云存儲中一種抗竊聽攻擊的弱安全再生碼
劉 建 王會梅 鮮 明 黃 昆
?
云存儲中一種抗竊聽攻擊的弱安全再生碼
劉 建*王會梅 鮮 明 黃 昆
(國防科技大學電子信息系統復雜電磁環境效應國家重點實驗室 長沙 410073)
糾刪碼和再生碼是保證云存儲可靠性的有效機制,但是它們并不能提供節點被竊聽情況下存儲數據的機密性。該文設計了兩類抗竊聽攻擊的弱安全再生碼方案,方案結合All-or-Nothing變換與精確修復再生碼策略,保證了攻擊者在竊聽能力有限的情況下無法獲取關于原始數據符號的任何有意義信息,同時具有較小的數據修復帶寬。該文給出了通用編碼構造方法,證明了其安全性,并通過實驗進行了對比分析,結果表明與其它安全再生碼相比該方案的編解碼時間更短,且具有更好的秘密數據存儲能力。
云存儲;再生碼;安全;竊聽;All-or-Nothing變換
1 引言
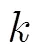

本文主要結構如下:第2節主要介紹一些基本知識、模型和準則;第3節介紹了弱安全最小帶寬再生碼和弱安全最小存儲再生碼并給出了通用的編碼構造方法;隨后在第4節進行了安全性分析、設計實驗分析了計算復雜度、存儲開銷等方案性能;第5節總結全文。
2 模型與準則
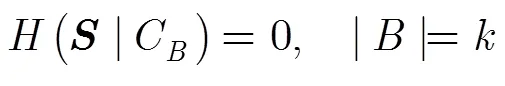
2.1 All-or-Nothing 變換
該變換由Rivest[16]首先提出,保證了攻擊者在獲得全部密文之前無法獲取任何單個明文符號。定義如下:
2.2 攻擊者模型

2.3 安全準則
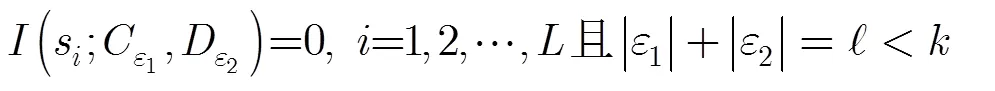
3 抗竊聽攻擊的弱安全再生碼
3.1 弱安全最小帶寬再生碼(WSMBRC)
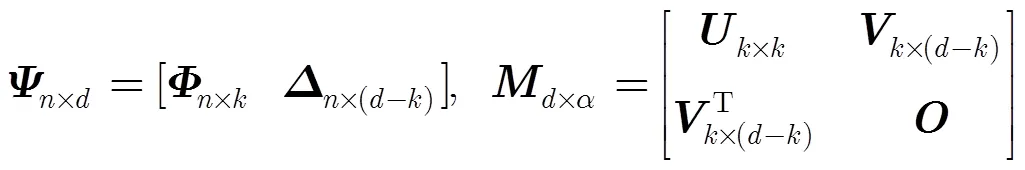
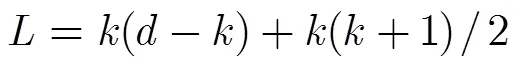
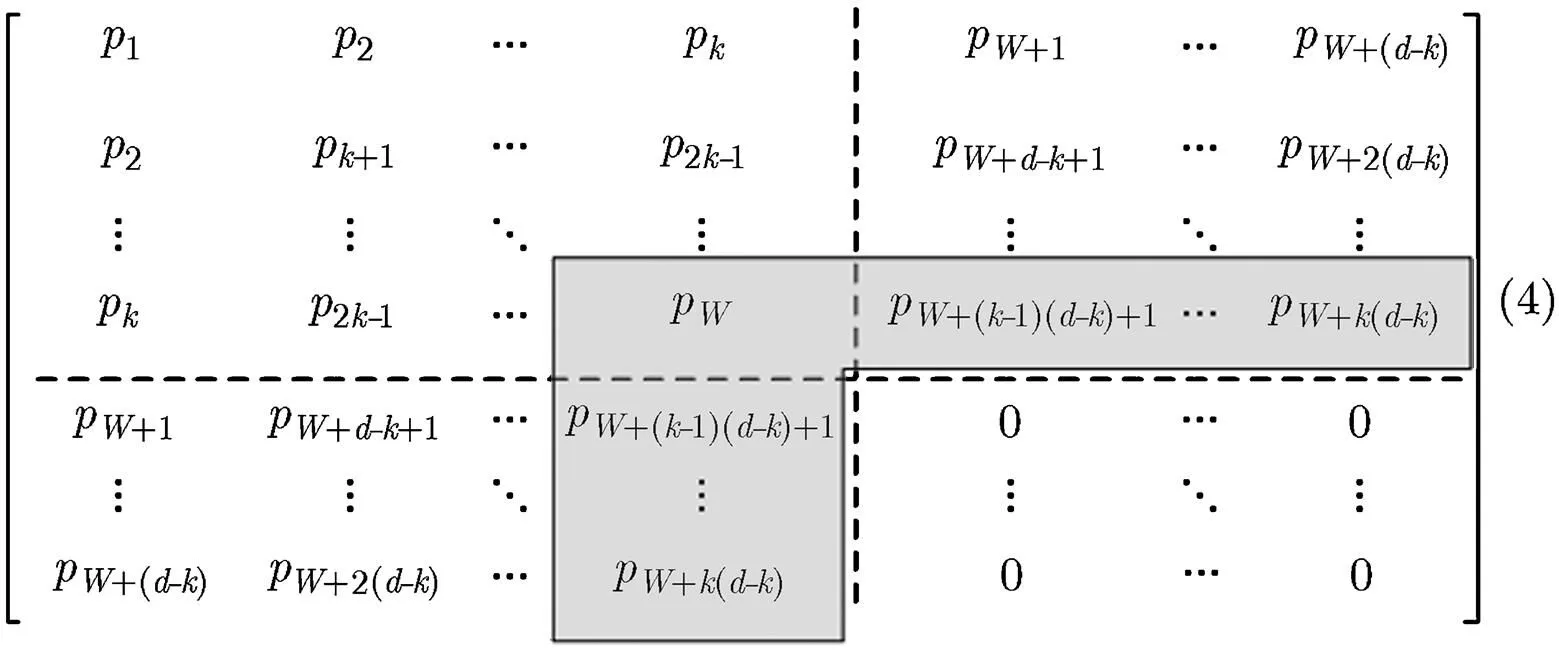
