五風(fēng)藤的化學(xué)成分研究
顧 健,李國(guó)友,楊 濤,方冬梅,黃田鈁 ,張國(guó)林,陳曉珍
中國(guó)科學(xué)院成都生物研究所,成都 610041
Holboellia latifolia,a medicinal herb,is mainly distributed in China,Nepal,Bhutan and India[1]. This genus,substituted for traditional Chinese medicine,bayuegua,has the effiency of clearing away heat-evil and diuretic,soothing the liver,regulating qi and promoting blood flow to smooth menstruation. It's reported that the hederagenin with a glucose moiety has been isolated from the stems of H. Latifolia[2]. In biologic screening,n-BuOH-resolvable fraction from the EtOH(95%)extract exhibited cytotoxic activity in vitro. In this study on the chemical constituents of H.Latifolia,twelve compounds were isolated from the aqueous ethanolic extract of the plant. They were elucidated to be lup-20(29)-en-3-one (1),lupeol (2),β-sitosterol(3),oleanolic acid(4),ursolic acid (5),β-daucosterol (6),Eleutheroside K (7),hederagenin3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 →2)-α-L-arabinopyranoside (8)2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acetic acid (9),3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1 →2)-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 →3)]-α-L-arabinopyranosy1 oleanolic acid 28-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-Dglucopyranosyl ester (10),3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl oleanolic acid (11),3-O-(β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid)-oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (12),on the basis of spectral evidence or comparison with authentic samples.
Experimental
Plant material
The aerial part of H.latifolia was collected in Yanbian of Sichuan Province in May 2004 and identified by Prof.Fadin Fu in Chengdu Institute of Biology,the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). A voucher specimen (A-176)was deposited at the Herbarium of Chengdu Institute of Biology,CAS.
General
Melting points were determined on an X-6 precise melting point apparatus (Beijing Fukai Science and Technology Development,Beijing,China)and were uncorrected.UV and IR spectra were obtained on a Perkin-Elmer Lambda 35 US/vis spectrometer and a Perkin-Elmer FT-IR spectrometer (KBr disk),respectively.Optical rotations were measured on a Perkin-Elmer 341 automatic polarimeter.Mass spectra were obtained on a Finnigan-LCQDECAmass spectrometer (Thermoquest LC/MS Division,San Jose,CA,USA;ESI-MS). NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Advance 600 MHz spectrometer with TMS as internal standard. Silica gel(160-200 and 200-300 mesh,Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co.,Ltd.)and RP-C18(40-63 μm,Merck KGaA,Darmstadt,Germany)were used for column chromatography (CC).MCI gel (CHP 20P,75-150 μm;Mitsubishi Chemical Industries,Tokyo,Japan)and macroporous resin (D101,pore size 13-14 nm,26-60mesh)was obtained from Tianjin Haiguang Chemical Co.,Ltd.,respectively. All solvents were distilled prior to use. Precoated plates (silica gel GF254,10-40 μm,Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co.,Ltd.),activated at 110 °C for 2 h,were used for TLC. All solvents were distilled prior to use.
Extraction and Isolation
The air-dried and powdered plant (5. 2 Kg)was soaked with 95% EtOH (20 L ×3,each 10 days)at room temperature.The combined extract was evaporated under reduced pressure to give 344 g residue,which was suspended in H2O (1.5 L)and portioned successively with petroleum ether (1.5 L ×2),EtOAc (1.5 L×5)and n-BuOH (1.5 L×6)to give corresponding fractions A (2.3 g),B (42.5 g)and C (164.7 g).Fraction B(42.5 g)was subjected to CC over silica gel on silica gel (1.5 kg,ф 8 ×45 cm)eluted with petroleum ether-acetone (20∶1,5∶1,1∶1,each 5.0 L)to afford nine subfractions B1-B9.B2 (1.4 g)was separated by CC over silica gel (60 g;petroleum ether-acetone,15∶1,2.5 L,ф 2.5 ×18 cm)to give 1 (40 mg).B5 (7.5 g)was separated by CC over silica gel (330 g;petroleum ether-acetone,15 ∶1,500 mL;5:1,280 mL,ф 3 ×15 cm)to give 2 (115 mg)and 3 (68 mg).4 (36 mg)and 5 (4 mg)were obtained from B8(5.1 g)separated by CC on silica gel (180 g,ф3.5 cm × L27 cm )eluted with petroleum ether-acetone(13:1,850 mL).6 was precipitated from B9 (3.4 g),F(xiàn)raction C was subjected to a macroporous resin column (D101,ф 10 × L 60 cm)to remove sugar by H2O and eluted with EtOH-H2O (30%,5 L;60%,4.6 L,95%,3L)to afford three subfractions C1 (51.2 g),C2 (9.4 g)and C3 (30.1 g).
Fraction C1 was subjected to CC on silica gel (1.0 kg,ф7.0 × 50 cm)eluted with CHCl3-CH3OH (10:1,5:1,each 5.0 L)to give four fractions C1A-C1D.C1B(5.6 g)was separated by CC over silica gel (400 g,CHCl3-CH3OH,10∶1,2 L;ф5 ×20 cm)to give 7 (2.1 g). C1C (11.6g)was separated by CC over silica gel (500 g,CHCl3-CH3OH,8∶1,2 L;ф6 ×22 cm)to give 8 (28 mg).
Fraction C2 was subjected to CC on silica gel (500 g,ф 5 × 20 cm)eluted with CHCl3-CH3OH (5∶1,3.5 L)to give 9 (22 mg).
Fraction C3 was resolved in methanol (350 mL)and acetone (500 mL)was added to yield precipitation(8.4 g). The precipitation was separated by CC over silica gel (360 g,CHCl3-CH3OH,6∶1,1.4 L;ф5 ×25 cm)to afford two subfractions C3A (4.2 g)and C3B(2.6 g).10 (225 mg)was obtained from C3A separated by CC on RP-C18(180 g,ф3.5cm ×L25cm )eluted with CH3OH-H2O (4∶6,1.2 L).C3B was subjected to CC on RP-C18(80 g,ф3 × 20 cm)eluted with CH3OH-H2O (3∶7,600 mL)to give 11 (5 mg)and 12 (12mg).
Bioassay
Cancer cell lines Bre-04 (MDA-MB-231),Lu-04(NCIH460),and N-04 (SF-268)were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC)and cultured according to the supplier's instruction. The cells were seeded into 96-well plates,incubated for 16 h at 37 °C,and treated with compounds 1,3,and 4 at different concentrations for 48 h. Taxol was used as a positive control.The cytotoxic activities were examined by means of a colorimetric chemosentivity assay with SRB (sulforodhamine B). The GI50 value (the drug concentration required to inhibit the cell growth by 50%)was used as a parameter for cytotoxicity[3,4].
Structure identification

