示該原始研究統計效能較高。網絡在線(http://ihg.gsf.de/cgi-bin/hw/hwa2.pl)評估對照組基因型頻率是否符合hardy-weinberg遺傳平衡(hardy-weinberg equilibrium,HWE)。若P≤0.05,提示不符合HWE,原始文獻為低質量研究;若P>0.05,提示符合HWE,原始文獻為高質量研究[3]。
1.6統計學方法利用RevMan 5.3進行Meta分析。計數資料采用優勢比(odds ratio,OR)及其95%置信區間(confidence interval,CI)表示。若異質性明顯(P<0.1, I2>50%),Meta分析采用隨機效應模型(即M-H,Random模型),且分析異質性來源;若異質性不明顯(P≥0.1, I2<50%),采用固定效應模型(即M-H,Fixed模型)[3]。當納入文獻較少(低于10篇)時,發表偏倚不評估[4]。檢驗水平設置為α= 0.05。
2結果
2.1文獻基本情況按檢索策略總檢出104篇文獻,排除不相關文獻86篇,獲得18篇關于AIS易感性的文獻,再排除13篇各數據庫重復的文獻而獲得5篇,全文閱讀后發現1篇中文內容和1篇英文內容相似,排除其中1篇中文文獻,最終納入4篇英文文獻。文獻篩選流程見圖1。兩組的基本資料見表1。
2.2Meta分析結果
2.2.1GG基因型異質性明顯(P=0.10,I2=52%),隨機效應模型的結果示兩組差異無統計學意義[OR=1.21,95%CI(0.93,1.56),P=0.15],即GG基因型與AIS的易感性無關聯性,見圖2。
2.2.2AA基因型異質性不明顯(P=0.49,I2=0%),固定效應模型的結果示兩組差異無統計學意義[OR=0.92,95%CI(0.75,1.13),P=0.44],即AA基因型與AIS的易感性無關聯性,見圖3。
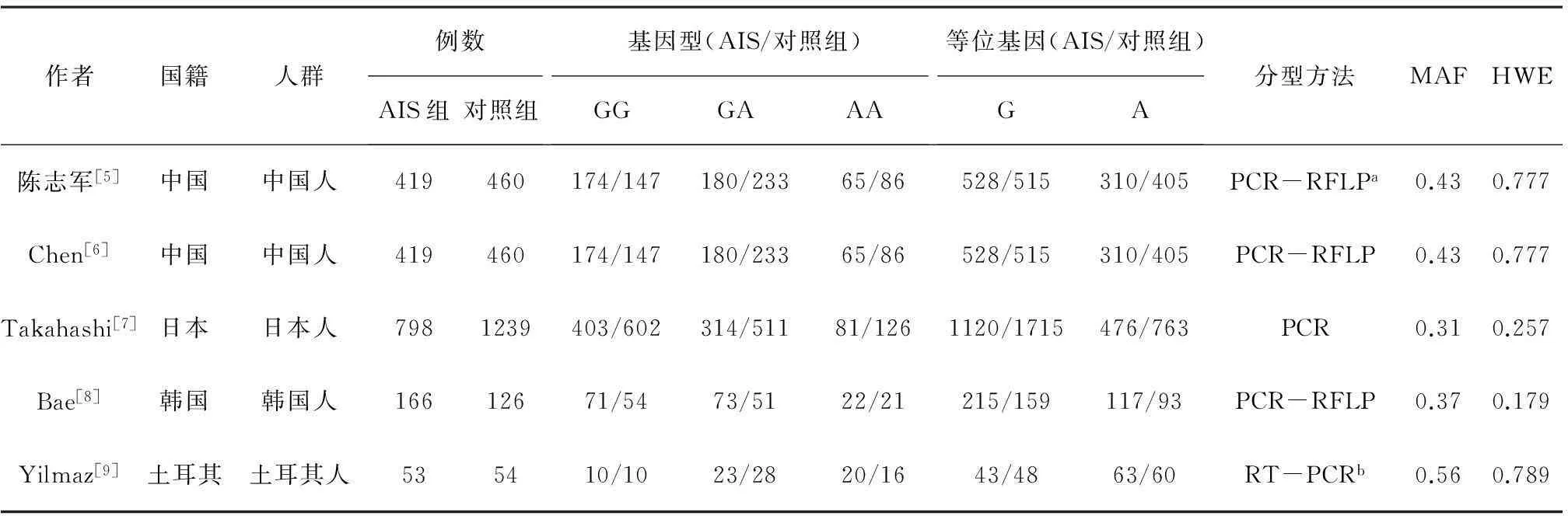
表1 AIS組和對照組的基本資料
注:a聚合酶鏈反應限制性片段長度多態性(polymerase chain reaction restriction-fragment-length polymorphism,PCR-RFLP);b實時聚合酶鏈反應(real-time polymerase chain reaction,RT-PCR)。
2.2.3G等位基因異質性不明顯(P=0.15,I2=44%),固定效應模型的結果示兩組差異有統計學意義[OR=1.12,95%CI(1.01,1.24),P=0.03],即G等位基因與AIS的易感性有關聯性,提示G等位基因攜帶者對AIS的易感性增加,見圖4。
2.2.4A等位基因異質性不明顯(P=0.15,I2=44%),固定效應模型的結果示兩組差異有統計學意義[OR=0.89,95%CI(0.80,0.99),P=0.03],即A等位基因與AIS的易感性有關聯性,提示A等位基因攜帶者對AIS的易感性降低,見圖5。
2.3敏感性分析方法學質量評價顯示納入的4個研究的對照組MAF和HWE均無統計學意義(表1),提示這4個研究均為高質量。僅GG基因型的研究間有明顯異質性,當剔除Chen等[6]時異質性降低(P=0.95,I2=0),結果無明顯變化[OR=1.07,95%CI(0.91,1.26),P=0.44]。當剔除Bae等[8]時,異質性仍明顯(P=0.06,I2=65%),結果也無明顯變化[OR=1.26,95%CI(0.91,1.75),P=0.16]。當剔除Yilmaz等[9]時,仍有明顯異質性(P=0.05,I2=68%),采用隨機效應模型分析,結果未發生明顯變化[OR=1.22,95%CI(0.91,1.63),P=0.19]。當剔除Takahashi等[7]時,異質性降低(P=0.19,I2=41%),結果有明顯變化[OR=1.39,95%CI(1.10,1.75),P=0.005],提示其為異質性來源之一。