WSMBRC方案主要包括3個過程,分別是數據編碼與分發、失效數據修復以及數據重構與恢復。其中失效數據修復過程與傳統PM-MBR相同,下面主要介紹其余兩過程:
(1)數據編碼與分發
式中=(+1)/。
(2)數據重構與恢復
3.2 弱安全最小存儲再生碼(WSMSRC)
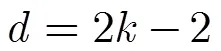
類似地,WSMSRC也主要包括3個過程:數據編碼與分發、失效數據修復以及數據重構與恢復。這里主要介紹第1個部分,另外兩個部分參考WSMBRC,此處不再詳述。
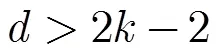
3.3 通用構造方案
由2.1節可知,WSMBRC與WSMSRC本質上是AONT變換與PM-MBR/MSR編碼的級聯。如果將其中的PM-MBR/MSR編碼替換為其它采用精確修復策略的MBR/MSR編碼(如圖1所示),只要相關參數滿足特定條件,就可以保證數據存儲的弱安全。對于其安全性證明及需要滿足的條件將在4.1節詳細分析。
4 討論
4.1 安全性分析
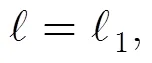
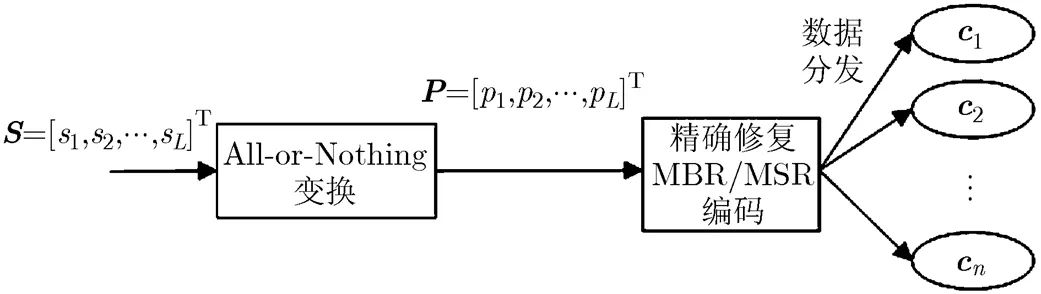
圖1 弱安全再生碼構造方法
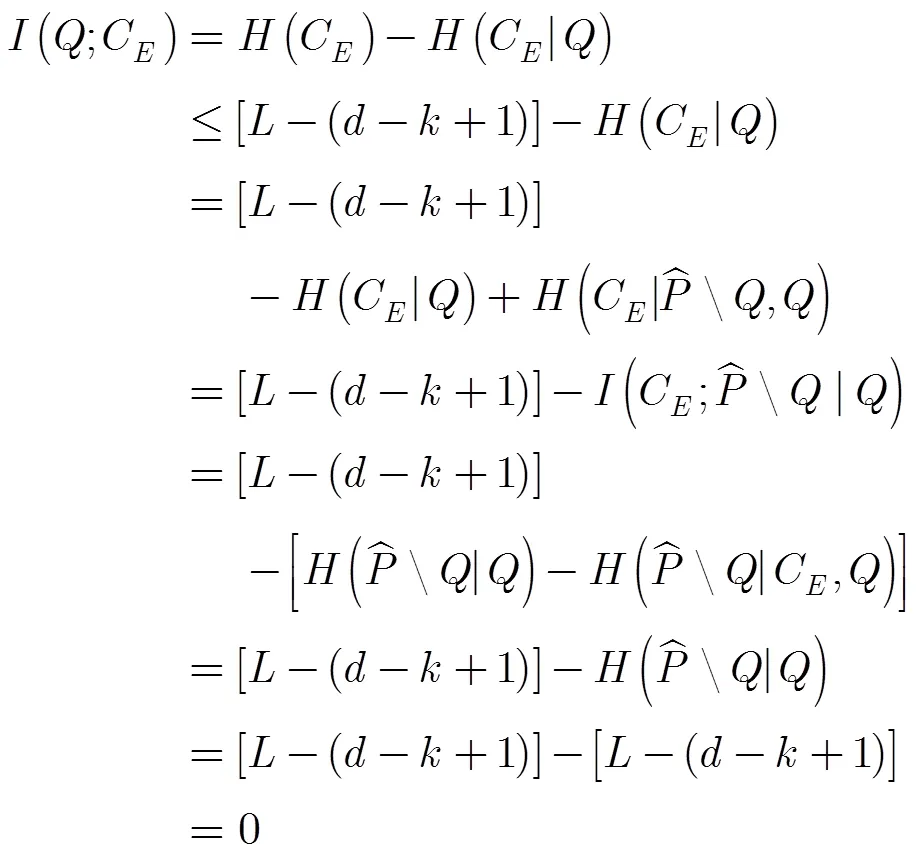
證畢
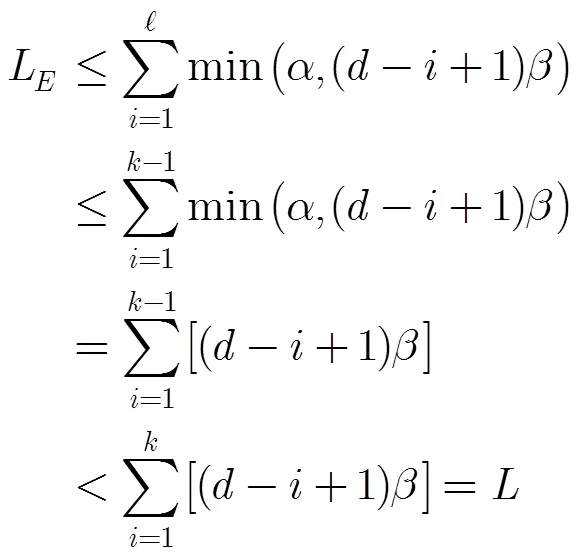
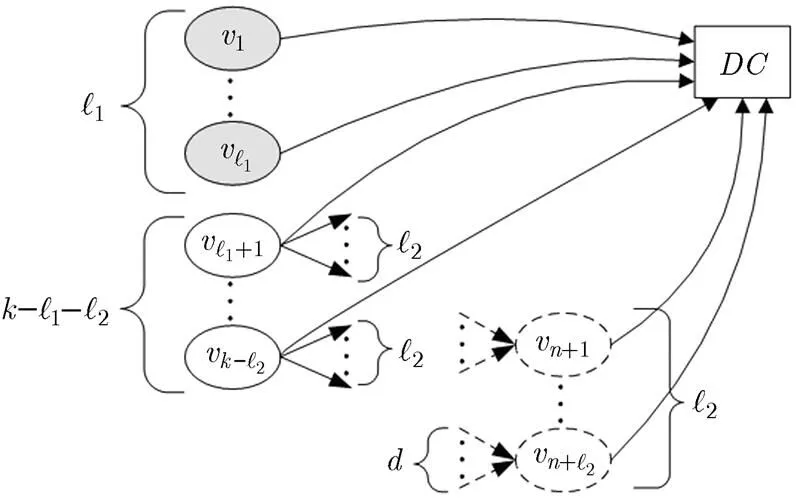
圖2 MSR情況下數據重構示意圖

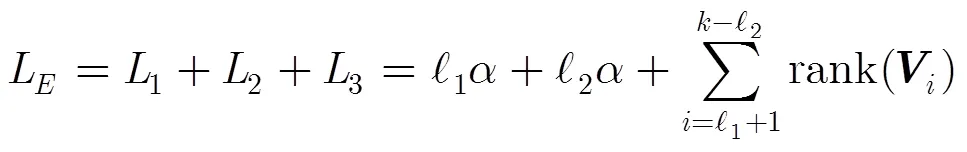
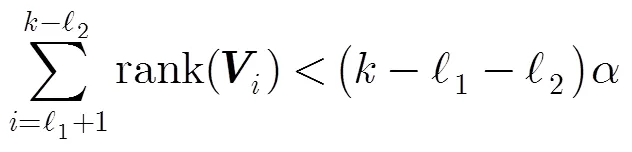
此時攻擊者所獲取的數據量為
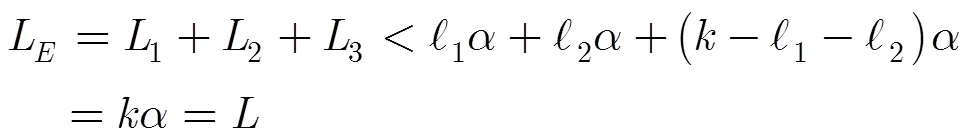
(4)竊聽能力對安全性的影響 方案利用范德蒙矩陣實現了AONT變換,由文獻[5]中的定理1可知:
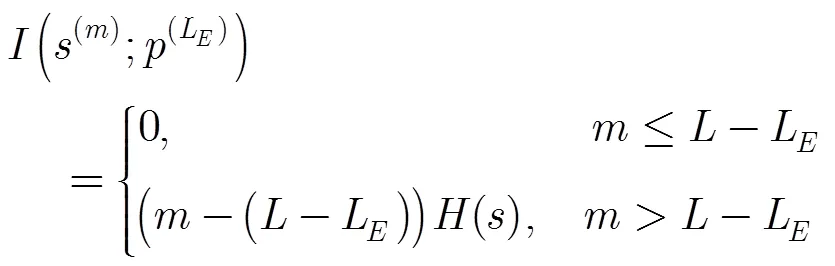