Oleanolic acid (4) Colourless needles (CH3Cl),m.p. >280 ℃,ESIMS (negative mode)m/z:455.2[M-H]-,1H NMR (600 MHz,CDCl3)δ:5. 20(1H,m,H-12),3.10(1H,m,H-3),1.04(3H,s,H-27),0.88(3H,s,H-23),0.83(3H,s,H-24),0.80(6H,s,H-29,30),0.68(3H,s,H-26),0.67(3H,s,H-25)。1H NMR data were consistent with those reported[12].
Ursolic acid (5) White powder (CH3Cl),mp. >280 ℃;ESIMS (positive mode)m/z:495[M +K]+;IRνmaxcm-1:3432,2927,2871,1692,1457,1388,1377,1285,1187,1029;1H NMR (600 MHz,C5D5N)δ:5.51(1H,m,H-12),3.48(1H,dd,J =10.2,5.6 Hz,H-3),2.65(1H,d,J =11.4 Hz,H-18),2.34(1H,td,J=13.5,4.5 Hz,H-2a),2.14(1H,td,J =13.5,4.5 Hz,H-2b),1.26(3H,s,H-27),1.24(3H,s,H-23),1.07(3H,s,H-25),1.04(3H,s,H-24),1.02(3H,d,J=6.4 Hz,H-29),0.97(3H,d,J =6.2 Hz,H-30),0.90(3H,s,H-26)。1H NMR data were consistent with those reported[13].
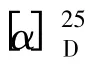


3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 →2)-α-L-arabinopyranosyl oleanolic acid (11) White powder(MeOH)mp.239.2-242.6℃,[α]25D= -3.9o(c 0.60,CH3OH);ESIMS (positive mode)m/z:919[M+Na]+,925[M+K]+;1H NMR(C5D5N)δ:6.25 (1H,s,rha-h-1),5.48 (1H,s,H-12),5.15 (1H,d,J = 7.7 Hz,glc-H-1),4.88 (1H,d,J = 5.0 Hz,ara-H-1),1.29 (3H,s,H-27),1.24(3H,s,H-23),1.23 (3H,s,H-24),1.14 (3H,s,H-30),0.99 (3H,s,H-29),0.94 (3H,s,H-26),0.82(3H,s,H-25);13C NMR (C5D5N)data were given in Table 2 and Table 3. The optical rotation and NMR data were in accordance with those reported[10].
3-O-(β-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid )-oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl ester (12) White powder (MeOH),m. p.218.7-220.4 ℃;[α]25D= +15.9°(c 0.10,MeOH);ESIMS (positive mode)m/z:817[M + Na]+;833 [M + Na]+;IRνmaxcm-1:3435,2945,1742,1620,1388,1161,1077,1030;1H NMR (C5D6N)δ:6.28 (1H,d,J = 7.2 Hz,glc-H-1),5.40 (1H,s,H-12),5.11 (1H,J = 7.2 Hz,glu-H-1),3.27 (1H,d,J = 9.6 Hz,H-18),3.16 (1H,d,J = 10.8 Hz,H-3),1.25 (3H,s,H-27),1.24(3H,s,H-23),1.05 (3H,s,H-24),0.93 (3H,s,H-30),0.91 (3H,s,H-29),0.87 (3H,s,H-26),0.80(3H,s,H-25).13C NMR (C5D5N)data were given in Table 2 and Table 3. The optical rotation and NMR data were in accordance with those reported[11,12].
Compounds 2,3,6 and 9 were identified as lupeol,βsitosterol,oleanolic acid,2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acetic acid by TLC,m. p. and comparing them with authentic samples.