3討論
Matrilin-1又稱軟骨基質蛋白,是非膠原性細胞外基質蛋白家族之一,其基因位于1p35區域,主要表達于骨和軟骨組織[10-12]。Montanaro等[13]對特發性脊柱側凸家系的Matrilin-1基因微衛星標記進行傳遞不平衡檢驗分析,103 bp位點有明顯的優先傳遞,提示家族性AIS可能與Matrilin-1有關聯性。AIS患者Matrilin-1蛋白水平顯著比對照組低,在進展型AIS患者中表達更低,提示Matrilin-1蛋白可能與AIS的發病有關[14]。陳志軍等[5,15]首先認為Matrilin-1 rs1149048 SNP與AIS的易感性有關聯性,且與AIS的嚴重程度呈正相關。但國外學者在日本人群、韓國人群及土耳其人群中并未證實該位點SNP與AIS的易感性存在關聯性或具有預測價值[7-9]。
在GG基因型比較中異質性明顯,經敏感性分析異質性可能來源于Takahashi等[7]的研究,但其MAF和HWE結果提示為高質量研究,異質性可能與種族差異,基因分型方法的選用及各研究所選擇的病例和對照人群差異有關。Chen等[6]和Bae等[8]的對照組為健康者,而Takahashi等[7]的對照組為部分健康者、部分頸椎后縱韌帶骨化患者和膝關節骨性關節炎患者,Yilmaz等[9]的對照組為因不同病因于就診于康復科的非脊柱側凸門診患者。目前尚無關于Matrilin-1基因rs1149048 SNP與頸椎后縱韌帶骨化和骨性關節炎易感性有無關聯性的報道,選用患者作為對照組對結果是否有影響,尚無證據支持。
結合多個數據庫進行檢索以防漏檢文獻,同時以主題詞與自由詞檢索提高文獻查全率,并制定規范的文獻篩選標準,剔除重復報道的文獻,將選擇偏倚控制至最小。本研究的局限性在于語言偏倚,僅納入了英文和中文文獻,除中英文文獻外可能還有其他語種的文獻未被檢索及納入。4個研究中心采用的基因檢測方法不完全相同,有研究內偏倚,可能對結果有一定的影響。
綜上所述,除Matrilin-1 rs1149048 GG和AA基因型外,僅能明確G和A等位基因與AIS的易感性有關聯性,G等位基因攜帶者對AIS的易感性增高,可能為AIS易感的因素之一。后期仍需進行設計良好(年齡匹配、對照組為健康人群等)、大樣本的病例對照研究進一步證實Matrilin-1 rs1149048 SNP與AIS易感性的關系。
參考文獻:
[1]Miyake A,Kou I,Takahashi Y,et al.Identification of a susceptibility locus for severe adolescent idiopathic scoliosis on chromosome 17q24.3[J].PLoS One,2013,8(9):e72802.
[2]Tilley MK,Justice CM,Swindle K,et al.CHD7 gene polymorphisms and familial idiopathic scoliosis[J].Spine(Phila Pa 1976),2013,38(22):E1432-E1436.
[3]陳銀河,劉曉敏,申才良,等.TNF-α-850位點基因多態性與強直性脊柱炎易感性的Meta分析[J].安徽醫藥,2014,18(4):649-653.