4.2 實驗結果及其分析
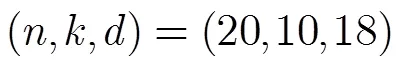
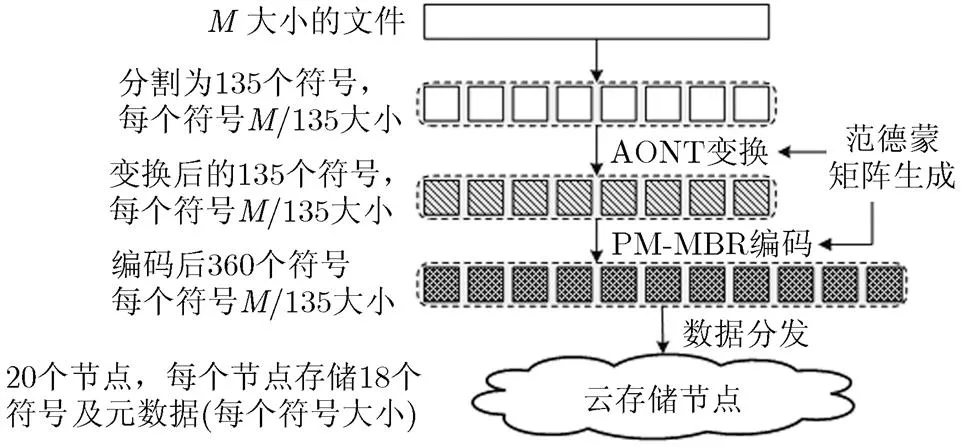
圖3 WSMBRC方案數據編碼上傳過程
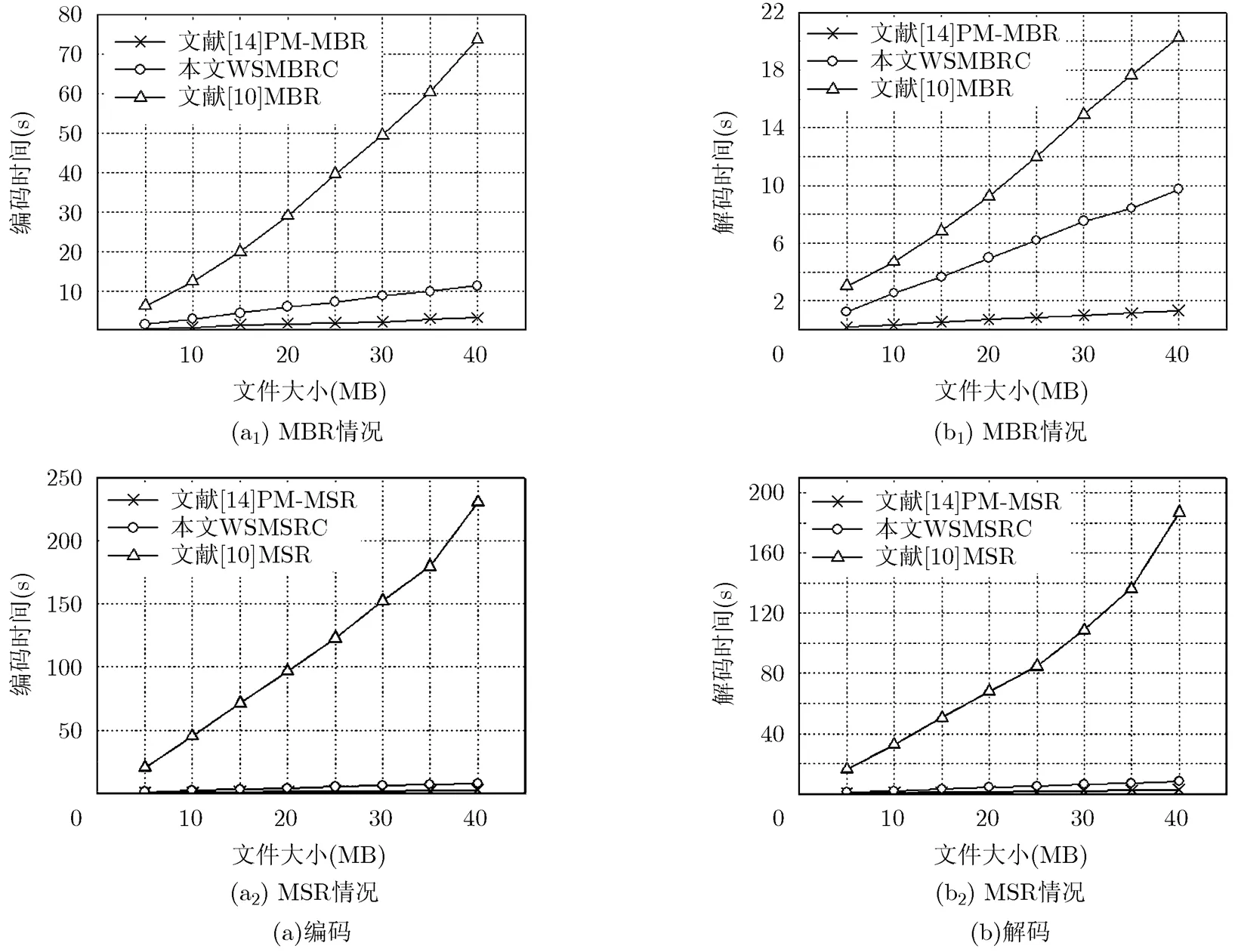
圖4 方案編解碼時間對比
本文方案計算復雜度雖然優于文獻[10]方案,但是仍增加了數據上傳和下載時延,因此適用于保存歸檔數據,而且對實時性要求不高的存儲場合,這與傳統的非系統再生碼/糾刪碼的應用場合是一致的。
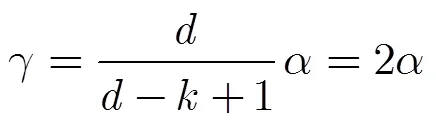

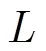
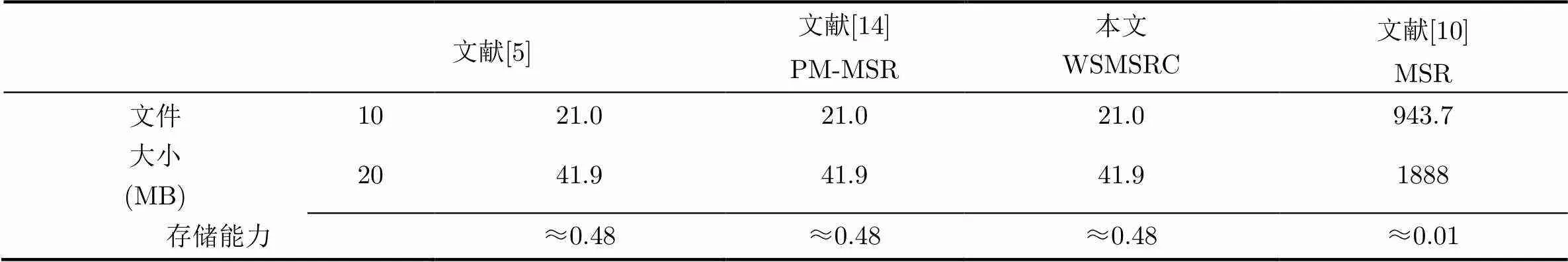
表1 MSR情況下存儲空間對比(MB)
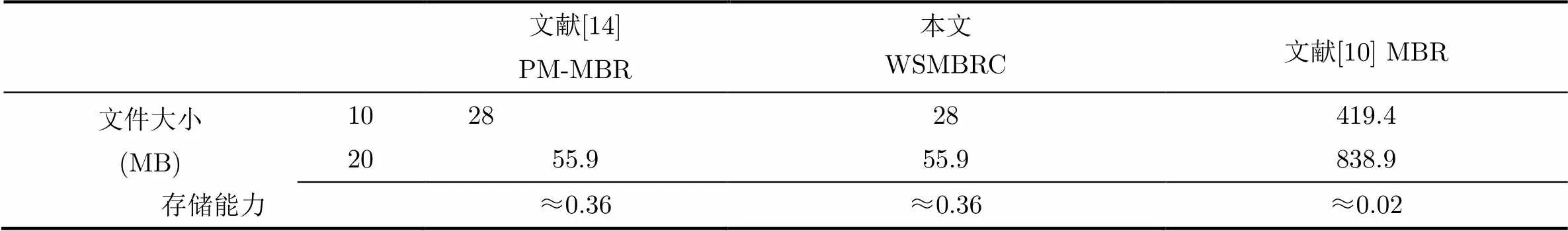