Table 113C NMR Chemical shifts of aglycone moieties(C5D5N)

619.419.020.118.418.5 734.133.734.033.032.5 840.640.640.539.539.9 948.949.149.047.848.0 1037.937.838.036.836.9 1124.624.724.723.523.7 12123.4123.5123.8123.6122.9 13145.7145.7145.0144.6144.1 1443.142.843.041.942.1 1529.229.229.028.128.3 1624.624.624.623.723.6 1747.647.547.946.747.0 1842.943.042.641.541.7 1947.447.347.146.246.2 2031.931.831.730.730.8 2135.135.134.934.034.0 2234.134.133.433.033.2 2329.064.829.227.828.3 2417.914.917.916.817.0 2516.417.016.615.315.6 2618.318.318.417.117.5 2727.127.027.025.926.1 28181.1181.1177.4180.1176.5 2934.234.133.132.933.2 3024.724.724.323.423.8

Table 213C NMR Chemical shifts of sugar moieties(C5D5N)

79.078.078.2 4 74.971.273.6 5 79.778.476.4 6 63.462.3 171.0 28-O sugur Inner Glc-196.695.7 2 74.774.0 3 79.179.3 4 70.171.1 5 76.378.8 6 71.062.2 Outer Glc-1105.8 2 75.6 3 77.4 4 79.2 5 78.0 6 62.1 Rha-1103.7 2 73.4 3 73.7 4 70.9 5 71.2 3 6 19.4
Results and Discussion
Main constituents of the plant are triterpenes and triterpenoid saponins that possess many vital bioactivities.In biologic screening,7 showed moderate cytotoxicity against Lu06,N04 and Bre04.8 showed moderate cytotoxicity against N04.In view of their structures,7 with 23-CH3was different from 8 bearing CH2OH at 23.

Table 3 Cytotoxic activity of 7 and 8(GI50,μg/mL)
1 Institute of Botany,Chinese Academy of Sciences.Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae,Vol 29. Beijing:Science Press,1984.20.
2 Mitra AK,Karrer P.Holboellia latifolia,a new source of hederagenin,Helv Chim Acta,1953,36:1401.
3 Skehan P,Storing R,Scudiero D,et al. J Natl Cancer Inst,1990,82:1107-1112.
4 Rubinstein LV,Shoemaker R. H,Paul KD,et al. J Natl Cancer Inst,1990,82:1113-1118.
5 Shiojima K,Masuda K,Suzuki H,et al. Composite constituents:forty-two triterpenoids including eight novel compounds isolated from Pocris hicracioides subsp,japonica.Chem pharm bull,1995,43:1634-1639.
6 Maillard M,Adewunmi C O,Hostettman K.A triterpene glycoside from the fruits of Tetrapleura tetraptera. Phytochem,1992,31:1321-1323.
7 Zhao H,Wang BZ,Ma BR,et al. The chemical constituents of the stem of Actinidia arguta(Sieb. et Zucc.)Planck,ex Miquel.Chin Pharm J,1994,29:523-524.
8 Lu JC,Xu BB,Zhang XY,et al.Study on chemical constituents of rhizome of Anemone raddeana.Yaoxue Xuebao,2002,37:709-712.
9 Cioffi G,Braca A,Autore G,et al. Cytotoxic saponins from Schefflera fagueti.Planta Med,2003,69:750-756 .
10 Shao CJ,Kasa R,Xu JD,et al.Saponins from Roots of Kalopanax septemlobus (Thunb.)Koidz.,Ciqiu:Stuctures of Kalopanaxsaponins C,D,E and F.Chem Pharm Bull,1989,37:311-314.
11 Wang XJ,Zhu LJ.Studies on the saponin constituents of Niu Qi (Achyrathes bidentata). J Fourth Milit Med Univ,1996,17:427-430.
12 Woldemichael GM,Wink M.Identification and biological activities of triterpenoid saponins of Chenopodium quinoa.J Agric Food Chem,2001,49:2327-2332.