[4]Xing D,Ma XL,Ma JX,et al.A meta-analysis of cervical arthroplasty compared to anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for single-level cervical disc disease[J].J Clin Neurosci,2013,20(7):970-978.
[5]陳志軍,邱勇,俞楊,等.Matrilin-1基因多態性與青少年特發性脊柱側凸易感性的關系[J].中華外科雜志,2009,47(17):1332-1335.
[6]Chen Z,Tang NL,Cao X,et al.Promoter polymorphism of matrilin-1 gene predisposes to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in a Chinese population[J].Eur J Hum Genet,2009,17(4):525-532.
[7]Takahashi Y,Matsumoto M,Karasugi T,et al.Lack of association between adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and previously reported single nucleotide polymorphisms in MATN1,MTNR1B,TPH1,and IGF1 in a Japanese population[J].J Orthop Res,2011,29(7):1055-1058.
[8]Bae JW,Cho CH,Min WK,et al.Associations between matrilin-1 gene polymorphisms and adolescent idiopathic scoliosis curve patterns in a Korean population[J].Mol Biol Rep,2012,39(5):5561-5567.
[9]Yilmaz H,Zateri C,Uludag A,et al.Single-nucleotide polymorphism in Turkish patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis:curve progression is not related with MATN-1,LCT C/T-13910,and VDR BsmI[J].J Orthop Res,2012,30(9):1459-1463.
[10] Deák F,Wagener R,Kiss I,et al.The matrilins:a novel family of oligomeric extracellular matrix proteins[J].Matrix Biol,1999,18(1):55-64.
[11] Foradori MJ,Chen Q,Fernandez CA,et al.Matrilin-1 is an inhibitor of neovascularization[J].J Biol Chem,2014,289(20):14301-14309.
[12] Neacsu CD,Ko YP,Tagariello A,et al.Matrilin-1 is essential for zebrafish development by facilitating collagen II secretion[J].J Biol Chem,2014,289(3):1505-1518.