表2 MBR情況下存儲空間對比(MB)
5 結束語
本文主要考慮云存儲系統中部分節點被竊聽的條件下數據存儲的安全性,針對傳統糾刪碼或再生碼策略無法提供該類安全需求的問題,提出了基于AONT變換和精確修復再生碼的弱安全再生碼——WSMBRC和WSMSRC,隨后給出了通用的編碼構造方案并證明了其安全性。該方案具有如下特點:其安全性不依賴于傳統加解密體制,不需要密鑰管理與分配等操作,因而具有較低的系統設計復雜度;相比其它安全再生碼方案具有較小的編解碼時間;提供弱安全保證,即當攻擊者竊聽能力低于門限值時無法獲取關于原始數據符號的任何有意義信息;與其它門限存儲方案相比,具有較低的失效數據修復帶寬,且沒有造成任何的存儲容量損失,即安全存儲的信息量達到了系統存儲容量。
本文利用線性AONT變換實現了弱安全性,但造成了較大的計算復雜度。因此如何降低方案的計算復雜度,以及非線性AONT變換對數據安全性和計算復雜度會產生何種影響將是下一步的工作方向。
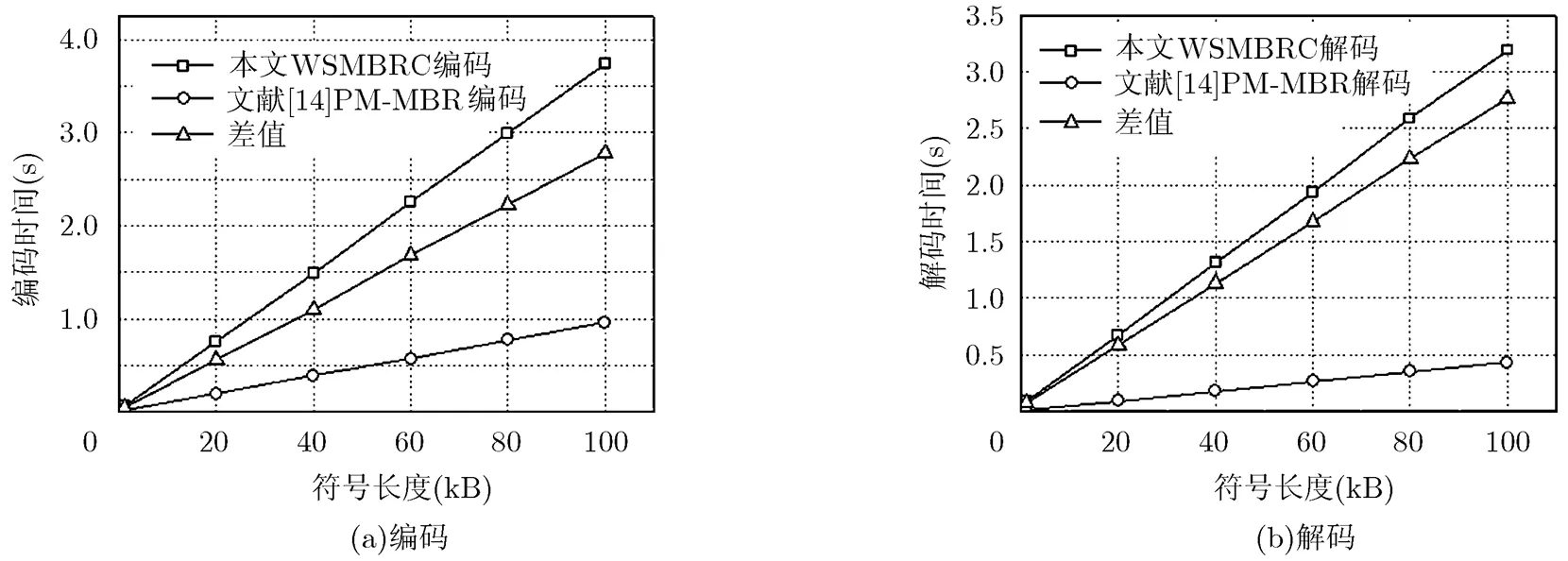
圖5 編解碼時間隨符號長度變化情況
[1] Bessani A, Correia M, Quaresma B,.. DepSky: dependable and secure storage in a cloud-of-clouds[C]. Proceedings of ACM EuroSys, Salzburg, Austria, 2011: 31-46.
[2] Dimakis A G, Godfrey P G, Wu Y,.. Network coding for distributed storage systems[J]., 2010, 56(9): 4539-4551.
[3] Shamir A. How to share a secret[J]., 1979, 22(11): 612-613.
[4] Yamamoto H. Secret sharing system using (,,) threshold scheme[J].(), 1986, 69(9): 46-54.
[5] Oliveira P F, Lima L, Vinhoza T T V,.. Coding for trusted storage in untrusted networks[J]., 2012, 7(6): 1890-1899.
[6] Kurihara M and Kuwakado H. Secret sharing schemes based on minimum bandwidth regenerating codes[C]. 2012 International Symposium on Information Theory and its Applications (ISITA), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 2012: 255-259.
[7] Rawat A S, Koyluoglu O O, Silberstein N,.. Optimal locally repairable and secure codes for distributed storage systems[OL]. http://arxiv.org/pdf/1210.6594v2.pdf, 2013.
[8] Rawat A S, Koyluoglu O O, Silberstein N,.. Secure locally repairable codes for distributed storage systems[OL]. https://webspace.utexas.edu/ok756/www/pdfs/ISIT13\_SecrecyLocal.pdf, 2013.
[9] Pawar S, Rouayheb E S, and Ramchandran K. Securing dynamic distributed storage systems against eavesdropping and adversarial attacks[J]., 2012, 58(10): 6734-6753.
[10] Shah N B, Rashmi K V, and Kumar P V. Information-theoretically secure regenerating codes for distributed storage[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Houston, TX, USA, 2011: 1-5.
[11] Silva D and Kschischang F R. Universal weakly secure network coding[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Volos, Greece, 2009: 281-285.
[12] Dimakis A G, Ramchandran K, Wu Y,.. A survey on network codes for distributed storage[J]., 2011, 99(3): 476-489.
[13] Suh C and Ramchandran K. Exact-repair mds code construction using interference alignment[J].2011, 57(3): 1425-1442.
[14] Rashmi K, Shah N B, and Kumar P V. Optimal exact-regenerating codes for distributed storage at the MSR and MBR points via a product-matrix construction[J].2011, 57(8): 5227-5239.
[15] Tamo I, Wang Z, and Bruck J. Zigzag codes: MDS array codes with optimal rebuilding[J].2013, 59(3): 1597-1616.
[16] Rivest R. All-Or-Nothing Encryption and the Package Transform[M]. New York: Springer, 1997: 210-218.
[17] Stinson D R. Something about All-Or-Nothing (transforms)[J]., 2001, 22(2): 133-138.
[18] Shah N B, Rashmi K V, Kumar P V,.. Explicit codes minimizing repair bandwidth for distributed storage[C]. Proceedings of IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Cairo, 2010: 1-5.
[19] Goparaju S, Rouayheb S E, Calderbank R,Data secrecy in distributed storage systems under exact repair[OL]. http://arxiv.org/pdf/1304.3156v2.pdf, 2013.
[20] Gohberg I and Olshevsky V. Fast algorithms with preprocessing for matrix-vector multiplication problems[J]., 1994, 10(4): 411-427.
劉 建: 男,1986年生,博士生,研究方向為網絡安全.
王會梅: 女,1981年生,講師,研究方向為網絡安全、電子信息系統建模仿真與評估.
鮮 明: 男,1970年生,研究員,博士生導師,研究方向為網絡安全、電子信息系統建模仿真與評估.
黃 昆: 男,1989年生,博士生,研究方向為網絡安全.
Weakly Secure Regenerating Codes for Cloud Storage against Eavesdropper
Liu Jian Wang Hui-mei Xian Ming Huang Kun
(,,410073,)
Erasure codes and regenerating codes can guarantee data reliability, but fail to provide data confidential when some nodes are observed by eavesdropper. Thus, two regenerating code schemes satisfying the security property against the eavesdropper are proposed in this paper. Combining the All-or-Nothing transform and exact repair regenerating codes, the proposed schemes not only ensure that an intruder eavesdropping limited number of nodes are unable to obtain any meaningful information about the original data symbols, but also provide data reliability with low repair bandwidth. Furthermore, a general construction method is presented, and the security is proved, and the performance of the proposed scheme is evaluated by a serial of experiments. The result shows that the proposed schemes achieve faster encode/decode procedures and better secrecy capacity compared with other secure regenerating coding schemes or threshold storage schemes.
Cloud storage; Regenerating codes; Security; Eavesdropper; All-or-Nothing transform
TP393; TP309
A
1009-5896(2014)05-1221-08
10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.01035
劉建 ljabc730@nudt.edu.cn
2013-07-16收到,2013-11-27改回