[13] Montanaro L,Parisini P,Greggi T,et al.Evidence of a linkage between matrilin-1 gene(MATN1)and idiopathic scoliosis[J].Scoliosis,2006,1:21.
[14] 王斌,陳志軍,邱勇,等.青少年特發性脊柱側凸患者血漿matrilin-1蛋白水平及其臨床意義[J].中華外科雜志,2009,47(21):1638-1641.
[15] 陳志軍,邱勇,王斌,等.Matrilin-1基因多態性對青少年特發性脊柱側凸進展的預測價值[J].中華骨科雜志,2009,29(5):499-502.
A Meta-analysis on the association between rs1149048 polymorphism of
Matrilin-1 gene and susceptibility to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
LIU Xiao-min1,CHEN Yin-he2,SHEN Cai-liang3
(1.DepartmentofNeurology,theAffiliatedProvincialHospitalofAnhuiMedicalUniversity,Hefei,Anhui230001,
China;2.DepartmentofOrthopaedicSurgery,theAffiliatedFuyangHospitalofAnhuiMedicalUniversity,Fuyang,
Anhui236000,China;3.DepartmentofOrthopaedicSurgery,theFirstAffiliatedHospitalofAnhuiMedical
University,Hefei,Anhui230022,China)
Abstract:ObjectiveTo investigate the association between rs1149048 polymorphism of Matrilin-1 gene and the susceptibility to AIS by a meta-analysis.MethodsCase-control studies were searched from Medline,Cochrane Library,Ovid,Wiley Online Library,EBSCO,Elsevier Science Direct,Springer,CBM,CNKI,Wan Fang and Wei Pu databases for the association between Matrilin-1 rs1149048 polymorphisms and the susceptibility to AIS.Meta-analysis was performed by Revman 5.3 and Stata 12.0 software.Pooled odds ratio(OR)with 95% confidence interval(CI)were derived from random-effects or fixed-effects models to assess the strength of the association.ResultsFour case-control studies were included in the final meta-analysis.No statistically significant differences between AIS and controls group were observed between the susceptibility to AIS and Matrilin-1 rs1149048 genotype GG [OR=1.21,95%CI(0.93,1.56),P=0.15] and AA [OR=0.92,95%CI(0.75,1.13),P=0.44];however,significant differences in allele G [OR=1.12,95%CI(1.01,1.24),P=0.03] and allele A [OR=0.89,95%CI(0.80,0.99),P=0.03] were observed between AIS and control groups.There was obvious heterogeneity among the studies in Genotype GG(P=0.10,I2=52%),sensitivity analysis performed by omitting one study at a time.When a Japanese study was omitted,the heterogeneity decreased(P=0.19,I2=41%),and the pooled results were statistically significant [OR=1.39,95%CI(1.10,1.75),P=0.005],indicating that it might be a source of heterogeneity.Because there were only four studies included,the assessment of publication bias was not performed.ConclusionsThis meta-analysis reveals that alleles G and A of Matrilin-1 rs1149048 are associated with the susceptibility to AIS.G-allele carriers have higher susceptibility.
Key words:scoliosis;adolescent;Matrilin-1;single nucleotide polymorphism;Meta-analysis青少年特發性脊柱側凸(adolescent idiopathic scoliosis,AIS)是青少年期最常見的脊柱畸形,發病率為2%~3%[1]。AIS的發病機制仍未明確,AIS的家族聚集現象提示遺傳因素在其發病中可能起一定作用[2]。目前國內外報道數篇Matrilin-1基因rs1149048單核苷酸多態性(single nucleotide polymorphism,SNP)與AIS易感性的研究,結論不統一,為明確AIS易感性與Matrilin-1 rs1149048 SNP的關聯性而行此Meta分析。
(收稿日期:2015-03-10,修回日期:2015-05-25)
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1009-6469.2015.10.026

